Key Points
Global DNA methylation analysis reveals significant DMRs comparing WM with IgM-MGUS and IgM gammopathies with controls across genomic regions.
Epigenetic influence on cellular pathways, including cell signaling and inflammatory response pathways, was observed.
Visual Abstract
Currently, the role of DNA methylation in the immunoglobulin M (IgM) monoclonal gammopathy disease spectrum remains poorly understood. In the present study, a multiomics prospective analysis was conducted integrating DNA methylation, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and whole-exome sequencing data in 34 subjects (23 with Waldenström macroglobulinemia [WM], 6 with IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance [MGUS], and 5 normal controls). Analysis was focused on defining differences between IgM gammopathies (WM/IgM-MGUS) compared with controls, and specifically between WM and IgM-MGUS. Between groups, genome-wide DNA methylation analysis demonstrated a significant number of differentially methylated regions that were annotated according to genomic region. Next, integration of RNA-seq data was performed to identify potentially epigenetically deregulated pathways. We found that pathways involved in cell cycle, metabolism, cytokine/immune signaling, cytoskeleton, tumor microenvironment, and intracellular signaling were differentially activated and potentially epigenetically regulated. Importantly, there was a positive enrichment of the CXCR4 signaling pathway along with several interleukin (interleukin 6 [IL-6], IL-8, and IL-15) signaling pathways in WM compared with IgM-MGUS. Further assessment of known tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes uncovered differential promoter methylation of several targets with concordant change in gene expression, including CCND1 and CD79B. Overall, this report defines how aberrant DNA methylation in IgM gammopathies may play a critical role in the epigenetic control of oncogenesis and key cellular functions.
Introduction
Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a non-Hodgkin lymphoma often preceded by an immunoglobulin M (IgM) monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS).1 The factors underlying the malignant progression from IgM-MGUS to WM remain to be fully elucidated; however, the stepwise accumulation of genomic abnormalities has been hypothesized as a potential driver. Most recent investigations in the IgM-MGUS disease spectrum have focused on mutational status and the coding genome, whereas the role of noncoding mutations and epigenetic regulators, specifically DNA methylation, remains underexplored. DNA methylation is necessary for cell differentiation and is important in normal cells; however, aberrant DNA methylation is a hallmark of oncogenesis and has been shown to play a critical role in the progression of malignancies.2,3 This study aimed to assess differential DNA methylation between WM and IgM-MGUS and compared with normal controls. Using a multiomics approach of enhanced reduced representation bisulfite sequencing integrated with RNA sequencing and whole-exome sequencing (WES) data, we aimed to identify the role of differential methylation on transcription and clarify the epigenetic regulation of oncogenes/tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) and potential methylation-regulated cellular pathways.
Study design
The study included samples from 34 subjects (23 with WM, 6 with IgM-MGUS, and 5 normal controls) (Table 1). WM was defined as ≥10% bone marrow (BM) involvement by lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma and a serum IgM monoclonal protein of any size. IgM-MGUS was defined as <10% BM involvement by lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, serum IgM monoclonal protein <3 g/dL, with no signs/symptoms of active WM. Bone marrow samples were prospectively collected, and selection for CD19+ and/or CD138+ B cells was performed. Subsequently, genome-wide DNA methylation analysis with enhanced reduced representation bisulfite sequencing was performed on selected B cells. CpG methylation ratios were segmented into 200-bp regions, and differentially methylated regions (DMRs) comparing groups of interest were determined. DMRs with a false discovery rate <0.05 and absolute methylation difference of ≥10% were considered significant and used for analysis. DMRs were annotated according to genomic regions of interest (promoters, 3’ untranslated region [UTR], 5’UTR, introns, exons, CpG islands, and CpG shores). Next, to identify methylation influence on transcription, total RNA extraction was performed on selected B cells, and differential gene expression was determined using a log2(fold change) >0.5 or <−0.5 and false discovery rate <0.05. Differentially expressed mRNAs with biologically corresponding promoter DMR (ie, hypomethylated promoter and upregulated mRNA, and vice versa) were identified as being potentially epigenetically regulated. Next, these identified genes were annotated for pathway analysis using Ingenuity pathway analysis. Pathways with a corrected P < .05 were considered statistically significant, and a z value was calculated based on the degree of differential activation. From our previously published work, DNA mutational analysis using WES data was available in 23 patients (19 with WM, 4 with IgM-MGUS) to assess the mutational status of targets of interest.4
Patient characteristics of IgM gammopathy samples
| Parameter . | IgM gammopathies (n = 29) . | WM (n = 23) . | IgM-MGUS (n = 6) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, y | 61 (46-80) | 61 (47-80) | 65 (52-78) | .51 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 16 (55) | 13 (57) | 3 (50) | .78 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.7 (8.1-16.2) | 11.6 (8.1-15.8) | 12.6 (11.1-16.2) | .17 |
| Platelets, ×109/L | 235 (77-512) | 222 (77-512) | 262 (207-338) | .28 |
| β2-Microglobulin, μg/mL | 3.1 (1.4-16.7) | 3.1 (1.6-16.7) | 2.8 (1.4-3.2) | .52 |
| IgM, mg/dL | 1770 (173-10 000) | 3340 (173-10 000) | 575 (283-1770) | .01 |
| BM involvement, % | 35 (0-95) | 50 (10-95) | 3.5 (0-10) | <.001 |
| Abnormal FLC ratio, n (%) | 7 (24) | 5 (28) | 2 (50) | .39 |
| MYD88 mutated, n (%) | 19 (83) | 16 (84) | 3 (75) | .66 |
| CXCR4 mutated, n (%) | 6 (26) | 6 (32) | 0 | .19 |
| Dx to LFU, mo | 92 (3-201) | 92 (3-194) | 87 (26-201) | .94 |
| Parameter . | IgM gammopathies (n = 29) . | WM (n = 23) . | IgM-MGUS (n = 6) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, y | 61 (46-80) | 61 (47-80) | 65 (52-78) | .51 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 16 (55) | 13 (57) | 3 (50) | .78 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.7 (8.1-16.2) | 11.6 (8.1-15.8) | 12.6 (11.1-16.2) | .17 |
| Platelets, ×109/L | 235 (77-512) | 222 (77-512) | 262 (207-338) | .28 |
| β2-Microglobulin, μg/mL | 3.1 (1.4-16.7) | 3.1 (1.6-16.7) | 2.8 (1.4-3.2) | .52 |
| IgM, mg/dL | 1770 (173-10 000) | 3340 (173-10 000) | 575 (283-1770) | .01 |
| BM involvement, % | 35 (0-95) | 50 (10-95) | 3.5 (0-10) | <.001 |
| Abnormal FLC ratio, n (%) | 7 (24) | 5 (28) | 2 (50) | .39 |
| MYD88 mutated, n (%) | 19 (83) | 16 (84) | 3 (75) | .66 |
| CXCR4 mutated, n (%) | 6 (26) | 6 (32) | 0 | .19 |
| Dx to LFU, mo | 92 (3-201) | 92 (3-194) | 87 (26-201) | .94 |
All characteristics at the time of sample collection. IgM-gammopathies group contained all WM and IgM-MGUS samples. FLC data were available in 22 patients (18 WM, 4 IgM-MGUS). MYD88 and CXCR4 mutational data were available in 23 patients (19 WM, 4 IgM-MGUS). Unless specified, values represent median (range). Values in bold reach the signficance threshold of P < 0.05.
B2, β-2; BM, bone marrow; Dx, diagnosis; FLC, free light chain; IgM, immunoglobulin M; LFU, last follow-up.
Institutional review board approval was obtained through the Mayo Clinic Institutional Review Board Committee before any data collection, and informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study.
Results and discussion
In first assessing genome-wide DNA methylation, a significant number of DMRs were observed when comparing IgM gammopathies (WM/IgM-MGUS) with normal controls (Figure 1A). Analysis of genomic regions revealed that there was a significantly greater number of hypomethylated DMRs in the 3’UTR, intron, and CpG shores (all P < .0001). Conversely, a greater number of hypermethylated DMRs were observed in the promoter, 5’UTR, exon, and CpG island regions (all P < .001). Next, the comparison of WM to IgM-MGUS (Figure 1B) showed a significantly greater number of hypomethylated DMRs in the promoter, 3’UTR, intron, exon, and CpG shore regions (all P < .001). Conversely, a greater number of hypermethylated DMRs were seen in the 5’UTR and CpG island regions (all P < .001). The number of DMRs and regions is included in supplemental Table 1 (available on the Blood website).
DMR analysis and corresponding pathways. Analysis of DMRs and methylation-based pathway analysis integrating RNA expression data in IgM gammopathies compared with normal controls (A,C) and WM compared with IgM-MGUS (B,D). DMR statistical analysis was conducted using the Pearson χ2 analysis comparing expected with observed values to determine P value. AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ECM, extracellular matrix; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; ERBB4, erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; ILK, integrin-linked kinase; MSP-RON, macrophage stimulating protein-recepteur d'origine nantais; PAK, p21 activated protein kinases; PD-1, programmed cell death protein; PDL-1, programmed death-ligand 1; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RXR, retinoid X receptor; TGF, transforming growth factor; Th1, T helper cell 1; TME, tumor microenvironment; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
DMR analysis and corresponding pathways. Analysis of DMRs and methylation-based pathway analysis integrating RNA expression data in IgM gammopathies compared with normal controls (A,C) and WM compared with IgM-MGUS (B,D). DMR statistical analysis was conducted using the Pearson χ2 analysis comparing expected with observed values to determine P value. AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ECM, extracellular matrix; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; ERBB4, erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; ILK, integrin-linked kinase; MSP-RON, macrophage stimulating protein-recepteur d'origine nantais; PAK, p21 activated protein kinases; PD-1, programmed cell death protein; PDL-1, programmed death-ligand 1; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RXR, retinoid X receptor; TGF, transforming growth factor; Th1, T helper cell 1; TME, tumor microenvironment; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Integrating mRNA expression, in IgM gammopathies compared with controls, 360 mRNAs (69 down, 291 up) were found to be differentially expressed with concordant differential methylation in the gene promoter. Analysis of these differentially expressed genes revealed multiple pathways involved in the regulation of the cell cycle/genome, metabolism, cytokine/immune signaling, cytoskeleton, tumor microenvironment, and intracellular signaling (Figure 1C). There was a significant enrichment of multiple cytokine and immune regulation pathways, including activation of multiple members of the interleukin family (interleukin 2 [IL-2], IL-3, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-8). Additionally, several cell signaling pathways, including the JAK/STAT and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (AKT) pathways, were identified. Underlying multiple cytokine and cell signaling pathways, mRNA upregulation with associated promoter hypomethylation of cell signaling genes, including MAP2K2, MAPK3, PIK3R2, and JAK3, along with downregulation of PTEN with promoter hypermethylation were observed. These genes are critical in cell signaling pathways and code for proteins that perform cytokine signal transduction and have been demonstrated to regulate WM cell survival.5-7 Further investigation identified enrichment of the CXCR4 signaling pathway, which has been demonstrated to play a central role in cancer development, especially in IgM-gammopathy pathogenesis.8 Gain-of-function mutations of CXCR4 are present in 30% of patients with WM and are associated with poor outcomes.1 Underlying the activation of this pathway was promoter hypomethylation with associated upregulation of mRNAs, including the G-protein subunits, GNB2 and GNB3, along with multiple members of the MAPK/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PIK3) family, MAP2K2, MAPK3, and PIK3R2. These genes play a role downstream of the CXCR4 receptor. From WES analysis, only 6 patients (26%) had CXCR4 mutations. However, additional investigation of the correlation between CXCR4 status and altered methylation did not identify a significant difference between CXCR4-mutated compared with wild-type samples in relation to the degree of CXCR4 promoter methylation (P = .36) or CXCR4 gene expression (P = .32). Furthermore, when excluding CXCR4-mutated samples and comparing only CXCR4 wild-type samples with normal controls, the CXCR4 pathway remained significantly upregulated (z score = 1.6, P = .02). Thus, these findings highlight that epigenetic regulation of genes in the CXCR4 pathway may play a pathogenic role beyond CXCR4-activating mutations and is mutually exclusive of mutational status in IgM gammopathies.
Assessing WM compared with IgM-MGUS, 431 genes (352 down, 79 up) were differentially expressed with concordant promoter methylation. Analysis of these targets demonstrated an array of important pathways to be potentially epigenetically altered (Figure 1D). Of significance, an overall inactivation of cytokine and immune regulation pathways was observed, including IL-6, IL-8, and IL-15. Additionally, inactivation of cell signaling pathways, including STAT3 signaling, was found. Underlying multiple cytokines and cell signaling pathways were decreased expression and corresponding promoter hypermethylation of EGFR, FGFR2, FLT4, and IL1R1. Notably, our group has previously demonstrated the microRNA-based influence on the IL-6, IL-8, and IL-15 pathways in IgM gammopathies via transcripts, including microRNA-146a, microRNA-20b, and microRNA-34a.9 Thus, these current findings indicate that multiple epigenetic regulators are playing a role in the regulation of cytokine pathways in WM.
Evaluating a database of 299 known TSGs/oncogenes, multiple genes were identified to be potentially epigenetically regulated (supplemental Table 2).10 In IgM gammopathies compared with controls, 11 mRNAs (4 oncogenes, 7 TSGs) were differentially expressed with concordant methylation dysregulation. Here, the oncogene CCND1 was found to be upregulated with corresponding promoter hypomethylation. CCND1 plays a role in cell cycle and proliferation, and is a pan-cancer oncogene that is upregulated in multiple tumor types.11 Assessing WM compared with IgM-MGUS, 17 genes (11 oncogenes, 6 TSGs) were differentially expressed with concordant promoter methylation. This included CD79B, which was upregulated with corresponding promoter hypomethylation. CD79A and CD79B form a complex with the B-cell receptor and are important in cell signaling. CD79B is frequently mutated in B-cell lymphomas and a subset of patients with WM.12 In analysis of our WES data, only 2 patients (1 with WM, 1 with IgM-MGUS) from the cohort were found to have CD79B mutations. Thus, these findings implicate epigenetic regulation may play an important role in the expression of this critical B-cell surface protein.
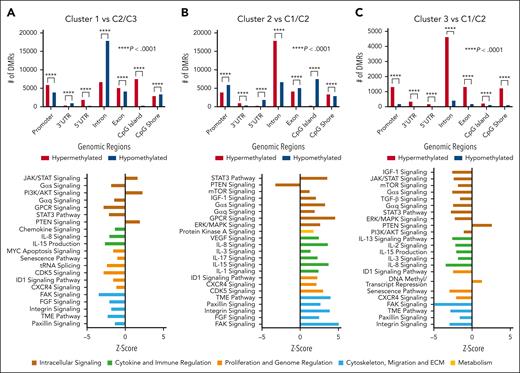
Previously, our group published an analysis of IgM gammopathies where we identified 3 unique molecular clusters (C1, C2, and C3). Each cluster had distinct pathway activation and metabolomic, immune, and clinical features.4 C2 was proposed to represent an early stage of disease with low BM involvement/tumor burden and inflammatory milieu, C1 had a clinically aggressive course, greater cell proliferation, and immune suppression thought to be a progression from C2, and C3 represented an intermediate state of disease. In methylation analysis of these clusters, we found a significant number of DMRs (Figure 2). Specifically, several pathways linked to immune regulation and cell signaling were differentially regulated on the basis of methylation levels. As previously observed, there was an opposite activation in C1 compared with C2 on methylation-based pathway analysis.4 Specifically, in line with the proteomic analysis revealing downregulation of the tumor microenvironment and CXCR4 pathways in C1, with upregulation of the same in C2, we observed similar results in our methylation-based analysis. Additionally, C2 was noted to have upregulation of inflammatory response proteins, with the opposite trend toward decreased inflammation in C1, which was further demonstrated in the present analysis with opposite activation of cytokines, including IL-8 and IL-15. Overall, these findings indicate that DNA methylation-based epigenetic regulation may be underlying the observed proteomic-based pathway differences. Overall, with notable differences seen in methylation along with differential pathway activation within each cluster, these results build on the importance of more nuanced biological stratification in IgM gammopathies. Further investigation in larger studies may reveal that multiomics approaches allow for improvements in prognostication and tailoring of therapeutics.
Cluster analysis of DMRs and corresponding pathway analysis. Analysis of DMRs and methylation-based pathway analysis integrating RNA expression data between clusters. Cluster 1 compared with cluster 2 and cluster 3 (A), cluster 2 compared with cluster 1 and cluster 3 (B), and cluster 3 compared with cluster 1 and cluster 2 (C). DMR statistical analysis was conducted using the Pearson χ2 analysis comparing expected with observed values to determine P value. AKT, protein kinase B; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; ECM, extracellular matrix; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptors; ID1, inhibitor of DNA binding 1; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; TGF, transforming growth factor; TME, tumor microenvironment; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Cluster analysis of DMRs and corresponding pathway analysis. Analysis of DMRs and methylation-based pathway analysis integrating RNA expression data between clusters. Cluster 1 compared with cluster 2 and cluster 3 (A), cluster 2 compared with cluster 1 and cluster 3 (B), and cluster 3 compared with cluster 1 and cluster 2 (C). DMR statistical analysis was conducted using the Pearson χ2 analysis comparing expected with observed values to determine P value. AKT, protein kinase B; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; ECM, extracellular matrix; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptors; ID1, inhibitor of DNA binding 1; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; TGF, transforming growth factor; TME, tumor microenvironment; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
This study demonstrates differential DNA methylation in IgM gammopathies and specifically between WM and IgM-MGUS. Using a multiomics approach with integrated mRNA and promoter-methylation–based analysis, we identify multiple oncogenes/TSGs and an array of cellular pathways as potentially epigenetically regulated. These results underscore the influence of epigenetic regulators in the IgM-gammopathy disease spectrum and indicate the potential role of aberrant DNA methylation underlying the malignant progression from IgM-MGUS to WM. A limitation of this study is the lack of direct functional validation at the proteomic level, which should be explored in future work. Further investigation with larger patient cohorts and longer follow-up may implicate certain methylation signatures having prognostic value and may help in diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Additionally, given the efficacy of hypomethylating agents in hematological malignancies, further investigation into the utility of these agents in WM is warranted.13
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research funding from the BINK Foundation and the International Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia Foundation to S.M.A. and the Mayo Clinic.
Authorship
Contribution: K.C., J.P., S.D., and S.M.A. designed this study, analyzed/interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript; P.M., J.P.N., J.P.A., K.W., Z.-Z.Y., S.J., V.B., J.E.K., E.B., M.K.M., A.P., C.B.R., S.A., A.C.-K., P.K., R.A.K., M.A.G., and A.J.N. interpreted the data and assisted in writing the manuscript; and all authors provided final approval of the manuscript and are accountable for all aspects of the work.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.M.A. receives research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Seattle Genetics, Affimed Therapeutics, Regeneron, Trillium Therapeutics, AI Therapeutics, and ADC Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Stephen M. Ansell, 200 1st St SW, Rochester, MN 55905; email: ansell.stephen@mayo.edu.
References
Author notes
K.C. and J.P. contributed equally to this work.
RNA data are available at the Gene Expression Omnibus under the accession number GSE232994. Methylation data are available on Zenodo under the record number 11206554. For additional patient data, please contact the corresponding author.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal