Investigations were performed to define the factor XII (FXII) binding site(s) on cultured endothelial cells (HUVECs). Biotin- or fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–FXII in the presence of 10 μM Zn2+ specifically binds to HUVEC monolayers or cells in suspension. Collagen-stimulated platelets release sufficient Zn2+ to support FXII binding. On laser scanning confocal microscopy or electron microscopy, FITC-FXII or Nanogold-labeled FXII, respectively, specifically bind to HUVECs. Antibodies to gC1qR, urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and, to a lesser extent, cytokeratin 1 (CK1) block FXII binding to HUVECs as determined by flow cytometry and soluble or solid phase binding assays. FITC-FXII on endothelial cells colocalizes with gC1qR, uPAR and, to a lesser extent, CK1 antigen. Combined recombinant soluble uPAR and CK1 inhibit 80% FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs. Peptide Y(39)HKCTHKGR(47) (YHK9) from the N-terminal region of FXII and peptide H(479)KHGHGHGKHKNKGKKNGKH(498) from HK's domain 5 cell-binding site block FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs. Peptide YHK9 also inhibits FXIIa's activation of prekallikrein and FXI on HUVECs. These combined investigations indicate that FXII through a region on its fibronectin type II domain binds to the same multiprotein receptor complex that comprises the HK binding site of HUVECs. However, plasma concentrations of HK and vitronectin inhibit FXII binding to HUVECs 100% and 50%, respectively, and plasma albumin and other proteins prevent a sufficient level of free Zn2+ to be available to support FXII binding to HUVECs. Thus, physiologic FXII expression on HUVECs is secondary to HK binding and highly restricted in its ability to initiate prekallikrein or FXI activation.
Introduction
Investigations reveal that high molecular weight kininogen (HK) alone or in complex with prekallikrein (PK) assembles on a multiprotein receptor complex on endothelial cells.1This multiprotein receptor complex consists of gC1qR, urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), and cytokeratin 1 (CK1).2-7 Although previously controversial, recent studies show that gC1qR is constitutively expressed on the membrane of unperturbed, cultured endothelial cells.1,7-10 When PK is bound to HK bound to this multiprotein receptor complex, PK becomes activated to kallikrein.11 Formed kallikrein digests its receptor HK to liberate bradykinin.11,12 The released bradykinin then binds to the bradykinin B2 receptor to stimulate nitric oxide formation.12 Released bradykinin also stimulates tissue plasminogen activator release and prostacyclin formation from endothelial cells.13 14
Activation of PK when assembled on HK on endothelial cells is independent of factor XII (FXII) and its activated forms.11,15 In certain circumstances, FXII activation on endothelial cells is dependent upon prior PK activation.15,16 Activated FXII increases the rate and extent of kallikrein formation on endothelial cells and initiates FXI activation in certain circumstances.10,15-17 FXII specifically binds to the endothelial cell membrane, and HK blocks FXII binding.18 FXII also binds to gC1qR.2 3 The expression of FXII on endothelial cells may be closely localized to the receptor complex for HK. The following investigations reveal that FXII by its amino-terminal region binds to gC1qR, uPAR, and CK1 on endothelial cells. However, this interaction is highly restricted by plasma concentrations of HK and the availability of free Zn2+.
Materials and methods
Materials
Human FXII with a specific activity of 37 to 54 U/mg, single-chain HK with a specific activity of 13 U/mg, and human PK and human FXI with a specific activity of 22 U/mg or 200 U/mg, respectively, were purchased from Enzyme Research Laboratories (South Bend, IN). Recombinant soluble uPAR (suPAR) was generously provided by Dr Douglas B. Cines of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Urokinase (no. 128) was purchased from American Diagnostica, Greenwich, CT. Vitronectin was purchased from Molecular Innovations, Southfield, MI. A biotinylating kit, ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase, and peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, 3,3′, 5,5′ tetramethylbenzidine dihydrochloride (turbo-TMP), were supplied by Pierce Chemical (Rockford, IL). Nanogold and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) protein labeling kits were purchased from Nanoprobes (Yaphank, NY) and Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR), respectively. Purified recombinant cytokeratins (rCK131, rCK128, and rCK114 [recombinant CK1 at 31, 28, and 14 kd, respectively]) were prepared as previously reported.6 Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), endothelial cell growth medium, trypsin–ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and trypsin-neutralizing solutions were purchased from Clonetics (San Diego, CA).
Peptides and antibodies
The sequential synthetic peptides I(1)PPWEAPKEHKYKAEEHTV(19) (IPP19), F(30)PFQYHRQL(37) (FPF9), or Y(39)HKCTHKGR(47) (YHK9) to the N-terminal region of the heavy chain of FXII and scrambled YHK9 peptide, GYKTKHCRH (GYK9), were synthesized at Multiple Peptide Systems (San Diego, CA). Peptide from domain 5 of the kininogen, H(479)KHGHGHGKHKNKGKKNGKH(498) (HKH20), was synthesized and purified in the Protein and Carbohydrate Structure Facility of the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, MI). The numbering for the peptides from FXII and HK start from the amino-terminal end of the mature protein.19 Peptide G(143)PVCSPGGIQEVTINQSLLQ(162) (GPV20) from human CK1 was used to immunize goats for the production of antisera (anti-GPV20) at Quality Controlled Biochemicals (Hopkinton, MA).1 6 Monoclonal antibody to gC1qR (clone 74.5.2) was purchased from Covance Research Products (Richmond, CA). A monoclonal antibody against uPAR (3B10FC) was generously provided by Dr Robert F. Todd III at the University of Michigan. Monoclonal antibodies to von Willebrand factor and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) were purchased from Enzyme Research Laboratories and Bio-Source Laboratories (Camarillo, CA), respectively.
Labeling of FXII
Biotinylation.
FXII with a specific activity of 37 to 54 U/mg in 4 mM sodium acetate–HCl and 0.15 M NaCl, pH 5.3, was dialyzed against 0.01 M sodium phosphate, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 7.4, and biotinylated according to the procedure of Pierce Chemical.20 Biotin-FXII had a specific activity of 43.3 U/mg.
FITC labeling.
FXII was fluorescein labeled according to the procedure of Molecular Probes. A specific activity of 36 U/mg for FITC-FXII was measured by coagulant and protein assays, and the integrity of the protein was checked by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. No activation of FXII occurred during the labeling procedure.
Nanogold labeling.
FXII was Nanogold labeled according to the procedure of Nanoprobes. The specific activity of Nanogold-FXII was 53 U/mL by coagulant assay, and on reduced 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis there was no evidence of activation of FXII during the labeling procedure.
Endothelial cell culture
HUVECs were obtained and cultured according to Clonetics' recommendations. Cells between the first and fifth passage were subcultured onto fibronectin-treated (1 μg per well) 96-well plates 24 hours prior to the start of the experiment. The endothelial cell line EA.hy926, provided by Dr Cora-Jean S. Edgell of the Department of Pathology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, was cultured as previously reported.1
Isolation of human platelets
Fresh whole blood was collected from individual healthy volunteers into one-tenth volume of 10 μM Phe-Pro-Arg-chloromethyl ketone in saline (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA) and centrifuged at 180g for 20 minutes at room temperature. Collection of blood from healthy donors took place after their informed consent and with the approval of the Institutional Review Board of the University of Michigan. The platelet-rich plasma was removed; its pH was adjusted to 6.5; and prostaglandin I2, 1 μM final concentration, was added. The platelet-rich plasma was then centrifuged at 1200g for 10 minutes at room temperature. After removing the plasma, the platelet pellet was resuspended in HEPES carbonate buffer (HCB) (137 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, 12 mM NaHCO3, 14.7 mM HEPES, 5.5 mM dextrose containing 0.1% gelatin, 2 mM CaCl2, and 1 mM MgCl2), pH 6.5, containing 250 μM Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (Sigma) and centrifuged again at 1200gfor 10 minutes. The final platelet pellet was resuspended in HCB, pH 7.4, and the platelets were counted in a Z1-series Coulter counter (Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL). In all studies, the platelets were examined for their ability to aggregate (Chrono-Log aggregometer, Hatboro, PA) to 5 μg/mL collagen (Nycomed Arzneimittel, Munchen, Germany).
FXII binding to endothelial cells
A biotin-FXII binding assay to confluent monolayers of HUVECs on 96-well microtiter plates was established. After washing with HCB, pH 7.4, the cells were usually incubated with 10 nM biotin-FXII in the presence or absence of 10 μM Zn2+. After incubation, the cells were washed 3 times with HCB. The relative biotin-FXII binding to the cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate (Pierce) and turbo-TMP (Pierce) as previously described.20 Bound biotin-XII was determined by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311 from Bio-Tek Instruments (Winooski, VT).
An FITC-FXII binding assay to HUVECs in suspension also was established. HUVECs were detached from culture plates with a trypsin-EDTA solution (GIBCO, Grand Island, NY) and washed and resuspended with HCB, pH 7.4. Usually binding was performed with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the presence or absence of 10 μM Zn2+. HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension in HCB in a 96-well filtration plate were incubated on a prewetted hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (pore size 1.2 μm) with low protein-binding capacity (Millipore, Bedford, MA) for 2 hours at 37°C.21 At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed and filtered using multiScreen Separation System Vacuum Manifold from Millipore. The fluorescence of cell-bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs bound to the PVDF membrane of the filtration plate was measured on CytoFluor4000 fluorescence plate reader from PerSeptive Biosystems (Framingham, MA) with 485 nm excitation and 530 nm emission filters.
FXII binding to HUVECs in the presence of collagen-stimulated washed platelets
Biotin-FXII (10 nM) in HCB, pH 7.4, was added to confluent HUVEC monolayers in the presence of increasing concentrations of platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) and in the presence or absence of 5 μg/mL collagen. The cells were incubated for 90 minutes at 37°C on a rotating mixer maintained at 50 rpm. After completion of the incubation, the cells were washed 3 times with binding buffer, and the relative amount of biotin-FXII bound to the adherent HUVECs was determined as described above. In certain experiments, the gelatin in the HCB was removed and was substituted with 3.5 mg/mL or 40 mg/mL bovine serum albumin. In these cases, the albumin-containing buffers were supplemented with 50 μM and 3 mM Zn2+, respectively.
Laser scanning confocal microscopy
HUVECs grown on microscope slides were used in laser scanning confocal microscopy experiments as previously reported.1The cells were incubated with 300 nM FITC-FXII in the presence or absence of 10 μM Zn2+ or 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXII. In other experiments, cells were incubated simultaneously with 300 nM FITC-FXII in the presence of 10 μM Zn2+ and goat immunoglobulin G (IgG) (300 μg/mL), mouse IgG (4 μg/mL), affinity-purified goat anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL), mouse anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL), mouse anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL), or mouse anti-ICAM (anti-CD54) (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 1 hour at 37°C. At the end of the incubation, cells were washed and incubated with an Alexa Fluor 594–labeled donkey antigoat IgG (H+L) conjugate (10 μg/mL) or Alexa Fluor 594–labeled goat antimouse IgG conjugate (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at room temperature while protected from light. The slides were covered with an antifading prolong mounting medium from Molecular Probes and were visualized by using a confocal fluorescence microscope (Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA). Optical scanning and digital processing of the images were performed to determine the topographic distribution of the FITC or Alexa Fluor/IgG associated with HUVECs as previously reported.1
Electron microscopic visualization of Nanogold-FXII on EA.hy926 endothelial cells
Subconfluent EA.hy926 endothelial cells were made into cell suspensions by treating the cells with a solution containing 0.05% trypsin, 0.53 mM EDTA, dissolved in Hanks balanced salt solution for 2 to 4 minutes. The trypsin was inactivated by washing the cells with Dulbecco modified Eagle medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum followed by washing 3 times for 5 minutes each with HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM ZnCl2. Next, the cells were incubated with 210 nM Nanogold-FXII for various times (5, 15, 30, 60, and 120 minutes) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. After incubation, the cells were washed 3 times with the same buffer and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 30 minutes. The small 1.4-nm gold particles coupled to FXII were enhanced by incubating the cells with IntenSEsilver enhancement kit (Amersham Life Science, England) for 20 minutes at 22°C. Before enhancement the cells were exhaustively washed with buffer to remove all traces of fixative and with distilled water to eliminate buffer salts. When the silver enhancement procedure was completed, aliquots of the cells were visualized at the light microscopic level or were postfixed with 0.25% osmium tetroxide for 1 hour at 4°C and dehydrated and embedded according to standard procedures in an epon-araldite mixture. Thin sections prepared from this material were contrasted with lead citrate and observed in a Hitachi H-700 electron microscope.
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry was performed with HUVECs (5 × 106/mL). A total of 100 μL of the detached HUVECs was incubated with 200 nM FITC-XII in HCB containing 1 mg/mL human γ-globulin in the presence or absence of 10 μM Zn2+. In other experiments HUVECs were incubated with FITC-XII in the presence or absence of goat IgG (300 μg/mL), mouse IgG (4 μg/mL), affinity-purified goat anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL), anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL), or anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL) antibodies in binding buffer containing 10 μM Zn2+ and 1 mg/mL human γ-globulin with occasional gentle mixing for 1 hour at 37°C as described previously.1 At the end of the incubation, HUVECs were washed 3 times by centrifigation at 400g and resuspended in the same buffer. The bound FITC-labeled FXII to HUVECs was monitored with an Epics-C flow cytometer (Coulter Electronics) as previously reported.1
Inhibition of FITC-XII binding to endothelial cells by anti-GPV20, anti-uPAR, and anti-gC1qR antibodies or peptides on HUVECs in suspension
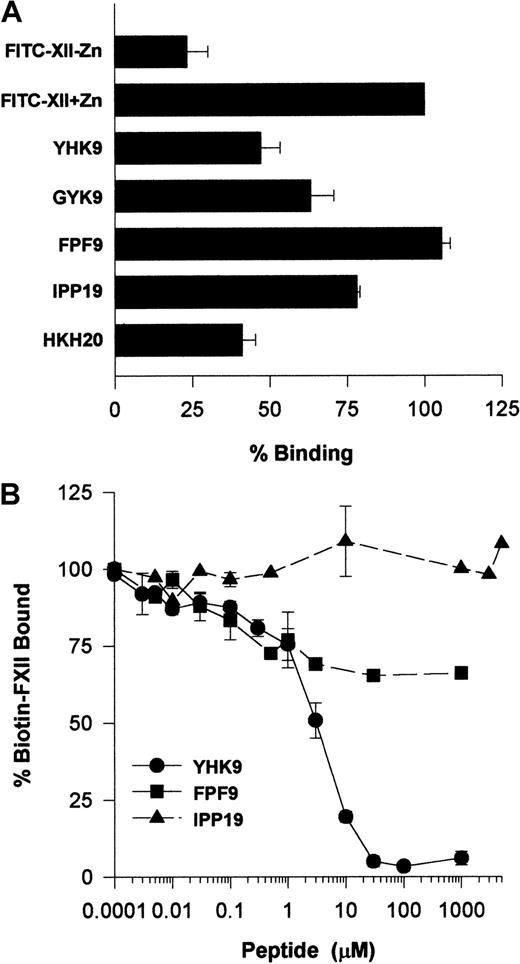
HUVECs (4 × 104 per well) in suspension in HCB were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in 96-well filtration plates in the presence or the absence of mouse anti-gC1qR (1.2 μM), mouse anti-uPAR (1.2 μM), mouse anti–von Willebrand factor (1.2 μM), mouse anti-ICAM (1.2 μM), goat anti-GPV20 (2.5 μM), mouse IgG (1.2 μM), or goat IgG (2.5 μM). In other experiments, the cells were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in 96-well filtration plates in the presence or the absence of 100 μM of peptides YHK9, GYK9, FPF9, IPP19, or HKH20. After 2 hours of incubation at 37°C, the cells were washed and filtered using multiScreen Separation System Vacuum Manifold from Millipore, and the fluorescence of cell bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was measured on a fluorometer as described above.
Inhibition of biotin-XII binding to endothelial cells by anti-uPAR and anti-gC1qR antibodies or peptides on HUVEC monolayers
Biotin-FXII (10 nM) was added to confluent monolayers of HUVECs in the presence or the absence of increasing concentrations of mouse IgG (0-500 nM), mouse anti-gC1qR (0-500 nM), or mouse anti-uPAR (0-500 nM) antibodies. Similarly, the influence of peptides YHK9, GYK9, FPF9, IPP19, or HKH20 at 100 μM each on 10 nM biotin-FXII binding to confluent monolayers of HUVECs was determined after 90 minutes incubation at 37°C. The relative biotin-FXII binding of binding to the cells was determined as described above.20
Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to endothelial cells by suPAR and cytokeratin on HUVEC suspension
HUVECs were detached and washed with binding buffer. The cells were then resuspended in the same buffer in the presence or absence of 10 μM Zn2+. The suspension of HUVECs (4 × 104 per well) was incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the absence or the presence of increasing concentrations of suPAR (0.01-6 μM) and/or rCK131 (0.01-10 μM) on prewetted hydrophilic PVDF membranes. The relative level of FITC-FXII binding was determined as described above.
Inhibition of FXI and PK activation amplified by FXII on endothelial cells by peptides on HUVEC suspension
HUVECs were grown in endothelial cell growth medium containing human FXII–deficient serum. Confluence monolayers of HUVECs then were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2. In the PK activation assay, 10 nM HK, 10 nM PK, and 20 nM FXII were simultaneously added to HCB in the presence or absence of 100 μM of peptides YHK9 or FPF9 and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed, 1 mM S2302 (DiaPharm, Franklin, OH) was added in HCB, and hydrolysis proceeded for an additional hour. The generated S2302 hydrolytic activity was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 405 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311 (Bio-Tek Instruments). In the FXI activation assay, the cells were incubated with 10 nM HK, 5 nM FXI, and 20 nM FXII in binding buffer in the presence or absence of 100 μM of peptides YHK9, FPF9, or IPP19 for 1 hour at 37°C.16 22 At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed, 0.8 mM S2366 (DiaPharm) was added in HCB, and hydrolysis proceeded for an additional hour. The generated FXIa was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 405 nm.
Measurement of Zn2+ after platelet–endothelial cell interactions
The concentration of released Zn2+ from the same collagen-stimulated platelets that were used in the biotin-FXII binding experiments to HUVECs was measured by colorimetric assay.23 These platelet samples were prepared simultaneously with the performance of the binding experiments. A Zn2+ standard curve was determined by adding 10 μL of known amount of Zn2+ (0.1-30 μM) or samples of collagen-treated platelet releasates with 90 μL of 20 μM 5-Br-PAPS (2-(5-bromo-2-pyridylazo)-5-(propyl-N-sulfopropylamino)-phenol sodium salt) (Wako Chemicals, Richmond, VA) in 0.01 M Tris, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 7.4. The absorbance was monitored at 552 nm that arises from the complex formation of Zn2+ with 5-Br-PAPS.
Results
FXII binding to HUVECs
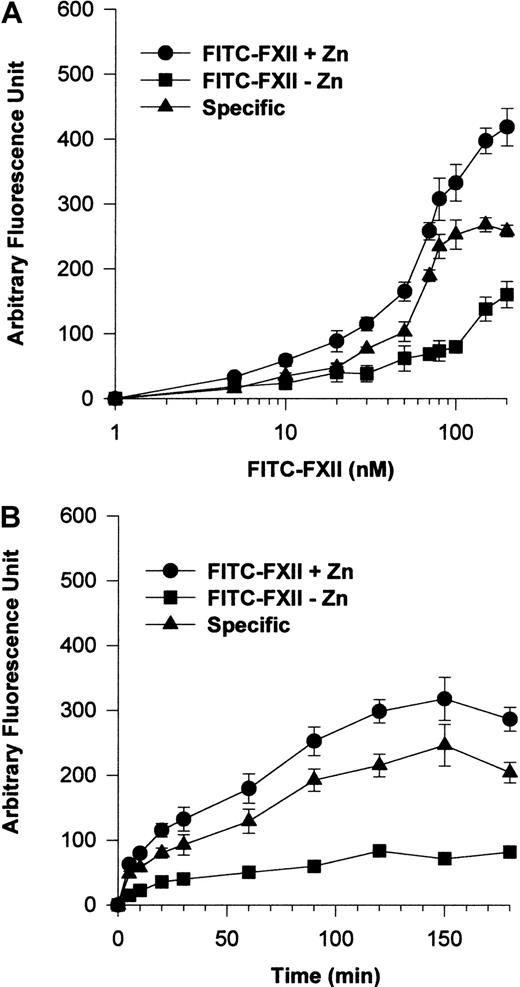
Experiments determined the characteristics of FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers (Figure 1). No Zn2+ or 200-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXII demonstrated specific biotin-FXII binding to HUVECs (Figure 1A). The degree of biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers depended upon the ambient free Zn2+ concentration that varied depending upon the carrier protein (Figure 1B). Using gelatin, a carrier protein that does not bind Zn2+,15 the optimal Zn2+ concentration for biotin-FXII binding was 10 μM. When 40 mg/mL bovine serum albumin was substituted for gelatin in the same buffer, 3 mM added Zn2+ was necessary for specific binding. When biotin-FXII binding was performed in FXII-deficient serum, 3 mM added Zn2+ also was necessary to observe specific binding as seen with gelatin buffer. These data indicate that the ambient free Zn2+ concentration modulated biotin-FXII binding to HUVECs. Last, the addition of 10 nM biotin-FXII was optimal for specific FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers (Figure 1C).
Biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers.
(A) HUVEC monolayers (4 × 104 cells per well) were incubated with 10 nM biotin-FXII for 0 to 180 minutes at 37°C in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM Zn2+ or in the presence of 10 μM Zn2+ and 200-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXII (▴). (B) HUVEC monolayers (4 × 104cells per well) were incubated with 10 nM biotin-FXII for 0 to 180 minutes at 37°C in HEPES carbonate gelatin buffer (HC-Gelatin) (●), HCB containing 40 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (HC-BSA) (▪), or FXII-deficient serum (▴) in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of Zn2+ (0.1-3000 μM). (C) HUVEC monolayers (4 × 104 cells per well) were incubated with increasing concentrations of biotin-FXII (1-70 nM) for 90 minutes at 37°C in HEPES carbonate gelatin buffer in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM Zn2+. The specific binding curve (▴) is calculated by subtracting binding in the absence of added Zn2+ from that in the presence of Zn2+. Biotin-FXII binding to the cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate and peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, turbo-TMP (see “Materials and methods”). Bound biotin-FXII was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311 (Bio-Tek Instruments). The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers.
(A) HUVEC monolayers (4 × 104 cells per well) were incubated with 10 nM biotin-FXII for 0 to 180 minutes at 37°C in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM Zn2+ or in the presence of 10 μM Zn2+ and 200-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXII (▴). (B) HUVEC monolayers (4 × 104cells per well) were incubated with 10 nM biotin-FXII for 0 to 180 minutes at 37°C in HEPES carbonate gelatin buffer (HC-Gelatin) (●), HCB containing 40 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (HC-BSA) (▪), or FXII-deficient serum (▴) in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of Zn2+ (0.1-3000 μM). (C) HUVEC monolayers (4 × 104 cells per well) were incubated with increasing concentrations of biotin-FXII (1-70 nM) for 90 minutes at 37°C in HEPES carbonate gelatin buffer in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM Zn2+. The specific binding curve (▴) is calculated by subtracting binding in the absence of added Zn2+ from that in the presence of Zn2+. Biotin-FXII binding to the cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate and peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, turbo-TMP (see “Materials and methods”). Bound biotin-FXII was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311 (Bio-Tek Instruments). The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Additional investigations were performed to establish a specific FITC-FXII binding assay to suspensions of HUVECs (Figure2). The addition of 70 nM FITC-FXII in the presence of 10 μM Zn2+ was found to be optimal for detection of specific FXII binding to suspensions of HUVECs (Figure2A). Under these conditions, FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs was maximal at 90 minutes' incubation in the presence of 10 μM Zn2+(Figure 2B).
FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs in suspension.
(A) HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension were incubated with 1 to 200 nM FITC-FXII for 120 minutes at 37°C over a PVDF membrane in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM ZnCl2. The specific binding curve (▴) is calculated by subtracting binding in the absence of Zn2+ from binding in the presence of Zn2+. (B) HUVECs (4 × 104cells per well) in suspension were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII for 0 to 180 minutes at 37°C over a PVDF membrane in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM ZnCl2. The specific binding curve (▴) is shown. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed and the HUVEC-bound FITC-FXII was quantified by using CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 to 5 independent experiments.
FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs in suspension.
(A) HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension were incubated with 1 to 200 nM FITC-FXII for 120 minutes at 37°C over a PVDF membrane in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM ZnCl2. The specific binding curve (▴) is calculated by subtracting binding in the absence of Zn2+ from binding in the presence of Zn2+. (B) HUVECs (4 × 104cells per well) in suspension were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII for 0 to 180 minutes at 37°C over a PVDF membrane in the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 10 μM ZnCl2. The specific binding curve (▴) is shown. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed and the HUVEC-bound FITC-FXII was quantified by using CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 to 5 independent experiments.
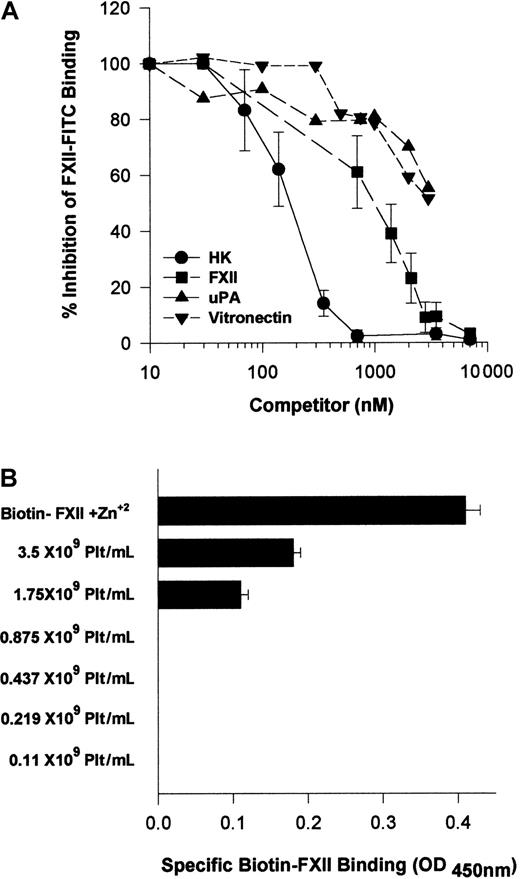
Activated platelets provide Zn2+ to support FXII binding to HUVECs
The requirement for 10 μM Zn2+ to support FXII binding suggested that FXII binding is distinguished from HK binding to HUVECs that required only 0.3 μM Zn2+.12Investigations determined if activated platelets that contain high concentrations of intracellular Zn2+ provided this divalent cation to support FXII binding.24 Washed human platelets in varying concentrations (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) and 10 nM biotin-FXII in HCB were incubated over monolayers of HUVECs in the presence or absence of collagen (Figure 3A). Specific biotin-FXII binding to HUVECs was detected when at least 2.2 × 108 platelets per milliliter were activated by collagen. These data suggested that activation of physiologic concentrations of platelets provided sufficient Zn2+ to support specific FXII binding to HUVECs in this buffer. When the releasates of 2.2 × 108 collagen-activated platelets per milliliter were examined for the ambient Zn2+concentration, it was found to be about 10 μM (Figure 3B). This value was consistent with the required divalent cation concentration necessary to support biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers in buffer alone (Figure 1B).
Collagen-stimulated platelets promote FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers.
(A) Washed human platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) in HCB, pH 7.4, with no added Zn2+ were incubated over washed HUVEC monolayers in microtiter plate cuvette wells in the same buffer in the presence of 10 nM biotin-FXII and the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 5 μg/mL collagen for 90 minutes at 37°C on a rotating shaker. Specific biotin-FXII binding (▴) was determined by subtracting the level of binding seen with unactivated platelets from that occurring with collagen-activated platelets. At the completion of the incubation, the microtiter plate cuvette wells were washed and the amount of biotin-FXII bound to the HUVECs was determined as described in the legend to Figure 1. The single symbol ▾ represents 10 nM specific biotin-FXII binding in HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM Zn2+in the absence of platelets. (B) The concentration of Zn2+was determined in the releasate of collagen-activated platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) after the level of Zn2+ in the suspension media of unactivated platelets was subtracted. The concentration of Zn2+ was determined by a colorimetric assay (see “Materials and methods”). The results presented for both panels are the means ± SEM for 5 experiments.
Collagen-stimulated platelets promote FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers.
(A) Washed human platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) in HCB, pH 7.4, with no added Zn2+ were incubated over washed HUVEC monolayers in microtiter plate cuvette wells in the same buffer in the presence of 10 nM biotin-FXII and the presence (●) or absence (▪) of 5 μg/mL collagen for 90 minutes at 37°C on a rotating shaker. Specific biotin-FXII binding (▴) was determined by subtracting the level of binding seen with unactivated platelets from that occurring with collagen-activated platelets. At the completion of the incubation, the microtiter plate cuvette wells were washed and the amount of biotin-FXII bound to the HUVECs was determined as described in the legend to Figure 1. The single symbol ▾ represents 10 nM specific biotin-FXII binding in HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM Zn2+in the absence of platelets. (B) The concentration of Zn2+was determined in the releasate of collagen-activated platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) after the level of Zn2+ in the suspension media of unactivated platelets was subtracted. The concentration of Zn2+ was determined by a colorimetric assay (see “Materials and methods”). The results presented for both panels are the means ± SEM for 5 experiments.
FXII expression on HUVECs
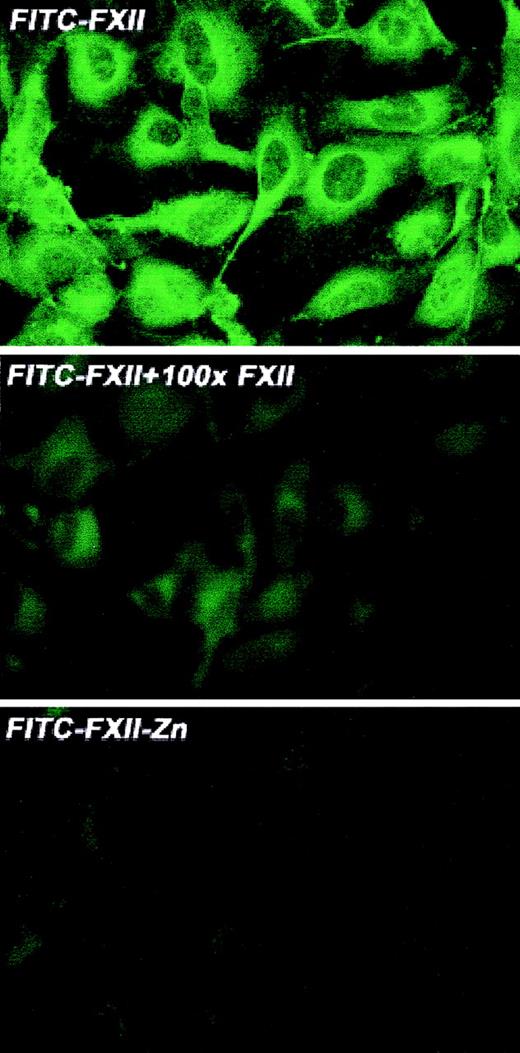
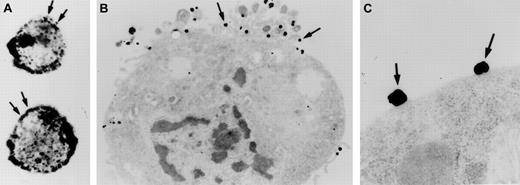
Investigations were performed to characterize FXII expression on HUVECs and determine the protein(s) it bound to. On laser scanning confocal microscopy, FITC-FXII diffusely bound to endothelial cell surfaces (Figure 4). The binding of FITC-FXII to HUVECs was specific because 100-fold molar excess of FXII or FITC-FXII added to HUVECs in the absence of Zn2+ did not specifically bind to the cells (Figure 4). The use of Nanogold-FXII demonstrated the binding of this molecule to endothelial cells at the electron microscopic level (Figure 5). On light microscope cell examination, there was an intense labeling with Nanogold-FXII that was marked on the cell periphery (Figure 5A). Nanogold-FXII binding was detected as early as 5 minutes of incubation at 37°C. After 20 minutes of silver enhancement, the 1.4-nm gold particles coupled to FXII increased irregularly in size to reach 100 to 200 nm in diameter. The ultrastructural analysis showed that most of the gold-labeled probe was associated to the endothelial cell membrane, though some of the particles were observed in cytoplasm vesicles (Figure 5B,C).
Laser scanning confocal microscopy of FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs.
Nonpermeabilized, paraformaldehyde (2%)–fixed HUVECs were grown on microscope slides. HUVECs were incubated with 300 nM FITC-FXII in HCB in the presence or absence of 10 μM ZnCl2 or 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXII for 1 hour at 37°C. Detection of FITC-FXII on the HUVECs is described in “Materials and methods.” The panels are photomicrographs of the laser scanning confocal microscopy. The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
Laser scanning confocal microscopy of FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs.
Nonpermeabilized, paraformaldehyde (2%)–fixed HUVECs were grown on microscope slides. HUVECs were incubated with 300 nM FITC-FXII in HCB in the presence or absence of 10 μM ZnCl2 or 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXII for 1 hour at 37°C. Detection of FITC-FXII on the HUVECs is described in “Materials and methods.” The panels are photomicrographs of the laser scanning confocal microscopy. The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
Visualization of Nanogold-FXII on EA.hy926 endothelial cells.
Cell suspensions were incubated for 60 minutes at 37°C with 210 nM Nanogold-FXII in HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM Zn2+, and then gold particles were enhanced with silver. Panel A shows the silver-enhanced FXII (arrows) at the light microscopic level. Panel B represents a low-power electron microscope view of an endothelial cell with clusters of silver-enhanced FXII on the cell surface (arrows). Panel C shows a high magnification of the irregular silver-enhanced Nanogold-FXII particles (arrows).
Visualization of Nanogold-FXII on EA.hy926 endothelial cells.
Cell suspensions were incubated for 60 minutes at 37°C with 210 nM Nanogold-FXII in HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM Zn2+, and then gold particles were enhanced with silver. Panel A shows the silver-enhanced FXII (arrows) at the light microscopic level. Panel B represents a low-power electron microscope view of an endothelial cell with clusters of silver-enhanced FXII on the cell surface (arrows). Panel C shows a high magnification of the irregular silver-enhanced Nanogold-FXII particles (arrows).
Investigations next were performed to determine if the same proteins that make up the HK binding site on HUVECs, CK1, gC1qR, and uPAR also contributed to FXII binding to HUVECs. The relative contribution of uPAR, gC1qR, and CK1 to FXII binding to HUVECs was determined by flow cytometry (Figure 6). On flow cytometry, FITC-FXII alone bound to the HUVEC membrane (Figure 6A). The presence of a monoclonal antibody to uPAR or gC1qR decreased the extent of expression of FITC-FXII on the membrane of HUVECs in suspension (Figure6B,D). The presence of a polyclonal antibody to CK1 directed to the HK binding site blocked FITC-FXII binding less (Figure 6C). These data suggested that uPAR and gC1qR and perhaps CK1 were FXII binding sites on HUVECs.
Flow cytometry of FITC-FXII expression on HUVECs.
Flow cytometry was performed with suspensions of washed, unfixed, and nonpermeabilized HUVECs (5 × 106/mL). HUVECs were incubated for 1 hour at 37°C in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 in the presence (shaded curve) or the absence (dotted curve) of 70 nM FITC-FXII or in the presence of 70 nM FITC-FXII (solid curves) and mouse anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL), goat anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL), mouse anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL), goat IgG (300 μg/mL), or mouse IgG (4 μg/mL). The binding of these antibodies to HUVECs was detected by a shift in the solid curve to the left in comparison to FITC-FXII alone (shaded curve). The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
Flow cytometry of FITC-FXII expression on HUVECs.
Flow cytometry was performed with suspensions of washed, unfixed, and nonpermeabilized HUVECs (5 × 106/mL). HUVECs were incubated for 1 hour at 37°C in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 in the presence (shaded curve) or the absence (dotted curve) of 70 nM FITC-FXII or in the presence of 70 nM FITC-FXII (solid curves) and mouse anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL), goat anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL), mouse anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL), goat IgG (300 μg/mL), or mouse IgG (4 μg/mL). The binding of these antibodies to HUVECs was detected by a shift in the solid curve to the left in comparison to FITC-FXII alone (shaded curve). The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
The colocalization of FXII and uPAR or gC1qR on the HUVEC membrane was examined by laser scanning confocal microscopy (Figure7). Like FXII, both gC1qR and uPAR antigen diffusely stained the surface of HUVECs although not to the same extent as FITC-FXII. Mouse IgG had no staining on these cells as previously reported1 (data not shown). When both fluorescent probes were examined simultaneously, FXII and gC1qR or uPAR were simultaneously localized to a central juxtanuclear position (Figure 7). However, the external rim of the HUVECs stained only for FXII. These data indicated that the membrane localization of FXII and uPAR or gC1qR was overlapping.
Colocalization of FITC-FXII with uPAR or gC1qR on HUVECs.
Nonpermeabilized, paraformaldehyde (2%)–fixed HUVECs were grown on microscope slides. HUVECs were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 300 nM FITC-FXII in the presence of anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL) or anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 1 hour at 37°C. The dual detection of the antigens was performed with a secondary antibody labeled with Alexa Fluor 594–labeled goat antimouse IgG conjugate (10 μg/mL) and FITC-FXII as described in “Materials and methods.” The panels are photomicrographs of the laser scanning confocal microscopy. The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
Colocalization of FITC-FXII with uPAR or gC1qR on HUVECs.
Nonpermeabilized, paraformaldehyde (2%)–fixed HUVECs were grown on microscope slides. HUVECs were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 300 nM FITC-FXII in the presence of anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL) or anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 1 hour at 37°C. The dual detection of the antigens was performed with a secondary antibody labeled with Alexa Fluor 594–labeled goat antimouse IgG conjugate (10 μg/mL) and FITC-FXII as described in “Materials and methods.” The panels are photomicrographs of the laser scanning confocal microscopy. The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
Additional investigations determined the colocalization of FXII and CK1 (Figure 8). CK1 antigen diffusely stained the endothelial cell, whereas FITC-FXII was more central in location (Figure 8). The pattern of distribution of FXII and CK1 was overlapping, with some colocalization in the perinuclear region although much less so than that seen with uPAR or gC1qR. The pattern of distribution of ICAM-1 and FXII also showed some colocalization of the 2 proteins around the nucleus (Figure 8). These combined data suggested that gC1qR and uPAR colocalized with the membrane expression of FXII. CK1 antigen was found to be associated with FXII to a lesser extent.
Colocalization of FITC-FXII with CK1 or ICAM on HUVECs.
Nonpermeabilized, paraformaldehyde (2%)–fixed HUVECs were grown on microscope slides. HUVECs were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 300 nM FITC-FXII in the presence of anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL) or anti-ICAM-1 (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 1 hour at 37°C. The dual detection of the antigens was performed with secondary antibodies labeled with Alexa Fluor 594–labeled donkey antigoat IgG (H+L) conjugate (10 μg/mL) or Alexa Fluor 594–labeled goat antimouse IgG (10 μg/mL) and FITC-FXII as described in “Materials and methods.” The panels are photomicrographs of the laser scanning confocal microscopy. The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
Colocalization of FITC-FXII with CK1 or ICAM on HUVECs.
Nonpermeabilized, paraformaldehyde (2%)–fixed HUVECs were grown on microscope slides. HUVECs were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 300 nM FITC-FXII in the presence of anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL) or anti-ICAM-1 (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 1 hour at 37°C. The dual detection of the antigens was performed with secondary antibodies labeled with Alexa Fluor 594–labeled donkey antigoat IgG (H+L) conjugate (10 μg/mL) or Alexa Fluor 594–labeled goat antimouse IgG (10 μg/mL) and FITC-FXII as described in “Materials and methods.” The panels are photomicrographs of the laser scanning confocal microscopy. The figure is a representative presentation of 3 independent experiments.
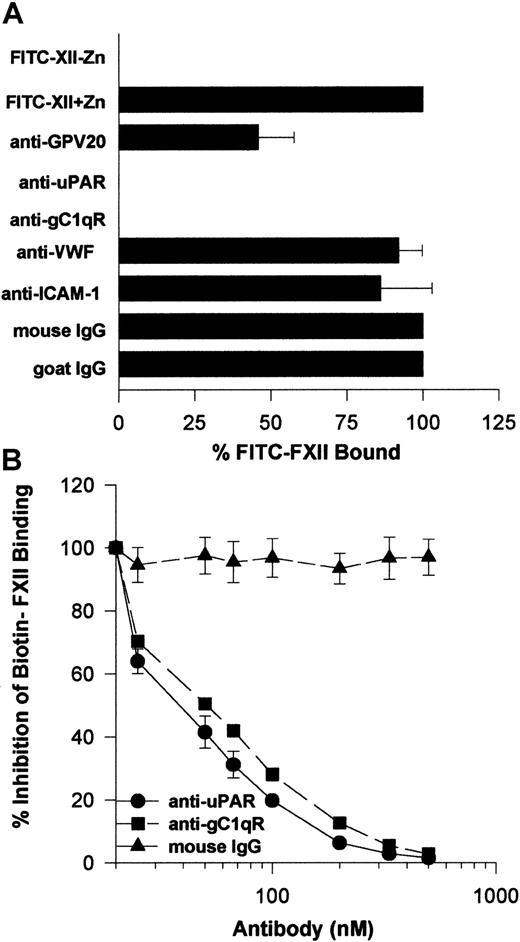
Further investigations determined that the monoclonal antibodies to uPAR or gC1qR used to describe the membrane expression of these proteins completely blocked FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions (Figure 9A). Alternatively, mouse IgG and monoclonal antibodies to von Willebrand factor or ICAM had no influence on FITC-FXII binding. Goat antibody to the HK binding site on CK1 also inhibited FITC-FXII binding about 50% under the conditions of the assay. Further studies confirmed these findings in a biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers assay (Figure 9B). Increasing concentrations of monoclonal antibodies to uPAR and gC1qR blocked biotin-FXII binding with a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 400 and 500 nM, respectively. These data suggested that the same proteins that serve as the HK binding site on HUVECs also participate in FXII expression in these cultured cell-binding assays.
Inhibition of FXII binding to HUVECs by antibodies to CK1, uPAR, and gC1qR.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions. HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 in the presence or absence of mouse IgG (4 μg/mL), goat IgG (300 μg/mL), affinity-purified goat anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL), mouse anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL), mouse anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL), mouse anti–von Willebrand factor (VWF) (4 μg/mL), or mouse anti–ICAM-1 (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 2 hours at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was determined using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers. Confluent monolayers of HUVECs were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2. Afterward, biotin-FXII (10 nM) was added to the HUVECs in the presence or the absence of increasing concentrations of mouse IgG (▴), anti-uPAR (●), or anti-gC1qR (▪) antibodies for 90 minutes at 37°C. Biotin-FXII binding to the cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate and peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, turbo-TMP (see “Materials and methods”). Bound biotin-FXII was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311 (Bio-Tek Instruments). The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Inhibition of FXII binding to HUVECs by antibodies to CK1, uPAR, and gC1qR.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions. HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 in the presence or absence of mouse IgG (4 μg/mL), goat IgG (300 μg/mL), affinity-purified goat anti-GPV20 (300 μg/mL), mouse anti-uPAR (4 μg/mL), mouse anti-gC1qR (4 μg/mL), mouse anti–von Willebrand factor (VWF) (4 μg/mL), or mouse anti–ICAM-1 (4 μg/mL) antibodies for 2 hours at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was determined using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers. Confluent monolayers of HUVECs were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2. Afterward, biotin-FXII (10 nM) was added to the HUVECs in the presence or the absence of increasing concentrations of mouse IgG (▴), anti-uPAR (●), or anti-gC1qR (▪) antibodies for 90 minutes at 37°C. Biotin-FXII binding to the cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate and peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, turbo-TMP (see “Materials and methods”). Bound biotin-FXII was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311 (Bio-Tek Instruments). The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Investigations were performed to determine a physical interaction between FXII and uPAR or CK1. Increasing concentrations of suPAR blocked FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs in suspension with an IC50 of 2 μM (Figure10A). Likewise, increasing concentrations of rCK131 blocked FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs in suspensions with an IC50 of 5 μM (Figure 10A). The FXII binding site on CK1 was partially mapped. Sequential 20 amino acid peptides from protein coded by exons 1, 2, and a small part of 3 of CK1 did not inhibit FITC-FXII binding to suspensions of HUVECs (data not shown). However, in addition to rCK131, which consists of protein coded by exons 1 to 7, rCK128 or rCK114, which consists of protein coded by exons 1 to 5 and 3 to 5, respectively, also blocked FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs in suspension (Figure 10B). These data indicated that the FXII binding region on CK1 is contained within a 100–amino acid section of protein coded by exons 3 to 5.6 Last, when the IC50 of suPAR and IC50 of rCK131 were combined, FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs was blocked by 80% (Figure 10C).
Influence of suPAR and CK1 on FXII binding to HUVECs.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions by suPAR or CK1. HUVECs in suspension were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of suPAR (●) or rCK131 (▪) for 2 hours at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspension by recombinant cytokeratins. HUVECs in suspension were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the absence or presence of 10 μM rCK131, rCK128, or rCK114 for 2 hours at 37°C. (C) Combined inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs by suPAR and rCK131. Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs was determined in the presence of 6 μM rCK131 alone, 3 μM suPAR, or combined 5 μM rCK131 and 2 μM suPAR. In all cases, the level of binding seen in the absence of added Zn2+ was subtracted from the total. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Influence of suPAR and CK1 on FXII binding to HUVECs.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions by suPAR or CK1. HUVECs in suspension were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of suPAR (●) or rCK131 (▪) for 2 hours at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspension by recombinant cytokeratins. HUVECs in suspension were incubated in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the absence or presence of 10 μM rCK131, rCK128, or rCK114 for 2 hours at 37°C. (C) Combined inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs by suPAR and rCK131. Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs was determined in the presence of 6 μM rCK131 alone, 3 μM suPAR, or combined 5 μM rCK131 and 2 μM suPAR. In all cases, the level of binding seen in the absence of added Zn2+ was subtracted from the total. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Determination of the region on FXII that interacts with HUVECs
Investigations ascertained what region on FXII interacted with HUVECs. Recent investigations indicated that certain highly charged amino acids on the N-terminal region of FXII interacted with artificial negatively charged surfaces.22 Studies examined whether peptides of this region also interfered with FXII binding to HUVECs in suspension (Figure 11A). Peptide YHK9 of the fibronectin type II domain of FXII inhibited FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs 50%. No inhibition occurred with an adjacent peptide FPF9 (Figure 11A). The inhibition of FXII binding by peptide YHK9 was not sequence-specific. A scrambled form of peptide YHK9, peptide GYK9, also inhibited binding 40%. In addition, a peptide from HK's domain 5 binding site, HKH20, blocked binding to the same extent as peptide YHK9. This latter result could have arisen from the charge of peptide HKH20 or its ability to bind to the same receptor proteins on HUVECs that FXII bound.1 Last, peptide IPP19, to the first 19 amino acids on the N-terminal region of FXII, blocked binding 25%.
Determination of a region on FXII that binds to HUVECs.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions by FXII peptides. HUVECs in suspension were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 in the absence or presence of 100 μM of peptides YHK9, GYK9, FPF9, IPP19, or HKH20 for 2 hours at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers by FXII peptides. Confluent monolayers of HUVECs were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2. Biotin-FXII (10 nM) was added to HUVECs in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of peptides YHK9 (●), FPF9 (▪), or IPP19 (▴) for 90 minutes at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the relative binding of biotin-FXII binding to cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate followed by peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, turbo-TMP. Bound biotin-FXII was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Determination of a region on FXII that binds to HUVECs.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions by FXII peptides. HUVECs in suspension were incubated with 70 nM FITC-FXII in HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 in the absence or presence of 100 μM of peptides YHK9, GYK9, FPF9, IPP19, or HKH20 for 2 hours at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Inhibition of biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers by FXII peptides. Confluent monolayers of HUVECs were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2. Biotin-FXII (10 nM) was added to HUVECs in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of peptides YHK9 (●), FPF9 (▪), or IPP19 (▴) for 90 minutes at 37°C. After the incubation, the cells were washed and the relative binding of biotin-FXII binding to cells was determined using ImmunoPure streptavidin horseradish peroxidase conjugate followed by peroxidase-specific fast-reacting substrate, turbo-TMP. Bound biotin-FXII was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 450 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Additional studies determined if peptide YHK9 blocked biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers (Figure 11B). At 30 μM, peptide YHK9 blocked biotin-FXII binding to HUVECs completely, whereas its adjacent peptide, FPF9, inhibited binding only 30% at 1 mM. Alternatively, peptide IPP19 did not inhibit biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers at concentrations above 1 mM.
Influence of HUVEC-bound FXII on PK and FXI activation
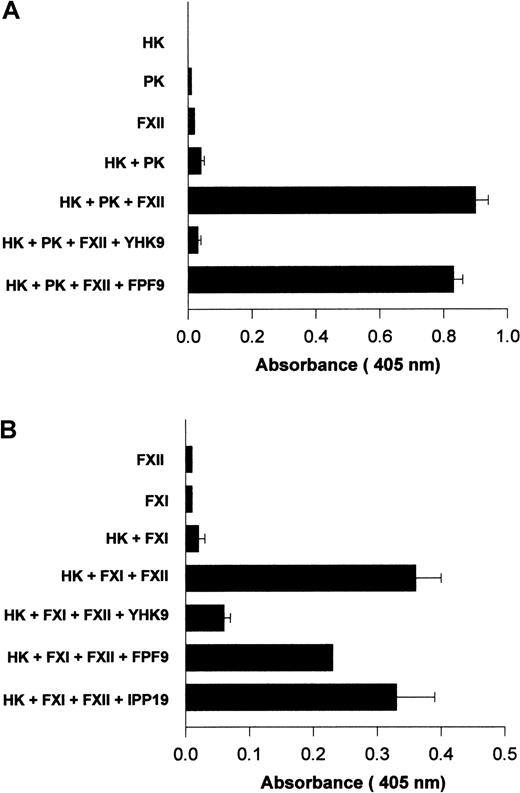
Investigations determined if interference with FXII binding to HUVECs influenced its activated forms' catalytic activity on PK and FXI. Using HUVECs grown in human FXII-deficient serum and concentrations of HK and PK that were suboptimal for endogenous PK activation, the catalytic activity of formed FXIIa on PK activation was examined11 (Figure 12A). The addition of FXII to HK and PK increased the extent of hydrolytic activity measured (Figure 12A). When peptide YHK9 was present, FXII binding was blocked and the catalytic activity of activated forms of FXII on PK was inhibited (Figure 12A). Alternatively, peptide FPF9 that had no ability to inhibit FXII binding to HUVECs did not inhibit the catalytic activity of formed FXIIa on PK (Figure 12A).
Inhibition of FXIIa amplification of PK and FXI activation on HUVECs.
HUVECs were grown in endothelial cell culture media containing human FXII-deficient serum. When confluent, the cells were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 . (A) Amplification of PK activation. HUVECs were incubated with 10 nM HK, 10 nM PK, and 20 nM FXII in HCB in the absence or presence of 100 μM of peptide YHK9 or FPF9 for 1 hour at 37°C. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed, 1 mM S2302 was added in HCB, and hydrolysis of the substrate was monitored for an additional hour. The extent of kallikrein/FXIIa hydrolytic activity was determined by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 405 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311. (B) Initiation of FXI activation. HUVECs were incubated with 10 nM HK, 5 nM FXI, and 20 nM FXII in HCB in the absence or presence of 100 μM of peptide YHK9, FPF9, or IPP19 for 1 hour at 37°C. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed, 0.8 mM S2366 was added in HCB, and hydrolysis of the substrate was monitored for an additional hour. The generated FXIa was determined by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 405 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Inhibition of FXIIa amplification of PK and FXI activation on HUVECs.
HUVECs were grown in endothelial cell culture media containing human FXII-deficient serum. When confluent, the cells were washed 3 times with HCB containing 10 μM ZnCl2 . (A) Amplification of PK activation. HUVECs were incubated with 10 nM HK, 10 nM PK, and 20 nM FXII in HCB in the absence or presence of 100 μM of peptide YHK9 or FPF9 for 1 hour at 37°C. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed, 1 mM S2302 was added in HCB, and hydrolysis of the substrate was monitored for an additional hour. The extent of kallikrein/FXIIa hydrolytic activity was determined by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 405 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311. (B) Initiation of FXI activation. HUVECs were incubated with 10 nM HK, 5 nM FXI, and 20 nM FXII in HCB in the absence or presence of 100 μM of peptide YHK9, FPF9, or IPP19 for 1 hour at 37°C. At the end of the incubation, the cells were washed, 0.8 mM S2366 was added in HCB, and hydrolysis of the substrate was monitored for an additional hour. The generated FXIa was determined by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 405 nm using a microplate autoreader EL 311. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Surface-bound FXII was catalytic for FXI activation.17 The addition of FXII was essential for activation of FXI on HUVECs when cultured in FXII-deficient serum.17 Peptide YHK9 from the fibronectin type II domain of FXII inhibited the catalytic role of activated forms of FXII on FXI activation (Figure 12B). Peptide FPF9 from an adjacent region also inhibited FXIIa activation of FXI by 38%. Alternatively, peptide IPP19 from the extreme N-terminal region of FXII that has been reported as the FXI binding region on FXII25inhibited FXIIa-catalyzed FXI activation by only 6%. The interference of FXII binding to HUVECs blocked its catalytic role in PK and FXI activation.
Investigations to determine if FXII binding to HUVECs is physiologic
Because HK and FXII bound to the same multiprotein receptor and HK is known to block FXII binding,18 investigations were performed to determine which protein, HK or FXII, would take precedence in binding to HUVECs. Increasing FXII concentrations blocked FITC-FXII binding with an IC50 of 900 nM (Figure13A). HK, however, was a more potent inhibitor of FITC-FXII binding to suspensions of HUVECs because it blocked FXII binding with an IC50 of 180 nM (Figure 13A). At plasma concentrations of HK (600 nM), FITC-FXII binding to HUVECs is completely inhibited. Further, plasma concentrations of vitronectin (2.5 μM) inhibited FITC-FXII binding 50%. Similarly, 2.5 μM urokinase also blocked FITC-FXII binding 50%. These data indicated that normal plasma concentrations of HK and vitronectin blocked FXII binding, suggesting that HK in plasma had precedence in binding to this multiprotein receptor on HUVECs.
Regulation of FXII binding to HUVECs.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions by HK or vitronectin. HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension were incubated in HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM Zn2+ with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the presence or absence of 1- to 100-fold molar excess of HK (●), FXII (▪) (10-7000 nM), urokinase (uPA) (▴) (10-3500 nM), or vitronectin (▾) (10-3500 nM) for 2 hours at 37°C. At the conclusion of the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) The influence of albumin on biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers. Washed human platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) in HCB containing 3.5 mg/mL bovine serum albumin and 50 μM Zn2+, pH 7.4, were incubated over washed HUVEC monolayers in microtiter plate cuvette wells in the same buffer in the presence of 10 nM biotin-FXII and the presence or absence of 5 μg/mL collagen for 90 minutes at 37°C on a rotating shaker. At the completion of the incubation, the microtiter plate cuvette wells were washed and the amount of biotin-FXII specifically bound to the HUVECs was determined as described in the legend to Figure 1. The data are presented as a bar graph of specific biotin-FXII binding determined by subtracting the level of binding seen with unactivated platelets from that occurring after collagen-activated platelets. The column “Biotin-FXII + Zn2+” represents the level of specific biotin-FXII binding alone to HUVEC monolayers in HCB, pH 7.4, and 10 μM Zn2+. These data are the mean ± SEM of 5 individual experiments.
Regulation of FXII binding to HUVECs.
(A) Inhibition of FITC-FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions by HK or vitronectin. HUVECs (4 × 104 cells per well) in suspension were incubated in HCB, pH 7.4, containing 10 μM Zn2+ with 70 nM FITC-FXII in the presence or absence of 1- to 100-fold molar excess of HK (●), FXII (▪) (10-7000 nM), urokinase (uPA) (▴) (10-3500 nM), or vitronectin (▾) (10-3500 nM) for 2 hours at 37°C. At the conclusion of the incubation, the cells were washed and the bound FITC-FXII to HUVECs was monitored using a CytoFluor4000 plate reader. The results presented are the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) The influence of albumin on biotin-FXII binding to HUVEC monolayers. Washed human platelets (0.1 × 109 to 3.5 × 109/mL) in HCB containing 3.5 mg/mL bovine serum albumin and 50 μM Zn2+, pH 7.4, were incubated over washed HUVEC monolayers in microtiter plate cuvette wells in the same buffer in the presence of 10 nM biotin-FXII and the presence or absence of 5 μg/mL collagen for 90 minutes at 37°C on a rotating shaker. At the completion of the incubation, the microtiter plate cuvette wells were washed and the amount of biotin-FXII specifically bound to the HUVECs was determined as described in the legend to Figure 1. The data are presented as a bar graph of specific biotin-FXII binding determined by subtracting the level of binding seen with unactivated platelets from that occurring after collagen-activated platelets. The column “Biotin-FXII + Zn2+” represents the level of specific biotin-FXII binding alone to HUVEC monolayers in HCB, pH 7.4, and 10 μM Zn2+. These data are the mean ± SEM of 5 individual experiments.
Additional investigations were performed to determine if there were other physiologic modifiers of FXII binding to HUVECs. Because FXII binding to HUVECs required a higher free Zn2+ concentration than HK, and human plasma contains a high concentration of albumin, studies were performed to determine if the plasma albumin concentration modulated the level of free Zn2+ available for FXII binding. Biotin-FXII was incubated with collagen-activated washed platelets over HUVECs in the presence of 3.5 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (Figure 13B). Unlike the results seen when there was a carrier protein present that did not bind Zn2+ (Figure 3), more than 1 × 109 collagen-activated platelets per milliliter were necessary to provide sufficient Zn2+ to support specific FXII binding in the presence of 3.5 mg/mL albumin (Figure13B). Likewise, when the ambient albumin concentration was made 40 mg/mL as seen in plasma, there was no specific FXII binding when incubated with collagen-activated platelets (data not shown). These data indicated that under physiologic conditions, FXII binding was secondary to HK binding and highly regulated by plasma proteins and the ambient free Zn2+ concentration.
Discussion
These investigations indicate that FXII interacts with the same multiprotein receptor complex on HUVECs that assembles the HK-PK complex.1 The investigations by Reddigari et al show Zn2+-dependent binding of FXII to HUVECs and that FXII blocks HK binding to HUVECs.18 Our investigations indicate the proteins that FXII binds on HUVECs and a region on FXII that participates in cell binding. Confirmation that FXII and HK interact with the same proteins on HUVECs is shown by the finding that all the antibodies that block HK binding to HUVECs also interfere with FXII binding. Using antibodies to gC1qR and uPAR, FXII binding to HUVECs is completely blocked. Previous studies indicate that FXII binds to gC1qR.2 3 It was not expected that uPAR would also bind FXII. Confirmation that uPAR interacts with FXII was shown by the observation that suPAR competes FXII binding to HUVEC suspensions. It is also unexpected that CK1 inhibits FXII binding to HUVECs. The antibody to CK1 is not as effective an inhibitor to binding as antibodies to uPAR or gC1qR because it is an antipeptide antibody raised to the unique peptide sequence on CK1 that HK binds on protein coded by exon 1. Inhibition studies with variously sized recombinant CK1 indicate that the FXII binding region on CK1 is on protein coded by exons 3 to 5. This interpretation may explain why FITC-FXII and anti-CK1 antibody to the HK binding site colocalizes less than that seen with other FXII-HUVEC binding proteins. Last, when suPAR and rCK1 are combined, FXII binding is reduced further than when either protein alone is used as an inhibitor.
FXII binding to HUVECs appears to be highly restricted. It has several properties that distinguish it from HK binding. Zinc ion is an essential divalent cation for HK binding to HUVECs.26Recent investigations indicate that only 0.3 μM Zn2+ is necessary to support HK binding to HUVECs when the carrier protein is gelatin and not bovine serum albumin.12,15 The reason for this difference is due to the fact that albumin binds zinc ion and gelatin does not.15 Alternatively, specific FXII binding to HUVECs requires 10 μM added Zn2+ in gelatin buffer. This zinc ion requirement is identical to the Zn2+requirement for FXI binding to HK on HUVECs in the same buffer.17 Under physiologic conditions some activation state must occur to liberate zinc ion from some storage repository to promote FXII binding to its putative receptors.27 28Activated platelets provide sufficient Zn2+ to support FXII binding in gelatin buffer. However, plasma concentrations of albumin restrict the availability of released platelet-free Zn2+ to support binding. Physiologic concentrations of collagen-activated platelets provide insufficient free Zn2+ to support FXII binding in buffers containing plasma levels of albumin. Thus, regulation of the ambient Zn2+ concentration modulates FXII binding to HUVECs. Other factors also regulate FXII binding to HUVECs. Plasma concentrations of HK and vitronectin prevent FXII binding. In plasma, HK would preferentially bind to endothelium over FXII. Because FXII binding to endothelial cells is restricted, physiologic PK and FXI activation on HUVECs must proceed by mechanisms other than activated forms of FXII.
The role of FXII in the revised hypothesis for assembly and activation of the proteins of the plasma kallikrein/kinin system needs better definition. PK activation on endothelial cells proceeds in the absence of added FXII by an endothelial cell–associated serine protease that specifically activates PK.11,15,16 Recent preliminary evidence suggests that this protease is prolyl carboxypeptidase, an enzyme previously known only to degrade angiotensin II to angiotensin II1-7.29 The presence of FXII potentiates the activation of membrane-associated PK, similar to what is accepted on artificial surfaces. When suboptimal concentrations of HK and PK for PK activation are incubated with HUVECs cultured in FXII-deficient serum, FXII activation by a small amount of formed kallikrein amplifies the activation of PK. The fact that the fibronectin type II domain of FXII contains a cell-binding region may be important in understanding the functional activity or activities of FXII on the HUVEC membrane. The expression of FXII on HUVECs may have growth-promoting activities as previously suggested.30,31It is of interest that the same region of FXII that participates in binding of the protein to artificial, negatively charged surfaces also contributes to its binding to cell membranes.22 This region is charge-specific and not sequence-specific.22These results are similar to those found for peptides derived from HK's domain 5. Peptide HKH20 of HK, a charge-specific sequence from domain 5, is the best region to bind to artificial, negatively charged surfaces and HUVEC membranes to inhibit HK binding and angiogenesis.32 33 Because FXII binding to HUVECs is secondary to that of HK, further studies are needed to fully understand the physiologic role of FXIIa in events associated with PK activation on endothelial cell membranes.
We thank Dr Cora-Jean Edgell of the University of North Carolina for providing the EA.hy926 cells.
Supported by grant HL52779 from the National Institutes of Health to A.H.S.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Alvin H. Schmaier, University of Michigan, 5301 MSRB III, 1150 W Medical Center Dr, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-0640; e-mail:aschmaie@umich.edu.







This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal