In the article by Anderson et al entitled “Immunization of allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients with tumor cell vaccines enhances graft-versus-tumor activity without exacerbating graft-versus-host disease,” which appeared in the April 1, 2000, issue of Blood (95:2426-2433), the key legends from Figures 1, 8, 9, and 10 were omitted. The figures are published below in their entirety.
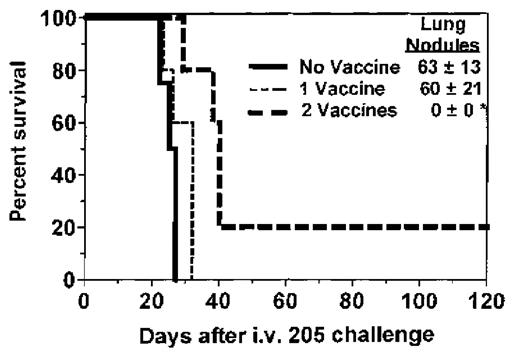
Immunization of BMT recipients increases survival and GVT activity.
One month after BMT, SW→B6 recipients were immunized with 205IL-2/TK cells and ganciclovir. Two weeks after the first vaccine, micrometastases were established by intravenous injection of 1 × 105 205 tumor cells, at which time 1 group of recipients received a second vaccine. Lung nodules were counted at the time of death or after day 100 for each recipient. The deaths that occurred in the recipient group immunized twice resulted from the growth of a nonpulmonary metastasis (sacral/pelvic mass) that necessitated sacrifice. Groups and sizes were: no vaccine, n = 4; 1 vaccine, n = 5; and 2 vaccines, n = 5. *P < .05 for lung nodules compared to 1 or no vaccine controls. **P = .004 compared to nonimmunized recipient survival.
Immunization of BMT recipients increases survival and GVT activity.
One month after BMT, SW→B6 recipients were immunized with 205IL-2/TK cells and ganciclovir. Two weeks after the first vaccine, micrometastases were established by intravenous injection of 1 × 105 205 tumor cells, at which time 1 group of recipients received a second vaccine. Lung nodules were counted at the time of death or after day 100 for each recipient. The deaths that occurred in the recipient group immunized twice resulted from the growth of a nonpulmonary metastasis (sacral/pelvic mass) that necessitated sacrifice. Groups and sizes were: no vaccine, n = 4; 1 vaccine, n = 5; and 2 vaccines, n = 5. *P < .05 for lung nodules compared to 1 or no vaccine controls. **P = .004 compared to nonimmunized recipient survival.
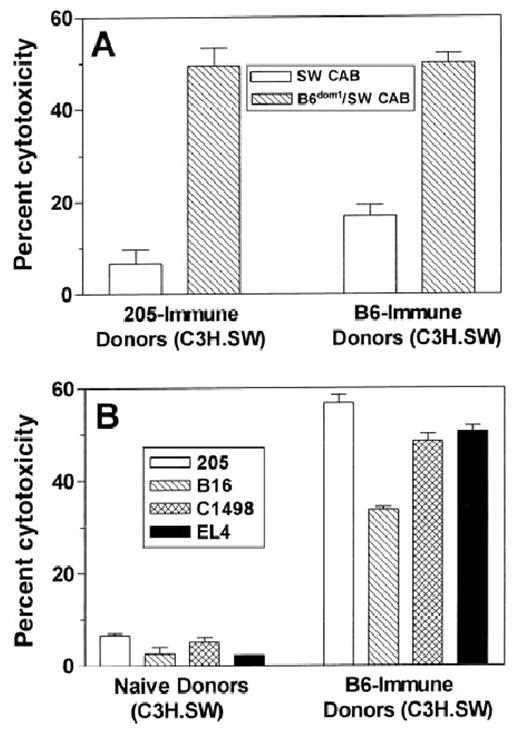
Tumor immunization of BMT recipients increases antitumor cytolytic activity and induces limited alloreactivity compared to immune C3H.SW controls.
Three months (A) or 1 month (B, C) after BMT, C3H.SW→ B6 recipients were immunized twice with irradiated 205IL-2/TK cells (205-immune) or irradiated C1498 leukemia cells (C1498-immune) at a 1-week interval. Control C3H.SW donors were also immunized in an identical manner. Ten days after the 2nd vaccine, spleens were harvested, and spleen cells were stimulated for 4 days in vitro with irradiated 205 (A, B) or C1498 (C). A 51Cr-release assay was performed using targets specified in the legends. B6 CAB are C57BL/6 ConA lymphoblasts. A, B, and C represent independent experiments with different panels of targets; neither P815 nor Yac cells were used as targets in experiment C because other experiments had demonstrated little or no LAK or NK activity. Data shown are at an E:T ratio of 200:1, and each effector:target condition was performed in triplicate using splenocytes pooled from 2 or 3 mice.
Tumor immunization of BMT recipients increases antitumor cytolytic activity and induces limited alloreactivity compared to immune C3H.SW controls.
Three months (A) or 1 month (B, C) after BMT, C3H.SW→ B6 recipients were immunized twice with irradiated 205IL-2/TK cells (205-immune) or irradiated C1498 leukemia cells (C1498-immune) at a 1-week interval. Control C3H.SW donors were also immunized in an identical manner. Ten days after the 2nd vaccine, spleens were harvested, and spleen cells were stimulated for 4 days in vitro with irradiated 205 (A, B) or C1498 (C). A 51Cr-release assay was performed using targets specified in the legends. B6 CAB are C57BL/6 ConA lymphoblasts. A, B, and C represent independent experiments with different panels of targets; neither P815 nor Yac cells were used as targets in experiment C because other experiments had demonstrated little or no LAK or NK activity. Data shown are at an E:T ratio of 200:1, and each effector:target condition was performed in triplicate using splenocytes pooled from 2 or 3 mice.
Tumor immunization of C3H.SW BMT donors induces a response to the mHAg B6dom1 found on all C57BL/6 tumor targets tested. C3H.SW (donor strain) mice were immunized twice with 5 × 106irradiated 205IL-2/TK cells (205-immune) or 20 × 106 C57BL/6 spleen cells (B6-immune) at a weekly interval, or they were not immunized (naı̈ve). Ten days after the 2nd vaccine, their splenocytes were stimulated for 5 days in vitro with C3H.SW spleen cells loaded exogenously with B6dom1 peptide. A 51Cr-release assay was performed using the targets specified in the graphs. B6dom1/SW CAB indicates C3H.SW ConA lymphoblast targets that were loaded exogenously with B6dom1 peptide, whereas SW CAB were not loaded with peptide. Data shown are at an E:T ratio of 100:1, and each effector:target condition was performed in triplicate using splenocytes pooled from 2 or 3 mice. Panels A and B represent data from the same experiment.
Tumor immunization of C3H.SW BMT donors induces a response to the mHAg B6dom1 found on all C57BL/6 tumor targets tested. C3H.SW (donor strain) mice were immunized twice with 5 × 106irradiated 205IL-2/TK cells (205-immune) or 20 × 106 C57BL/6 spleen cells (B6-immune) at a weekly interval, or they were not immunized (naı̈ve). Ten days after the 2nd vaccine, their splenocytes were stimulated for 5 days in vitro with C3H.SW spleen cells loaded exogenously with B6dom1 peptide. A 51Cr-release assay was performed using the targets specified in the graphs. B6dom1/SW CAB indicates C3H.SW ConA lymphoblast targets that were loaded exogenously with B6dom1 peptide, whereas SW CAB were not loaded with peptide. Data shown are at an E:T ratio of 100:1, and each effector:target condition was performed in triplicate using splenocytes pooled from 2 or 3 mice. Panels A and B represent data from the same experiment.
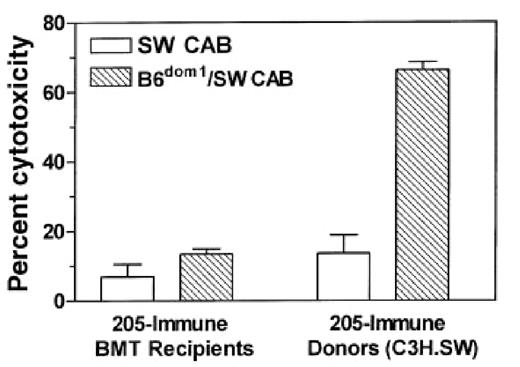
Unresponsiveness to the recipient mHAg B6dom1 is not reversed by post-transplant tumor immunization of recipients.
One month after BMT, allogeneic BMT recipients or control C3H.SW donors were immunized twice with irradiated 205IL-2/TK cells at a 1-week interval. Ten days after the second vaccine, their splenocytes were stimulated for 5 days in vitro with B6dom1-loaded C3H.SW spleen cells. A 51Cr-release assay was then performed using C3H.SW ConA lymphoblast targets that were either loaded with B6dom1 peptide (B6dom1/SW CAB) or not loaded with peptide (SW CAB). Data shown are at an E:T ratio of 50:1, and each effector:target condition was performed in triplicate using splenocytes pooled from 2 or 3 mice.
Unresponsiveness to the recipient mHAg B6dom1 is not reversed by post-transplant tumor immunization of recipients.
One month after BMT, allogeneic BMT recipients or control C3H.SW donors were immunized twice with irradiated 205IL-2/TK cells at a 1-week interval. Ten days after the second vaccine, their splenocytes were stimulated for 5 days in vitro with B6dom1-loaded C3H.SW spleen cells. A 51Cr-release assay was then performed using C3H.SW ConA lymphoblast targets that were either loaded with B6dom1 peptide (B6dom1/SW CAB) or not loaded with peptide (SW CAB). Data shown are at an E:T ratio of 50:1, and each effector:target condition was performed in triplicate using splenocytes pooled from 2 or 3 mice.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal