Abstract
Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway as an anticancer therapeutic strategy was realized with the approval of the orally bioavailable small molecule PI3Kδ inhibitor idelalisib. In this focused review, we highlight the rationale for targeting the pathway in lymphomas, provide a brief summary of the preclinical data, and describe the clinical experience with this agent in patients with lymphoma. We describe some of the idiosyncratic toxicities of this agent, some of the mechanisms of resistance, and some of the ongoing combination strategies.
Introduction
The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway plays an important role in multiple cellular functions, including proliferation, differentiation, and trafficking, and deregulation of PI3K is a hallmark of many malignancies, including hematologic cancers.1 The PI3K p110δ isoform inhibitor idelalisib (Zydelig; Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA) was the first agent in a new class of isoform-specific inhibitors to receive regulatory approval. Indications for idelalisib approved by the US Food and Drug Administration include relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in combination with rituximab in comorbid patients and relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL) with 2 or more prior therapies. The activity of idelalisib in CLL has been reviewed comprehensively elsewhere and will not be discussed further here.2-4
Rationale for targeting PI3K in lymphoma
PI3K comprises a group of related enzymes that collectively regulate pleotropic downstream effector functions.5 Class I PI3Ks are heterodimers comprising regulatory (p85) and catalytic (p110) subunits. The p110 subunit exists as 4 isoforms (α, β, δ, γ) with nonoverlapping functions and differing expression profiles. The α and β isoforms are expressed ubiquitously, whereas the γ and δ isoforms are expressed primarily in the hematopoietic system.6 PI3Kδ appears critical to normal B-cell development, as PI3KCD knockout mice have defective antibody production and kinase-dead mice develop inflammatory bowel disease.7 The PI3K pathway is deregulated in a subset of cases in a variety of lymphoma subtypes, including Hodgkin,8 diffuse large B-cell,9 mantle cell (MCL),10 and FL.11 Downstream effectors of PI3K signaling include the protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamicin (mTOR) pathway, which governs oncogenic processes such as metabolism, chemoresistance, cell cycle regulation, growth, and proliferation.12 Although pan-PI3K inhibition as a therapeutic strategy is problematic because of the ubiquitous expression of the α and β isoforms, inhibition of δ isoform-specific PI3K signaling is an attractive target in lymphoid malignancies.
Preclinical data
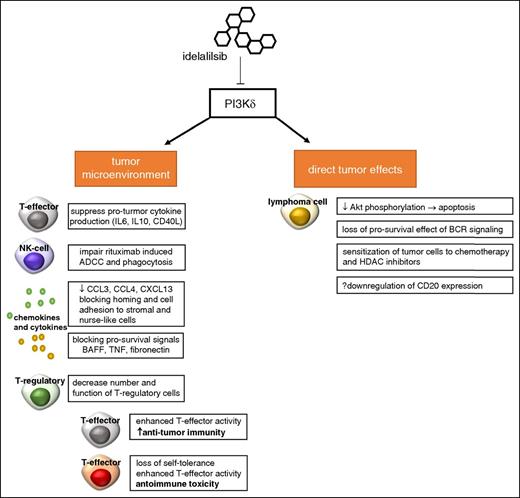
Idelalisib is an orally available, highly selective PI3Kδ small molecule inhibitor identified in kinome-wide screening assays. The 50% inhibitory concentration for the p110δ catalytic subunit of PI3K is 2.5 nM, at least 40- to 300-fold more potent than other PI3K isoforms.13 Furthermore, a 401 kinase screening assay at 10 nM did not identify significant off-target activity.13 In initial experiments performed at Ohio State University, idelalisib induced caspase-dependent death of malignant CLL cells, suppressed protumor cytokine production by T and NK cells, and abrogated prosurvival microenvironmental signals such as B-cell activating factor, tumor necrosis factor α, and fibronectin.14 Using both patient-derived samples and cell lines, Lannutti et al showed preferential in vitro activity of idelalisib in B-cell malignancies resulting from inhibition of constitutively activated PI3K signaling, ultimately resulting in decreased Akt phosphorylation and apoptosis.13 Hoellenriegel et al showed that idelalisib blocks nurse-like cell and B-cell receptor-derived survival signals; reduces secretion of chemokines CCL3, CCL4, and CXCL13; and sensitizes CLL cells to cytotoxic agents.15 These important preclinical investigations corresponded with observed changes in cytokine levels in patients with CLL and subsequent trafficking of malignant lymphocytes out of bone marrow and nodal sites into the peripheral blood.15 The potential mechanisms of action of idelalisib are summarized in Figure 1. These studies highlight the pleotropic cellular effects of idelalisib and have provided rationale for clinical development, both as a single agent and in combination with other biologic agents and conventional cytotoxics.
Potential effects of idelalisib. Selective inhibition of PI3Kδ does appear to act directly on lymphoma cells, reducing Akt phosphorylation limitation activation of the mTOR/Akt and NF-κN pathways. This leads to apoptosis through a caspase-dependent mechanism. Prosurvival signals from the B-cell receptor via PI3K are abrogated by idelalisib. In addition, it appears that idelalisib sensitizes malignant B cells to both chemotherapy and histone deacetylase inhibitors. Idelalisib also exerts pleiotropic effects on the tumor microenvironment. T-cell cytokine production and release are governed in part by PI3K, and idelalisib appears to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-10, and CD40L. Similar to ibrutinib, idelalisib alters chemokines and blocks adhesion of tumor cells to supporting stromal cells. To a lesser extent than ibrutinib, idelalisib has been shown to partially abrogate antibody-mediated cell mediate cytotoxicity induced by anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies such as rituximab. Finally, recent data indicate idelalisib-treated patients who experience severe immune toxicity have decreased number and function T-regulatory cells in the peripheral blood. T-regulatory cells play a critical role in regulating the activity of T-effector cells; in the absence of function, deregulated T-effector cell activity can cause both increased antitumor immunity and loss of self-tolerance with unwanted autoimmune toxicity. ADCC, antibody-mediated cell mediate cytotoxicity; BAFF, B-cell activating factor; BCR, B-cell receptor; CCL3/4, chemokine ligand 3/4; CXCL13, chemokine ligand 13; HDAC, histone deacetylase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Potential effects of idelalisib. Selective inhibition of PI3Kδ does appear to act directly on lymphoma cells, reducing Akt phosphorylation limitation activation of the mTOR/Akt and NF-κN pathways. This leads to apoptosis through a caspase-dependent mechanism. Prosurvival signals from the B-cell receptor via PI3K are abrogated by idelalisib. In addition, it appears that idelalisib sensitizes malignant B cells to both chemotherapy and histone deacetylase inhibitors. Idelalisib also exerts pleiotropic effects on the tumor microenvironment. T-cell cytokine production and release are governed in part by PI3K, and idelalisib appears to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-10, and CD40L. Similar to ibrutinib, idelalisib alters chemokines and blocks adhesion of tumor cells to supporting stromal cells. To a lesser extent than ibrutinib, idelalisib has been shown to partially abrogate antibody-mediated cell mediate cytotoxicity induced by anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies such as rituximab. Finally, recent data indicate idelalisib-treated patients who experience severe immune toxicity have decreased number and function T-regulatory cells in the peripheral blood. T-regulatory cells play a critical role in regulating the activity of T-effector cells; in the absence of function, deregulated T-effector cell activity can cause both increased antitumor immunity and loss of self-tolerance with unwanted autoimmune toxicity. ADCC, antibody-mediated cell mediate cytotoxicity; BAFF, B-cell activating factor; BCR, B-cell receptor; CCL3/4, chemokine ligand 3/4; CXCL13, chemokine ligand 13; HDAC, histone deacetylase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Clinical data
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Idelalisib displays linear pharmacokinetics, and biotransformation occurs primarily through the action of aldehyde oxidase; secondary metabolic pathways include cytochrome P4503A and glucuronidation.16 Concomitant use of the CYP3A inducers reduce idelalisib exposure and should be avoided.17 CYP3A inhibitors and moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment increase idelalisib exposure but do not necessitate dose modification; however, careful monitoring for toxicity is recommended.17 Data regarding the distribution of idelalisib into nonplasma compartments, such as cerebrospinal fluid, are unavailable at the time of writing.
Phase 1/2 studies
An overview of clinical trials involving idelalisib as a single agent in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is presented in Table 1. The phase 1a study in healthy volunteers both established oral bioavailability and confirmed that drug levels were achievable in the plasma at levels shown to achieve pharmacologic inhibition of PI3K.18 The phase 1b study (101-02) included patients with relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies; from this, Flinn et al reported the outcomes of 64 patients with relapsed/refractory indolent B-NHL: 38 (59%) with FL, 11 (17%) with small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), 9 (14%) with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL), and 6 (9%) with marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).16 Patients had a median age of 64 years and 4 prior therapies, with 37 (58%) refractory to the immediately preceding line of therapy. A variety of different dosing schedules were explored, including from 50 mg daily to 350 mg twice daily, 150 to 300 mg once daily, and 3 weeks on/1 week off. Interestingly, exposure to idelalisib did not result in a change in serum immunoglobulin levels or a change in T-helper, cytotoxic T-cell, or NK-cell numbers. Responses were observed across histologic subtypes: among response-evaluable patients, 85% experienced reduction in lymphadenopathy, with an objective response rate (ORR) across all dose levels of 48% (complete response [CR], 2%) after a median of 1.3 months. The median duration of response (DOR) was 18.4 months (range, 0.03-34 months). Both ORR (59% vs 37%) and median progression-free survival (PFS) (16.8 vs 3.7 months) were greater among patients treated continuously at dose levels of 150 mg or more twice daily. Considering dose-exposure data, 150 mg twice daily was selected as the recommended phase 2 dose.
On the basis of these data, Gopal et al performed an international multicenter phase 2 study in rituximab and alkylator-refractory indolent B-cell lymphomas (101-09, DELTA).19 This registration study enrolled 125 patients at centers across North America and Europe who were treated with idelalisib 150 mg twice daily until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or death. The median age of patients was 64 years (range, 33-87 years); their histologic subtypes included FL (n = 72; 58%), SLL (n = 28; 22%), MZL (n = 15; 12%), and LPL (n = 10; 8%); and they were heavily pretreated, with a median of 4 prior lines of therapy (range, 2-12 prior lines of therapy). Ninety percent were refractory to the immediately preceding line of therapy. Despite this, significant antitumor activity was observed, with 90% of patients experiencing tumor reduction. An independent review committee determined the ORR to be 57% (CR, 7%), with no significant differences observed between predefined subgroups. After a median follow-up of 9.7 months, the median PFS and overall survival were estimated at 11.0 months (range, 0.03-16.6 months) and 20.3 months (range, 0.7-22.0 months), respectively. A more than 3-fold increase in absolute lymphocyte from baseline occurred in 7/11 (64%) patients with SLL, 7/38 (18%) with FL, 1/6 (17%) with MZL, and 0/9 with LPL. In a subset analysis of 37 patients from the phase 2 study with FL and early disease progression (defined as event-free survival 24 or fewer months after frontline chemo-immunotherapy), idelalisib retained significant activity (ORR, 57%; CR, 13%) with a median PFS of 11.1 months.20 A recent pooled subgroup analysis included patients with MZL from the phase 1b (101-02; n = 6) and phase 2 (101-09; n = 15) studies. The MZL subtypes included mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (n = 12), nodal MZL (n = 7), and splenic MZL (n = 2). The ORR in the 2 studies was 2/6 (33%) and 7/15 (47%), with a median PFS of 7.4 and 6.6 months, respectively.21
Given the importance of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in pathogenesis,22,23 exploring the activity of idelalisib in MCL was logical. Kahl et al reported the results from 40 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL treated in the phase 1b study.24 The study population included many heavily pretreated (median number of prior therapies, 4; range, 1-14 prior therapies) patients, but excluded ibrutinib-exposed patients. The dose ranges explored were identical to those used in indolent NHL. The ORR across all doses was 40% (CR, 2%). Patients treated at the phase 2 dose or higher were more likely to respond than those treated at lower doses (ORR, 69% v 21%). The median DOR and PFS were 2.7 and 3.7 months, respectively, with a trend toward longer PFS among less heavily pretreated patients (mPFS, 8.2 vs 3.7 months, dichotomized at 6 prior therapies). In particular, 8/40 (20%) experienced clinical benefit exceeding 12 months. Treatment-emergent lymphocytosis was rare relative to patients with CLL/SLL; 5 (12%) experienced more than 3-fold elevation in absolute lymphocyte count relative to baseline. The limited duration of response in patients with MCL suggests the rapid development of resistance to p110δ inhibition.
Toxicity
The toxicities caused by this agent merit further discussion. The most common adverse events reported in the phase 1b and phase 2 studies were fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, rash, chills, and pyrexia, whereas the most frequent grade 3 or above adverse events were diarrhea and pneumonitis.16,19 Grade 3 or higher elevation of serum transaminases occurred in 16 patients (25%). Although reversible in most cases, up to a quarter of patients experience recurrent elevation on rechallenge.25 Careful monitoring of liver function tests during treatment and avoidance of concomitant hepatotoxic medications is therefore advised. Grade 3 or higher neutropenia occurred in 16 patients (25%), although no relationship with dose level was evident. The median time to onset of grade 3 or higher elevation in transaminases was 5.3 weeks. In all instances, transaminitis resolved to grade 1 after a median of 3 weeks. Diarrhea was common, with 2 patterns apparent: within the first 8 weeks a milder form responsive to antimotility agents, and a more severe form that occurs later and is not responsive. Grade 3 or higher diarrhea (defined as >7 stools/day above baseline) has been observed in ∼14% of patients in reported clinical trials.16,19,24,26 In anecdotal reports, oral budesonide appears to shorten symptoms.25 Intestinal perforation was rare and occurred in less than 1% of patients treated. Pneumonitis was reported in 3% of patients treated in single-agent studies and was rarely fatal (<0.5%).19,24,27 Pneumonitis generally occurred after several months of treatment (median, 7.8 months) and typically presented with cough, dyspnea, and fever with ground-glass opacities noted on computed tomography of the chest.28
Unexpected and severe toxicity in idelalisib combination studies
Given the success of idelalisib as monotherapy, attempts have been made to combine it with other agents. Idelalisib has been combined with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in patients with CLL without significant increases in toxicity, apart from increased rates of grade 3 or higher neutropenia (34% vs 22%).26 The triplet of lenalidomide, idelalisib, and rituximab caused serious toxicity, resulting in the closure of 3 early-phase studies. Smith et al described grade 3 or higher adverse events including transaminitis, rash, hypotension, lung infection, and culture-negative sepsis syndrome among 8 patients treated in the Alliance A051201 and A051202 studies.29 Cheah et al reported grade 3 or higher transaminitis in 6/7 patients (86%) in a phase 1 study of the triplet, including 2 deaths: 1 from hepatic failure and another from with respiratory failure in the setting of gram-positive bacteremia.30 Barr et al reported grade 3 or higher pneumonitis in 11 (17%) of patients in a prematurely terminated phase 2 study of the spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor entospletinib and idelalisib. In 5 patients (8%), mechanical ventilation was required, and 2 patients died of respiratory failure.31 The authors noted increases in Th1 cytokines among patients who experienced pneumonitis, and bronchoalveolar lavages showed a CD8+ T-cell infiltrate, which is consistent with an immune, noninfectious pneumonitis. These sobering experiences provide important lessons for the further development of biologic doublet and triplet combinations, particularly involving dual B-cell receptor pathway modulators or immunomodulators. These findings also add to the accumulating evidence that liver, gut, and lung toxicities are immune mediated. It is likely that PI3Kδ inhibition of Treg cells results in both qualitative and quantitative abnormalities in T-cell subsets, with subsequent loss of tolerance32 leading to the cytotoxic T-cell organ infiltration. This hypothesis may explain observed findings in biopsies of the liver,33 colonic mucosa,34,35 and lung25 tissue in affected patients. Treatment-naive patients with more intact immune systems also appear more likely to develop grade 3 or higher toxicities than relapsed/refractory patients.33 Preliminary data from ongoing studies suggest patients with severe toxicities had lower baseline levels of Treg functional markers and decreased Treg effector markers (granzyme β, human leukocyte antigen-D related, and progammed cell death-1) after treatment relative to those who do not.33 Although these observations require confirmation, baseline Treg profiling may be a potential method for prospectively identifying patients at greatest risk for toxicity.
Opportunistic infections halt phase 3 studies
Recent data indicate idelalisib combinations cause immune deficiency in addition to autoimmune toxicity. A recent safety analysis of 3 phase 3 studies in subjects with previously untreated CLL (bendamustine/rituximab ± idelalisib) and previously treated indolent B-cell NHL (rituximab ± idelalisib and bendamustine/rituximab ± idelalisib) were recently halted because of an excess of deaths and serious adverse events among patients treated in the idelalisib-containing groups (combined mortality rate, 49/664 [7.4%] vs 14/402 [3.5%]) (Gilead Sciences Inc., written communication, March 11, 2016). These were largely attributable to increased opportunistic infections; notably, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation. Among the 20% of patients in whom PJP prophylaxis was administered, no deaths occurred. An increased risk for opportunistic infections has previously been reported among patients treated with bendamustine-containing regimens.36-38 Nonetheless, because of the apparent increase in risk, we have modified our practice to include mandatory PJP prophylaxis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.39 Patients receiving idelalisib presenting with fever, hypoxia, and pulmonary infiltrates should discontinue idelalisib and be treated empirically until P. jirovecii can be excluded. If noninfectious pneumonitis is suspected, prednisone should be continued. Before commencing idelalisib, all patients should have CMV status assessed. CMV seronegative patients should receive CMV-negative or filtered blood products. For seropositive patients, we have extrapolated from alemtuzumab guidelines40 and perform regular (eg, monthly) CMV antigen or quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. Idelalisib should be discontinued and ganciclovir or valganciclovir preemptively initiated in patients with positive CMV PCR/antigen and symptoms consistent with CMV infection, patients presenting with fever and no clear source in whom quantitative CMV testing is unavailable, and asymptomatic patients with increasing viral load. We have provided a summary of recommendations for the management of toxicity associated with idelalisib, incorporating our synthesis of the US prescribing information,41 expert consensus guidelines,25 and recommendations arising from the recent safety warning (Gilead Sciences Inc., written communication, March 11, 2016) in Table 2. Although the increased risk for opportunistic infection appears to result in patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab ± bendamustine, until further safety data are available, the suggestions regarding PJP prophylaxis and CMV monitoring should be considered for all patients treated with the agent.
Mechanisms of resistance
At this point, limited data are available regarding the mechanisms of resistance to idelalisib. Iyengar et al studied PI3K class IA isoforms in primary patient MCL samples and demonstrated that although p110δ was widely overexpressed, p110α expression was variable, and significant increases occurred with disease progression.42 Further, they noted that although PI3Kδ inhibition was sufficient to abrogate B-cell receptor-mediated PI3K signaling, switching off constitutive activation of PI3K required blockade of both PI3Kα and PI3Kδ. Whole-exome sequencing identified PI3KCA gain-of-function mutations (N345K, P539R, E970K) in 3 independently generated idelalisib-resistant WSU-FSCCL FL cell line clones and compensatory activation in SFK and WNT pathways were documented.43 In an idelalisib-resistant ABC diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell line, loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog protein expression, modest upregulation of PI3Kγ, activation of the PI3K and MAPK pathway, and loss of c-Myc downregulation by idelalisib were identified as potential mechanisms of resistance.44 Both studies hinted at potential combinatorial strategies that could overcome resistance. Compagno et al recently presented preclinical data suggesting idelalisib enhances activation-induced deaminase activity in B cells, leading to genomic instability in both normal and malignant B cells,45 an observation with potentially important clinical implications for disease biology after relapse.
Other PI3K inhibitors
Other PI3K inhibitors are under development. Duvelisib (IPI-145) is an oral, potent dual p110δ/γ inhibitor.46 In the phase 1 study in 32 patients with relapsed/refractory indolent NHL, the ORR was 65%, with 5 CRs seen in patients with FL. Similar to idelalisib, transaminitis (41%) and diarrhea (22%) were the most common grade 3 or higher adverse events.27 Copanlisib is a PI3Kα/δ inhibitor. A phase 2 study in 11 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL demonstrated substantial activity (ORR, 64%) with mDOR ∼5 months.47 Inhibition of PI3Kα seems to result in hyperglycemia and hypertension, which may be problematic with extended exposure. Other PI3K inhibitors in early clinical development include TGR-1202, a PI3K p110δ inhibitor that may result in lower rates of hepatotoxicity and colitis48 ; AMG-319;49 and INCB-40093.50 CUDC-907 is a bifunctional molecule engineered to incorporate hydroxamic acid into a PI3K inhibitory structure, thus targeting both class I PI3K and class I/II histone deacetylase enzymes with 1 molecule.51 In the phase 1 study, responses were observed in 6/11 (55%) response-evaluable patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.52
Conclusion
Idelalisib provides an important option for patients with relapsed/refractory indolent B-cell lymphoma. Although most adverse events are manageable, careful monitoring for opportunistic infections such as PJP and CMV reactivation, and immune toxicities including elevation of serum transaminases, colitis, and pneumonitis, is necessary. Some of these adverse events may be more prevalent in the frontline setting and are exacerbated when combined with other immunostimulatory biologic agents. Careful design and conduct of studies will define the optimal combinations and populations most likely to derive benefit (and experience unacceptable toxicity) from this important new therapy.
Authorship
Contribution: C.Y.C. and N.H.F. performed the literature review, wrote the manuscript, and created the tables and figure.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.Y.C. consulted for Gilead and served on the advisory board for Janssen. N.H.F. served on the advisory board for Gilead, received research funding and served on the advisory board for TG Therapeutics, and received research funding from and served on the advisory board for Infinity.
Correspondence: Nathan H. Fowler, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 1515 Holcombe Blvd #429, Houston, TX 77030-4009; e-mail: nfowler@mdanderson.org.