Abstract
Controversy has existed about CD34 expression by hematopoietic stem cells. We recently reported that CD34 expression reflects the activation state of stem cells by using a murine transplantation model. It has been generally held that mobilized blood stem cells express CD34.However, it has also been reported that mobilized stem cells and progenitors are in G0/G1 phases of the cell cycle. To address the state of CD34 expression by the mobilized stem cells, we again used the mouse transplantation model. We prepared CD34− and CD34+ populations of nucleated blood cells from granulocyte colony-stimulating factor–treated Ly-5.1 mice and assayed each population for long-term engrafting cells in lethally irradiated Ly-5.2 mice. The majority of the stem cells were in the CD34+population. The CD34 expression by mobilized stem cells was reversible because re-transplantation of Ly-5.1 CD34− marrow cells harvested from the Ly-5.2 recipients of CD34+-mobilized stem cells 8 months posttransplantation revealed long-term engraftment. These results may support the use of total CD34+ cells in mobilized blood as a predictor for engraftment and CD34 selection for enrichment of human stem cells.
Introduction
CD34 expression has been the hallmark of hematopoietic stem cells following the successful transplantation in baboons with selected CD34+ bone marrow cells a decade ago.1 Regarding murine stem cells, Krause et al,2 with the use of polyclonal antibodies raised against murine CD34, demonstrated that CD34+ bone marrow cells are capable of 30- and 60-day hematopoietic reconstitution in lethally irradiated mice. However, controversy arose recently because investigators in a number of laboratories demonstrated that significant populations of stem cells in the bone marrow of normal adult mice are CD34−. First, Osawa et al.,3 by using monoclonal anti-CD34 antibody, RAM34, reported that only the CD34− fraction of lineage (Lin)−, Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)+, c-kit+ bone marrow cells of normal adult mice are capable of long-term reconstitution. By using the same antibody, Morel et al.4,5 and Donnelly et al6reported that stem cells are in both CD34+ and CD34− cell populations of normal mice. Independently from these observations, studies performed by Goodell et al.7,8also raised serious questions about CD34 expression by murine stem cells. They observed that the side population cells, which are defined by Hoechst dye and are highly enriched for stem cells, are CD34−/low. Also, studies using xenotransplantation methods indicated that both CD34− and CD34+ human marrow cell populations contain stem cells.9 10 These observations raised a serious possibility that we may inadvertently discard significant numbers of stem cells by CD34 selection of human samples.
In our laboratory, we used a murine transplantation model and clearly documented that CD34 expression reflects the activation state of stem cells.11 Currently, increasing cases of clinical stem cell transplantation are carried out by using mobilized peripheral blood (PB) stem cells. Often, selected CD34+ blood cells are transplanted to reduce the risks of recurrence of tumors or occurrence of graft-versus-host disease. It is important, therefore, that we ascertain the status of CD34 expression by mobilized stem cells. It is possible that the mobilized stem cells are “activated” and, therefore, express CD34. However, investigators in two laboratories documented the noncycling state of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mobilized stem cells and progenitors.12 13Noncycling stem cells may not express CD34. In this paper, we used the murine transplantation model and examined CD34 expression by stem cells from mobilized PB. The results clearly demonstrated that the majority of stem cells mobilized by G-CSF express CD34.
Materials and methods
Monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) and hybridomas
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated RAM34 (anti-CD34; rat IgG2a), phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated D7 (anti-Sca-1; rat IgG2a), allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated 2B8 (anti-c-kit; rat IgG2b), biotin-conjugated A20 (anti-Ly-5.1; mouse IgG2a), biotin-conjugated 30-H12 (anti-Thy-1.2; rat IgG2b), biotin-conjugated RA3-6B2 (anti-CD45R/B220; rat IgG2a), biotin-conjugated RB6-8C5 (anti-Gr-1; rat IgG2b), and biotin-conjugated M1/70 (anti-Mac-1; rat IgG2b) were purchased from Pharmingen (San Diego, CA). Some antibodies were received as either nonlabeled antibodies or hybridomas. MoAb ACK4 (anti-c-kit; rat IgG2a) was provided by SI Nishikawa (Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan). Hybridoma RB6-8C5 (anti-Gr-1; rat IgG2b) was provided by RL Coffman (DNAX, Palo Alto, CA). MoAb TER-119 (anti-erythrocytes; rat IgG2b) was a gift from T Kina (Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan). Hybridomas 14.8 (anti-B220; rat IgG2b), M1/70.15.11.5 (anti-Mac-1; rat IgG2b), GK1.5 (anti-CD4; rat IgG2b), and 53-6.72 (anti-CD8; rat IgG2a) were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD). For fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) purified antibodies were conjugated to FITC or biotin in our laboratory.
Cell preparation
Male C57BL/6-Ly-5.1 10- to 12-week-old mice (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME) were used as PB donors. Female C57BL/6-Ly-5.2 10- to 14-week-old mice (Charles River Laboratories, Raleigh, NC) were used as irradiated recipients and as the source of compromised bone marrow cells. Human recombinant G-CSF (filgrastim; Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA) was used to mobilize murine stem cells. Mice were injected at 12-hour intervals subcutaneously with 125 μg/kg of G-CSF in 0.1 mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 5 consecutive days. Three hours after the last injection, PB was collected by cardiac puncture by using methoxyflurane anesthesia. For retransplantation studies, bone marrow cells were flushed from femurs and tibiae and pooled. Cells were washed twice with PBS containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), made into single-cell suspension by repeated pipetting, and filtered through 40-μm nylon mesh. The cells with densities ranging from 1.063 to 1.077 g/mL were collected by gradient separation with the use of Nycodenz (Accurate Chemical and Scientific Corp, Westbury, NY). Bone marrow cells reacting to anti-Mac-1, anti-Gr-1, anti-B220, anti-CD4, anti-CD8, and TER-119 were removed by using two depletions with immunomagnetic beads (Dynabeads M-450 coupled to sheep anti-rat IgG; DYNAL, Great Neck, NY) to prepare lineage (Lin)− cells. For preparation of Lin− PB cells, anti-Mac-1 was omitted from the cocktail because of possible expression of Mac-1 by the “activated” stem cells.14For cell sorting the resulting Lin− cells were stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD34 (RAM34), PE-conjugated anti-Sca-1, and biotin-conjugated anti-c-kit. Those cells were further stained with streptavidin-conjugated APC (Caltage Laboratories, San Francisco, CA). After addition of propidium iodide (PI) at a concentration of 1 μg/mL, the cells were washed twice, resuspended in PBS containing 0.1% BSA, and kept on ice until cell sorting. In the serial transplantation experiments, cells were stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD34 and PE-conjugated anti-Ly-5.1. Subsequently, after staining by PI, the cells were washed twice. Cell sorting was performed on FACS Vantage (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA), with appropriate isotype-matched controls. The PB cells and the marrow cells were first enriched for c-kit+, Sca-1+ cells and then the cells were sorted again according to CD34 expression. In some experiments, PB cells were sorted on the basis of CD34 expression without prior enrichment. The accuracy of sorting was determined by reanalysis of the resulting cells and was more than 96% throughout the experiments.
Hematopoietic reconstitution
Ly-5.2 mice were administrated a single 850-cGy dose of total body irradiation by using 4 × 106 V linear accelerator. FACS-sorted cells from donor (Ly-5.1) mice were injected into the tail vein of irradiated Ly-5.2 mice together with 4 × 105compromised Ly-5.2 marrow cells. Compromised marrow cells had been subjected to 2 previous rounds of transplantation and regeneration. These cells were enriched for short-acting progenitors but contained only small numbers of stem cells.15 For determination of the levels of engraftment, PB was obtained from the retro-orbital plexus by using heparin-coated micropipets (Drummond Scientific, Broomall, PA) 2 to 8 months after transplantation. Red cells were lysed by using 0.15 mol/L NH4Cl. The samples were stained with FITC-conjugated anti-Ly-5.1 and analyzed for donor-derived cells on a FACS Calibur. Donor (Ly-5.1) cells in T-cell, B-cell, granulocyte, and monocyte/macrophage lineages at 4 months posttransplantation were analyzed by staining with biotin-conjugated anti-Thy-1.2, biotin-conjugated anti-B220, biotin-conjugated anti-Gr-1, and biotin-conjugated anti-Mac-1, followed by staining with streptavidin-conjugated PE.
Retransplantation
Mice that had been transplanted with Lin−c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ PB cells of G-CSF–treated mice were killed 8 months after transplantation. Ly-5.1 Lin− c-kit+ Sca-1+CD34− cells and Ly-5.1 Lin−c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ cells were prepared from the marrow of these mice and injected into secondary Ly-5.2 recipients together with 4 × 105 Ly-5.2 compromised cells. PB was analyzed for Ly-5.1 nucleated cells 5 months after the secondary transplantation.
Results
Transplantation of Lin− CD34− and Lin− CD34+ PB cells
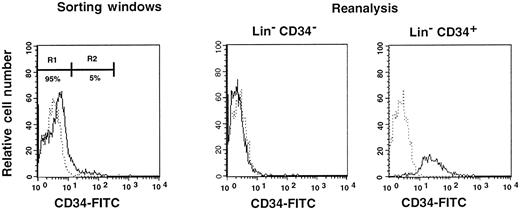
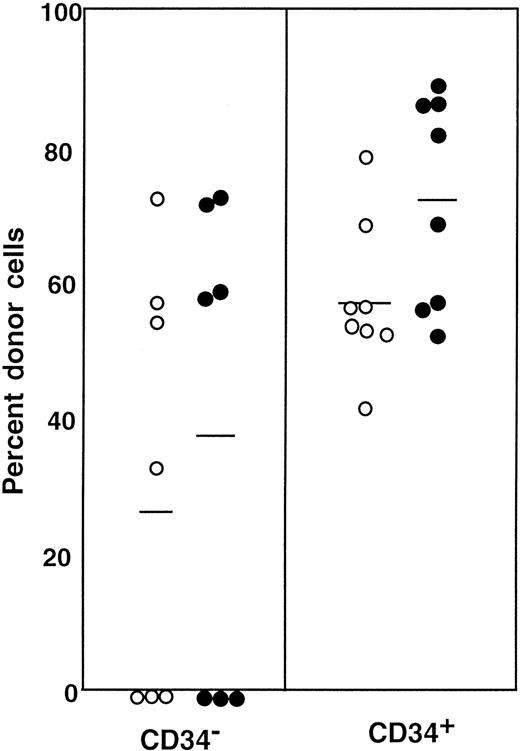
First, we separated Lin− cells into CD34− and CD34+ cell populations with the use of the electronic cell sorting regions (R1 and R2) shown in Figure1. Reanalysis of the sorted CD34− and CD34+ cells revealed purities of 99.8% and 96.3%, respectively (Figure 1). Because the ratio of the Lin− CD34− (R1) cells to Lin−CD34+ (R2) cells was 20:1, we transplanted 2 × 105 CD34− cells or 1 × 104 CD34+ cells into individual mice. The levels of engraftment were determined by measuring the percentage of donor (Ly-5.1) PB nucleated cells at 2 and 4 months following transplantation. The results are presented in Figure2. The average engraftment levels of 7 mice transplanted with 2 × 105 CD34− cells was 26.3% ± 30.9% at 2 months and 37.0% ± 34.9% at 4 months posttransplantation. Eight mice transplanted with 1 × 104 CD34+ cells revealed average engraftment levels of 57.1% ± 11.2% and 71.1% ± 15.5%, respectively, at 2 and 4 months posttransplantation. Multilineage engraftment seen in individual mice is presented in Table1.
Sorting regions used for preparation of CD34− and CD34+ cell populations.
First, Lin+ cells were removed from mononuclear PB cells by using immunomagnetic beads. The Lin− cells were then sorted on the basis of CD34 expression using R1 and R2 windows. Results of reanalysis of the sorted cells are presented on the right. Dotted and solid lines represent cells stained with IgG2a-FITC and CD34-FITC, respectively.
Sorting regions used for preparation of CD34− and CD34+ cell populations.
First, Lin+ cells were removed from mononuclear PB cells by using immunomagnetic beads. The Lin− cells were then sorted on the basis of CD34 expression using R1 and R2 windows. Results of reanalysis of the sorted cells are presented on the right. Dotted and solid lines represent cells stained with IgG2a-FITC and CD34-FITC, respectively.
Percentage of donor nucleated cells in the blood of individual mice.
The mice had been transplanted with 4 × 105 compromised marrow cells of Ly-5.2 mice and either 2 × 105Lin− CD34− cells or 1 × 104Lin− CD34+ test (Ly-5.1) cells. The numbers of the transplanted CD34− and CD34+ cells reflected the ratio of the cells in R1 and R2 windows presented in Figure 1. ○, 2 months posttransplantation; ●, 4 months posttransplantation.
Percentage of donor nucleated cells in the blood of individual mice.
The mice had been transplanted with 4 × 105 compromised marrow cells of Ly-5.2 mice and either 2 × 105Lin− CD34− cells or 1 × 104Lin− CD34+ test (Ly-5.1) cells. The numbers of the transplanted CD34− and CD34+ cells reflected the ratio of the cells in R1 and R2 windows presented in Figure 1. ○, 2 months posttransplantation; ●, 4 months posttransplantation.
Multilineage reconstitution*
| G-CSF-mobilized stem cells† . | Ly-5.1 CD34− bone marrow stem cells of primary recipients‡ . | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD34−cells . | CD34+ cells . | |||||||
| G + M . | T . | B . | G + M . | T . | B . | G + M . | T . | B . |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 31 | 89 | 7 | 8 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 38 | 57 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 26 | 43 | 56 | 20 | 43 | 46 | 34 | 7 | 1 |
| 74 | 16 | 4 | 15 | 44 | 30 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 42 | 85 | 69 | 56 | 46 |
| 18 | 17 | 43 | 66 | 32 | 61 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 35 | 28 | 38 | 54 | 44 | 65 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 29 | 45 | 42 | 20 | 2 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 15 | ||||||
| G-CSF-mobilized stem cells† . | Ly-5.1 CD34− bone marrow stem cells of primary recipients‡ . | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD34−cells . | CD34+ cells . | |||||||
| G + M . | T . | B . | G + M . | T . | B . | G + M . | T . | B . |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 31 | 89 | 7 | 8 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 38 | 57 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 26 | 43 | 56 | 20 | 43 | 46 | 34 | 7 | 1 |
| 74 | 16 | 4 | 15 | 44 | 30 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 42 | 85 | 69 | 56 | 46 |
| 18 | 17 | 43 | 66 | 32 | 61 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 35 | 28 | 38 | 54 | 44 | 65 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 29 | 45 | 42 | 20 | 2 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 15 | ||||||
G+M indicates granulocytes and/or macrophages; T, T lymphocytes; B, B lymphocytes.
Numbers indicate the percentage of cells within each lineage that expressed Ly-5.1. Peripheral blood nucleated cells were stained with anti-Ly-5.1 and either anti-Gr-1 and anti-Mac-1, anti-Thy-1.2, or anti-B220.
Engraftment at 4 months posttransplantation by 2 × 105 Lin− CD34− or 1 × 104 Lin− CD34+ granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mobilized cells shown in Figure 2.
Engraftment at 5 months posttransplantation by 1 × 104 Ly-5.1 CD34− bone marrow cells of primary recipients shown in Figure 6.
Transplantation of Lin− c-kit+Sca-1+ cells separated on the basis of CD34 expression
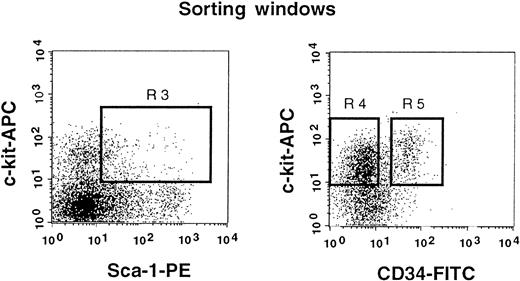
The results shown in Figure 2 clearly indicate that a significant population of stem cells in G-CSF–mobilized blood is CD34+. In the next experiment, we tested highly enriched PB cells that were separated on the basis of CD34 expression. We used Lin− c-kit+ Sca-1+ cells for this experiment because they are highly enriched for stem cells.3 11 Because the ratio of CD34− (Figure3, R4) to CD34+ (Figure 3, R5) cells in G-CSF–mobilized blood was approximately 5:1, we transplanted 5000 CD34− or 1000 CD34+ cells per mouse. Purities of the sorted cell populations assessed with an additional sample prepared in an identical manner were close to 99%. The levels of engraftment are presented in Figure4 and are similar to the results of an experiment, using cruder cell populations, shown in Figure 3. The levels of engraftment were 11.6% ± 15.8% (n = 7) and 38.1% ± 20.5% (n = 8) at 2 months posttransplantation, 24.2% ± 35.1% (n = 7) and 39.0% ± 30.9% (n = 8) at 5 months posttransplantation and 21.8% ± 34.3% (n = 7) and 31.2% ± 27.9% (n = 7) at 8 months posttransplantation for CD34− cells and CD34+ cells, respectively. All mice showed evidence for multilineage engraftment at 8 months posttransplantation. These results clearly demonstrated that the majority of G-CSF–mobilized PB stem cells are in the CD34+ cell population.
Sorting regions used for preparation of c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34− and c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ cell populations.
First, Lin+ cells were removed from mononuclear PB cells using immunomagnetic beads. The Lin− cells were then enriched for c-kit+ Sca-1+ cells by using R3 window and again sorted on the basis of CD34 expression by using R4 and R5 windows.
Sorting regions used for preparation of c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34− and c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ cell populations.
First, Lin+ cells were removed from mononuclear PB cells using immunomagnetic beads. The Lin− cells were then enriched for c-kit+ Sca-1+ cells by using R3 window and again sorted on the basis of CD34 expression by using R4 and R5 windows.
Percentage of donor nucleated cells in the blood of individual mice.
The mice had been transplanted with 4 × 105 Ly-5.2 compromised cells and either 5000 Lin− c-kit+Sca-1+ CD34− cells or 1000 Lin−c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ test (Ly-5.1) cells. The numbers of the transplanted CD34− and CD34+ cells reflected the ratio of cells in R4 and R5 windows of Figure 3. ○, 2 months posttransplantation; ●, 5 months posttransplantation; ■, 8 months posttransplantation.
Percentage of donor nucleated cells in the blood of individual mice.
The mice had been transplanted with 4 × 105 Ly-5.2 compromised cells and either 5000 Lin− c-kit+Sca-1+ CD34− cells or 1000 Lin−c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ test (Ly-5.1) cells. The numbers of the transplanted CD34− and CD34+ cells reflected the ratio of cells in R4 and R5 windows of Figure 3. ○, 2 months posttransplantation; ●, 5 months posttransplantation; ■, 8 months posttransplantation.
Reversion of CD34+ stem cells to CD34− state
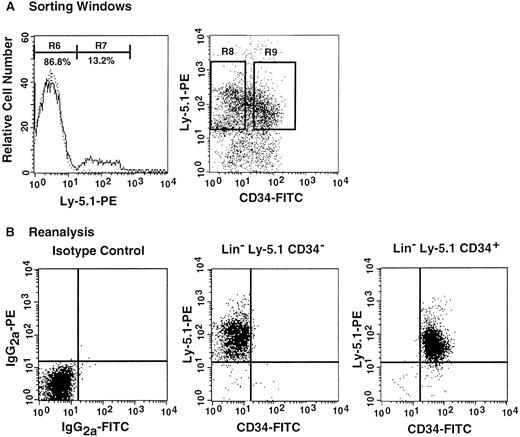
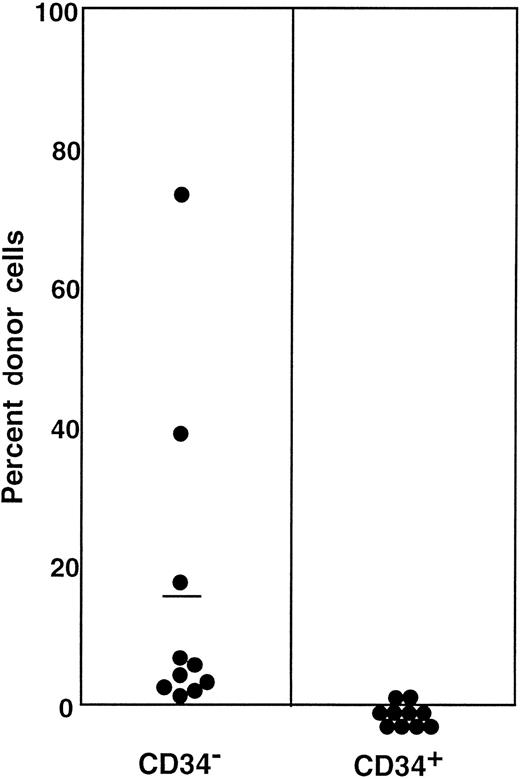
The preceding 2 studies suggested that CD34 expression occurs as the result of stem cell activation by G-CSF. If so, the circulating CD34+ stem cells should return to the bone marrow and become CD34− when the bone marrow attains a steady state. In the next experiment, we tested this hypothesis by retransplantation of the CD34+ cells. We used the 7 Ly-5.2 primary recipients that had been transplanted with Lin−c-kit+ Sca-1+ CD34+ cells after analysis of 8-month posttransplantation engraftment (Figure 4). After pooling the cells, 13.2% of the Lin− marrow cells of these mice were of donor-origin (Ly-5.1) (Figure5A). The marrow cells were then sorted for Ly-5.1 cells that were further separated on the basis of CD34 expression (Figure 5A, R8 and R9). Reanalysis of the sorted cells revealed more than 98% purity (Figure 5B). Because the ratio of CD34− (R8) to CD34+ (R9) cells was 1:1, 1 × 104 CD34− or CD34+ cells were injected into each secondary Ly-5.2 recipient. The results of analysis of engraftment at 5 months posttransplantation by Ly-5.1 cells are presented in Figure 6. All mice transplanted with CD34− cells revealed engraftment by Ly-5.1 cells at 15.3% ± 23.4% (n = 10). The multilineage engraftment seen in individual mice is presented in Table 1. Only 2 of 10 mice transplanted with CD34+ cells revealed engraftment at 1.2% and 1.3%. The remaining 8 mice showed no Ly-5.1 cells. These results clearly demonstrated that the mobilized stem cells return to the bone marrow and that when the bone marrow recovers from the radiation-induced hypoplasia and attains steady state, CD34 expression of the stem cells is down-regulated to undetectable levels.
Analysis, sorting windows, and purities of Lin− marrow cells from primary recipients at 8 months posttransplantation.
The primary recipients were the 7 mice presented in Figure 4 that had been transplanted with CD34+ G-CSF–mobilized cells. (A) Dotted and solid lines represent cells stained with isotype-matched immunoglobulin and Ly-5.1-specific antibody, respectively. A total of 13.2% of the Lin− marrow cells of the primary recipients were donor-derived (Ly-5.1) cells. R8 and R9 describe sorting regions used for preparation of Ly-5.1 CD34− and Ly-5.1 CD34+ cells to be transplanted into secondary recipients. The ratio of the cells in R8 to R9 was approximately 1:1. (B) Results of analysis of the purity of the sorted Ly-5.1 CD34− and Ly-5.1 CD34+ bone marrow cells.
Analysis, sorting windows, and purities of Lin− marrow cells from primary recipients at 8 months posttransplantation.
The primary recipients were the 7 mice presented in Figure 4 that had been transplanted with CD34+ G-CSF–mobilized cells. (A) Dotted and solid lines represent cells stained with isotype-matched immunoglobulin and Ly-5.1-specific antibody, respectively. A total of 13.2% of the Lin− marrow cells of the primary recipients were donor-derived (Ly-5.1) cells. R8 and R9 describe sorting regions used for preparation of Ly-5.1 CD34− and Ly-5.1 CD34+ cells to be transplanted into secondary recipients. The ratio of the cells in R8 to R9 was approximately 1:1. (B) Results of analysis of the purity of the sorted Ly-5.1 CD34− and Ly-5.1 CD34+ bone marrow cells.
Percentage of donor (Ly-5.1) cells in the blood of individual secondary recipients transplanted with either Ly-5.1 CD34− or Ly-5.1 CD34+ bone marrow cells of primary recipients described in Figure 5.
Initially, Ly-5.1 Lin− CD34+ G-CSF–mobilized PB cells were transplanted to Ly-5.2 primary recipients. Eight months later 4 × 105 Ly-5.2 compromised marrow cells and either 1 × 104 Ly-5.1 CD34− or 1 × 104 Ly-5.1 CD34+ bone marrow cells of the primary recipients were transplanted to individual secondary Ly-5.2 recipients. Analysis was performed at 5 months posttransplantation.
Percentage of donor (Ly-5.1) cells in the blood of individual secondary recipients transplanted with either Ly-5.1 CD34− or Ly-5.1 CD34+ bone marrow cells of primary recipients described in Figure 5.
Initially, Ly-5.1 Lin− CD34+ G-CSF–mobilized PB cells were transplanted to Ly-5.2 primary recipients. Eight months later 4 × 105 Ly-5.2 compromised marrow cells and either 1 × 104 Ly-5.1 CD34− or 1 × 104 Ly-5.1 CD34+ bone marrow cells of the primary recipients were transplanted to individual secondary Ly-5.2 recipients. Analysis was performed at 5 months posttransplantation.
Discussion
Active controversy exists about CD34 expression by hematopoietic stem cells. Following the successful long-term hematopoietic reconstitution with selected CD34+ marrow cells in baboons,1 ample documentation has been made of long-term engraftment capabilities of CD34+ human cells. Therefore, the recent discovery in the murine system that the majority of long-term engrafting cells are CD34−3 was a surprise to many hematologists and investigators. In a recent report from our laboratory,11 we documented that the CD34 expression by mouse stem cells is influenced by activation of the stem cells. In the current paper, we further documented that a significant population of G-CSF–mobilized hematopoietic stem cells express CD34. This observation in a murine model agrees, in general, with clinical observations in man. First, in transplantation of mobilized blood cells, the total number of CD34+ cells in the graft has been proposed as a prognostic indicator of engraftment.16,17 Our observations described in this paper may provide scientific basis for this practice. Second, several reports18-22 document with markers the successful engraftment by selected CD34+ cells in both autologous and allogeneic transplantation. The majority of the cases in those studies appear to be engraftment by CD34+ mobilized stem cells. Our data from these mouse studies may indicate that G-CSF not only mobilizes stem cells into circulation but also activates the stem cells to express CD34.
This documentation of CD34 expression by G-CSF–mobilized murine hematopoietic stem cells may appear to contradict the reports from two laboratories of the noncycling state of mobilized stem cells and progenitors. Roberts and Metcalf12 demonstrated that only a small portion of mobilized progenitor cells are in S phase by using the tritiated thymidine suicide technique. More recently, Uchida et al13 carried out flow cytometric analysis with Hoechst 33342 dye of murine, c-kit+, Thy-1.1low, Lin−/low, Sca-1+ mobilized cells and observed that virtually none of the cells are in the cell cycle. The apparent contradiction may be due to differences in the experimental techniques. For example, although Roberts and Metcalf12 studied colony-forming cells, we studied long-term engrafting cells. Likewise, although the studies by Uchida et al13 were based on quantitation of DNA in the highly enriched mobilized cells, the exact number of stem cells in this population is unknown. It is more likely, however, that the changes in the surface antigens may not be directly linked to the cell cycling status of the stem cells. Regardless of the underlying mechanism, our studies of a murine model appear to support the current practice of using CD34 expression as a guide for harvesting and purifying human mobilized PB stem cells.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Haiqun Zeng for assistance in FACS sorting, Dr Pamela N. Pharr and Anne G. Livingston for assistance in preparation of this manuscript, and the staff of Radiation Oncology Department of the Medical University of South Carolina for assistance in irradiation of mice.
Supported by grants RO1-DK54197 and PO1-CA78582 from the National Institutes of Health and by the Office of Research and Development, Medical Research Services, Department of Veterans Affairs.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Makio Ogawa, Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical Center, 109 Bee Street, Charleston, SC 29401-5799; e-mail: ogawam@musc.edu.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal