Abstract
The gastrointestinal immune system is traditionally thought to be composed of lymphocytes located within Peyer's patches and the lamina propria. We have recently reported that eosinophils also reside in the gastrointestinal tract during healthy states, in particular, within the lamina propria, and that these cells substantially increase after oral allergen exposure. We now demonstrate the presence of eosinophils in Peyer's patches and characterize the signals that regulate the accumulation of eosinophils in Peyer's patches. In contrast to the lamina propria, intestinal Peyer's patches have very low levels of eosinophils under healthy states. However, elevated levels of interleukin-5 (IL-5), generated by transgenic or pharmacologic approaches, result in a dramatic increase in eosinophil levels in Peyer's patches. Most eosinophils are located in the outer cortex and interfollicular regions of the Peyer's patches. To dissect the mechanism of eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches, the role of eotaxin was examined. Mice transgenic for IL-5 and genetically deficient in eotaxin were found to have reduced levels of eosinophils in Peyer's patches compared with IL-5-transgenic mice. To prove that eosinophils also traffic to Peyer's patches in wild-type mice, allergic hypersensitivity was induced and Peyer's patches were examined. Exposure to mucosal allergen promoted marked accumulation of eosinophils in Peyer's patches and this process was attenuated in eotaxin-deficient mice. In summary, these data demonstrate that elevated levels of IL-5 and mucosal allergen exposure promote eotaxin-dependent eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches. These studies suggest that eosinophils may cooperate with lymphocytes in the development of mucosal immune responses in the gastrointestinal tract.
Introduction
Eosinophils are proinflammatory cells implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous inflammatory processes especially allergic disorders.1,2 They are recruited from the circulation into inflammatory foci, where they are thought to modulate responses by releasing an array of molecules, including cytotoxic proteins, cytokines, and lipid mediators.3 Increased levels of eosinophils are frequently seen in gastrointestinal tissue obtained from patients with a variety of pathologic disorders (eg, food allergy). In some of these diseases (eg, eosinophilic gastroenteritis), eosinophils are believed to be the principal effector cell, whereas in other diseases (eg, inflammatory bowel disease and gastroesophageal reflux), the significance of eosinophils in tissues is an enigma.1-4 Under healthy conditions, eosinophil numbers in the gastrointestinal tract are substantially higher than in hematopoietic tissues; however, most investigations of eosinophils have focused on their evaluation in hematopoietic and pulmonary tissues. Understanding the processes that regulate eosinophil trafficking in the gastrointestinal tract is not only important in clinical diseases but may also have important implications in further understanding the role of eosinophils in innate immune responses.
The gastrointestinal immune system is primarily composed of immune cells located in 3 regions: Peyer's patches, lamina propria, and intraepithelial compartments. After antigen uptake by the specialized epithelium overlying Peyer's patches (M cells), antigen-presenting dendritic cells have a critical role in initiating B- and T-cell activation within Peyer's patches before the lymphocytes eventually disseminate to other organs.5 The processes that regulate mucosal immune responses (eg, hypersensitivity reactions) have only been partially elucidated. To fully characterize the mucosal immune system, it is imperative to characterize the spectrum of cells residing in the gastrointestinal tract and the participation of each cell type in mucosal immune responses. We have recently reported that the gastrointestinal immune system also consists of lamina propria eosinophils.6,7 Eosinophils home into the lamina propria during embryonic development and their levels are largely independent of viable intestinal flora.7 Furthermore, in contrast to the lung, eotaxin, an eosinophil-selective chemokine, has a critical role in regulating eosinophil levels in the lamina propria at baseline6 and after oral allergen exposure.8On the basis of these findings, reports that eotaxin is the most selective eosinophil chemoattractant identified to date,9-12 and the profound results of neutralizing eotaxin's activity,6,13-16 it has been concluded that eotaxin is a significant eosinophil chemoattractant. Interestingly, the biologic activity of eotaxin is enhanced by interleukin-5 (IL-5), an eosinophil-selective growth factor, which increases the circulating pool of eosinophils and primes eosinophils to have enhanced responsiveness to eotaxin.17-19 In our effort to further characterize the gastrointestinal immune system, in particular, gastrointestinal eosinophils, we now report the conditions and mechanisms that promote the accumulation of eosinophils to Peyer's patches.
Materials and methods
Mice
Specific pathogen-free 129SvEv and BALB/c mice (8-10 weeks old) were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Eotaxin-deficient inbred mice were maintained with age- and sex-matched controls from Taconic Farms (Germantown, PA) as described.13 The mice were backcrossed from the original 129 SvEv background by 10 successive crosses with BALB/c mice. Mice transgenic for IL-5 (on a CBA background) were originally obtained from Dr Colin Sanderson and were backcrossed into the BALB/c background and analyzed after 6 to 10 backcrosses.20
Generation of eotaxin-deficient IL-5-transgenic mice
IL-5-transgenic mice (Balb/c) carrying the eotaxin wild-type or gene-targeted allele were generated by breeding F1 littermates (from eotaxin gene-targeted mice crossed with IL-5–transgenic mice) with eotaxin gene-targeted mice and screening tail DNA by Southern blot analysis for the eotaxin gene-targeted allele and the IL-5 transgene.
Histologic analysis
Segments of the small intestine containing Peyer's patches were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate buffer pH 7.4, embedded in paraffin, cut into 5 μm sections, fixed to positive charge slides, and immunostained with antiserum against mouse eosinophil major basic protein (anti-MBP) as described.6 In brief, endogenous peroxidase in the tissues was quenched with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol, followed by nonspecific protein blocking with normal goat serum. Tissue sections were then incubated with rabbit anti-MBP (1:16 000) overnight at 4°C, followed by 1:200 dilution of biotinylated goat antirabbit IgG secondary antibody and avidin-peroxidase complex (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) for 30 minutes each. These slides were further developed with nickel diaminobenzidine-cobalt chloride solution to form a black precipitate, and counter stained with nuclear fast red. Negative controls, to check endogenous biotin and peroxidase activity, were conducted by replacing the primary antibody with normal rabbit serum, and revealed no immunoreactivity. Quantification of immunoreactive cells in the lamina propria of the jejunum in wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice was performed by counting the positively stained cells on each tissue section using a 10 × 10 μm ocular micrometer (B & B Microscopes, Ltd, Warrendale, PA), and eosinophil levels are expressed as the number of eosinophils per mm2. In the Peyer's patches, quantification of immunoreactive cells was conducted by morphometric analysis using the Metamorph Imaging System (Universal Imaging Corporation, West Chester, PA). To control for regional variations in eosinophil localization within Peyer's patches, the entire area of the Peyer's patches, located within the jejunum (2-5 Peyer's patches per mouse), were scanned for immunopositive cells, and eosinophil levels are expressed as the units of MBP staining per unit area (%). For comparison, levels of 0.1%, 1.0%, and 10% MBP staining per unit area (%) corresponded to 0.7 ± 0.03, 8.0 ± 1.6, and 90 ± 25 (mean ± SEM, n = 5-12) eosinophils per mm2, respectively.
IL-5 delivery
Mice were anesthetized through an inhaled Isoferin/O2 mixture and their ventral skin was shaved and washed with hibitane. Mini-osmotic pumps (ALZA Pharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA) containing 500 and 1000 pmol/kg body weight of human IL-5 (a kind gift of Robert Egan, Schering Plough, Kenilworth, NJ) or control vehicle (10 mmol/L phosphate-buffered saline [PBS]/0.1% bovine serum albumin [BSA], pH 7.4 intraperitoneally [ip]) were implanted surgically under sterile conditions and the wound was sealed as described.19 The mini-osmotic pump delivers IL-5 or control vehicle in the mouse peritoneum at the rate of 1 μL/h (ie, approximately 2 or 4 pmol IL-5/kg body weight per hour) for 7 days. After 8 days, all mice were killed and their blood and Peyer's patches were analyzed for eosinophil levels.
Blood eosinophil analysis
Peripheral blood samples were collected in heparinized tubes (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) by tail bleeding. Blood eosinophil levels were determined by counting cells with a Neubauer hemacytometer by staining whole blood with Discombe's solution.21
Oral allergen treatment of mice
A mouse model of allergic gastrointestinal disease has been recently established.8 In brief, mice were sensitized by ip injection with ovalbumin (OVA) (50 μg) per alum (1 mg) in 0.9% sterile saline on day 0. On days 12 and 15, mice were lightly anesthetized with Metofane inhalation (methoxy-fluorane; Pittman-Moore, Mundelein, IL) and orally administered 20 mg of encapsulated enteric-coated OVA or placebo microbeads, followed by 300 μL of acidified water (pH 2.0).22 Mice were analyzed 72 hours after the last oral treatment.
Intranasal allergen treatment of mice
A mouse model of allergic lung disease was established using methods previously described.7 Briefly, mice were lightly anesthetized with Metofane inhalation and 100 μg (50 μL) ofAspergillus fumigatus antigen (Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Spokane, WA) or 50 μL of normal saline alone was applied to the nares, using a micropipette with the mouse held in the supine position. After instillation, mice were held upright until alert. After 3 treatments per week for 3 weeks, mice were killed between 16 and 18 hours after the last intranasal challenge. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was obtained with 2 replicate volumes (0.8 mL) of normal saline containing 0.5 mmol/L EDTA and analyzed as previously reported.7
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance comparing different sets of mice was determined by Studentt test.
Results
Peyer's patches have rare eosinophils at baseline
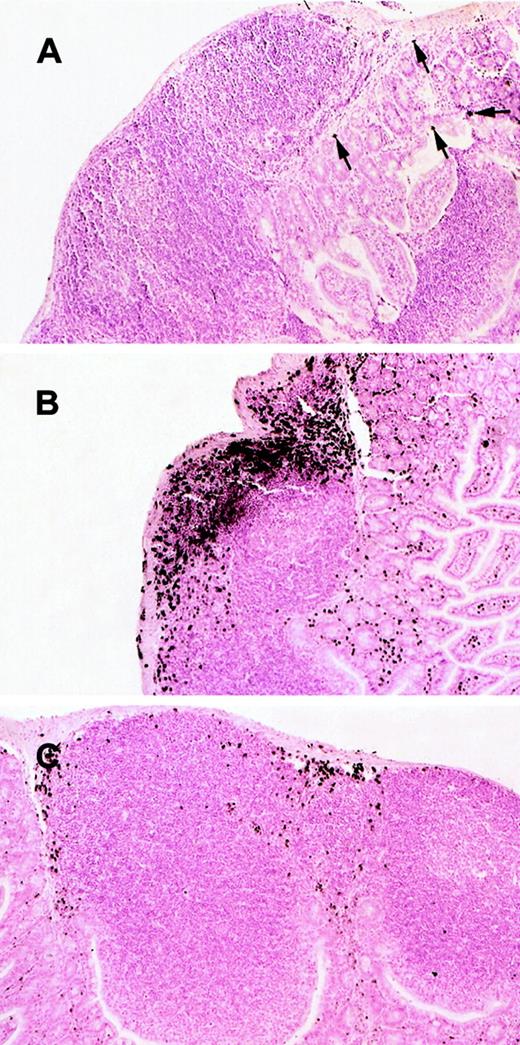
We have recently reported that eosinophils are residents of the gastrointestinal lamina propria during normal healthy states.6,7 We were therefore interested in determining whether eosinophils also resided in intestinal Peyer's patches. The presence of eosinophils in the Peyer's patches from wild-type mice was assessed by immunohistochemical analysis with anti-MBP staining. Interestingly, eosinophils were barely detected in any region of the Peyer's patches (Figure 1A). In contrast, the same mice had detectable eosinophils within the lamina propria (Figure 1A) consistent with our previous investigations.6 7
Histologic analysis of eosinophils in Peyer's patches of wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice.
Eosinophils were evaluated in the Peyer's patches of wild-type (A), IL-5–transgenic (B), and IL-5–transgenic eotaxin-deficient (C) mice. Eosinophils were identified by anti-MBP immunostaining. In (A), eosinophils are indicated with arrowheads. The original magnification is × 106.
Histologic analysis of eosinophils in Peyer's patches of wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice.
Eosinophils were evaluated in the Peyer's patches of wild-type (A), IL-5–transgenic (B), and IL-5–transgenic eotaxin-deficient (C) mice. Eosinophils were identified by anti-MBP immunostaining. In (A), eosinophils are indicated with arrowheads. The original magnification is × 106.
Eosinophils infiltrate Peyer's patches in IL-5–transgenic mice
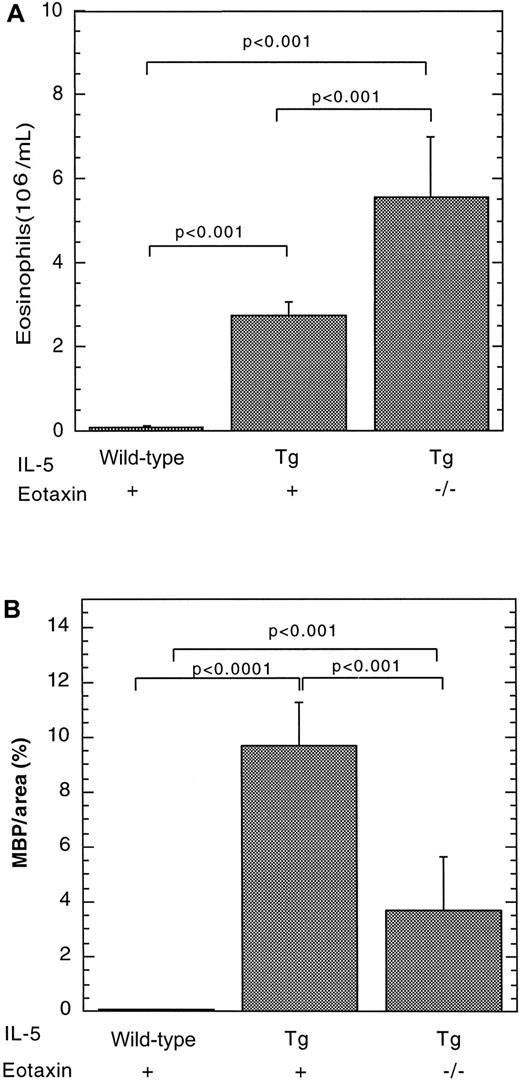
We have recently reported that IL-5 overexpression is associated with eosinophil accumulation in the lamina propria of the small intestine.7 We were therefore interested in determining whether eosinophils accumulated in Peyer's patches under conditions in which IL-5 is overproduced. As an initial analysis, we investigated eosinophil levels in the Peyer's patches of mice transgenic for IL-5 under the control of the T-cell promoter CD2. These transgenic mice were found to have a marked increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood (Figure 2A) and Peyer's patches (Figures 1B and 2B), compared with wild-type mice. For example, the eosinophil levels in the Peyer's patches of wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice were 0.043 ± 0.025 (n = 8) and 9.71 ± 1.56 (mean ± SEM, n = 12) MBP per area (%), respectively (Figure 2). The number of eosinophils in the lamina propria of the small intestine of the same IL-5 transgenic and wild-type control mice were measured in parallel and exhibited a smaller increase in eosinophils (only 5-fold higher). In particular, eosinophils in the lamina propria were 44 ± 10 and 193 ± 36/mm2 for wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice, respectively. Eosinophils in IL-5–transgenic mice were distributed in the outer cortex and interfollicular regions of Peyer's patches (Figure 1B).
The effect of the IL-5 transgene on eosinophils in wild-type or eotaxin-deficient mice.
Eosinophils were quantitated in the blood (A) and Peyer's patches (B) of wild-type, IL-5–transgenic (Tg), and eotaxin-deficient (−/−) IL-5–transgenic mice. The level of eosinophils in Peyer's patches was determined by immunohistochemical staining with anti-MBP, followed by morphometric analysis and represented as mean ± SEM (n = 8-11). Statistical significance of experimental groups was analyzed using the unpaired Student t test. Normalization of Peyer's patch eosinophils per mm2 resulted in 0.62 ± 0.39 and 90 ± 25 (mean ± SEM, n = 8-14) eosinophils/mm2for wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice, respectively.
The effect of the IL-5 transgene on eosinophils in wild-type or eotaxin-deficient mice.
Eosinophils were quantitated in the blood (A) and Peyer's patches (B) of wild-type, IL-5–transgenic (Tg), and eotaxin-deficient (−/−) IL-5–transgenic mice. The level of eosinophils in Peyer's patches was determined by immunohistochemical staining with anti-MBP, followed by morphometric analysis and represented as mean ± SEM (n = 8-11). Statistical significance of experimental groups was analyzed using the unpaired Student t test. Normalization of Peyer's patch eosinophils per mm2 resulted in 0.62 ± 0.39 and 90 ± 25 (mean ± SEM, n = 8-14) eosinophils/mm2for wild-type and IL-5–transgenic mice, respectively.
Pharmacologic administration of systemic IL-5 promotes the recruitment of eosinophils to Peyer's patches
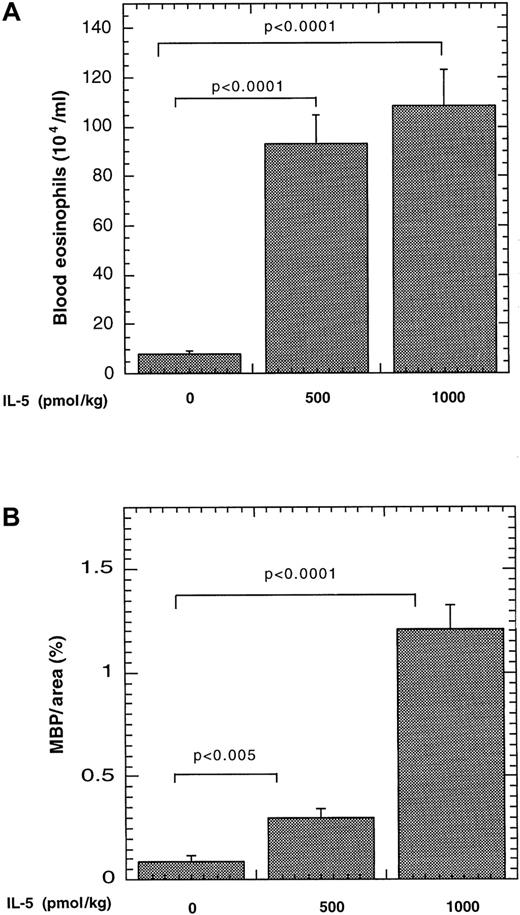
We were next interested in determining whether IL-5 promoted eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches by its systemic effects on eosinophilopoiesis or by local effects of the transgene expressed by lymphocytes present within the Peyer's patches. To examine this, we examined the effect of systemically increasing IL-5 by pharmacologic administration. IL-5 administration resulted in marked elevations of eosinophils in the blood and Peyer's patches, compared with mice treated with vehicle alone (Figure 3). For example, the number of eosinophils in the blood increased from 8 ± 1 × 104 to 93 ± 11 × 104/mL and 108 ± 14 × 104/mL (mean ± SEM, n = 6-8) after 500 and 1000 pmol/kg, respectively (Figure 3A). In Peyer's patches, eosinophil levels increased from 0.09 ± 0.03 MBP per area (%) to 0.3 ± 0.04 MBP per area (%) and 1.21 ± 0.12 MBP per area (%) (mean ± SEM, n = 4-7) after 500 and 1000 pmol/kg IL-5, respectively (Figure 3B). It should be noted that the level of eosinophils in Peyer's patches is still higher in IL-5–transgenic mice (Figure 2), compared with mice that received pharmacologic administration of IL-5. These results establish that administration of exogenous IL-5 in the intraperitoneal cavity, a site distinct from the gastrointestinal tract, is sufficient for eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches.
Effect of pharmacologic administration of IL-5 on eosinophils in the blood and Peyer's patches.
Saline alone or containing IL-5 (500 or 1000 pmol/kg) was delivered to mice via a mini-osmotic pump. The level of eosinophils in the blood (A) and Peyer's patches (B) was determined after 8 days. The number of MBP immunopositive cells is expressed as MBP per area (%) by morphometric analysis and represented as mean ± SEM (n = 6-8). The statistical significance of experimental groups was analyzed using the unpaired Student t test. Normalization of Peyer's patch eosinophils per mm2 resulted in 0.79 ± 0.36, 1.96 ± 0.93, and 12.3 ± 7.0 (mean ± SEM, n = 5-7) eosinophils/mm2 after saline and 500 and 1000 pmol of IL-5, respectively.
Effect of pharmacologic administration of IL-5 on eosinophils in the blood and Peyer's patches.
Saline alone or containing IL-5 (500 or 1000 pmol/kg) was delivered to mice via a mini-osmotic pump. The level of eosinophils in the blood (A) and Peyer's patches (B) was determined after 8 days. The number of MBP immunopositive cells is expressed as MBP per area (%) by morphometric analysis and represented as mean ± SEM (n = 6-8). The statistical significance of experimental groups was analyzed using the unpaired Student t test. Normalization of Peyer's patch eosinophils per mm2 resulted in 0.79 ± 0.36, 1.96 ± 0.93, and 12.3 ± 7.0 (mean ± SEM, n = 5-7) eosinophils/mm2 after saline and 500 and 1000 pmol of IL-5, respectively.
IL-5–mediated eosinophil recruitment to Peyer's patches is partially dependent on eotaxin
We were next interested in determining the relationship between IL-5 and eotaxin in regulating eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches. To address this, we generated IL-5–transgenic mice that were either genetically wild-type or deficient in eotaxin and evaluated for the presence of eosinophils in Peyer's patches. The level of eosinophils in Peyer's patches was markedly increased in IL-5–transgenic mice and reduced in eotaxin-deficient IL-5–transgenic mice (Figure 2B). In the absence of the eotaxin, there was an approximate 3-fold reduction in the number of eosinophils in Peyer's patches compared with IL-5–transgenic mice. Eosinophil levels were 9.7 ± 1.6 (mean ± SEM, n = 11) and 3.7 ± 1.9 (mean ± SEM, n = 8) in IL-5–transgenic mice and eotaxin-deficient IL-5–transgenic mice, respectively. However, the level of eosinophils in eotaxin-deficient IL-5–transgenic mice was significantly higher than the level in wild-type mice. Interestingly, in the absence of eotaxin, IL-5–transgenic mice had increased levels of peripheral blood eosinophils compared with IL-5–transgenic mice with wild-type eotaxin (Figure 2A), further supporting the observation that eotaxin has an important role in regulating eosinophil accumulation.7Collectively, these data indicate the presence of IL-5–mediated eotaxin dependent and independent pathways for eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches.
Eosinophils accumulate in Peyer's patches after allergen challenge
We were next interested in determining whether eosinophils migrated into Peyer's patches during Th2-associated conditions induced by experimental challenge with mucosal allergens. We therefore subjected mice to 2 distinct models of mucosal allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation. In the first approach, we used a well-accepted model of allergic airways disease that is characterized by elevated levels of IL-4, IL-5, and eosinophils.23,24 In particular, we exposed mice to repeated doses of intranasal A fumigatus antigen. After 9 doses of the antigen, the mice developed marked increases (greater than 50-fold) in eosinophils in the peripheral blood and lung, as previously reported (data not shown).7 Interestingly, when the Peyer's patches from these mice were examined, they were found to have marked levels of eosinophils after the allergen challenge (Figure4A). After placebo treatment, eosinophils in Peyer's patches remained at low levels (Figure 4B). Most eosinophils were predominantly located in the outer cortex and interfollicular regions of the Peyer's patches (data not shown) similar to their location in IL-5–transgenic mice. Morphometric analysis of eosinophil levels confirmed a marked increase in eosinophil levels in the Peyer's patches for A fumigatusantigen–challenged mice compared with placebo-challenged mice (Figure4A). Interestingly, Aspergillus antigen challenge did not increase eosinophil levels in the lamina propria after allergen challenge (data not shown), as we have previously reported.7 We also examined eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches after another Th2-associated allergic hypersensitivity response. We have recently determined that exposure of OVA-sensitized mice to enteric-coated OVA beads induces Th2-associated accumulation of eosinophils in the peripheral blood and gastrointestinal lamina propria, compared with mice challenged with placebo beads.8 We therefore induced experimental gastrointestinal allergy and examined for the presence of eosinophils in intestinal Peyer's patches. Interestingly, after oral allergen challenge, eosinophils were readily detectable in Peyer's patches (Figure 4B). After placebo bead treatment, eosinophils in Peyer's patches remained at low levels (Figure 4B). In particular, after placebo and allergen treatment, wild-type mice had 0.08 ± 0.03 and 1.32 ± 0.35 MBP per area (%). These results demonstrated that eosinophils traffic to Peyer's patches during Th2 responses after mucosal allergen exposure.
Effect of allergen challenge on eosinophil levels in Peyer's patches.
Eosinophils were quantitated in the Peyer's patches of wild-type mice subjected to intranasal (A) or oral (B) allergen or placebo challenge. Eosinophils in the Peyer's patches were determined by anti-MBP immunostaining and the results are expressed as MBP per Peyer's patches area (%), based on morphometric analysis. The results are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 9-12). Statistical significance of experimental groups was analyzed using the unpaired Studentt test. Normalization of Peyer's patch eosinophils per mm2 resulted in 0.32 ± 0.21 and 16.1 ± 4.6 (mean ± SEM, n = 6) eosinophils/mm2 for saline andA fumigatus antigen–challenged mice, respectively; and 0.76 ± 0.42 and 15.0 ± 8.7 (mean ± SEM, n = 7-10) for placebo- and OVA-challenged mice, respectively.
Effect of allergen challenge on eosinophil levels in Peyer's patches.
Eosinophils were quantitated in the Peyer's patches of wild-type mice subjected to intranasal (A) or oral (B) allergen or placebo challenge. Eosinophils in the Peyer's patches were determined by anti-MBP immunostaining and the results are expressed as MBP per Peyer's patches area (%), based on morphometric analysis. The results are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 9-12). Statistical significance of experimental groups was analyzed using the unpaired Studentt test. Normalization of Peyer's patch eosinophils per mm2 resulted in 0.32 ± 0.21 and 16.1 ± 4.6 (mean ± SEM, n = 6) eosinophils/mm2 for saline andA fumigatus antigen–challenged mice, respectively; and 0.76 ± 0.42 and 15.0 ± 8.7 (mean ± SEM, n = 7-10) for placebo- and OVA-challenged mice, respectively.
Allergen-induced eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches is partially dependent on eotaxin
We were next interested in determining the role of eotaxin in allergen-induced recruitment of eosinophils into Peyer's patches. We therefore subjected eotaxin-deficient and wild-type mice to the experimental asthma regime. As expected, allergen challenge of wild-type mice promoted eosinophil accumulation in the blood (data not shown), lung (Figure 5A), and Peyer's patches of wild-type mice as previously found (Figure 5B). In the absence of eotaxin, there was reduced accumulation of eosinophils in Peyer's patches and the lung, compared with wild-type mice (Figure 5). However, in the absence of eotaxin, allergen challenge still induced eosinophil infiltration into Peyer's patches, compared with mice that were challenged with placebo alone (Figure 5B). In particular, wild-type mice subjected to placebo or allergen challenge had 0.014 ± 0.01 and 1.53 ± 0. 46 MBP per area (%) (mean ± SEM, n = 7), respectively. Eotaxin-deficient mice subjected to placebo or allergen challenge had 0.008 ± 0.004 and 0. 89 ± 0.16 MBP per area (%) (mean ± SEM, n = 5), respectively.
Effect of intranasal allergen challenge on eosinophil levels in eotaxin-deficient mice.
Mice were subjected to the induction of allergic airway inflammation by repeated challenges with A fumigatus antigen (+) or saline (−) and the level of eosinophils was measured 18 hours after the last challenge. The level of eosinophils was quantitated in the (A) bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and (B) Peyer's patches of wild-type (+/+) or eotaxin-deficient (−/−) mice. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 7).
Effect of intranasal allergen challenge on eosinophil levels in eotaxin-deficient mice.
Mice were subjected to the induction of allergic airway inflammation by repeated challenges with A fumigatus antigen (+) or saline (−) and the level of eosinophils was measured 18 hours after the last challenge. The level of eosinophils was quantitated in the (A) bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and (B) Peyer's patches of wild-type (+/+) or eotaxin-deficient (−/−) mice. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 7).
Discussion
During allergic responses, it has been postulated that eosinophils traffic from the bone marrow to the peripheral circulation and eventually into inflamed tissues. In this study, we demonstrate that eosinophils also traffic to intestinal Peyer's patches under Th2-associated conditions (eg, after allergen exposure and/or IL-5 overexpression). There has been only a limited analysis of eosinophils in Peyer's patches,25 compared with extensive studies on lymphocytes in Peyer's patches. These later studies have demonstrated that Peyer's patches serve as major sites for lymphocyte activation and as conduits for lymphocyte trafficking. The localization of eosinophils in the outer cortex and interfollicular region is similar to the location of T cells,5 suggesting that eosinophils may communicate with T cells in Peyer's patches. Consistent with this finding, eosinophils are known to express several molecules involved in antigen presentation such as H-2 class II molecules and co-stimulatory molecules (eg, B7-1).26-28 Additionally, preliminary investigations with human eosinophils in vitro have shown that eosinophils have the capacity to present antigen to T cells.26,27 It has been proposed that lymph node eosinophils in patients with Hodgkin's disease may provide cellular ligands for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily receptors and CD30, thereby transducing proliferation and antiapoptotic signals.29,30 Furthermore, gastrointestinal eosinophils have been shown to be a chief source for calprotectin, a cytosolic protein with antimicrobial and antiproliferative properties.25 Thus, eosinophils may be involved in initiating, perpetuating, or modulating immune responses within Peyer's patches after oral allergen challenge.
In this study, we have shown that eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches is induced by allergen exposure. Furthermore, IL-5–transgenic mice are shown to have a marked increase in the level of eosinophils in Peyer's patches. We hypothesized that IL-5 may serve as a local eosinophil chemoattractant within Peyer's patches because the CD2-expressing lymphocytes are present within the lymphoid tissue. Interestingly, our study demonstrated that pharmacologic delivery of IL-5, which results in marked expansion of eosinophil levels in the blood, is sufficient to induce eosinophil accumulation within Peyer's patches. This suggests that eosinophil homing to Peyer's patches can occur during conditions in which IL-5 is overproduced. It is interesting to speculate that IL-5 primes eosinophils to respond to their homing receptor within Peyer's patches. In particular, the α4β7 integrin is coexpressed by murine eosinophils and lymphocytes.31,32 On lymphocytes, this integrin undergoes increased avidity for its homing receptor MadCAM-1, after cytokine treatment.5,33 Previous experiments conducted with freshly isolated human eosinophils have shown that IL-5 does not alter the expression of CCR3.34 Experiments are currently underway testing the effect of IL-5 on eosinophil α4β7 expression and activation in eosinophils.
In this study, we also demonstrate that trafficking of eosinophils to Peyer's patches is dependent in part on eotaxin using 2 different approaches in eotaxin-deficient mice. First, we demonstrated that the ability of the IL-5 transgene to mediate eosinophil accumulation in Peyer's patches is attenuated in the absence of eotaxin. Secondly, we show that allergen-induction of eosinophil recruitment to Peyer's patches is likewise attenuated in the eotaxin-deficient animals. Interestingly, in both of these conditions, eotaxin-deficient mice still have markedly elevated eosinophil levels in Peyer's patches, compared with baseline wild-type mice or mice treated with placebo alone. This indicates the cooperation of eotaxin with other eosinophil-active chemoattractants in the regulation of eosinophil trafficking to Peyer's patches. Consistent with this, eosinophils respond to a variety of chemokines, including other CCR3 ligands (MCP-2, -3, RANTES, and eotaxin-2 and -3).3,35,36Interestingly, the reduced levels of eosinophils in Peyer's patches of eotaxin-deficient is accompanied by elevated levels of eosinophils in the peripheral blood. Additionally, the level of CCR3 expression on eosinophils and the amount of IL-5 produced by antigen-stimulated splenocytes is not altered in eotaxin-deficient mice (unpublished findings). Taken together, these findings suggest that the reduced level of eosinophils in Peyer's patches of eotaxin-deficient mice is not simply related to reduced levels of circulating eosinophils, eosinophil CCR3 expression, or IL-5 production. Previous reports concerning eosinophil accumulation in lymphoid tissue have primarily focused on the examination of eosinophils in lymph nodes from patients with Hodgkin's disease.37 In these studies, eosinophil levels have been associated with local production of IgE, IL-5, and eotaxin, but no causal link was established. In particular, TNF-alpha derived from Reed-Sternberg cells have been shown to induce fibroblasts to secrete eotaxin.38
In summary, these results establish that eosinophils traffic to Peyer's patches after allergen exposure and/or conditions in which IL-5 levels are increased. Furthermore, these results establish that eotaxin is required in part for eosinophil recruitment to Peyer's patches. Further understanding the role of eosinophils in Peyer's patches and the processes associated with their accumulation will likely lead to further elucidation of the biologic and pathologic roles of gastrointestinal eosinophils.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs Mitchell Cohen, Susan Wert, and Sam Pope for helpful discussions and review of the manuscript, Dr Robert Egan (Schering-Plough) for providing IL-5, and Alicia Emley for graphic assistance.
Supported in part by the National Health Medical Research Council (Australia) C.J. Martin Post-doctoral Fellowship (S.P.H.), NIH grants R01 AI42242-02 (M.E.R.), R01 AI45898-01 (M.E.R.) and the Human Frontier Science Program (M.E.R.).
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Marc E. Rothenberg, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Pediatrics, Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH 45229; e-mail:Rothenberg@chmcc.org.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal