Abstract
Evidence of factor XI (FXI) activation in vivo is scarce. In addition, it remains uncertain whether thrombin, factor XIIa (FXIIa), or perhaps another protease is responsible for FXI conversion. We investigated the activation of FXI in eight healthy volunteers after infusion of a low dose of endotoxin (4 ng/kg of body weight). Activation of prekallikrein FXII, FXI, and prothrombin was measured with sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), and FXI activation was measured with a novel enzyme capture assay that detects noncomplexed FXIa. Activation of FXI was apparent with a significant plasma peak level of noncomplexed FXIa of 10 to 11 pmol/L at 1 and 2 hours after endotoxin infusion, followed by a gradual increase in FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes, measured in the ELISAs, with a summit of 11 to 15 pmol/L at 6 and 24 hours, respectively. In accordance with previous studies, thrombin generation was detected 1 hour after endotoxin infusion to become maximal after 3 to 4 hours. In contrast, we did not find any evidence of contact activation, because markers of activation of prekallikrein and FXII remained undetectable. From the FXIa data a theoretical model was constructed which suggested that inhibition of FXIa does not take place in the plasma compartment, but is localized on a surface. These data provide the first evidence for FXI activation in low-grade endotoxemia and suggest that FXI is activated independently of FXII.
© 1998 by The American Society of Hematology.
IN 1991 IT WAS SHOWN that, besides factor XII (FXII), thrombin is capable of activating factor XI (FXI) in vitro.1,2 Thrombin-dependent activation of FXI constitutes an amplification pathway because activation of FXI leads, via activation of factors IX and X, to the formation of additional thrombin.3 This additional thrombin may be important for the activation of a carboxypeptidase B, called TAFI (thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor), resulting in the attenuation of fibrinolysis.4-6 FXII-independent activation of FXI would provide an explanation for the observed difference in clinical phenotype between FXII-deficient patients who do not have an increased bleeding risk, and FXI-deficient patients who do show a bleeding tendency.7,8 Although FXII-independent activation of FXI has been shown in plasma and in the presence of high molecular weight kininogen (HK)9,10, the physiological significance is questioned11 12 and there is no in vivo evidence for the existence of this activation pathway.
The administration of endotoxin, the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) part of the gram-negative bacterial cell membrane, to human volunteers under controlled experimental conditions elicits a procoagulant response. This model has been used to study the activation of the hemostatic system in great detail.13 In animal studies, is was clearly shown that initiation of the coagulation system in low-grade endotoxemia as well as lethal Escherichia coli sepsis proceeded via the tissue factor-factor VIIa (TF-FVIIa) complex, because inhibition of FVIIa or TF attenuated activation of the coagulation system.14-16 In contrast, no effect on coagulation was observed when FXII was inhibited in a lethal sepsis model.17 Therefore, although activation of the contact system occurs in induced endotoxemia in humans and animals18,19 as well as in patients with sepsis,20 21 it does not contribute to activation of the coagulation system.
We used the low-grade endotoxin model in humans to study the activation of FXI. FXI activation was assessed with sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for FXIa in complex with C1-inhibitor, α1-antitrypsin, α2-antiplasmin, or antithrombin.22Furthermore, we developed a sensitive enzyme capture assay (ECA) for measurement of noncomplexed FXIa. FXI activation was studied in relation to thrombin formation and contact activation, which was analyzed by novel ELISAs that measure complexes of FXIIa or kallikrein irreversibly bound to C1-inhibitor.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study group and design.
Eight volunteers (mean, 23 years; range, 19-32 years) were injected with endotoxin. The E coli LPS (endotoxin) preparation, lot EC-5 (D. Hochstein, Bureau of Biologics, Food and Drug Administration, Bethesda, MD) was administered as a 1-minute infusion in an antecubital vein at a dose of 4 ng/kg. All study subjects had a normal medical history, physical examination, and routine laboratory examination.
The study was approved by the Research and Ethical Committees of the Academical Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and written informed consent was obtained from all volunteers before the study entry.
Blood sampling.
Venous blood was collected by separate punctures from antecubital veins at t = 0 (before LPS infusion) and at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 24 hours after the LPS infusion in siliconized vacutainer tubes (sodium citrate, 0.105 mol/L or EDTA, 0.34 mol/L; Becton Dickinson, NJ). To the EDTA tubes a solution of 0.4 mL containing Polybrene (Janssen Chimica, Beerse, Belgium) to yield a final concentration of 0.05% wt/vol and 100 mmol/L benzamidine (Acros, NJ) was added to prevent any ex vivo activation of clotting factors and subsequent complex formation to inhibitors. Platelet-poor plasma was obtained by centrifuging the blood samples at 1.600g for 20 minutes at room temperature. Plasma samples were stored at −70°C until assayed.
Proteins.
Lyophilized purified human FXIa (Kordia Laboratory Supplies, Leiden, The Netherlands) was reconstituted with distilled water to the original volume. This FXIa preparation had been made by incubating FXI with FXIIa, after which FXIIa had been removed by absorption onto a corn trypsin inhibitor column. Complete activation of FXI was observed on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels. Human α-thrombin was a generous gift from Dr P.J. Lentink (Department of Coagulation, CLB, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). Activated human protein C was a kind gift from Dr J.C.M. Meijers (Department of Haematology, Academic Hospital Utrecht, The Netherlands).
FXIIa was made by incubating human FXII, purified via affinity chromatography, by a monoclonal antibody (MoAb) F3 with dextran sulfate (DXS; final concentration, 10 μg/mL) for 3 hours at 37°C.23 Plasmin and kallikrein were purified as described.24
FXI-deficient plasma was obtained from a female patient with a homozygous FXI deficiency (FXI: c < 1%; FXI: Ag < 1%). HK-, prekallikrein-, and FXII-deficient plasmas were obtained from George King Biomedical (Overland Park, KS).
Amidolytic assay.
The amidolytic activity of FXIa was measured as follows: A mixture of 95 μL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, containing the chromogenic substrate S-2366 (Chromogenix, Mölndal, Sweden) 1 mmol/L (final concentration) and 5 μL of FXIa at different final concentrations (range, 8-500 pmol/L), preincubated with or without benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration), were added to wells of microtiter plates (Dynatech, Plochingen, Germany). Microtiter plates were read on a Multiskan plate reader (Labsystems, Helsinki, Finland) after incubation for 72 hours at room temperature at 405 nm.
In vitro contact activation.
Varying concentrations of DXS (molecular weight, 500,000; Pharmacia Fine Chemicals, Uppsala, Sweden), 0.05 and 0.2 mg/mL, or kaolin (Brocacef BV, Maarsen, The Netherlands), 2.5 and 5 mg/mL, were incubated with an equal volume of EDTA plasma for 20 minutes at 37°C. The activation was stopped by adding 3 vol of PBS containing 0.1 mg/mL soybean trypsin inhibitor (SBTI; Sigma Chemical Co, St Louis, MO) and 0.05% (wt/vol) Polybrene. Kaolin was removed by centrifuging the reaction mixture for 5 minutes at 13,000g.
Assays for FXI activation.
FXI antigen was measured in an ELISA as described,25 using MoAb XI-5 as a capture antibody and biotinylated MoAb XI-3 for detection of FXI antigen.
FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes were assayed as described.22The total amount of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes was calculated as the sum of the measured complexes in the four ELISAs.
A novel assay was developed for measuring noncomplexed FXIa, which was based on a previously described enzyme capture assay for activated protein C.26 Wells of microtiter plates (Dynatech) were incubated with MoAb XI-5 at 3 μg/mL in carbonate buffer, 0.1 mol/L, pH 9.5 (100 μL/well), overnight at 4°C. The plates were washed 5 times with wash buffer (PBS containing Tween 0.02% [wt/vol]; J.T. Baker Chemical, Philipsburg, NJ). Residual binding sites for proteins were blocked by incubating the wells for 30 minutes with 150 μL/well 2% (vol/vol) bovine milk in PBS. After washing 5 times with wash buffer, the wells were incubated for 1 hour with the test samples or standards diluted in dilution buffer, ie, PBS containing Tween 0.1% (wt/vol), gelatine 0.2% (wt/vol), normal mouse serum 1% (vol/vol) (CLB, Amsterdam, the Netherlands), Polybrene 0.05% (wt/vol), 1 mol/L NaCl, 2 μg/mL aprotinine (Boehringer Mannheim GmBH, Mannheim, Germany), and benzamidine 100 mmol/L (all final concentrations). Plates were then washed 9 times with wash buffer, incubated for a period of 10 minutes, and washed again for another 9 times (total, 18) to ensure complete removal of benzamidine as well as contaminating plasma enzymes, nonspecifically bound to the plate. After the last washing cycle the chromogenic substrate S-2366, 1 mmol/L in PBS, was added to the wells (100 μL/well). Plates were sealed and kept at room temperature. Hydrolysis of the substrate was monitored at 405 nm on a Multiskan plate reader after 72 hours of incubation time. Dilutions of purified FXIa were used as standard. Measured absorbance values of the samples were compared with those of the standards, and expressed as pmol/L. Molar concentrations of free FXIa activity were calculated based on a molecular weight of FXIa of 80 kD, thus calculating the active sites of FXIa.
The specificity of the assay was assessed by incubating FXI-deficient plasma, containing Polybrene (0.05%, final concentration) and benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration), with thrombin, plasmin, kallikrein, FXIIa, or activated protein C—all plasma proteases known to react with S-2366. The total amount of added protease corresponded to 10% activation of the zymogen concentration present in normal blood.
ELISAs for FXII and PK antigen.
Microtiter plates (Maxisorp, Nunc, Roshilde, Denmark) were coated overnight at room temperature with 100 μL of 2 μg/mL anti-human FXII MoAb B7C9 (kindly provided by Dr R.W. Colman, Philadelphia, PA) or anti-human PK MoAb K1520 in 0.1 mmol/L carbonate buffer, pH 9.6, and blocked for 30 minutes with 150 μL PBS, pH 7.4, containing 2% (vol/vol) bovine milk. All subsequent incubations were in 100-μL volumes at room temperature for 1 hour and plates were washed after each incubation with PBS containing Tween 0.02% (wt/vol). The plates were then incubated with plasma samples diluted in PBS-milk 2% (vol/vol) and bound FXII or PK were detected by biotinylated MoAbs F323 or 13G11 (also kindly provided by Dr R.W. Colman), diluted in PBS-milk 2% (vol/vol), respectively. FXII and PK were detected by streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (Amersham International plc, Amersham, UK) in High Performance ELISA buffer (CLB). The plates were developed with a solution of 100 μg/mL of 3,5,3′,5′-tetramethylbenzidin (TMB; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) with 0.003% (vol/vol) H2O2 in 0.11 mol/L sodium acetate, pH 5.5, for 30 minutes. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 2 mol/L H2SO4 to the wells and absorbance was read at 450 nm on a Multiskan plate reader.
Serial dilutions of normal pooled plasma from 30 volunteers was used as a 100% standard. The interassay coefficient of variation of these ELISAs was less than 10%. FXII or PK deficient plasma yielded no response in the corresponding assay.
ELISAs for FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes.
Microtiter plates (Maxisorp) were coated overnight at room temperature with 100 μL of 10 μg/mL MoAb KOK-12, which binds complexed and inactivated C1-inhibitor,20 in carbonate buffer, pH 9.6. Plates were blocked for 30 minutes with 150 μL PBS, pH 7.4, containing 2% (vol/vol) bovine milk. All subsequent incubations were in 100-μL volumes at room temperature for 1 hour and plates were washed after each incubation with PBS containing Tween 0.02% (wt/vol). The plates were then incubated with plasma samples diluted in PBS-milk 2% (vol/vol). FXIIa-C1-inhibitor complexes were detected by incubation of the plates with biotinylated MoAb F3, and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes were detected by incubation with biotinylated MoAb K15, each diluted in PBS containing milk 3% (vol/vol) and normal mouse serum 1%. Next, the plates were incubated for 30 minutes with a 1:10,000 dilution of polymerized horseradish peroxidase bound to streptavidin (poly-HRP; CLB) in PBS-milk 2% (vol/vol). The plates were developed and read as described above. As a standard, we used pooled EDTA plasma from normal volunteers, which was activated by incubation with 0.1 mg/mL (final concentration) DXS as described above. The plasma was stored in small quantities at −70°C.
The amount of complexes in DXS-activated plasma was quantitated by comparison with purified FXIIa- or kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes. FXIIa- or kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes were prepared by incubating 10 μmol/L C1-inhibitor (Behringwerke AG, Marburg, Germany) overnight at 37°C with 1.4 μmol/L FXIIa or 2.3 μmol/L kallikrein, respectively. None of the complex mixtures showed amidolytic activity against the chromogenic substrate S-2302 (Chromogenix). For the quantification of the complexes it was therefore assumed that in these mixtures FXIIa or kallikrein was completely bound to C1-inhibitor and that the amount of the complexes in the mixtures was equal to the initial molar concentration of FXIIa or kallikrein.
The specificity of the assays was assessed by incubating purified FXIIa-C1-inhibitor and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes in FXII-and PK-deficient plasma, respectively, and by DXS activation of FXII- and PK-deficient plasma for 20 minutes at 37°C.
Thrombin formation.
Prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 (F1 + 2) and thrombin-antithrombin (TAT) complexes were assayed using commercially available kits according to the manufacturers’ instructions (Enzygnost F1 + 2 and Enzygnost TAT, respectively; Behringwerke).
Data analysis.
Several theoretical models were constructed to simulate the in vivo generation and inhibition of FXIa. The calculated time course of the plasma concentrations of FXIa and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes was determined by stepwise calculation with 15-second time intervals using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation). First-order kinetics were assumed for association, dissociation, and elimination of the different substances.
Statistical analysis.
Results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Changes of variables over time were analyzed using Friedman’s nonparametric repeated measured test and Dunn’s test. FXI, FXII, and PK antigen levels were analyzed by ANOVA and Newman-Keuls test. A two-sided P value (P value over time) < .05 was considered to reflect a significant difference.
RESULTS
ECA for activated FXI.
To protect FXIa from irreversible ex vivo inactivation by plasma protease inhibitors in the plasma sample to be tested, addition of a sufficient amount of a reversible inhibitor in the dilution buffer as well as in the plasma samples was necessary. In the presence of benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration) only 3.4% ± 0.8% (n = 5) of added FXIa was complexed to its inhibitors within 1 hour, whereas in the presence of 50 mmol/L benzamidine the corresponding value was 9% ± 2.2% (n = 5) (results not shown). We therefore added 100 mmol/L benzamidine to all samples.
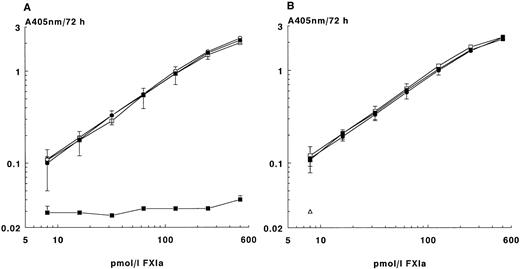
The amidolytic activity of FXIa in the ECA was similar to that of FXIa directly incubated with the chromogenic substrate S-2366, indicating almost complete binding of FXIa to the MoAb-coated plates used in the ECA (Fig 1A). As expected, no activity was found in the amidolytic assay in the presence of benzamidine. However, in the ECA, preincubation of FXIa with buffer containing benzamidine (100 mmol/L) yielded the same response as FXIa in buffer without benzamidine. This indicates the efficiency of the extensive washing cycle to remove benzamidine from the active sites of FXIa, allowing conversion of the added chromogenic substrate by FXIa in the final incubation step of the ECA.
Enzyme capture assay for FXIa. (A) Effect of benzamidine on the activity of purified FXIa in the amidolytic assay and in the ECA. Microtiter plates coated with MoAb XI-5 were incubated with various concentrations of FXIa in the presence or absence of benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration). The plates were washed extensively and incubated for 72 hours with S-2366. Results obtained were expressed as the change in absorbance at 405 nm and compared with those obtained with an amidolytic assay in which FXIa was incubated in the presence or absence of benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration) with S-2366. The means of four experiments ± SD are given. FXIa in the ECA incubated in the absence (○) or in the presence (•) of benzamidine. FXIa directly tested in the amidolytic assay in the absence (□) or in the presence (▪) of benzamidine. (B) Recovery in the ECA of purified FXIa added to plasma. Dilutions of purified FXIa were added to FXI-deficient plasma or EDTA plasma containing 100 mmol/L benzamidine. Samples were tested in the ECA as described in Materials and Methods. The means of four experiments ± SD are given. FXIa in dilution buffer (○), in FXI-deficient plasma (•), or in EDTA plasma (□). Control EDTA plasma without FXIa (▵).
Enzyme capture assay for FXIa. (A) Effect of benzamidine on the activity of purified FXIa in the amidolytic assay and in the ECA. Microtiter plates coated with MoAb XI-5 were incubated with various concentrations of FXIa in the presence or absence of benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration). The plates were washed extensively and incubated for 72 hours with S-2366. Results obtained were expressed as the change in absorbance at 405 nm and compared with those obtained with an amidolytic assay in which FXIa was incubated in the presence or absence of benzamidine (100 mmol/L, final concentration) with S-2366. The means of four experiments ± SD are given. FXIa in the ECA incubated in the absence (○) or in the presence (•) of benzamidine. FXIa directly tested in the amidolytic assay in the absence (□) or in the presence (▪) of benzamidine. (B) Recovery in the ECA of purified FXIa added to plasma. Dilutions of purified FXIa were added to FXI-deficient plasma or EDTA plasma containing 100 mmol/L benzamidine. Samples were tested in the ECA as described in Materials and Methods. The means of four experiments ± SD are given. FXIa in dilution buffer (○), in FXI-deficient plasma (•), or in EDTA plasma (□). Control EDTA plasma without FXIa (▵).
Besides benzamidine, NaCl (1 mmol/L) and aprotinine (2 μg/mL) were also added to the dilution buffer to minimize any nonspecific conversion of the chromogenic substrate S-2366 by proteases other than FXIa aspecifically sticking to the solid phase. Using these conditions, parallel curves were obtained when FXIa was diluted in the dilution buffer or in FXI-deficient EDTA plasma or normal EDTA plasma (1:10 diluted), both containing benzamidine (Fig 1B).
Hydrolysis of the chromogenic substrate was linear over time with different concentrations of FXIa, also showing the stability of FXIa during the 3 days of incubation.
Because other plasma proteases can also convert the chromogenic substrate S-2366,27 28 the specificity of the ECA was assessed by reconstituting FXI-deficient plasma with thrombin, plasmin, kallikrein, FXIIa, or activated protein C. The plasma samples, diluted 1:10, yielded a similar response in the ECA as FXI-deficient plasma or dilution buffer (results not shown).
MoAb XI-5 coated on the microtiter plates binds native as well as activated FXIa. Therefore, we investigated whether FXI competed with FXIa for binding to the limited amount of MoAb XI-5 bound to the microtiter plate. FXI-deficient plasma was reconstituted with 5 μg/mL FXI and diluted in the dilution buffer. Recovery of 100 pmol/L FXIa, added to the diluted, reconstituted plasma, was 106.6% ± 4.8% (n = 4) when tested in the ECA at a plasma dilution of 1:10, and was 63.8% ± 9.5% when diluted 1:5 (results not shown). Thus, at plasma sample dilutions of 1:10 or more, native FXI did not interfere with the measurement of FXIa.
The interassay coefficient of variation, calculated from the results of 30 samples measured on six different occasions in a 3-month period, was 6.1% ± 1.6%.
ELISAs for FXIIa and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes.
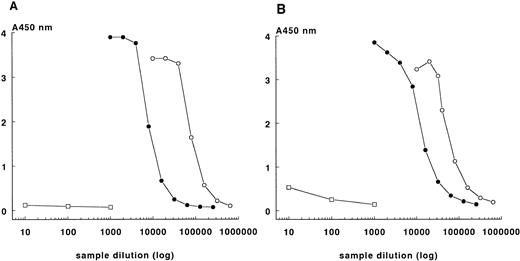
MoAb KOK-12, directed against complexed C1-inhibitor, was used to quantify FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes. In initial experiments the optimal conditions for the ELISAs to detect the FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes were established (see Materials and Methods). Parallel dose-response curves were obtained from the prepared FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes of known concentrations and those obtained with DXS-activated plasma, whereas background absorbance values were observed with dilutions of fresh plasma (Fig 2).
ELISAs for FXIIa-C1-inhibitor (A) and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor (B) complexes. Absorbance values of dilutions of preformed complexes of FXIIa-C1-inhibitor (A) or kallikreinC1-inhibitor (B) in PBS (○), and absorbance values of DXS-activated reference plasma (•) and of fresh plasma (□) are shown.
ELISAs for FXIIa-C1-inhibitor (A) and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor (B) complexes. Absorbance values of dilutions of preformed complexes of FXIIa-C1-inhibitor (A) or kallikreinC1-inhibitor (B) in PBS (○), and absorbance values of DXS-activated reference plasma (•) and of fresh plasma (□) are shown.
The specificity of the assays was assessed by incubating the preformed complexes in FXII- and PK-deficient plasmas and dilutions of these mixtures were tested in both the FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complex assays. Only in the corresponding ELISA was a significant signal detected. Activation of plasma deficient in FXII or PK with DXS yielded only a response in the FXIIa-C1-inhibitor ELISA for PK-deficient plasma, probably due to auto-activation of FXII (results not shown).29
Because the capture antibody KOK-12 not only binds complexed C1-inhibitor but also inactivated C1-inhibitor, which is present in normal plasma,30 we established the minimal dilution of the plasma samples to be tested at which no competition of inactivated C1-inhibitor was observed. Dilutions of normal plasma were added to the preformed complexes and tested in the respective ELISAs. At a plasma dilution of 1:20 no effect on the recovery of the preformed complexes was observed (results not shown). Therefore, plasma samples were diluted at least 1:20 in the ELISAs.
The lower detection limits of the ELISAs, set as the values that correspond to twice the absorbance of the background, were 80 pmol/L for each ELISA.
The interassay coefficient of variation, calculated from the results of four standard samples in a 2-month period, were 3.4% and 16.1% for the FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes, respectively.
In vitro contact activation.
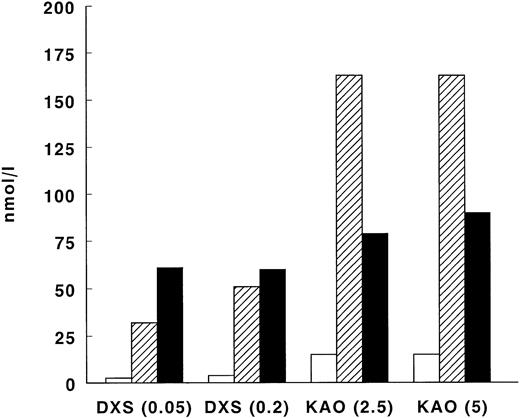
Because the detection limits of the assays for FXI activation were eightfold lower than those of the FXII- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complex ELISAs, we performed a series of experiments using DXS and kaolin as activators of the contact system to investigate the ratio between FXIIa- or kallikrein-C1-inhibitor and FXIa-C1-inhibitor complexes. Activation of EDTA plasma with 0.05 or 0.2 mg/mL DXS generated 2.6 and 3.9 nmol/L FXIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, 32 and 51 nmol/L FXIIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, and 61 and 60 nmol/L kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes, respectively. Kaolin activation, either 2.5 or 5 mg/mL, resulted at both concentrations in formation of 15 nmol/L FXIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, 163 nmol/L FXIIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, and 79 and 90 nmol/L kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes, respectively (Fig 3).
Generation of FXIa-, FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes on in vitro contact activation in plasma. EDTA plasma was activated with DXS (0.05 or 0.2 mg/mL, final concentration) or with kaolin (2.5 or 5 mg/mL), respectively. FXIa-, FXIIa-, and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes were measured using specific ELISAs (see Materials and Methods). White bars (□) represent FXIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, shaded bars (▨) represent FXIIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, and black bars (▪) represent kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes.
Generation of FXIa-, FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes on in vitro contact activation in plasma. EDTA plasma was activated with DXS (0.05 or 0.2 mg/mL, final concentration) or with kaolin (2.5 or 5 mg/mL), respectively. FXIa-, FXIIa-, and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes were measured using specific ELISAs (see Materials and Methods). White bars (□) represent FXIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, shaded bars (▨) represent FXIIa-C1-inhibitor complexes, and black bars (▪) represent kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes.
LPS infusion in volunteers.
In all eight volunteers, flu-like symptoms such as headache, chills, nausea, vomiting, myalgia, and fever were observed after LPS administration. After 24 hours all volunteers were symptom free.
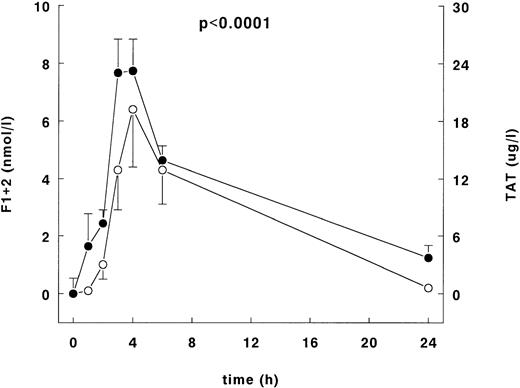
Infusion of LPS induced increases of the plasma levels of the prothrombin fragment F1 + 2 and TAT complex plasma concentrations with peak levels at 4 hours of 7.1 ± 2 nmol/L and 26.8 ± 3.3 μg/L, respectively (Fig 4). Both increases were significant over time (P < .0001). Thrombin generation was first evident after 1 hour by significant increase of TAT complexes of 8.5 ± 3.4 μg/L. Thrombin production was still detectable at 24 hours, 0.16 nmol/L and 3.6 μg/L for F1 + 2 and TAT complexes, respectively.
F1 + 2 and TAT complexes after LPS infusion. Mean ± SEM of F1+2 (○) and TAT complexes (•) after LPS administration (4 ng/kg). The left y-axis indicates the absolute difference from the mean value at t = 0 for F1 + 2, and the right y-axis indicates the absolute difference from the mean value at t = 0 of the TAT complexes. The P value indicates difference over time of both F1 + 2 and TAT complexes.
F1 + 2 and TAT complexes after LPS infusion. Mean ± SEM of F1+2 (○) and TAT complexes (•) after LPS administration (4 ng/kg). The left y-axis indicates the absolute difference from the mean value at t = 0 for F1 + 2, and the right y-axis indicates the absolute difference from the mean value at t = 0 of the TAT complexes. The P value indicates difference over time of both F1 + 2 and TAT complexes.
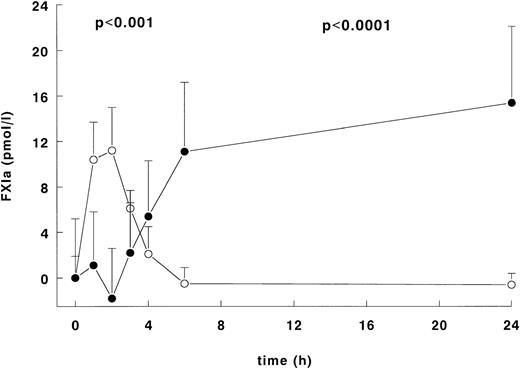
FXI activation was assessed using the ECA, which measures noncomplexed FXIa, and the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor ELISAs, which detect FXIa complexed to its inhibitors in plasma. As shown in Fig 5, the administration of LPS induced a significant increase in FXIa activity as measured in the ECA with a peak concentration at 2 hours of 11.2 ± 3.8 pmol/L, followed by a subsequent decline to baseline values at 6 and 24 hours. After a delay the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complex concentration also increased at 3 hours after LPS infusion and reached maximal levels at 6 and 24 hours of 11.1 ± 6.1 pmol/L and 15.4 ± 6.7 pmol/L, respectively (Pvalue over time, P < .001 for the ECA and P < .0001 for the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes).
Activation of FXI after LPS infusion. Mean ± SEM of FXIa levels measured in the ECA (○) and the total amount of the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes (•) after LPS administration (4 ng/kg). The y-axis presents the absolute difference from the mean value at t = 0 of both the ECA and the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes. TheP value indicates difference over time (P < .001 for the ECA, P < .0001 for the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes).
Activation of FXI after LPS infusion. Mean ± SEM of FXIa levels measured in the ECA (○) and the total amount of the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes (•) after LPS administration (4 ng/kg). The y-axis presents the absolute difference from the mean value at t = 0 of both the ECA and the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes. TheP value indicates difference over time (P < .001 for the ECA, P < .0001 for the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes).
As shown in Table 1, the activation of FXI was accompanied by a small but significant decline in FXI antigen levels after 2 hours as measured by ELISA; the levels returned to baseline values at 24 hours.
FXI, FXII, and PK Antigen Levels After LPS Infusion to Volunteers
| . | t = 0 . | t = 1 . | t = 2 . | t = 3 . | t = 4 . | t = 6 . | t = 24 . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXI:Ag | 100 | 106 ± 4.2 | 98 ± 4.2 | 92 ± 4.1 | 91 ± 3.7 | 90 ± 3.3 | 101 ± 5.6 | .003 |
| FXII:Ag | 100 | 100 ± 4.4 | 99 ± 4.3 | 108 ± 6.8 | 100 ± 5.2 | 100 ± 5.2 | 110 ± 9 | .3 |
| PK:Ag | 100 | 104 ± 4.8 | 101 ± 2.7 | 108 ± 7.6 | 102 ± 6.1 | 103 ± 4.1 | 97 ± 7.2 | .6 |
| . | t = 0 . | t = 1 . | t = 2 . | t = 3 . | t = 4 . | t = 6 . | t = 24 . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXI:Ag | 100 | 106 ± 4.2 | 98 ± 4.2 | 92 ± 4.1 | 91 ± 3.7 | 90 ± 3.3 | 101 ± 5.6 | .003 |
| FXII:Ag | 100 | 100 ± 4.4 | 99 ± 4.3 | 108 ± 6.8 | 100 ± 5.2 | 100 ± 5.2 | 110 ± 9 | .3 |
| PK:Ag | 100 | 104 ± 4.8 | 101 ± 2.7 | 108 ± 7.6 | 102 ± 6.1 | 103 ± 4.1 | 97 ± 7.2 | .6 |
Antigen levels of FXI, FXII, and PK were measured using ELISAs (see Materials and Methods). Baseline values before LPS infusion (4 ng/kg) from eight volunteers (t = 0) were set at 100%, and changes over time, expressed as mean ± SEM, were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance.
No changes over time were measured in the ELISAs for PK antigen and FXII antigen (Table 1) and also no increases of FXIIa- or kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes were detected (results not shown).
Data analysis.
The relationship between the observed time course of FXIa generation, measured by ECA, versus FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complex formation was studied by computer simulations.
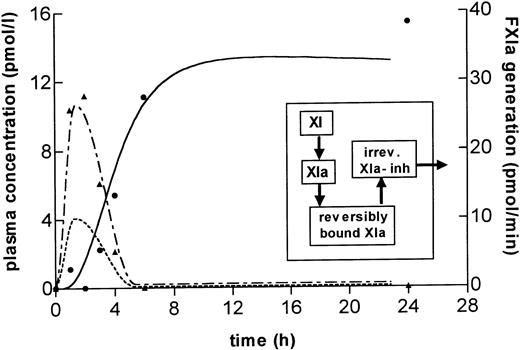
First, a theoretical model was constructed in which all processes related to FXIa generation and inhibition take place in the fluid phase of the plasma compartment. The parameter values chosen were based on observations in previous experiments, ie, a half-life for FXIa inhibition in the order of minutes31,32 and a plasma half-life of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes between 100 and 350 minutes.32 However, in this model there was virtually no time delay between the start of FXIa generation and the raise in FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes. Furthermore, the modeled FXIa plasma concentrations as measured in the ECA remained a factor 10 to 100 times lower than the concentrations of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes. Thus, this model could not provide a satisfactory fit to the experimental data assuming realistic parameter values. It was therefore concluded that inhibition of FXIa generated after in vivo LPS infusion differs from inhibition of FXIa infused intravenously. Other models were constructed to fit the observed time course of noncomplexed FXIa and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes. A satisfactory fit was obtained with the scheme shown in the inset of Fig 6, where it is assumed that FXIa is rapidly removed from the plasma compartment by reversibly binding to a surface or inhibitor (t½ = 1.5 minutes) and that the FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complex are formed or are liberated into the plasma compartment very slowly (t½ = 72 h) and cleared at a normal rate (t½ = 100 minutes). FXIa generation in this constructed model is maximal at 2 hours with 10 pmol/minute, but continues at a low rate until 23 hours, undetected by the ECA (Fig6). When assuming a plasma volume of 3 L, the total amount of generated FXIa is ± 670 pmol/L, which corresponds to 2% to 3% of the plasma concentration of FXI.
Computer simulation for FXIa activation and inhibition in LPS volunteers. A mathematical model was constructed to explain the course of FXIa concentrations as measured in the ECA and ELISAs. The inset shows a scheme of the assumed transfer of substances, in which the formation of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes occurs outside the fluid phase plasma compartment. The graph shows the calculated time course for the concentrations of noncomplexed FXIa (— - —) and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes (—) in the plasma compartment assuming inhibition of FXIa outside the plasma compartment, a slow dissociation of bound FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes into the plasma compartment, and a plasma half-life of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes of 100 minutes. The left y-axis represents the absolute increase in FXIa and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes in pmol/L, the right y-axis represents the formation of endogenous FXIa (----) in pmol/minute. The measured FXIa in the ECA (▴) and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes (•) are given for comparison.
Computer simulation for FXIa activation and inhibition in LPS volunteers. A mathematical model was constructed to explain the course of FXIa concentrations as measured in the ECA and ELISAs. The inset shows a scheme of the assumed transfer of substances, in which the formation of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes occurs outside the fluid phase plasma compartment. The graph shows the calculated time course for the concentrations of noncomplexed FXIa (— - —) and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes (—) in the plasma compartment assuming inhibition of FXIa outside the plasma compartment, a slow dissociation of bound FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes into the plasma compartment, and a plasma half-life of FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes of 100 minutes. The left y-axis represents the absolute increase in FXIa and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes in pmol/L, the right y-axis represents the formation of endogenous FXIa (----) in pmol/minute. The measured FXIa in the ECA (▴) and FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes (•) are given for comparison.
DISCUSSION
According to current views, FXI can be activated by thrombin and is primarily involved in sustaining thrombin formation.2,33,34However, there is no evidence for such a mechanism occurring in vivo. In this study we have used the well-characterized model of endotoxin-induced coagulation activation in humans to investigate FXI activation. For this purpose we developed a set of novel and sensitive immunoassays, including an ECA for measuring free, noncomplexed FXIa. This assay was developed because in a previous study it was shown that intravenously infused human FXIa in chimpanzees has a half-life time of inhibition of several minutes,32 indicating that also free, noncomplexed FXIa could be detectable in the circulation. For the ECA it was necessary to prevent any complexation of FXIa to its inhibitors ex vivo, which was achieved by collecting blood samples at high concentrations of the reversible inhibitor benzamidine.26With this assay we detected an absolute rise in plasma FXIa of 10 to 11 pmol/L at 1 and 2 hours, respectively, indicating that FXI was activated early after infusion of LPS (Fig 5). Thereafter, FXIa was inhibited, reflected by a significant increment in FXIa-FXIa inhibitor complexes after 2 hours, which was still detectable at 24 hours. Consistent with activation of FXI was the decrease in antigen levels after 2 hours, which remained low at least until 6 hours after the endotoxin infusion, indicative for continuous activation of FXI (Table1).
These data together with results from previous studies in chimpanzees and in vitro data were used to construct a model for FXI activation and inhibition (Fig 6). This model predicts that inhibition of endogenously formed FXIa does not take place in the plasma compartment, ie, is not a fluid phase inhibition. The late rise in FXIa-FXIa inhibitor concentrations as compared with the early detection of noncomplexed FXIa can be explained by assuming that the inhibition of FXIa occurs locally and that the FXI-FXIa inhibitor complexes are released very slowly from their site of formation into the plasma compartment. This site for FXIa inhibition is not necessarily the same as the site for activation because some free, noncomplexed FXIa was also measured in the plasma compartment. Possible locations for FXIa inhibition could be activated platelets or endothelial cells that are both capable of reversible binding of FXIa in vitro.35,36 Another possibility is that FXIa is complexed to inhibitors linked to the endothelial surface such as C1-inhibitor37 and antithrombin via glycoaminoglycans.38 Also, reversible inhibition of FXIa by protease nexin-2, an Kunitz-type inhibitor released by the α-granules of activated platelets,39 40 could explain the observed results. However, the exact inhibitory mechanism of FXIa in vivo is beyond the scope of this study and requires further investigation.
The revised model of coagulation assumes that activation of FXI is mediated by thrombin, generated via the TF-FVIIa pathway.2Thrombin generation was already detected at 1 hour after the endotoxin infusion and the levels of both TAT complexes and F1 + 2 reached peak levels at 3 and 4 hours (Fig 5). We speculate that the initial formation of small amounts of thrombin directly activated FXI, whereafter activation of factors IX and X contributed to the generation of the larger amounts of thrombin measured at 3 and 4 hours, which maintained a prolonged generation of FXIa.
Previous studies from our group and others have suggested that endotoxin-induced activation was solely dependent on the TF-FVIIa complex.14-16 To further establish this mechanism, we developed novel ELISAs for monitoring contact activation, together with measurements of FXII and PK antigen concentrations. The ELISAs for the detection of FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor were modified from previously published radioimmunoassays29 and detected as low as 80 pmol/L activation of FXII or PK. Assuming a plasma concentration of FXII and PK of 0.4 μmol/L and 0.47 μmol/L, respectively (as measured in pooled standard plasma from 30 normal volunteers), this corresponds to activation of 0.02% of total FXII or PK, which is 50- to 100-fold more sensitive compared with previously described assays.41 42
In this study we did not detect activation of the contact system, neither by an increase in FXIIa- or kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes nor by decreasing antigen levels of FXII or PK. Assuming similar ratios of FXIIa-, kallikrein-, and FXIa-C1-inhibitor complexes to be generated in vivo as observed in the in vitro experiments (Fig3), and in view of the amount of FXIa generated after LPS infusion, FXIIa- and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes should have been detected to explain FXI activation through the contact system. This finding corroborates an earlier study in which a lower dose of endotoxin also did not elicit detectable contact activation.43 However, it should be noted that activation of the contact system is notoriously difficult to measure in vivo, and only in some occasional patients with severe septic shock was clear evidence for activation found.20,21,25,44 Using a specific assay for kallikrein-α2-macroglobulin complexes, enhanced levels of this contact marker have been detected in a lethal animal model of sepsis,17,18 but also in a similar human endotoxemia model.19 An explanation for this discrepancy with our study may be a longer half-life of kallikrein-α2-macroglobulin complexes as compared with kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes.45 Thus, activation of the contact route cannot be excluded with certainty under these experimental conditions.
We conclude that activation of FXI occurs early after endotoxin infusion to humans. Given the established role of the TF-FVIIa complex in coagulation activation in the human endotoxemia model, and considering the lack of conclusive evidence for contact activation, our results are consistent with the notion that FXI is activated via a thrombin-dependent pathway in vivo.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank the members of the Laboratory of Special Hemostasis (AMC, G1) and Y.P.T. Lubbers from the Laboratory of Clinical and Experimental Immunology (CLB, U110) for their technical assistance.
M.L. is a fellow of the Royal Dutch Academy of Arts and Science.
Supported by Grant No. 94.024 from the Netherlands Heart Foundation (M.C.M.), and by Grant No. 32-47016.96 from the Swiss National Foundation for Scientific Research (W.A.W.).
Presented in part at the American Heart Association Meeting, held in New Orleans, LA, November 7-11, 1996.
Address reprint request to M.C. Minnema, MD, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Center for Hemostasis, Thrombosis, Atherosclerosis and Inflammation Research, F4-277, PO Box 22660, 1100 DD, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" is accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal