The mechanism(s) underlying the release of stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow into the circulation is poorly understood. We hypothesized that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), especially gelatinases, which are believed to participate in the proteolysis of basement membranes and in the migration of leukocytes, may facilitate this process. First, we investigated whether CD34+stem/progenitor cells express gelatinases A (MMP-2) and/or B (MMP-9) and whether growth factors and cytokines (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor [G-CSF], granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor [GM-CSF], stem cell factor [SCF], macrophage colony-stimulating factor [M-CSF], interleukin-3 [IL-3], IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor- [TNF-]) are able to modulate their expression. Next, we examined the transmigration of these stem/progenitor cells through reconstituted basement membrane (Matrigel) and its modulation by growth factors and cytokines. CD34+ cells were obtained from steady-state bone marrow and peripheral blood (from leukapheresis products collected either in steady-state hematopoiesis or after mobilization with G-CSF plus chemotherapy or G-CSF alone). We found that peripheral blood CD34+ cells, regardless of whether they were mobilized or not, strongly expressed both gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in contrast to steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells, which did not. However, all the growth factors and cytokines tested could induce MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion by the latter cells. Moreover, the stimulatory effects of G-CSF and SCF on both MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion were found to be significantly higher in CD34+ cells isolated from bone marrow than in those from peripheral blood. In addition TNF-, GM-CSF, and IL-6 increased the secretion of a partially active form of MMP-2. Basal transmigration of bone marrow CD34+ cells through Matrigel was lower than that of peripheral blood CD34+ cells (P < .0001), but growth factors and cytokines increased it by 50% to 150%. Positive correlations were established between expression of gelatinases and CD34+cell migration (r > .9). The stimulatory effect of G-CSF was significantly greater on the migration of CD34+ cells from bone marrow than on those from peripheral blood (P = .004). Moreover, CD34+ cell migration was reduced to approximately 50% by antibodies to MMP-2 and MMP-9, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (rhTIMP-1 and -2), ando-phenanthroline. TNF-–induced gelatinase secretion and migration of CD34+ cells and of clonogenic progenitors (colony-forming unit–granulocyte-macrophage [CFU-GM], burst-forming unit-erythroid [BFU-E], colony-forming unit granulocyte, erythroid, monocyte, megakaryocyte [CFU-GEMM], and colony-forming unit-megakaryocyte [CFU-MK]) were dose-dependent. Therefore, this study demonstrated that CD34+ cells that are circulating in peripheral blood express both MMP-2 and MMP-9 and transmigrate through Matrigel. In contrast, CD34+ cells from steady-state bone marrow acquire similar properties after exposure to growth factors and cytokines, which upregulate expression of gelatinases and transmigration of these cells when they enter the bloodstream. Hence, we suggest that growth factors and cytokines induce release of stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow into peripheral blood during mobilization, as well as during steady-state hematopoiesis, by signaling through gelatinase pathways.
PERIPHERAL BLOOD stem/progenitor cells (PBSC) collected after mobilization with various stimuli, mostly hematopoietic growth factors alone or in combination with chemotherapy, have become the predominant source for autologous and more recently even for allogeneic transplantation.1 However, the mechanisms that either govern the trafficking of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells between the bone marrow and blood in steady-state hematopoiesis or upregulate their release into peripheral blood (after administration of various mobilizing agents) remain poorly understood. It is generally believed that peripheral blood stem/progenitor cells, such as mobilized CD34+ cells, originate from bone marrow and that alteration of bone marrow stem/progenitor cell–stroma adhesive interactions and subsequent transmigration of stem/progenitor cells through the subendothelial basal lamina and the endothelial cell layer occurs during mobilization.1-3 This latter step may involve breaching of the basement membrane, which would necessitate the production of matrix-degrading enzymes, especially those capable of degrading type IV collagen. Gelatinases/type IV collagenases are expressed by mature leukocytes and have been known to facilitate transmigration of these cells from the bloodstream into peripheral tissues (reviewed in Goetzl et al4), but their expression and their role in the transmigration of stem/progenitor cells has not been investigated.
Gelatinases/type IV collagenases belong to the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family of at least 16 known endopeptidases (reviewed in Birkedal-Hansen et al,5 Stetler-Stevenson et al,6 and Chambers and Matrisian7) and consist of 72-kD gelatinase A (MMP-2) and 92-kD gelatinase B (MMP-9). Gelatinases are secreted as zymogens and possess a zinc-binding domain at the active catalytic site like all other MMPs but, uniquely, have an additional fibronectin-related collagen-binding domain. Both MMP-2 and MMP-9 degrade denatured collagens (gelatins) as well as native collagen type IV (which forms the basic scaffolding network of basement membrane structures) and native collagen type V, vitronectin, and elastin. In addition, MMP-2 can digest fibronectin, laminin, and collagen types VII and X. The activation of MMP zymogens (pro-MMPs) involves cleavage of the N-terminal propeptide, which maintains latency by binding the zinc at the active site, to produce an active form of lower molecular weight.8 Pro-MMP-9 is activated through cleavage by other MMPs such as MMP-3,9 whereas a membrane-type of MMP (MT-MMP) has been shown to mediate the activation of pro-MMP-2.10,11 MMPs are susceptible to inhibition by natural tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs; TIMP-1, -2, -3, and -4)12 as well as synthetic inhibitors, eg,o-phenanthroline. TIMPs inhibit metalloproteinase activity by forming noncovalent complexes with active MMPs; however, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 may also form complexes with pro-MMP-9 and pro-MMP-2, respectively.5,6,12 TIMP-2 also plays a role in the cellular activation of MMP-2 by forming a complex with cell surface MT1-MMP, which acts as a receptor for pro-MMP-2. Small amounts of TIMP-2 added to cells expressing MT1-MMP can enhance pro-MMP-2 activation, because this increases the concentration of the MT1-MMP/TIMP-2 receptor for pro-MMP-2 on the cell surface. However, at high TIMP-2 concentrations, all of the MT1-MMP molecules on the cell surface are complexed with TIMP-2 and no active MT1-MMP remains to initiate activation of pro-MMP-2.11
Gelatinases are produced by many cell types, including connective tissue, endothelial, epithelial, and hematopoietic cells. Recently, we reported that immature acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cells express gelatinases and are able to penetrate reconstituted basement membrane (Matrigel13-15); other investigators have demonstrated the same phenomena for malignant lymphoma cells.16 Among mature leukocytes, the secretion of gelatinases varies and is modulated by cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. MMP-9, stored in the specific and gelatinase granules of neutrophils, is released immediately upon stimulation by tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) or interleukin-8 (IL-8).17-19 In monocytes/macrophages, MMP-9 synthesis is upregulated by TNF-α and IL-1β.20,21 T lymphocytes secrete MMP-9 constitutively, with IL-2 stimulating its production as well as inducing MMP-2 secretion in these cells.22 These MMPs not only degrade connective tissue matrices to allow chemotaxis of leukocytes across basement membranes and tissues, but have also been reported to facilitate the release of active cytokines and growth factors, eg, TNF-α, insulin-like growth factor (IGF), and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β).4
The growth factors and cytokines that have been shown to stimulate mobilization of stem/progenitor cells into peripheral blood include granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), stem cell factor (SCF), IL-3, erythropoietin, IL-6, IL-1, IL-8, macrophage inflammatory protein-1α, and Flt3 ligand (reviewed in To et al1). To shed some light on the mechanism(s) regulating the release of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow, we investigated whether various growth factors and cytokines, including those used for mobilization, modulate the expression of gelatinases in these cells and whether they have any effect on migratory properties. We present evidence that growth factors and cytokines are able to induce the production of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in bone marrow steady-state CD34+ cells and stimulate the migration of these cells through reconstituted basement membrane.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
CD34+ cells.
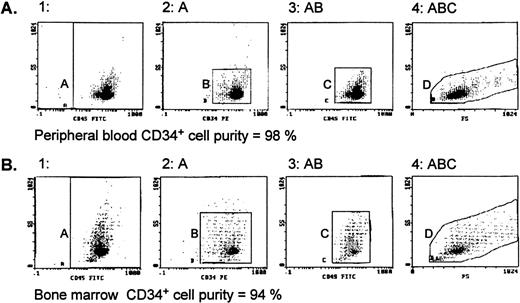
Normal bone marrow cells were obtained from unrelated or related donors (Foothills Hospital [Calgary, Alberta, Canada] or Cross Cancer Institute [Edmonton, Alberta, Canada]) or from hematologically normal patients undergoing open heart surgery (University of Alberta Hospitals, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada) with donors’ informed consent. Peripheral blood cells were collected by apheresis (at the Edmonton Blood Centre) from (1) donors in steady-state hematopoiesis, (2) donors mobilized with G-CSF (Filgrastim [Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA] at 5 μg/kg/d subcutaneously), and (3) patients with stage II/III breast cancer without bone marrow involvement who had been mobilized with chemotherapy consisting of 500 mg/m2intravenous (IV) 5-fluorouracil, 50 mg/m2 IV adriamycin, and 500 mg/m2 IV cyclophosphamide (FAC) and G-CSF (same dose as given above). Cells were suspended at a concentration of 7.5 × 106 cells/mL in serum-free Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s medium (IMDM; GIBCO Laboratories, Grand Island, NY), layered over 60% Percoll (Pharmacia-Canada, Montreal, Quebec, Canada), and centrifuged (700g for 20 minutes at 20°C), and the interphase cells were collected. After washing 2× with IMDM, cells were processed according to the CD34+ progenitor cell isolation kit protocol (Miltenyi Biotec, Auburn, CA). Briefly, cells were resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; GIBCO) containing 5 mmol/L EDTA and 0.5% bovine serum albumin (BSA; Sigma, Oakville, Ontario, Canada), spun, labeled with monoclonal hapten-conjugated CD34 antibody (clone QBEND/10) and an anti-hapten antibody conjugated to colloidal super-paramagnetic Microbeads, and passed through MidiMACS columns placed in the magnetic field of the MACS separator. The CD34+ cells were obtained by removing the column from the magnetic field and eluting with buffer and then reloading cells to a second MidiMACS column and eluting as before. The evaluation of CD34+ cell population purity was performed in the EPICS-XL flow cytometry system (Coulter Electronics, Burlington, Ontario, Canada). Cells were labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-CD45 (clone J33) and phycoerythrin (PE)-CD34 (clone 581) monoclonal antibodies (Immunotech, Marseille, France). A mouse IgG1-FITC conjugate was used as the isotype control. Cell fractions showing a CD34+ cell purity of 90% or greater, as exemplified by representative histograms shown in Fig 1, were used for subsequent experiments.
Evaluation of CD34+ cell purity by flow cytometry. CD34+ cell fractions from peripheral blood (A) and bone marrow (B), separated using MidiMACS columns described in Materials and Methods, were stained with CD45-FITC (J33)/CD34-PE (581) monoclonal antibodies and sequential gating applied. Region A shows CD45 events versus side scatter (SS) that are then analyzed for CD34-PE staining (region B). The CD34+ events are then displayed on another CD45 versus SS dot plot (region C), where the CD34+ cells form a distinct cluster characterized by low CD45/SS expression. Finally, the events in region C are analyzed by SS and forward scatter (FS) parameters (region D) to define the true CD34+ cells. The same gating regions for the CD45-FITC/CD34-PE stained samples were used to analyze the IgG1/FITC isotype control, and these events were subtracted from the number of events in regions A and D to calculate the cell purity.
Evaluation of CD34+ cell purity by flow cytometry. CD34+ cell fractions from peripheral blood (A) and bone marrow (B), separated using MidiMACS columns described in Materials and Methods, were stained with CD45-FITC (J33)/CD34-PE (581) monoclonal antibodies and sequential gating applied. Region A shows CD45 events versus side scatter (SS) that are then analyzed for CD34-PE staining (region B). The CD34+ events are then displayed on another CD45 versus SS dot plot (region C), where the CD34+ cells form a distinct cluster characterized by low CD45/SS expression. Finally, the events in region C are analyzed by SS and forward scatter (FS) parameters (region D) to define the true CD34+ cells. The same gating regions for the CD45-FITC/CD34-PE stained samples were used to analyze the IgG1/FITC isotype control, and these events were subtracted from the number of events in regions A and D to calculate the cell purity.
Cell-conditioned media.
After washing in serum-free IMDM, CD34+ cells and CD34− mononuclear cells (MNC) were aliquoted into sterile Eppendorf tubes (concentration of 1 to 2 × 106 cells/mL) and incubated for 2, 16, and 24 hours (at 37°C and 5% CO2) in the presence or absence of growth factors or cytokines. Human recombinant G-CSF, GM-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), IL-3, and IL-6 (all from Genetics Institute, Cambridge, MA), SCF, and IL-8 (R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) were added at a final concentration of 100 ng/mL each. Human recombinant TNF-α (Genentech, San Francisco, CA; and R & D Systems) was added at final concentrations of 0.1, 1.0, and 20.0 ng/mL. The cell-conditioned media (supernatants) were collected and analyzed by zymography or stored at −20°C until use. In addition, serum-free media conditioned by HT-1080 and KG-1 cells (known to secrete MMP-2 and MMP-9) were also collected as previously described14,15 and used as positive controls for zymographic analysis. In some experiments, 1 mmol/L of aminophenyl mercuric acetate (APMA; Sigma), a synthetic MMP activator,23 was added to media conditioned by peripheral blood CD34+ cells.
Zymographic analysis.
Gelatinolytic activities were assessed under nonreducing conditions using a modified sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.24 Fifteen microliters of supernatants mixed with 5 μL of loading buffer (0.16 mol/L Tris-HCl, 50% glycerol, 8% SDS, and 0.08% bromophenol blue) were applied onto a 10% or 12% polyacrylamide gel copolymerized with 2 mg/mL gelatin (Sigma). Electrophoresis was performed using a mini-PROTEAN II electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada) under constant voltage (150 V) for 2 to 4 hours at 4°C. The gels were washed 3× for 20 minutes each with 2.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma) to remove the SDS and to allow the electrophoresed enzymes to renature before being incubated in zymography buffer (0.15 mol/L NaCl, 5 mmol/L CaCl2, 0.05% NaN3, 50 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5) for 24 to 48 hours at room temperature. The gels were then stained with 0.05% Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 (Sigma) in 2.5:1:7 ethanol:acetic acid:water and destained with 2:1:7 isopropanol:acetic acid:water. Prestained standard high range (47 to 201 kD) protein markers (Bio-Rad) were used to determine the molecular weights of the gelatinases. To determine whether zones of lysis detected by zymography were produced by MMPs, parallel gels were incubated in the presence of 1.0 mmol/L o-phenanthroline (Sigma), a synthetic inhibitor of MMPs. Gels were laminated using BioDesign GelWrap (BioDesign Inc, Carmel, NY) and photographed or processed using a ScanJet 3c scanner and DeskScan II software (Hewlett Packard, Palo Alto, CA). The intensity of the bands in zymography was quantified using the Scion Image for Windows software (Scion Corp, Frederick, MD).
Matrigel assay.
In vitro cell migration was determined in the Matrigel-based assay as described25 and modified by our group.13Briefly, 13-mm polycarbonate filters of 8-μm pore size (Costar/Nucleopore, Toronto, Ontario, Canada) were coated with 25 μg of Matrigel (Collaborative Biomedical Products, Bedford, MA). The lower compartments of the modified (blind well) Boyden chambers (Neuro Probe Inc, Gaithersburg, MD) were filled with IMDM supplemented with 0.1% BSA, and the Matrigel-coated filters were placed between the upper and lower compartments. CD34+ cells (freshly isolated from steady-state bone marrow or mobilized peripheral blood) were suspended in IMDM/0.1% BSA at a concentration of 1.5 × 106cells/mL, placed in the upper compartments, and incubated for 3 hours at 37°C in 5% CO2. Cells that had migrated through the Matrigel-coated filters were recovered from the lower compartments and counted using a Neubauer hemocytometer. Percentage cell migration was calculated from the ratio of the number of cells recovered from the lower compartment to the total number of cells loaded in the upper compartment. Each experiment was performed using at least four chambers for each CD34+ cell sample and repeated at least 2×.
To examine the role of MMPs in the migration of CD34+ cells through Matrigel, the specific inhibitors of MMPs,o-phenanthroline (Sigma), recombinant human TIMP-1 (rhTIMP-1; provided by Dr Dylan Edwards, The University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada), rhTIMP-2 (Cedarlane Laboratories, Hornby, Ontario, Canada), anti-MMP-2, and anti-MMP-9 monoclonal antibodies (Oncogene Research Products, Cambridge, MA) were also used. For these inhibition experiments cells were preincubated for 30 minutes with 0.5 mmol/Lo-phenanthroline or for 2 hours with 10 μg/mL each of rhTIMP-1, rhTIMP-2, anti-MMP-2, and anti-MMP-9 antibodies before being loaded into the upper compartments of the Boyden chambers, and the Matrigel assay was performed as before. The concentrations of the inhibitors were determined as optimal for inhibition in preliminary experiments using KG-1 cells.15 Incubation of the CD34+ cells in the presence of o-phenanthroline for 3 hours and with the other inhibitors for up to 18 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2 had a negligible effect on cell viability, which was 95% to 100% as determined by trypan blue staining.
To assess whether cytokines modulate migration through Matrigel, the CD34+ cells were preincubated with 1.0 ng/mL TNF-α or 100 ng/mL GM-CSF, IL-6, G-CSF, IL-3, or SCF for 16 hours before the Matrigel assay. The percentage of cell migration through Matrigel was calculated from the ratio of percentage of cell migration assayed in the presence of MMP inhibitors or cytokines to that in their absence (controls).
Clonogenic assay.
The clonogenic assays were performed on input cells and cells transmigrating through Matrigel as recovered from the lower Boyden chambers. Briefly, not more than 1 × 103cells suspended in 1 mL IMDM containing 0.9% methylcellulose (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada), supplemented with 30% human plasma, 10% phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human leukocyte-conditioned medium (PHA-LCM), 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma), and 1 U/mL human erythropoietin (R & D Systems) were plated in duplicate as previously described.26 Colony-forming unit granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM), burst-forming unit-erythroid (BFU-E), colony-forming unit granulocyte, erythroid, macrophage, megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM), and colony-forming unit-megakaryocyte (CFU-MK) were counted after 14 days of incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2 in air. In addition, the effect of varying concentrations of rhTNF-α (0.1, 1.0, and 20.0 ng/mL) on migration of clonogenic progenitors through Matrigel was also assessed. For these experiments, cells were preincubated with TNF-α before loading onto the upper Boyden chambers and then equal volumes of cell suspensions were obtained from the lower chambers and plated as before.
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis.
Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 at the nucleic acid level was investigated in CD34+ and CD34− (control) cells using RT-PCR. The isolation of RNA was performed using the acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction method.27 Approximately 2 μg of RNA was added to each reaction mixture containing 4 μL GIBCO-BRL 5× First Strand Buffer (375 mmol/L KCl, 15 mmol/L MgCl2, 250 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 8.3, at room temperature), 2 μL N6 random oligonucleotides (100 pmol), 2 μL dNTP mixture (containing 10 mmol/L each of the deoxynucleotides dATP, dGTP, dCTP, and dTTP at neutral pH), 2 μL GIBCO-BRL SuperScript RT RNase H− Reverse Transcriptase, 0.2 μL of 1 mol/L dithiothreitol (DTT), 0.3 μL of ribonuclease inhibitor (RNAguard; Pharmacia), and 9.5 μL GIBCO water (ddH2O, RNase-free). The samples were incubated at 42°C for 90 minutes and then heated to 95°C for 5 minutes to inactivate the enzyme. Finally, the RT products were cooled to 4°C and stored until use. Multiplex PCRs were performed in a primer-dropping technique modelled after Wong et al.28 Each reaction mixture contained RT product (template DNA), the volume of which was determined by the amount necessary to equalize the intensities of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) bands visualized during agarose gel electrophoresis. Additional ingredients added to the reaction mixture were 5 μL of 10× PCR buffer (500 mmol/L KCl, 15 mmol/L MgCl2, and 100 mmol/L Tris-HCl), 1 μL of dNTP mixture (containing 10 mmol/L of each of the 4 deoxynucleotides), and 1 μL each of 5′ and 3′ starter primer pair (each primer had a concentration of 20 μmol/L). Sequences for human MMP-2 and MMP-9 were obtained from GenBank (Los Alamos, NM) and used to design primer pairs. The sequence for the GAPDH primer was obtained from Wong et al.28 The primers used were as follows: MMP-2: 5′-primer, 5′GGCCCTGTCACTCCTGAGAT, and 3′-primer, 5′GGCATCCAGGTTATCGGGGA; MMP-9: 5′-primer, 5′CAACATCACCTATTGGATCC, and 3′-primer, 5′CGGGTGTAGAGTCTCTCGCT; and GAPDH: 5′-primer, 5′CGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGTCGTAT, and 3′-primer, 5′AGCCTTCTCCATGGTTGGTGAAGAC.
All of the reagents were kept on ice and Taq polymerase (0.2 μL for each sample; Pharmacia) was added to the cold reaction mixture. Thermocycling was started using a Perkin-Elmer Cetus thermocycler (Norwalk, CT) at the optimum cycle number for each primer. Each PCR cycle consisted of a heat-denaturation step at 94°C for 1 minute, a primer-annealing step at 55°C for 1 minute, and a strand-elongation step at 72°C for 1 minute. Aliquots of PCR product (∼10 μL) were electrophoresed on 1.8% agarose gels containing 0.1 mg/mL ethidium bromide. Loading was equalized to the internal control mRNA (GAPDH) to give equivalent signals. Gels were illuminated with UV light and photographed using Polaroid film (Polaroid Corp, Cambridge, MA).
RNA was also extracted from peripheral blood and bone marrow CD34+ cell pellets obtained after 24 hours of incubation with TNF-α and subjected to RT-PCR analysis for MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression.
Statistical analysis.
Results of the densitometric analyses, Matrigel, and clonogenic assays are shown as bar graphs and error bars representing the mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. Significant differences between means of paired samples were determined using the Student’s t-test (Microsoft Excel, Redmond, WA) and a P value less than .05 was considered statistically significant. Correlation between MMP expression (quantified by densitometry) and migratory potential was determined using linear regression analysis (Microsoft Excel).
RESULTS
Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by CD34+ cells from peripheral blood but not from steady-state bone marrow.
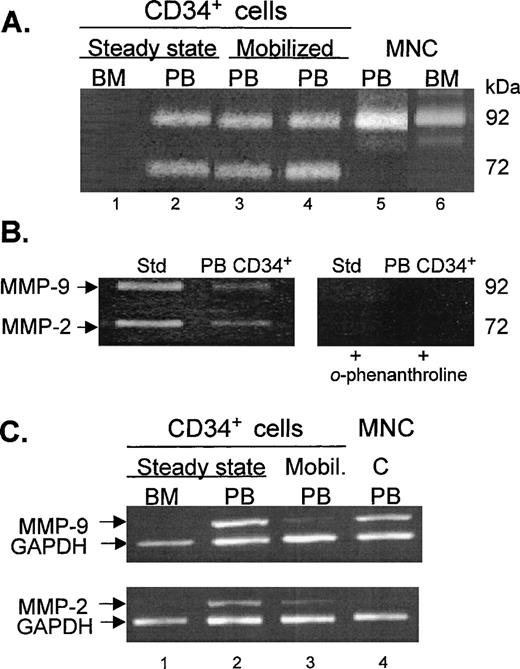
A comparison of the gelatinolytic activities in media conditioned by high purity CD34+ cells (as shown in Fig 1), separated from steady-state bone marrow and steady-state peripheral blood, after incubation in serum-free media for 24 hours is shown in Fig 2A (lanes 1 and 2). Gelatinolytic activities were not detectable in media conditioned by bone marrow CD34+ cells, whereas both 92- and 72-kD activities were found in media conditioned by peripheral blood CD34+ cells. Similarly, both gelatinolytic activities were present in media conditioned by peripheral blood CD34+ cells obtained from donors mobilized with G-CSF alone (lane 3) and from patients mobilized with chemotherapy and G-CSF (lane 4). Light-density MNC separated from leukapheresis products exhibited a very pronounced 92-kD activity but no 72-kD activity (lane 5), which was identical to the gelatinase secretion pattern found in media conditioned by MNC obtained from steady-state bone marrow (lane 6). Previously, we showed that the 92-kD activity is detectable by zymography in media conditioned for 24 hours by 1 × 106 cells/mL MNC but not by 1 × 105 cells/mL or fewer, which makes highly unlikely the possibility that the 92-kD activity observed in media conditioned by peripheral blood CD34+ cell preparations in this study is due to contamination by MNC.14 Figure 2B shows that bands corresponding to 92- and 72-kD activities found in media conditioned by KG-1 (standard) and by CD34+ cells were not detectable in experiments with the inhibitor o-phenanthroline, indicating that these bands of lysis were produced by MMP-9 and MMP-2.
Comparison of gelatinolytic activities and gene expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in CD34+ cells obtained from various sources. (A) Zymogram of media conditioned by CD34+ cells from steady-state bone marrow (BM, lane 1), steady-state peripheral blood (PB, lane 2), G-CSF–mobilized PB (lane 3), G-CSF plus chemotherapy-mobilized PB (lane 4), and CD34− MNC from PB (lane 5) and BM (lane 6). The cells were incubated in serum-free IMDM at 37°C and 5% CO2for 24 hours and the cell-conditioned media were electrophoresed in 10% acrylamide containing 2 mg/mL gelatin. The data presented here are representative of 12 BM, 2 unmobilized PB, 3 G-CSF–mobilized PB, and 12 G-CSF plus chemotherapy-mobilized PB experiments. (B) Effect of the MMP inhibitor o-phenanthroline on the expression of gelatinases by PB CD34+ cells. Media conditioned by KG-1 cells, known to secrete MMP-9 and MMP-2, was used as the standard (Std). The gels were incubated in the absence (left gel) and in the presence of 1.0 mmol/L o-phenanthroline (right gel) after electrophoresis. (C) RT-PCR analysis of MMP-9 and MMP-2 mRNA transcripts expressed by steady-state BM (lane 1) and PB (lane 2) CD34+ cells, G-CSF–mobilized PB CD34+ cells (lane 3) and PB MNC (C, lane 4). PCR products were electrophoresed on 2% agarose gels containing 0.1 g/mL ethidium bromide. GAPDH was used as the mRNA internal control to ensure equivalence of loading.
Comparison of gelatinolytic activities and gene expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in CD34+ cells obtained from various sources. (A) Zymogram of media conditioned by CD34+ cells from steady-state bone marrow (BM, lane 1), steady-state peripheral blood (PB, lane 2), G-CSF–mobilized PB (lane 3), G-CSF plus chemotherapy-mobilized PB (lane 4), and CD34− MNC from PB (lane 5) and BM (lane 6). The cells were incubated in serum-free IMDM at 37°C and 5% CO2for 24 hours and the cell-conditioned media were electrophoresed in 10% acrylamide containing 2 mg/mL gelatin. The data presented here are representative of 12 BM, 2 unmobilized PB, 3 G-CSF–mobilized PB, and 12 G-CSF plus chemotherapy-mobilized PB experiments. (B) Effect of the MMP inhibitor o-phenanthroline on the expression of gelatinases by PB CD34+ cells. Media conditioned by KG-1 cells, known to secrete MMP-9 and MMP-2, was used as the standard (Std). The gels were incubated in the absence (left gel) and in the presence of 1.0 mmol/L o-phenanthroline (right gel) after electrophoresis. (C) RT-PCR analysis of MMP-9 and MMP-2 mRNA transcripts expressed by steady-state BM (lane 1) and PB (lane 2) CD34+ cells, G-CSF–mobilized PB CD34+ cells (lane 3) and PB MNC (C, lane 4). PCR products were electrophoresed on 2% agarose gels containing 0.1 g/mL ethidium bromide. GAPDH was used as the mRNA internal control to ensure equivalence of loading.
RT-PCR analysis of steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells did not show detectable levels of mRNA for either MMP-2 or MMP-9 (Fig 2C, lane 1), whereas steady-state peripheral blood CD34+ cells expressed high levels of both MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA (lane 2). G-CSF–mobilized peripheral blood CD34+ cells also showed bands for MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA, although these were faint (lane 3). MNC from mobilized peripheral blood expressed mRNA for MMP-9 but not for MMP-2 (lane 4). Gene expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 as evaluated by RT-PCR was consistent with the zymographic analysis of secreted proteins from the various cell samples (Fig 2A).
Migration of CD34+ cells through Matrigel and the effects of MMP inhibitors.
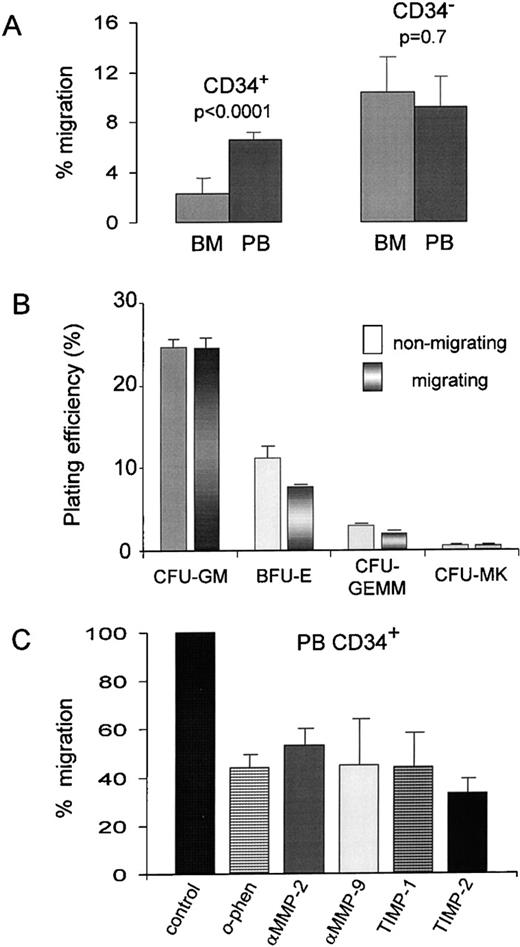
Assuming that the production of matrix-degrading MMPs by CD34+ cells facilitates their migration across basal lamina, we set out to investigate whether gelatinase secretion correlates with transmigration across a reconstituted basement membrane (Matrigel). CD34+ cells obtained from G-CSF–mobilized peripheral blood showed a significantly higher (2.7×) percentage of migration in the Matrigel-based assay than CD34+ cells from steady-state bone marrow (6.7% ± 0.5% v2.5% ± 0.8%, P < .0001; Fig3A, left bars). The migration of CFU-GM progenitors was higher by a similar fold (2.5×) for peripheral blood than for bone marrow (0.5% v 0.2%), based on a clonogenic assay of input and migrating cells (data not shown). On the other hand, CD34− cells (light-density mononuclear cells) from both bone marrow and leukapheresis products of peripheral blood had similar migration values (10.4% ± 4.1% v 9.2% ± 2.7%, P = .7; Fig 3A, right bars), which is consistent with the secretion of MMP-9 by these cells (Fig 2A).
Migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells through Matrigel and the effect of MMP inhibitors. (A) Migration of CD34+ cells isolated from steady-state BM and G-CSF–mobilized PB are shown (left bars). Migration of CD34− MNC obtained from the same sources is also presented (right bars). Graph bars show a significant difference between BM and PB CD34+ cells (P < .0001) in the percentage of migration, which is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3 for BM and n = 5 for PB), whereas the percentage of migration between the MNC was not statistically different (P= .7). (B) Plating efficiency of PB CD34+ cells that migrated through Matrigel compared with that of nonmigrating cells. Equal numbers of cells (1 × 103 cells/mL) from the upper (nonmigrating) and lower (migrating) compartments of Boyden chambers were plated in quadruplicate and colonies were scored for CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK after 14 days of incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2. (C) Effect of MMP inhibitors on the in vitro migration of PB CD34+ cells. The final concentrations ofo-phenanthroline, anti-MMP-2, anti-MMP-9, rhTIMP-1, and rhTIMP-2 and the preincubation conditions are described in Materials and Methods. The basal migration of PB CD34+ cells was set at 100% (control) and the percentages of migration in the presence of the various inhibitors are represented as the mean ± standard deviation from duplicate experiments relative to the control.
Migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells through Matrigel and the effect of MMP inhibitors. (A) Migration of CD34+ cells isolated from steady-state BM and G-CSF–mobilized PB are shown (left bars). Migration of CD34− MNC obtained from the same sources is also presented (right bars). Graph bars show a significant difference between BM and PB CD34+ cells (P < .0001) in the percentage of migration, which is expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3 for BM and n = 5 for PB), whereas the percentage of migration between the MNC was not statistically different (P= .7). (B) Plating efficiency of PB CD34+ cells that migrated through Matrigel compared with that of nonmigrating cells. Equal numbers of cells (1 × 103 cells/mL) from the upper (nonmigrating) and lower (migrating) compartments of Boyden chambers were plated in quadruplicate and colonies were scored for CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK after 14 days of incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2. (C) Effect of MMP inhibitors on the in vitro migration of PB CD34+ cells. The final concentrations ofo-phenanthroline, anti-MMP-2, anti-MMP-9, rhTIMP-1, and rhTIMP-2 and the preincubation conditions are described in Materials and Methods. The basal migration of PB CD34+ cells was set at 100% (control) and the percentages of migration in the presence of the various inhibitors are represented as the mean ± standard deviation from duplicate experiments relative to the control.
The plating efficiency of CFU-GM progenitors in the input population and in the population of cells that migrated through Matrigel was similar (P = .9; Fig 3B). There were only slight differences in the relative proportions of BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK among the cells that migrated through Matrigel compared with the input cells.
The synthetic inhibitor of MMPs, o-phenanthroline, which was found to obliterate gelatinolytic activities in zymograms (Fig 2B), was also found to reduce the ability of CD34+ cells to cross the Matrigel barrier to 44% of the control (lacking the inhibitor; Fig3C). Other specific inhibitors of MMPs, namely anti-MMP-2 monoclonal antibody, anti-MMP-9 monoclonal antibody, rhTIMP-1, and rhTIMP-2, also significantly reduced the percentage of migration to 53%, 44%, 44%, and 37% of the control, respectively (P < .0001 for all cases).
Growth factors and cytokines upregulate gelatinase secretion and cell migration of CD34+ cells through Matrigel.
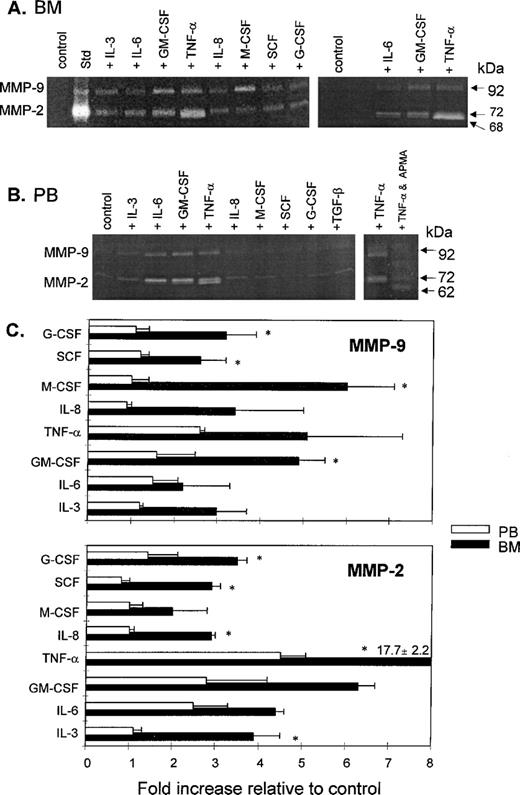
All of the growth factors and cytokines tested (G-CSF, GM-CSF, M-CSF, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α) induced the secretion of both MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities by bone marrow CD34+ cells in varying degrees. TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6 had the greatest stimulatory effect on MMP-2 secretion (up to 17-, 6-, and 4-fold increases, respectively), whereas M-CSF, TNF-α, and GM-CSF increased MMP-9 production by sixfold, fivefold, and fivefold, respectively (Fig 4A, left panel, and C). It is noteworthy that the gelatinase activity of lower molecular weight induced by TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6 in bone marrow CD34+cells appeared first as diffuse lytic zones covering a range of molecular weight rather than a distinct band of 72-kD activity. In fact, when we performed zymography using a 12% polyacrylamide gel, we were able to resolve the diffuse zones into two distinct bands corresponding to 72-kD and 68-kD activities (Fig 4A, right panel). A lower molecular weight band (62 kD) would have been expected had the pro-enzyme been cleaved to yield its fully active form and therefore it could be surmised that, in the presence of TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6, pro-MMP-2 became partly activated (see below). TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6 also significantly enhanced the expression of both MMP-2 (by 2.5- to 4.5-fold) and MMP-9 (by about 2-fold) activities in media conditioned by peripheral blood CD34+ cells, whereas the other growth factors tested (G-CSF, SCF, M-CSF, IL-8, and IL-3) appeared to exert only slight or no stimulatory effect (Fig 4B, left panel, and C). The upregulation of MMP-2 secretion brought about by IL-3, TNF-α, and IL-8 was significantly higher for steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells than for mobilized peripheral blood CD34+ cells (P = .02, .01, and .003, respectively), as was the stimulation of MMP-9 secretion by M-CSF and GM-CSF (P = .009 and .05, respectively). Interestingly, G-CSF and SCF produced a significantly higher increase in both MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion by CD34+ cells from bone marrow compared with those from peripheral blood (P = .02 and .001 for MMP-2, andP = .03 and .05 for MMP-9, respectively). Again, as in media conditioned by bone marrow CD34+ cells, in the presence of TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6, a lower molecular weight band corresponding to 68 kD was distinctly apparent in addition to the 72-kD band. The synthetic MMP activator, APMA, converted these proenzyme forms to the fully active 62-kD form (Fig 4B). It is therefore apparent that, in the presence of TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6, pro-enzyme and intermediate forms of MMP-2 are secreted into media conditioned by CD34+cells.
Effect of cytokines on gelatinase activity of CD34+ cells from BM and PB. The cells were incubated for 24 hours in serum-free IMDM in the absence (control) or presence of a cytokine, and then zymography was performed on 10% (A, left panel) or 12% (A, right panel, and B) acrylamide containing 2 mg/mL gelatin. Data are representative of at least three experiments using CD34+ cells from both BM and PB sources. The final concentrations of cytokines are given in Materials and Methods. Media conditioned by HT-1080 cells was used as the standard (Std) showing the positions of the 92-kD (MMP-9) and 72-kD (MMP-2) activities in the gel. To establish the identity of the band having molecular weight lower than 72 kD, cell-conditioned media in the presence of TNF- was preincubated with 1 mmol/L APMA for 30 minutes before loading of the gel (B, left panel). (C) Densitometric analysis of gelatinolytic activities (MMP-9 and MMP-2). The intensities of the bands were quantitated relative to the control and expressed as fold increase ± standard deviations from two or three zymograms. The asterisks indicate where statistical differences exist (P < .05) in MMP-9 and MMP-2 activities of CD34+ cells from BM versus PB in response to each cytokine.
Effect of cytokines on gelatinase activity of CD34+ cells from BM and PB. The cells were incubated for 24 hours in serum-free IMDM in the absence (control) or presence of a cytokine, and then zymography was performed on 10% (A, left panel) or 12% (A, right panel, and B) acrylamide containing 2 mg/mL gelatin. Data are representative of at least three experiments using CD34+ cells from both BM and PB sources. The final concentrations of cytokines are given in Materials and Methods. Media conditioned by HT-1080 cells was used as the standard (Std) showing the positions of the 92-kD (MMP-9) and 72-kD (MMP-2) activities in the gel. To establish the identity of the band having molecular weight lower than 72 kD, cell-conditioned media in the presence of TNF- was preincubated with 1 mmol/L APMA for 30 minutes before loading of the gel (B, left panel). (C) Densitometric analysis of gelatinolytic activities (MMP-9 and MMP-2). The intensities of the bands were quantitated relative to the control and expressed as fold increase ± standard deviations from two or three zymograms. The asterisks indicate where statistical differences exist (P < .05) in MMP-9 and MMP-2 activities of CD34+ cells from BM versus PB in response to each cytokine.
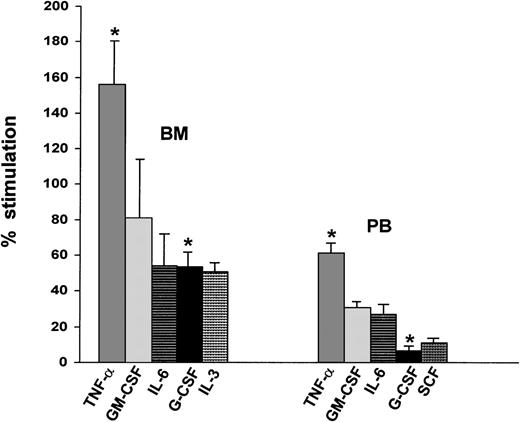
The percentage of migration of bone marrow CD34+ cells in the Matrigel assay was higher when the cells were preincubated with TNF-α, GM-CSF, IL-6, G-CSF, and IL-3. TNF-α had the greatest effect (Fig 5), which is consistent with the most pronounced stimulatory effect of this cytokine on gelatinase secretion. The stimulatory effects of TNF-α and G-CSF on the migratory potential of bone marrow CD34+ cells were significantly higher than their effects on peripheral blood CD34+ cells (P = .015 and .004, respectively), whereas the effects of the other growth factors and cytokines were not significantly different. The effects of TNF-α, GM-CSF, IL-6, and G-CSF on migration through Matrigel of peripheral blood CD34+ cells also correlated with the enhancement of both MMP-9 (r = .99) and MMP-2 (r = .998) activities by these cytokines. On the other hand, migration of bone marrow CD34+ cells through Matrigel correlated more strongly with MMP-2 (r = .986) than with MMP-9 activity (r = .76).
Stimulatory effect of cytokines on the in vitro migration of BM and PB CD34+ cells. The concentrations of TNF-, GM-CSF, IL-6, G-CSF, IL-3, and SCF and the calculations for the percentage of stimulation are described in Materials and Methods. Bar graphs represent the mean percentage of stimulation relative to the control, which is set at the baseline value of 0%, ± standard deviation from duplicate experiments. *Significant difference in the effect of TNF- and G-CSF on migration of BM versus PB CD34+ cells (P = .015 and .004, respectively).
Stimulatory effect of cytokines on the in vitro migration of BM and PB CD34+ cells. The concentrations of TNF-, GM-CSF, IL-6, G-CSF, IL-3, and SCF and the calculations for the percentage of stimulation are described in Materials and Methods. Bar graphs represent the mean percentage of stimulation relative to the control, which is set at the baseline value of 0%, ± standard deviation from duplicate experiments. *Significant difference in the effect of TNF- and G-CSF on migration of BM versus PB CD34+ cells (P = .015 and .004, respectively).
Stimulation of gelatinase expression and migration of progenitors through Matrigel are TNF-α dose-dependent.
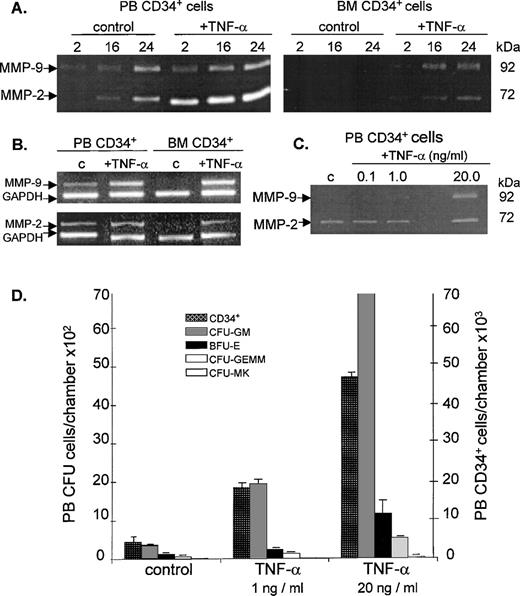
The secretion of both MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities by peripheral blood CD34+ cells increased with time and was further enhanced in a time-dependent fashion by TNF-α (Fig6A). Conversely, the media conditioned by bone marrow CD34+cells did not show any detectable level of either MMP-9 or MMP-2 activity despite incubation for up to 24 hours. However, after pretreatment of these cells with TNF-α, both gelatinolytic activities could be detected and became more prominent with prolonged incubation time. RT-PCR analysis of mRNA from TNF-α–treated bone marrow CD34+ cells showed an induction in MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression in comparison with untreated cells. In peripheral blood CD34+ cells, TNF-α stimulated mRNA expression of MMP-9 and MMP-2 (Fig 6B) by fourfold and sevenfold, respectively, as assessed by densitometric analysis. The stimulatory effects of TNF-α on gelatinolytic activities secreted by peripheral blood CD34+cells, as well as on the migration of these cells through Matrigel, were dose-dependent (Fig 6C and D). Preincubation of mobilized peripheral blood CD34+ cells with 1.0 and 20.0 ng/mL TNF-α for 16 hours before performing the Matrigel assay increased their migration fourfold and 10-fold, respectively, relative to the control (without TNF-α). Incubation with TNF-α also increased the migratory potential of hematopoietic progenitor cells in a dose-dependent manner (Fig 6D). Increasing the TNF-α concentration from 1 to 20.0 ng/mL increased by about fourfold the total number of all types of progenitors (CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK) that migrated through Matrigel into the lower chamber.
Effect of TNF- on gelatinolytic activities expressed by PB and BM CD34+ cells and on migration of clonogenic progenitors. (A) Time dependence of gelatinolytic activity and the effect of TNF-. The zymographic analysis of gelatinases secreted by CD34+ cells from PB and BM was performed in the absence (control lanes) and presence of TNF- (final concentration, 1 ng/mL). Cell-free supernates were withdrawn after incubating the cells at 37°C and 5% CO2 in serum-free IMDM at the times (2, 16, and 24 hours) indicated. Data are representative of three independent experiments using CD34+ cells from both steady-state BM and G-CSF–mobilized PB. (B) RT-PCR analysis of transcripts expressed by PB and BM CD34+ cells in the absence (c) or presence of 1 ng/mL TNF-. mRNA was isolated from cell pellets obtained after incubating the cells at 37°C and 5% CO2 in serum-free IMDM for 24 hours. GAPDH was used as the mRNA internal control to ensure equivalence of loading. (C) Dose-dependence of the stimulatory effect of TNF- on gelatinolytic activity of PB CD34+ cells. Zymographic analysis of media conditioned by PB CD34+ cells in the presence of various concentrations of TNF-. The cells were incubated in serum-free IMDM for 16 hours in the absence (c lane) and in the presence of 0.1, 1.0, and 20 ng/mL TNF-. (D) Migration of PB CD34+ cells and clonogenic progenitor cells in response to various concentrations of TNF- (0, 1.0, and 20.0 ng/mL). Bar graphs represent the mean and standard deviations of duplicate experiments. There was a significant increase in the percentage migration of CD34+ cells in the presence of TNF- relative to the control (P = .016 for 1 ng/mL TNF- and P = .001 for 20 ng/mL TNF-). For the clonogenic assay, cells suspended in equal volumes of media obtained from the lower compartments of the Boyden chambers were plated. The graph shows the mean number of CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK progenitors scored from quadruplicate plates. Except for the CFU-MK, the numbers of colony-forming progenitors in the presence of 1 and 20 ng/mL TNF- are significantly different (P ≤ .005) compared with the control.
Effect of TNF- on gelatinolytic activities expressed by PB and BM CD34+ cells and on migration of clonogenic progenitors. (A) Time dependence of gelatinolytic activity and the effect of TNF-. The zymographic analysis of gelatinases secreted by CD34+ cells from PB and BM was performed in the absence (control lanes) and presence of TNF- (final concentration, 1 ng/mL). Cell-free supernates were withdrawn after incubating the cells at 37°C and 5% CO2 in serum-free IMDM at the times (2, 16, and 24 hours) indicated. Data are representative of three independent experiments using CD34+ cells from both steady-state BM and G-CSF–mobilized PB. (B) RT-PCR analysis of transcripts expressed by PB and BM CD34+ cells in the absence (c) or presence of 1 ng/mL TNF-. mRNA was isolated from cell pellets obtained after incubating the cells at 37°C and 5% CO2 in serum-free IMDM for 24 hours. GAPDH was used as the mRNA internal control to ensure equivalence of loading. (C) Dose-dependence of the stimulatory effect of TNF- on gelatinolytic activity of PB CD34+ cells. Zymographic analysis of media conditioned by PB CD34+ cells in the presence of various concentrations of TNF-. The cells were incubated in serum-free IMDM for 16 hours in the absence (c lane) and in the presence of 0.1, 1.0, and 20 ng/mL TNF-. (D) Migration of PB CD34+ cells and clonogenic progenitor cells in response to various concentrations of TNF- (0, 1.0, and 20.0 ng/mL). Bar graphs represent the mean and standard deviations of duplicate experiments. There was a significant increase in the percentage migration of CD34+ cells in the presence of TNF- relative to the control (P = .016 for 1 ng/mL TNF- and P = .001 for 20 ng/mL TNF-). For the clonogenic assay, cells suspended in equal volumes of media obtained from the lower compartments of the Boyden chambers were plated. The graph shows the mean number of CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK progenitors scored from quadruplicate plates. Except for the CFU-MK, the numbers of colony-forming progenitors in the presence of 1 and 20 ng/mL TNF- are significantly different (P ≤ .005) compared with the control.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we examined whether gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9), which degrade extracellular matrix (ECM) basement membranes and are implicated in the migration of leukocytes as well as in the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells,4-7 are involved in the release of stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow. Our study shows that CD34+ cells that entered the peripheral blood, but not those located in the bone marrow during steady-state hematopoiesis, strongly express both MMP-2 and MMP-9 and that functional differences exist between these cells.
Cells expressing the CD34 surface antigen constitute a heterogeneous population of hematopoietic cells, including primitive stem cells with self-renewal capacity, and of progenitors committed to myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid development.29 There is some evidence that circulating CD34+ cells differ phenotypically and functionally from their bone marrow counterparts. Some investigators reported that a larger proportion of peripheral blood CD34+ cells expressed the CD33 antigen in comparison with bone marrow CD34+ cells,30 whereas others reported that a lower proportion of peripheral blood CD34+cells expressed the c-kit ligand.31 Another study demonstrated that, although CD34+ cells obtained from G-CSF–mobilized peripheral blood and steady-state bone marrow (of the same individuals) were equivalent on a cell-per-cell basis in the content of both committed and very primitive hematopoietic progenitors, these cells were found to have different cell cycling kinetics and responses to cytokines.32 It was also reported that steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells do not express Granzyme B and perforin, whereas peripheral blood CD34+cells mobilized with chemotherapy and G-CSF secrete these proteins.33 Our study shows further differences between steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells and circulating peripheral blood CD34+ cells, because we were able to demonstrate MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression, on both the gene and protein levels, in the latter but not in the former.
Furthermore, we found that peripheral blood CD34+ cells migrate through reconstituted basement membrane (Matrigel) more readily than steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells, which do not express gelatinases, suggesting that upregulation of MMP expression may lead to enhanced transmigration. Although only a small proportion of CD34+ cells transmigrated through Matrigel, we showed that these cells were multipotential and committed progenitors (CFU-GEMM, CFU-GM, BFU-E, and CFU-MK), indicating that, after transmigration, these CD34+ cells sustain their clonogenic potential. We also demonstrated that rhTIMP-1 and rhTIMP-2, monoclonal antibodies to MMP-2 and MMP-9, and o-phenanthroline significantly reduced the ability of peripheral blood CD34+ cells to traverse the reconstituted basement membrane, indicating the role of MMPs in the transmigration process. Previously, we reported that primary human immature AML blast cells secrete MMP-2 and/or MMP-9 and penetrate the Matrigel barrier, but we suggested that cysteine proteinases may also participate in cell invasion through Matrigel.14 15 In this study, because the complete obliteration of migratory ability in the presence of MMP inhibitors was not achieved, it may be inferred that other proteinases could also be involved in ECM proteolytic degradation and subsequent CD34+ cell migration.
One of the striking features of MMPs is that they are inducible, ie, their synthesis and secretion are controlled at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. There is now a growing body of experimental evidence for the regulatory role of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in the synthesis and secretion of MMPs (reviewed in Ries and Petrides34 and Borden and Heller35). In this study, we demonstrated that all of the growth factors and cytokines tested, namely G-CSF, GM-CSF, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, M-CSF, IL-8, and TNF-α, were able to induce the secretion of MMP-9 and MMP-2 by bone marrow CD34+ cells. The most pronounced stimulation of MMP-2 was observed with TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-6, whereas M-CSF, TNF-α, and GM-CSF had the greatest effects on MMP-9 activity.
Various cytokines and growth factors, including TNF-α, TNF-β, IL-1, IL-6, epidermal growth factor, and TGF-β, have been documented to upregulate the secretion of MMP-9 in a variety of cell types.4,34 For example, MMP-9 secretion in human CD3+ and CD4+ T cells36 and macrophages21 is augmented in response to TNF-α and IL-1, and in leukemic HL-60,37 KG-1 (our unpublished data), U-937,38 and human sarcoma cell lines39,40 in response to TNF-α. The MMP-9 promoter gene is regulated by a series of cis-acting elements, including activation protein-1 (AP-1), SP-1, and nuclear factor binding to a κB-like sequence (NF-κB), which are indispensable for cytokine-induced MMP-9 promoter activity.34,35,41 42Although in this study transcription factors were not studied, we may speculate that similar mechanisms could be operational in the induction of the MMP-9 gene in hematopoietic CD34+ cells.
Our finding that all of the growth factors and cytokines tested in this study upregulated expression of MMP-2 in bone marrow CD34+cells was surprising, especially in view of the fact that the promoter region of the MMP-2 gene does not have a TATA box or the common AP-1 element.35,43 In fact, upregulation of MMP-2 synthesis has only been reported for TGF-β in human fibroblasts,44 in keratinocytes,45 and for IGF-1 in a murine lung carcinoma cell line.46 The mechanism(s) regulating MMP-2 expression is still unclear, and factors such as increased calcium influx, ECM proteins (namely laminin and vitronectin, functioning via phospholipase and αvβ3 integrin signaling pathways, respectively), Ha-ras and c-erb oncogenes, and tissue-specific enhancer/promoter elements have all been suggested to play a role.46 Although our results provide clear evidence that growth factors and cytokines regulate MMP-2 synthesis in bone marrow CD34+ cells and show that TNF-α upregulates MMP-2 expression on gene and protein levels, the precise molecular mechanism(s) involved in the regulation of MMP-2 synthesis in hematopoietic progenitor cells remains to be defined.
Moreover, we found that TNF-α, as well as GM-CSF and IL-6, not only stimulated the 72-kD proenzyme form of MMP-2, but also seemed to trigger a catalytic cleavage of the propeptide to a partially activated form (68 kD). In synovial fibroblasts, TNF-α was reported to be able to induce the fully activated (62 kD) form of MMP-2 through a mechanism involving an MT-MMP.47 Previously, we described the constitutive expression of MT-MMP by primary leukemic and KG-1 cells.15 In the present study, we also observed MT1-MMP mRNA in normal CD34+ cells (data not shown), but the regulatory role of cytokines on MT-MMP expression in CD34+cells was not tested. It will be important to clarify further the specific molecular pathways involved in cytokine-induced regulation of MMPs in CD34+ cells.
Next, we demonstrated that the stimulatory effect of growth factors and cytokines on MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression by CD34+ cells translated into an enhancement of the migratory potential of these cells. Positive correlations between the level of expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and the percentage of migration of CD34+ cells were observed, implicating MMPs in this process. In particular, the dose-dependent stimulation of gelatinase activity by TNF-α resulted in a concomitant increase in the number of CD34+ cells as well as clonogenic CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM, and CFU-MK progenitors that were able to migrate through the reconstituted basement membrane. In other hematopoietic cells, eg, T lymphocytes, increased migration across reconstituted basement membrane (Matrigel) has been attributed to upregulation of MMP-9 and induction of MMP-2 by IL-222or upregulation of MMP-9 by IL-2 and IL-4.48 In a human osteosarcoma cell line, TNF-α induced MMP-9 production and enhanced osteosarcoma cell invasion through Matrigel.39
Growth factors and cytokines, apart from their well-established roles in stem/progenitor cell proliferation, differentiation, and maturation, have also been shown to alter the adhesive interactions between these cells and bone marrow stroma. For example, IL-3, GM-CSF, and SCF were shown to modify the functional states of very late antigen-4 (VLA-4) and VLA-5.49 Also, combined treatment with anti–VLA-4 and cytokines resulted in enhanced mobilization.50 It is likely that, under normal steady-state conditions, adhesive interactions between hematopoietic progenitor cells and the marrow stroma restrict stem/progenitor cells to the bone marrow niches and disruption of these interactions is necessary for the release of stem cells and their passage through the basal lamina and endothelial layers.2,3Furthermore, integrin/ECM interactions may also result in the induction of MMP production. It has been shown that adhesion of murine T cells to capillary endothelia through vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) can induce MMP-2 secretion, which facilitates the transmigration of these cells.51 Another study indicated that active MMP-2 directly binds αvβ3 integrin.52Thus, integrins may localize proteolytic activities to the cell surface.
We present evidence that all types of CD34+ cells circulating in the blood stream, regardless of whether they are mobilized (with G-CSF, with or without chemotherapy) or in steady-state hematopoiesis, express MMP-2 and MMP-9 and that a wide range of growth factors and cytokines, including those used for stem cell mobilization (eg, G-CSF, SCF, and GM-CSF), is able to induce these enzymes in steady-state bone marrow CD34+ cells. From these data it is tempting to speculate that various exogenously administered mobilizing factors and also those growth factors and cytokines that are endogenously secreted within the bone marrow microenvironment may facilitate release of CD34+ cells from the bone marrow through their modulatory effects on expression of MMPs. Moreover, secretion of various MMPs by fibroblasts or osteoclasts53may also be modulated by these factors and influence trafficking of stem/progenitors cells between the various niches of bone marrow stroma. Consequently, proteolysis of the basal lamina and migration of progenitors through the endothelial layer into marrow sinuses and peripheral blood could occur. In addition, we may speculate that the strong gelatinase expression by peripheral blood CD34+cells described here may suggest an explanation for the observed faster hematopoietic recovery after transplantation of mobilized PBSC in comparison with recovery after transplantation of steady-state bone marrow cells.54 This would also imply that gelatinases facilitate not only the efficient mobilization of stem/progenitor cells to peripheral blood, but also their engraftment after transplantation.
Supported by a grant to A.J.-W. from the CRCS Blood Services, Research & Development, and by Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research Summer Studentships to H.C. and J.R.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
Author notes
Address reprint requests to Anna Janowska-Wieczorek, MD, PhD, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta, 8249-114 St, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2R8; e-mail: annajanowska@bloodservices.ca.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal