Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–identical sibling bone marrow transplantation is an effective treatment for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. However, most children with this disease lack such donors and many patients receive transplants from alternative donors. This study compared outcomes of HLA-identical sibling, other related donor, and unrelated donor transplantation for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. The outcome of 170 transplantations for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, from 1968 to 1996, reported to the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry and/or National Marrow Donor Program were assessed. Fifty-five were from HLA-identical sibling donors, 48 from other relatives, and 67 from unrelated donors. Multivariate proportional hazards regression was used to compare outcome by donor type and identify other prognostic factors. Most transplant recipients were younger than 5 years (79%), had a pretransplantation performance score greater than or equal to 90% (63%), received pretransplantation preparative regimens without radiation (82%), and had non–T-cell–depleted grafts (77%). Eighty percent received their transplant after 1986. The 5-year probability of survival (95% confidence interval) for all subjects was 70% (63%-77%). Probabilities differed by donor type: 87% (74%-93%) with HLA-identical sibling donors, 52% (37%-65%) with other related donors, and 71% (58%-80%) with unrelated donors (P = .0006). Multivariate analysis indicated significantly lower survival using related donors other than HLA-identical siblings (P = .0004) or unrelated donors in boys older than 5 years (P = .0001), compared to HLA-identical sibling transplants. Boys receiving an unrelated donor transplant before age 5 had survivals similar to those receiving HLA-identical sibling transplants. The best transplantation outcomes in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome are achieved with HLA-identical sibling donors. Equivalent survivals are possible with unrelated donors in young children.
Introduction
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a lethal hematologic disorder primarily affecting the morphology and function of platelets and lymphocytes. This X-linked condition resulting from mutations in the WASP gene at Xp11.221 has a worldwide distribution with an estimated incidence of 4 per million live male births.2,3 In the 15 years since publication of the first of 3 retrospective reviews of the natural history of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome in North America, estimated median survival rose from 6.5 to 11 to 15 years of age.3-5 Causes of death, primarily infections and lymphoproliferative disorders, did not change appreciably despite more widespread use of splenectomy,4,5 intravenous immune globulin, and prophylactic antibiotics. During this period, only Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia disappeared as a fatal complication.6 As boys with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome survive longer, they face increasing risks of life-threatening autoimmune complications and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated lymphoproliferative disease.
There are several published reports of the treatment of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–identical siblings.7 Ten- to 26-year follow-up confirms that many of these patients are cured.7,8 During the 1980s, several transplant centers investigated use of T-cell–depleted haploidentical transplants from related donors for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.9,10 Results were discouraging, with high rates of graft rejection and fatal EBV-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD). These data likely contributed to the prevailing notion that transplantations from donors other than HLA-identical siblings are very risky. However, several recent case reports describe successful transplantations using closely HLA-matched unrelated donors.11-14
This report, generated through the collaborative use of 2 large observational databases, allows, for the first time, a multivariate analysis of the impact of donor- and treatment-related variables on the outcome of marrow transplantation for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
Patients, materials, and methods
Registries
The International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry (IBMTR) was founded 28 years ago to collect and analyze data on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on a voluntary worldwide basis. Today more than 400 transplant centers prospectively register consecutive transplantations and report comprehensive clinical data to the IBMTR to facilitate multi-institutional analyses of transplantation outcomes. Staff of the IBMTR Statistical Center at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee codify and validate patient data and perform biostatistical analyses for investigators around the world. Based on periodic worldwide surveys and data reported to the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the IBMTR estimates it captures data on about 40% of allogeneic transplantations worldwide.15-18
The National Marrow Donor Program (NMDP) was established in Minneapolis, MN, in 1986 through a contract from the US Navy and American Red Cross to facilitate recruitment and searches for closely HLA-matched unrelated bone marrow donors in North America. Currently operating under contract with the Health Resources and Services Administration, the NMDP has expanded its scope of activities to a worldwide basis and is responsible for collection, validation, and biostatistical analysis of outcome data on the transplantations it facilitates.19
Patients
One hundred and seventy males receiving allogeneic bone marrow transplants for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome between 1968 and 1996 are included in this report. Data for 125 patients were submitted to the IBMTR, and data for 45 patients receiving transplants from unrelated donors were contributed by NMDP. Bone marrow transplantations were performed at 60 centers worldwide. Forty-nine percent of transplantations were performed in US centers. Twenty patients received more than one transplant, generally from the same donor.
Statistical analyses
Complete ascertainment of recipient-, donor-, and transplant-related variables to be tested in univariate and multivariate analyses was attempted through correspondence and personal communication between IBMTR and NMDP staff and corresponding institutions. Donor type, recipient age at transplantation, and year of transplantation were known for all cases; pretransplantation infection status, degree of donor-recipient HLA match, conditioning regimen, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis, and donor sex were available for 94% to 98% of cases, and pretransplantation performance score for more than 91%. Comparisons of characteristics by donor type used the χ2 test for categorical and the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables. Probabilities of transplantation outcomes were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier product limit estimate. Univariate comparisons of survival used the log-rank test. Subsequently, multivariate analysis using Cox proportional hazards regression was performed with time to death as the end-point and donor relationship as the main effect to be tested. The following covariates were also considered: age less than 5 years versus more than 5 years, Lansky/Karnofsky performance score before transplantation less than 90% versus more than 90%, infection just prior to conditioning, donor-recipient HLA disparity (0-, 1-, or 2-antigen mismatch defined by serologic typing as reported by the team), donor sex (male, female), type of conditioning regimen (total body irradiation [TBI], no TBI), type of GVHD prophylaxis (cyclosporine A [CsA], methotrexate [MTX], CsA + MTX, or T-depletion ± other), year of transplantation (< 1985, 1985–1989, 1990–1996). All variables were checked to ensure that the assumption of the Cox model was valid using a time-dependent covariate approach; first-order interactions were also considered.20 A forward stepwise selection method with a significance level of 0.05 was used to select variables for the final model. The score test was used to determine if there were center-specific differences requiring adjustment.21 All analyses were done using PROC PHREG in SAS version 6.12.
Follow-up data also included testing for evidence of donor engraftment, development of grade II to IV acute GVHD (in those surviving −21 days after transplantation), development of chronic GVHD (in those surviving ≥ 90 days after transplantation), immune reconstitution, infection status, and the transplant center's assessment as to whether the patient was cured, improved, or not improved. Functional “cure” refers to patients described by the transplant center as cured or improved related to the underlying Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Reasons for second transplantations and causes of death were also summarized.
Results
Recipient-, donor-, and transplant-related variables
Characteristics of the 170 transplant recipients and donors are described in Table 1. Most boys received their transplant before their fifth birthday (79%), had a pretransplantation Lansky/Karnofsky performance score of at least 90% (63%), and had no serious infections in the 2 weeks before transplantation (76%). Data on pretransplantation splenectomy were available in 107 patients, of whom 20 had prior splenectomy. Specific information regarding pretransplantation lymphoma was available for 52 patients, of whom 5 had this complication. There were statistically significant differences among the 3 donor groups with respect to donor-recipient HLA match, GVHD prophylaxis, and year of transplantation. Among recipients of grafts from related donors other than HLA-matched siblings, more than half had donors mismatched at 2 or more loci; most of these transplants were T-cell depleted. In contrast, only one unrelated donor recipient pair was mismatched at 2 loci, and most unrelated donors were A, B, and DR (by serologic typing techniques for class I and molecular typing of DRB1) matched with their recipients. Most transplantations from unrelated donors were done in the 1990s. Median follow-up of survivors was 42 months (range, 2-304).
Characteristics of 170 patients receiving allogeneic BMT for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
| . | HLA-identical sibling donor (n = 55) . | Other related donor (n = 48) . | Unrelated donor (n = 67) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at BMT, median (range), y | 3 (< 1-16) | 2 (< 1-17) | 2 (< 1-32) | < .05 |
| Age at BMT | .26 | |||
| Younger than 1 y | 13/55 (24%) | 12/48 (25%) | 9/67 (13%) | |
| 1-2 y | 18/55 (33%) | 26/48 (54%) | 34/67 (51%) | |
| 3-4 y | 10/55 (18%) | 3/48 (6%) | 9/67 (13%) | |
| 5-9 y | 7/55 (13%) | 3/48 (6%) | 8/67 (12%) | |
| 10 y or older | 7/55 (13%) | 4/48 (8%) | 7/67 (10%) | |
| Lansky/Karnofsky performance score before BMT ≥ 90% | 26/45 (58%) | 28/47 (60%) | 43/63 (68%) | .48 |
| Infection in the 2 wk before BMT | 12/52 (23%) | 16/48 (33%) | 11/61 (18%) | .18 |
| Donor-recipient HLA mismatch | < .001 | |||
| 0 antigen mismatch | 55/55 (100%) | 3/43 (7%) | 43/62 (69%) | |
| 1 antigen mismatch | NA | 16/43 (37%) | 18/62 (29%) | |
| ≥ 2 antigen mismatch | NA | 24/43 (56%) | 1/62 (2%) | |
| Male donor | 23/51 (45%) | 32/48 (67%) | 35/64 (55%) | .10 |
| Year of transplant | < .001 | |||
| 1968-1979 | 5/55 (9%) | 2/48 (4%) | 0/67 (0%) | |
| 1980-1984 | 8/55 (15%) | 10/48 (21%) | 0/67 (0%) | |
| 1985-1989 | 13/55 (24%) | 13/48 (27%) | 3/67 (4%) | |
| 1990-1993 | 14/55 (25%) | 19/48 (40%) | 35/67 (52%) | |
| 1994-1996 | 15/55 (27%) | 4/48 (8%) | 29/67 (43%) | |
| TBI for conditioning pretransplant | 4/55 (7%) | 11/45 (24%) | 14/64 (22%) | < .05 |
| GVHD prophylaxis | < .001 | |||
| MTX + CsA | 20/55 (36%) | 14/48 (29%) | 37/64 (58%) | |
| MTX ± other | 19/55 (35%) | 2/48 (4%) | 3/64 (5%) | |
| CsA ± other | 14/55 (25%) | 3/48 (6%) | 13/64 (20%) | |
| T-cell depletion ± other | 0/55 (0%) | 26/48 (54%) | 11/64 (17%) | |
| Other (non–T-cell depleted) or none* | 2/55 (4%) | 3/48 (6%) | 0/64 (0%) |
| . | HLA-identical sibling donor (n = 55) . | Other related donor (n = 48) . | Unrelated donor (n = 67) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at BMT, median (range), y | 3 (< 1-16) | 2 (< 1-17) | 2 (< 1-32) | < .05 |
| Age at BMT | .26 | |||
| Younger than 1 y | 13/55 (24%) | 12/48 (25%) | 9/67 (13%) | |
| 1-2 y | 18/55 (33%) | 26/48 (54%) | 34/67 (51%) | |
| 3-4 y | 10/55 (18%) | 3/48 (6%) | 9/67 (13%) | |
| 5-9 y | 7/55 (13%) | 3/48 (6%) | 8/67 (12%) | |
| 10 y or older | 7/55 (13%) | 4/48 (8%) | 7/67 (10%) | |
| Lansky/Karnofsky performance score before BMT ≥ 90% | 26/45 (58%) | 28/47 (60%) | 43/63 (68%) | .48 |
| Infection in the 2 wk before BMT | 12/52 (23%) | 16/48 (33%) | 11/61 (18%) | .18 |
| Donor-recipient HLA mismatch | < .001 | |||
| 0 antigen mismatch | 55/55 (100%) | 3/43 (7%) | 43/62 (69%) | |
| 1 antigen mismatch | NA | 16/43 (37%) | 18/62 (29%) | |
| ≥ 2 antigen mismatch | NA | 24/43 (56%) | 1/62 (2%) | |
| Male donor | 23/51 (45%) | 32/48 (67%) | 35/64 (55%) | .10 |
| Year of transplant | < .001 | |||
| 1968-1979 | 5/55 (9%) | 2/48 (4%) | 0/67 (0%) | |
| 1980-1984 | 8/55 (15%) | 10/48 (21%) | 0/67 (0%) | |
| 1985-1989 | 13/55 (24%) | 13/48 (27%) | 3/67 (4%) | |
| 1990-1993 | 14/55 (25%) | 19/48 (40%) | 35/67 (52%) | |
| 1994-1996 | 15/55 (27%) | 4/48 (8%) | 29/67 (43%) | |
| TBI for conditioning pretransplant | 4/55 (7%) | 11/45 (24%) | 14/64 (22%) | < .05 |
| GVHD prophylaxis | < .001 | |||
| MTX + CsA | 20/55 (36%) | 14/48 (29%) | 37/64 (58%) | |
| MTX ± other | 19/55 (35%) | 2/48 (4%) | 3/64 (5%) | |
| CsA ± other | 14/55 (25%) | 3/48 (6%) | 13/64 (20%) | |
| T-cell depletion ± other | 0/55 (0%) | 26/48 (54%) | 11/64 (17%) | |
| Other (non–T-cell depleted) or none* | 2/55 (4%) | 3/48 (6%) | 0/64 (0%) |
BMT indicates bone marrow transplant; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; TBI, total body irradiation; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; MTX, methotrexate; CsA, cyclosporine A.
One patient with an HLA-identical sibling donor and 3 patients with other related donors received no GVHD prophylaxis.
Most patients were prepared for transplantation without TBI. Approximately one fourth of patients receiving transplants from donors other than HLA-matched siblings received TBI. The most common GVHD prophylaxis regimens used MTX or CsA or both, accounting for 96% of HLA-matched sibling transplants, 40% of other related donor transplants, and 83% of unrelated donor transplants. None of the grafts from HLA-matched siblings, 54% of those from other related donors, and 17% of those from unrelated donors were T-cell depleted. The method of T-cell depletion was specified for 24 of 26 T-cell–depleted transplants from related donors other than HLA-matched siblings. Nineteen of these 24 grafts were depleted with methods resulting in extensive (> 3 log) depletion (repeated E-rosetting with or without soybean lectin agglutination [n = 11], or soybean lectin agglutination alone [n = 3], or in vitro Campath 1 followed by in vivo pan T-cell antibody treatment [n = 5]), whereas 5 were depleted with anti–T-cell monoclonal antibodies that generally provide less complete T-cell depletion. Methods of T-cell depletion were available for 9 of 11 T-cell–depleted unrelated donor transplants. Two of these 9 grafts used extensive T-cell depletion and 7 used partial T-cell depletion methods.
Transplantation outcomes
Engraftment.
Information on engraftment was available for 154 of 159 patients surviving 28 or more days after transplantation. Hematopoietic recovery after the first transplantation occurred in 46 of 51 HLA-matched sibling, 32 of 41 other related donor, and 62 of 62 unrelated donor transplant recipients. Data on donor-recipient chimerism were available for 87 transplants; 27 of 29 HLA-matched sibling, 24 of 32 other related donor, and 26 of 26 unrelated donor transplant recipients who were tested had documented donor cell engraftment after the first transplantation; 10 had only recipient cells detected. One, 4, and 2 persons receiving HLA-matching sibling, other related, and unrelated donor transplants, respectively, had graft failure after initial hematopoietic recovery.
GVHD.
Grade II to IV acute GVHD occurred in 8 of 50 (16%) evaluable children receiving HLA-identical sibling transplants, 14 of 46 (30%) receiving other related donor transplants, and 36 of 64 (56%) receiving unrelated donor transplants. Chronic GVHD occurred in 4 of 47 (9%) evaluable children receiving HLA-identical sibling transplants, 8 of 36 (22%) receiving other related donor transplants, and 21 of 58 (36%) receiving unrelated donor transplants. Of the 33 patients in the entire cohort who developed chronic GVHD, 22 cases were reported as limited and 11 as extensive. In 4 patients, chronic GVHD contributed to death (1 after an HLA-matched sibling transplantation and 3 after unrelated donor transplantations). Among the 29 patients who survived after developing chronic GVHD, chronic GVHD resolved in 22 (76%) between 6 and 27 months after transplantation. The 7 patients with active chronic GVHD at last contact include 1 patient with limited disease after an HLA-matched sibling transplantation, 3 patients surviving 37 to 95 months after transplantation from an other related donor, and 3 patients surviving 7 to 24 months after unrelated donor transplantation.
Second transplantations.
Twenty patients received second transplants: 16 for failure to engraft or graft failure, 2 for myelodysplastic syndrome, 1 for persistent thrombocytopenia, and 1 for an unknown cause. Twelve are long-term survivors. Five of 20 patients had the same HLA-identical sibling donor for each transplantation, of whom 4 are alive. Ten of 20 patients had a related donor other than HLA-identical sibling for both transplantations, of whom 4 are alive. One of 20 patients is surviving after a second transplantation from an HLA-matched sibling donor, following graft failure after his first transplantation from an other related donor. Two of 20 patients had an unrelated donor for both transplants; 1 is alive. Two of 20 patients (1 with an HLA-matched sibling donor and 1 with an other related donor for the first transplant) are missing donor information for the second graft but are still alive.
Survival.
Overall 5-year probability of survival (95% confidence interval [CI]) was 70% (63%-77%). Table 2tabulates univariate analyses of survival according to various patient and transplant variables. The 5-year probabilities of survival were 87% (74%-94%) with HLA-identical sibling donors, 52% (37%-65%) with other related donors, and 71% (58%-80%) with unrelated donors (P = .0006). Within donor type groups, statistically significant univariate associations noted were (1) poorer survival with use of T-cell depletion for other related donor transplants, and (2) poorer survival in children older than age 5 years at time of unrelated donor transplantation. Year of transplantation was not associated with improved overall survival following HLA-identical sibling transplantation or other related donor transplantation. The 5-year survival rate following HLA-identical sibling transplantation has remained at about 85% since the late 1960s, and at about 60% following other related donor transplantation since 1985. Reliable 5-year survival estimates are not yet feasible for recipients of unrelated transplants because most were done in the mid-1990s.
Probability of survival (95% confidence interval) 5 years after allogeneic BMT for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (univariate analyses)
| Variable . | HLA-identical sibling . | Other relative . | Unrelated donor . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N . | Probability (95% CI) . | P . | N . | Probability (95% CI) . | P . | N . | Probability (95% CI) . | P . | |
| Donor | 55 | 87 (74-94)% | NA | 48 | 52 (37-65)% | NA | 67 | 71 (58-80)% | < .0006* |
| Age | .22 | .77 | < .0001 | ||||||
| No older than 5 years | 41 | 90 (75-96)% | 41 | 53 (37-67)% | 52 | 84 (70-92)% | |||
| Older than 5 years | 14 | 79 (47-93)% | 7 | 38 (6-72)% | 15 | 0 | |||
| Lansky/Karnofsky performance score | .20 | .92 | |||||||
| Below 90% | 19 | 84 (58-95)% | 19 | 41 (20-62)% | 20 | 70 (45-85)% | |||
| At least 90% | 26 | 96 (75-99)% | 28 | 61 (40-76)% | .20 | 43 | 71 (54-82)% | ||
| Infection pre-BMT | .16 | .13 | < .04 | ||||||
| No | 40 | 84 (68-93)% | 32 | 59 (41-74)% | 51 | 71 (56-82)% | |||
| Yes | 12 | 100% | 16 | 35 (13-59)% | 11 | 55 (23-80)% | |||
| Donor-recipient HLA match | NA | < .03 | .98 | ||||||
| 0-1 antigen mismatched related | 19† | 74 (48-88)% | — | ||||||
| At least 2 antigen mismatched related | 24 | 36 (18-55)% | — | ||||||
| 0 antigen mismatched unrelated | — | 44 | 69 (52-81)% | ||||||
| 1 antigen mismatched unrelated | — | 19‡ | 68 (43-84)% | ||||||
| Donor sex | .16 | .09 | .26 | ||||||
| Male | 23 | 95 (72-99)% | 32 | 59 (40-74)% | 35 | 65 (47-78)% | |||
| Female | 28 | 82 (62-92)% | 16 | 38 (15-60)% | 30 | 75 (55-87)% | |||
| Year of BMT | .81 | .30 | .87 | ||||||
| Before 1985 | 13 | 85 (51-96)% | 12 | 33 (10-59)% | 0 | — | |||
| 1985-1989 | 13 | 92 (57-99)% | 13 | 62 (31-82)% | 3 | 67 (5-95)% | |||
| 1990-1996 | 29 | 85 (65-94)% | 23 | 57 (34-74)% | 64 | 71 (58-81)% | |||
| Conditioning regimen | .37 | .46 | .17 | ||||||
| No TBI | 51 | 88 (75-94)% | 34 | 56 (38-71)% | 50 | 73 (58-83)% | |||
| TBI | 4 | 75 (13-96)% | 11 | 36 (11-63)% | 14 | 64 (34-83)% | |||
| GVHD prophylaxis | .29 | < .0002 | .56 | ||||||
| MTX | 19 | 94 (67-99)% | 2 | 0 | 3 | 33 (1-77)% | |||
| CsA | 14 | 93 (59-99)% | 3 | 100% | 13 | 68 (36-87)% | |||
| CsA + MTX | 20 | 80 (55-92)% | 14 | 79 (47-93)% | 37 | 69 (51-81)% | |||
| T-cell depletion | 0 | — | 26 | 34 (16-52)% | 11 | 82 (45-95)% | |||
| Variable . | HLA-identical sibling . | Other relative . | Unrelated donor . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N . | Probability (95% CI) . | P . | N . | Probability (95% CI) . | P . | N . | Probability (95% CI) . | P . | |
| Donor | 55 | 87 (74-94)% | NA | 48 | 52 (37-65)% | NA | 67 | 71 (58-80)% | < .0006* |
| Age | .22 | .77 | < .0001 | ||||||
| No older than 5 years | 41 | 90 (75-96)% | 41 | 53 (37-67)% | 52 | 84 (70-92)% | |||
| Older than 5 years | 14 | 79 (47-93)% | 7 | 38 (6-72)% | 15 | 0 | |||
| Lansky/Karnofsky performance score | .20 | .92 | |||||||
| Below 90% | 19 | 84 (58-95)% | 19 | 41 (20-62)% | 20 | 70 (45-85)% | |||
| At least 90% | 26 | 96 (75-99)% | 28 | 61 (40-76)% | .20 | 43 | 71 (54-82)% | ||
| Infection pre-BMT | .16 | .13 | < .04 | ||||||
| No | 40 | 84 (68-93)% | 32 | 59 (41-74)% | 51 | 71 (56-82)% | |||
| Yes | 12 | 100% | 16 | 35 (13-59)% | 11 | 55 (23-80)% | |||
| Donor-recipient HLA match | NA | < .03 | .98 | ||||||
| 0-1 antigen mismatched related | 19† | 74 (48-88)% | — | ||||||
| At least 2 antigen mismatched related | 24 | 36 (18-55)% | — | ||||||
| 0 antigen mismatched unrelated | — | 44 | 69 (52-81)% | ||||||
| 1 antigen mismatched unrelated | — | 19‡ | 68 (43-84)% | ||||||
| Donor sex | .16 | .09 | .26 | ||||||
| Male | 23 | 95 (72-99)% | 32 | 59 (40-74)% | 35 | 65 (47-78)% | |||
| Female | 28 | 82 (62-92)% | 16 | 38 (15-60)% | 30 | 75 (55-87)% | |||
| Year of BMT | .81 | .30 | .87 | ||||||
| Before 1985 | 13 | 85 (51-96)% | 12 | 33 (10-59)% | 0 | — | |||
| 1985-1989 | 13 | 92 (57-99)% | 13 | 62 (31-82)% | 3 | 67 (5-95)% | |||
| 1990-1996 | 29 | 85 (65-94)% | 23 | 57 (34-74)% | 64 | 71 (58-81)% | |||
| Conditioning regimen | .37 | .46 | .17 | ||||||
| No TBI | 51 | 88 (75-94)% | 34 | 56 (38-71)% | 50 | 73 (58-83)% | |||
| TBI | 4 | 75 (13-96)% | 11 | 36 (11-63)% | 14 | 64 (34-83)% | |||
| GVHD prophylaxis | .29 | < .0002 | .56 | ||||||
| MTX | 19 | 94 (67-99)% | 2 | 0 | 3 | 33 (1-77)% | |||
| CsA | 14 | 93 (59-99)% | 3 | 100% | 13 | 68 (36-87)% | |||
| CsA + MTX | 20 | 80 (55-92)% | 14 | 79 (47-93)% | 37 | 69 (51-81)% | |||
| T-cell depletion | 0 | — | 26 | 34 (16-52)% | 11 | 82 (45-95)% | |||
CI indicates confidence interval; BMT, bone marrow transplant; NA, not applicable; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; TBI, total body irradiation; CsA, cyclosporine A; MTX, methotrexate.
Comparison of survival by donor type.
Three donors phenotypically identical (0 antigen mismatch).
One donor-recipient pair mismatched for 2 antigens.
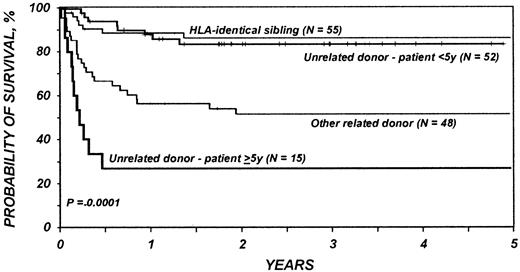
Results of multivariate analysis are shown in Table3. Significantly worse survival was associated with use of related donors other than HLA-identical siblings, regardless of recipient age, and with use of unrelated donors in patients over 5 years of age (Figure1). There was not a significant difference in the risk of mortality between HLA-matched sibling transplantations and transplantations in children younger than 5 years with an unrelated donor (Figure 1). In multivariate analysis, neither pretransplantation splenectomy, pretransplantation lymphoma, nor the use of T-cell depletion was a significant independent variable.
Results of multivariate analysis of survival after 170 allogeneic BMTs for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
| Covariate . | RR of death . | 95% CI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor type | .00013-150 | ||
| HLA-identical sibling | 1.00 | — | |
| Other related donor | 4.62 | (1.98, 10.77) | .00043-151 |
| Unrelated donor-patient < 5 y of age | 1.34 | (0.50, 3.61) | .563-151 |
| Unrelated donor-patient ≥ 5 y of age | 11.82 | (4.53, 30.88) | .00013-151 |
| Covariate . | RR of death . | 95% CI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor type | .00013-150 | ||
| HLA-identical sibling | 1.00 | — | |
| Other related donor | 4.62 | (1.98, 10.77) | .00043-151 |
| Unrelated donor-patient < 5 y of age | 1.34 | (0.50, 3.61) | .563-151 |
| Unrelated donor-patient ≥ 5 y of age | 11.82 | (4.53, 30.88) | .00013-151 |
Overall P value for effect of the categorical covariate using the Wald test.
P value for pairwise comparison of specific category with the reference (baseline) group.
Probabilities of survival for 170 patients receiving bone marrow transplants for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome by donor type and age.
There was not a significant difference in the risk of mortality after HLA-matched sibling transplants and after unrelated donor transplants in children younger than 5 years. Significantly worse survival was associated with use of related donors other than HLA-identical siblings, regardless of recipient age, and with use of unrelated donors in patients over 5 years of age.
Probabilities of survival for 170 patients receiving bone marrow transplants for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome by donor type and age.
There was not a significant difference in the risk of mortality after HLA-matched sibling transplants and after unrelated donor transplants in children younger than 5 years. Significantly worse survival was associated with use of related donors other than HLA-identical siblings, regardless of recipient age, and with use of unrelated donors in patients over 5 years of age.
Causes of death are listed in Table 4. Seven patients died after transplantations from HLA-identical siblings from a variety of causes. With transplants from other related donors, infection and new malignancy contributed to high mortality. The type of new malignancy in all cases was PTLD. EBV was confirmed in 3 of 5 and not reported in the remaining 2 cases. Four of the 5 patients with PTLD had received T-cell–depleted grafts. GVHD was the most frequent primary cause of death after unrelated donor transplantations. There were no cases of EBV-associated PTLD reported in recipients of unrelated donor transplants. One recipient of an unrelated transplant with mixed chimerism after transplantation developed acute myelogenous leukemia in host cells, which contributed to his death.
Causes of death after allogeneic BMT for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
| Cause of death . | HLA-identical sibling donor . | Other relative . | Unrelated donor . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graft failure | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| Malignancy | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| GVHD ± IPn | 0 | 4 | 7 |
| IPn | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Infection | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| Organ failure | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Hemorrhage | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Unknown/Missing | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Cause of death . | HLA-identical sibling donor . | Other relative . | Unrelated donor . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graft failure | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| Malignancy | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| GVHD ± IPn | 0 | 4 | 7 |
| IPn | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Infection | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| Organ failure | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Hemorrhage | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Unknown/Missing | 1 | 3 | 2 |
IPn indicates interstitial pneumonitis; for other abbreviations, see Table 1.
Resolution of underlying disease and performance status
Information regarding posttransplantation status of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome was available for 77% of surviving patients (92 of 120 cases; Table 5). These subjective assessments on the part of reporting institutions indicate that functional “cure” was achieved in about 75% of patients receiving HLA-identical sibling and unrelated donor transplants. A lower proportion of recipients of other related donor transplant, only 12 of 21 (57%) surviving patients, were reported as cured (P = .37). Among 90 patients alive at last contact and with at least 2 years of follow-up, Lansky or Karnofsky performance scores were available for 61 individuals at least once between 2 and 14 years after transplantation. The lowest reported performance score during that interval was 100% for 51 patients, 90% for 8 patients, 80% for 1 patient, and 20% for 1 patient. In summary, 59 of 61 (> 95%) reported a minimum performance score greater than or equal to 90%.
Assessment of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome in survivors following allogeneic BMT for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
| Disease status . | HLA-identical sibling donor (n = 48) . | Other related donor (n = 25) . | Unrelated donor (n = 47) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cured | 30 (73%) | 12 (57%) | 22 (73%) |
| Improved | 8 (20%) | 5 (24%) | 8 (27%) |
| Unchanged | 3 (7%) | 1 (5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Worse | 0 (0%) | 3 (14%) | 0 (0%) |
| Not reported | 7 | 4 | 17 |
| Disease status . | HLA-identical sibling donor (n = 48) . | Other related donor (n = 25) . | Unrelated donor (n = 47) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cured | 30 (73%) | 12 (57%) | 22 (73%) |
| Improved | 8 (20%) | 5 (24%) | 8 (27%) |
| Unchanged | 3 (7%) | 1 (5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Worse | 0 (0%) | 3 (14%) | 0 (0%) |
| Not reported | 7 | 4 | 17 |
Discussion
This analysis reviews outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treatment of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome in the current era. Results with allogeneic transplantation for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome are among the best achieved for any disease treated with stem cell grafting, rivaling those for good-risk patients with acquired aplastic anemia fortunate enough to have healthy HLA-identical sibling donors.22
Typically the diagnosis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is considered within the first few years of life based on clinical criteria. It can now be easily substantiated by quantitation of WASP in hematopoietic cells and definitively diagnosed by mutational analysis of theWASP gene. Although Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome appears to be a monogenic defect, variability in severity of the clinical syndrome in some families and, more recently, among unrelated individuals with identical mutations in the WASP gene, suggest that prognosis of a given patient is not predicted by mutational analysis alone.23,24 Quantitative analysis of WASP production in lymphoid cells, though the protein may be structurally imperfect, appears to correlate more closely with clinical severity.25
Although cure of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome with allogeneic stem cell transplantation has been recognized for many years, reluctance to recommend transplantation persists on the part of many hematologists and immunologists even when histocompatible sibling donors are available. Previous publications reviewing results with HLA-mismatched, especially T-cell–depleted, parental grafts are viewed, not surprisingly, as discouraging.
Many physicians and families hold out hope for the prompt availability of gene therapy. The current analysis offers a different perspective. With the advent of extensive computerized registries of unrelated donors of bone marrow worldwide, it is now possible to identify closely HLA-matched donors for most boys with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. The transplantation outcomes reported here, when compared with contemporary reports of the natural history of untransplanted Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome managed with supportive care, engender optimism for this curative approach. This analysis suggests that the late complication of chronic GVHD, although more common after unrelated than matched sibling donor transplantation, is predominantly limited in severity and resolves completely in most affected children.
As one might predict, the best transplant results are obtained when transplantation is undertaken with an HLA-matched sibling donor and in young subjects. Donor cell engraftment is predictable when closely HLA-matched unmanipulated grafts from related or unrelated donors are used, without the need for pretransplantation TBI. Other studies indicate that early mixed chimerism is usually stable due to the survival advantage of stem cells and hematopoietic precursors bearing the normal Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene,26,27 and may eventually progress to full donor hematopoiesis in the peripheral compartment. When extensive T-cell depletion of donor marrow is avoided, there is little risk of early posttransplantation EBV-associated PTLD as evidenced in this worldwide survey. Long-term risk of lymphoproliferative disease is markedly decreased following successful immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation when compared to the natural history of the disease.28
In this analysis, GVHD was responsible for about a quarter of failures after alternative donor transplantation. Because clinical GVHD has no demonstrated beneficial role with respect to durable engraftment or cure of the disease, efforts to reduce its incidence and severity (which do not compromise engraftment or seriously delay immune reconstitution) are likely to further improve transplantation results. Some promising approaches to accomplish this are use of partial T-cell depletion of unrelated donor bone marrow and new drugs for posttransplantation immune suppression such as mycophenolate mofetil.
The mainstay of current alternative palliative care is splenectomy and intravenous immune globulin,5,6 which provides freedom from life-threatening hemorrhage in many, but not all, subjects for months to years. Because most patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome have an inherent deficiency of antibody production to polysaccharide antigens, splenectomy in this setting carries a substantial risk of overwhelming pneumococcal sepsis unless meticulous adherence to prophylactic antibiotics and intravenous immune globulin is maintained. Boys who do not achieve safe platelet counts by surgical or medical means are restricted from many competitive athletic activities. Autoimmune complications of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome are currently managed by high-dose aspirin (in patients with vasculitis who have normal platelet counts after splenectomy), long-term corticosteroid therapy, or in extreme cases, palliative organ transplantations for end-stage renal29,30 or liver disease. At the opposite extreme, with the advent of reliable intrauterine diagnosis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, families may terminate affected pregnancies31 without benefit of the knowledge that early transplantation with a closely HLA-matched related or unrelated donor has substantial potential for eradicating the disease. Successful outcomes have also been observed with use of related and unrelated cord blood transplants for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Cord blood appears to be a reasonable alternative source of hematopoietic stem cells for small, cytomegalovirus-negative recipients, although a direct comparison of the relative efficacy of unrelated cord blood versus unrelated bone marrow transplants has not been reported for this disease. Finally, the use of gene therapy in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is in preclinical development and may play a greater role in the management of this disease in future years.
Supported by Public Health Service Grants P01-CA-40053 and U24-76518 from the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the US Department of Health and Human Services; and grants from Alpha Therapeutic Corporation; Amgen; Anonymous; Baxter Fenwal; Berlex Laboratories; BioWhitakker; Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association; Lynde and Harry Bradley Foundation; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Cell Therapeutics; Centeon; Center for Advanced Studies in Leukemia; Chimeric Therapies; Chiron Therapeutics; Charles E. Culpeper Foundation; Eleanor Naylor Dana Charitable Trust; Eppley Foundation for Research; Fromstein Foundation; Genentech; Human Genome Sciences; Immunex; Kettering Family Foundation; Kirin Brewery; Robert J. Kleberg, J. and Helen C. Kleberg Foundation; Herbert H. Kohl Charities; Nada and Herbert P. Mahler Charities; Milstein Family Foundation; Milwaukee Foundation/Elsa Schoeneich Research Fund; NeXstar Pharmaceuticals; Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation; Novartis Pharmaceuticals; Orphan Medical; Ortho Biotech; John Oster Family Foundation; Jane and Lloyd Pettit Foundation; Alirio Pfiffer Bone Marrow Transplant Support Association; Pfizer; RGK Foundation; Rockwell Automation Allen Bradley Company; Roche Laboratories; SangStat Medical; Schering AG; Schering-Plough Oncology; Searle; SEQUUS Pharmaceuticals; SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceutical; Stackner Family Foundation; Starr Foundation; Joan and Jack Stein Foundation; SyStemix; United Resource Networks; and Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Mary M. Horowitz, Statistical Center, International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry, Medical College of Wisconsin, 8701 Watertown Plank Rd, PO Box 26509, Milwaukee, WI 53226; e-mail: marymh@mcw.edu.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal