Abstract
CALGB study 9511 used pegylated asparaginase (PEG-ASP) in lieu of the native enzyme on days 5 and 22 of the 5-drug induction course and days 15 and 43 of the first intensification of the CALGB 8811 regimen (
Blood 1995; 85:2025
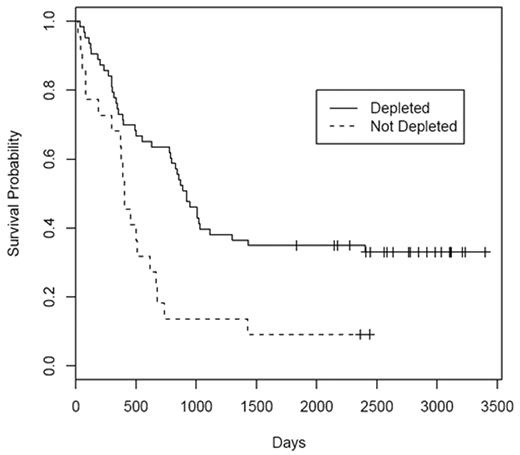
). The aim of the study was to explore differences in the overall-survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) profiles of those patients who did versus those who did not achieve asparagine depletion defined as enzyme levels > 0.03 units/ml for 14 consecutive days after at least one of four possible administrations of PEG-ASP (2000 U/m2, subcutaneously, capped at 3750 U). One hundred and four patients were enrolled between 7/95 and 12/97; 43F and 61M. Median age was 40 years (range, 17–71). Performance status (PS) was 0–1 in 81%. Thirty-one patients had an unfavorable [t(9;22), t(4;11), −7, +8] karyotype. Median WBC count was 86.5 x 109/L; 76/104 patients had > 30 x 109/L. PEG-ASP was tolerable (although grade 3 or 4 bilirubin occurred in 54%, hyperglycemia in 40%, and low fibrinogen in 30%). Treatment mortality was 9%. Antibodies to PEG-ASP were detected in 13/85 patients (15%). The complete remission (CR) rate was 76%. Median survival was 22 months [95% CI=13–29]. After a median follow-up of 90 months, 22 patients are alive without disease; three are alive after relapse. Samples were available from 85 eligible patients. Asparagine depletion was not significantly associated with achievement of CR (87.3% vs. 72.7%; P=0.55). Univariate analyses suggest that patients who achieved asparagine depletion (63 patients) had superior OS (two-sided P<0.0016; hazard ratio 2.4 [95%CI=1.4–4.2]) and DFS (P<0.011; hazard ratio 2.3 [95%CI=1.2–4.2]) profiles versus those who did not (22 patients). After adjusting, in the framework of an additive log-linear Cox model, for CR status (OS only), age, gender, PS, unfavorable karyotype, WBC count, detection of antibody to PEG-ASP, and transplantation, the difference between the OS profiles remained statistically significant (P<0.019; hazard ratio 2.1 [95%CI=1.1–3.9]) while the DFS profiles were borderline significant (P<0.052; hazard ratio 2.0 [95%CI=1.0–4.1]). We conclude that effective asparagine depletion with PEG-ASP as part of an intensive multi-agent therapeutic regimen in adult ALL is feasible and associated with improved outcomes.Author notes
Corresponding author
2005, The American Society of Hematology
2005

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal