Abstract
BACKGROUND: Ivosidenib, a potent mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (mIDH1) inhibitor, is being assessed in a phase 1 study of mIDH1 advanced hematologic malignancies (NCT02074839). We characterized the pharmacokinetics (PK) of ivosidenib in this population, and the effects of patient/disease characteristics and concomitant medications.
METHODS: Ivosidenib was given in continuous 28-day cycles at 100 mg twice daily and 300 mg, 500 mg, 800 mg, and 1200 mg once daily (QD). Enrollment is complete; 258 patients received ≥1 ivosidenib dose (78 in escalation, 180 in expansion); samples were available from 253 patients (223 received ivosidenib 500 mg QD). Ivosidenib concentrations were determined using validated liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)-based methods. Population PK modeling was conducted using NONMEM software. The impact of demographics, renal and hepatic function, disease type, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, and concomitant cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors/inducers and gastric acid reducers on ivosidenib PK was explored.
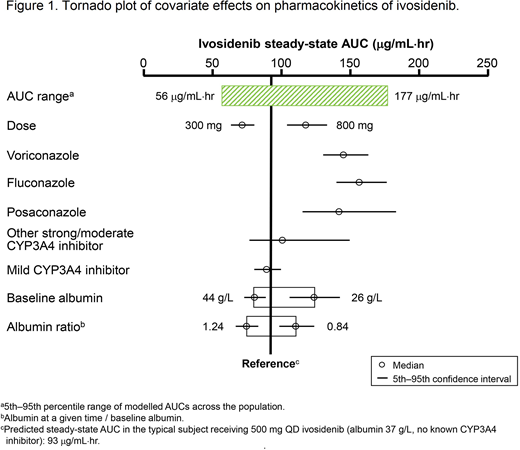
RESULTS: Ivosidenib PK were best described using a 2-compartment model with first-order absorption, dose-dependent bioavailability, and a time-dependent change in relative bioavailability and clearance between Day 1 and steady state. Mean steady-state apparent clearance (CL/F) was 5.39 L/h (between-patient variability ~35%) and mean central volume of distribution (Vc/F) was 234 L (~47%). Less than dose-proportional bioavailability was observed, with a dose doubling translating to a ~40% increase in exposure. The moderate/strong CYP3A4 inhibitors voriconazole, fluconazole, and posaconazole were associated with 36%, 41%, and 35% reductions in CL/F, and hence 57%, 69%, and 53% increases in area under the plasma ivosidenib concentration-time curve (AUC), respectively (Figure 1). Baseline body weight had a significant impact on Vc/F. Low albumin at baseline and during treatment correlated with decreased CL/F and Vc/F. However, the effects of body weight and albumin did not appear to be clinically relevant. No effects of creatinine clearance or measures of liver function (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, within the range studied) on ivosidenib CL/F were detected. Concomitant use of pantoprazole or famotidine did not affect ivosidenib CL/F.
CONCLUSION: This population PK model of ivosidenib suggests that no dose adjustments are needed based on the range of patient and disease characteristics analyzed.
Le:Millennium: Patents & Royalties; Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Wada:Certara: Employment; Agios: Consultancy. Dai:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Fan:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Liu:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Liu:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Attar:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Agresta:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership. Yang:Agios: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.