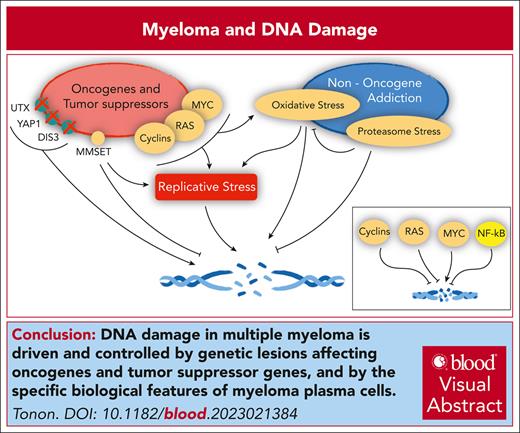
Visual Abstract
DNA-damaging agents have represented the first effective treatment for the blood cancer multiple myeloma, and after 65 years since their introduction to the clinic, they remain one of the mainstay therapies for this disease. Myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells. Despite exceedingly slow proliferation, myeloma cells present extended genomic rearrangements and intense genomic instability, starting at the premalignant stage of the disease. Where does such DNA damage stem from? A reliable model argues that the powerful oncogenes activated in myeloma as well the phenotypic peculiarities of cancer plasma cells, including the dependency on the proteasome for survival and the constant presence of oxidative stress, all converge on modulating DNA damage and repair. Beleaguered by these contraposing forces, myeloma cells survive in a precarious balance, in which the robust engagement of DNA repair mechanisms to guarantee cell survival is continuously challenged by rampant genomic instability, essential for cancer cells to withstand hostile selective pressures. Shattering this delicate equilibrium has been the goal of the extensive use of DNA-damaging agents since their introduction in the clinic, now enriched by novel approaches that leverage upon synthetic lethality paradigms. Exploiting the impairment of homologous recombination caused by myeloma genetic lesions or treatments, it is now possible to design therapeutic combinations that could target myeloma cells more effectively. Furthermore, DNA-damaging agents, as demonstrated in solid tumors, may sensitize cells to immune therapies. In all, targeting DNA damage and repair remains as central as ever in myeloma, even for the foreseeable future.
The mesmerizing myeloma genome
Healthy cells are very keen on preserving DNA integrity. Cancer cells, instead, strike a balance between DNA safeguarding while allowing some wiggle room for acquiring DNA changes. This genomic instability likely provides an evolutionary advantage to cancer cells, enhancing the clonal pool to be tapped into to withstand selective pressures exerted within the organism for example from the immune system, or from exogenous sources such as treatments. Although the hematological cancer multiple myeloma (MM) is no exception, because it is also richly bestowed with such ongoing genomic instability,1 it presents a degree of genomic changes that sets it apart from other blood cancers such as lymphomas and leukemias, which, instead, show genomes with much fewer genetic lesions.2
MM is a cancer of the post–germinal center plasma cells, usually disseminated throughout the bone marrow.3-5 MM initiates as a benign condition, named monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), which, in a small subset of patients, evolves toward an indolent form of myeloma (smoldering MM), and, ultimately, to full-blown myeloma. Despite great strides toward the identification of novel, more effective therapies, MM remains an incurable cancer.3-5 When compared with other tumors, and in particular hematological cancers, the MM genome is mesmerizing. Leukemias and lymphomas feature few chromosomal translocations and somatic mutations affecting few genes. Conversely, the genomes of MGUS and MM plasma cells are extensively rearranged.6-11 MGUS and MM cell lines, but also primary samples, do show widespread staining with phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX), considered a reliable marker of ongoing DNA damage.12,13 Indeed, a full gamut of genetic lesions is present. Chromosomal translocations are common from the inception of the disease, at the MGUS stage, in which powerful oncogenes, such as cyclin D1 and D3, NSD2 (MMSET)/fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), MAF, MAFB, and MAFA, are relocated under the transcriptional control of the immunoglobulin locus, nearby enhancer sequences (in most cases the immunoglobulin H, less frequently immunoglobulin L), driving a strong expression of the corresponding genes. These translocations are reciprocal (ie, 2 chromosomes exchange a portion without net loss of genomic material) and are defined as primary translocations.14 Later on during disease progression, again at odds with most blood cancers, in which single translocations are the norm, kaleidoscopic karyotypes often emerge, with more complex rearrangements, often engaging the oncogene MYC,15 and, in most cases, without the involvement of immunoglobulin loci. These chromosomal rearrangements are often not balanced and engage >2 chromosomes, their functional relevance still difficult to discern.14 One extreme example of complex rearrangements is chromothripsis, reported in MM as well,16 which consists of the shattering and random reconstitution of chromosomal fragments. Again, chromothripsis is rare in hematological cancers but common in epithelial cancers and MM.
Not only chromosomal changes but also the somatic mutational rate of MM cells is uncommonly high, more in par with epithelial than with blood cancers. The MM genome present, on average, 1.6 mutations per megabase, when compared with 0.4 in acute myeloid leukemia, 0.7 in prostate cancer, 1.2 in breast cancer, and 3.1 in colorectal cancer.17
A second paradox of MM stems from the exceedingly low proliferation rate of MM cells.18-20 Because the impact of DNA-damaging agents is thought to be particularly intense in actively proliferating cells, it is then somehow surprising that MM cells are sensitive to these compounds. The slow growth seen in MM cells also suggests that the complex genome detected in MM is unlikely to arise from the tumultuous proliferation seen in several epithelial cancers, in which the presence of extensive genetic lesions could be traced back to the breakage of DNA arising from the rampant growth of cancer cells. Could, then, the extensive DNA damage seen in MM originate from inadequate DNA repair? In other words, do MM cells present an unbalance between the physiological occurrence of DNA damage, ensuing during the normal life of a cell, and the ability of the cell to cope with these lesions?
DNA damage is recognized by a family of kinases, ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK,21 which then activate pathways specific to various genotoxic stresses.22-24 The most common types of DNA damage involve only 1 DNA strand, in the form of single-strand breaks or through the chemical modification of DNA bases. These lesions are repaired by the base excision repair or nucleotide excision repair pathways. Inaccurate DNA replication leads to the incorporation of mismatched bases, which are corrected by the mismatch repair machinery. Finally, the most threatening genetic lesions are represented by double strand breaks (DSBs), which are difficult to repair. Two DSB repair pathways have evolved. The homologous recombination (HR) pathway operates mostly during the S and G2 phases as well as in G1 phase to repair lesions at repetitive regions of the genome, such as ribosomal25 or centromeric DNA,26 or during meiosis.27 The HR pathway uses the homologous DNA strand as a template for repair. The nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway is, instead, less accurate and used during the other phases of the cell cycle.
In MM, however, at least judging from the genetic lesions affecting the DNA damage sensing and repair machineries, few mutations have been reported in the corresponding genes.10,28,29ATM and ATR are mutated in no more than 5% of patients with MM.6-10 Even p53, on which most DNA repair pathways converge,30 is mutated mostly in the later stages of the disease and in only ∼10% of patients.10 DNA repair seems, however, to be profoundly dysregulated in MM cells,28,29 especially the HR pathway response,31 and through the aberrant expression and activity of genes and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs)32,33 belonging to the various DNA repair pathways, including ligase III,34 RECQ1,35 and SIRT6.36
In a final paradox, despite such slow growth, some of the most powerful oncogenes are concomitantly and pervasively activated in MGUS and MM. As mentioned, cyclins start being deregulated at the MGUS stage, not only through chromosomal translocations but in cases in which these rearrangements are not present, through other, yet unclear, mechanisms.37 Another example of powerful oncogenes mutated in MM includes the RAS family genes. KRAS and NRAS are among the most frequently mutated oncogenes in MM,6,7 possibly driving the transition from MGUS to MM and are central players in MM tumorigenesis.38 Finally, the activation of the oncogene MYC represents a widespread phenomenon in both MGUS and MM. In the early stages of the disease, a robust upregulation of MYC is present,39-42 followed by genomic rearrangements affecting the MYC locus during the progression of the disease, further increasing its expression levels.15,43,44
To sum up, MM cells show extensive genomic rearrangements, intense genomic instability, and are bestowed with powerful oncogenes, but they proliferate slowly. Where is all this genomic complexity in MM originating from?
The case for replicative stress in MM
One of the potential suspects is replicative stress, a phenotype widely reported in epithelial cancers,45-47 which has also been recently proposed in MM13,48 (as recently reviewed49) (Figure 1). Replicative stress is commonly defined as the retardation or stalling of replicating forks leading to the fork collapse.45-47 Several mechanisms have been linked to increased replicative stress in cancer, including premature entry into S phase, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and depletion of nucleotide pools. Notably, MYC and RAS are able to trigger all these mechanisms to spark off intense replicative stress,47 which has been demonstrated also in MM, at least in the case of MYC and ROS production.50 Other oncogenes are more specific. For example, RB1 loss, cyclin E amplification, or MYC activation51 induce premature entry into S phase. Although the role of RB1 in MM is likely marginal52 and no strong ties between CCNE1 deregulation and MM have been reported, it is tempting to speculate that the pervasive deregulation of cyclins in MM may trigger replicative stress through this mechanism, which is not necessarily linked to increased proliferation, because it has been reported in other cancers.53 Such replicative stress may then lead to chromosomal instability54 as well as the somatic mutations.55
Cancer genes and the DNA damage response in MM. Oncogenes and tumor suppressors implicated in the control of replicative stress, DNA damage, and DNA repair in MM (left). (Right) Pathways engaged in MM that also affect the same pathways. In the inset, the overall net effect of major deregulated oncogenes and tumor suppressors on DNA damage in MM, as detailed in the text.
Cancer genes and the DNA damage response in MM. Oncogenes and tumor suppressors implicated in the control of replicative stress, DNA damage, and DNA repair in MM (left). (Right) Pathways engaged in MM that also affect the same pathways. In the inset, the overall net effect of major deregulated oncogenes and tumor suppressors on DNA damage in MM, as detailed in the text.
It is worthwhile to mention that besides inducing replicative stress, each of the oncogenes more frequently implicated in MM is directly engaged on DNA repair, albeit this specific role in MM for each pathway has, for the most part, not yet formally been assessed. MYC, for example, interferes with DNA repair, disabling p53-driven cell cycle arrest56 and interfering with DSB repair.57 Paradoxically, the other major oncogenic pathways implicated in MM exert a protective role on DNA. For example, cyclin D1 supports the activity of DNA-PK and ATM and interacts with several proteins engaged in DNA repair, in particular on the HR pathway.58 RAS promotes both the HR and NHEJ pathways.59 Another pathway pervasively altered in MM,60,61 the NF-κB pathway, is activated upon DNA damage and facilitates DSB resection.22
The myeloma genes and their roles in DNA damage and repair
Besides the major players listed earlier, a sizable number of MM genes are altered in patient subsets. Intriguingly, recent studies have revealed how these genes, when deregulated, affect DNA integrity in MM cells (Figure 1).
One example is represented by the histone methyltransferase NSD2 (MMSET).62 This gene is frequently engaged in a primary, reciprocal chromosomal translocation between chromosomes 4 and 14, t(4:14), affecting 2 genes, FGFR3 and NSD2, each juxtaposed to strong enhancer sequences as a result of the translocation.14,63 Of note, NSD2 is the main oncogenic driver of the rearrangement.64 Albeit not yet fully appreciated, NSD2 is a central player of DNA repair. NSD2 is recruited at DNA damage sites, mediating the accumulation of p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1), essential for NHEJ, through an increase of the levels of dimethylation and trimethylation of the histone residue H4K20.65,66 Knock down of NSD2 impairs both H4K20 methylation and 53BP1 engagement and ultimately DNA repair. Loss of NSD2 is also linked to increased replicative stress.66 More broadly, NSD2 also affects the HR pathway, through the control of expression and recruitments to sites of DNA damage of proteins belonging to the pathways.67 Considering that in MM the t(4;14) activates NSD2, does the role of NSD2 in DNA repair contribute to tumorigenesis? In MM cells, NSD2 overexpression leads to increased resistance to the DNA damage induced by chemotherapy agents, a possible explanation for the association of the t(4;14) translocation with poor prognosis.67 Surprisingly, however, MM cells overexpressing NSD2 do show increased DNA damage also in basal conditions, before any treatment.67 The enhanced DNA damage triggered by NSD2 overexpression may be related to the reported activity of NSD2 on increasing MYC protein levels, through MMSET-driven inhibition of the miR-126∗, which targets MYC messenger RNA, thus leading to MYC-induced replicative stress.68 Additionally, NSD2 methylates aurora kinase A, reducing the stability of p53.69 In all, these results suggest that on 1 side NSD2 protects MM cells from DNA-damaging agents, whereas, on the other, it triggers genomic instability, thus favoring tumorigenesis.
Another frequently mutated gene in MM is the exoribonuclease DIS3.6-10 DIS3 is the catalytic component of the RNA exosome. As such, DIS3 is engaged in the processing, turnover, and surveillance of several coding and ncRNAs,70 a function that has been shown also in MM cells.71,72 Intriguingly, DIS3 exerts a central role in B-cell development via its regulation of ncRNAs required for proper switch recombination and somatic recombination occurring at the immunoglobulin locus.73,74 DIS3 is also involved in MM, in which its loss contributes to enhanced DNA damage and increased genomic instability. Specifically, confirming similar findings in yeast,75 in MM cells, DIS3 loss has been associated with mitotic disruption due to centrosome amplifications.76 Recent results by Gritti et al77 further suggest that DIS3 inactivation triggers genomic instability in MM by inducing the accumulation of DNA-RNA hybrids on the genome, thus eliciting DSBs.78 Nascent RNA is transcribed at sites of single-strand DNA (ssDNA) breaks, at which it anneals to the template DNA strand, displacing the nontemplate DNA strand. If not properly displaced, these RNAs interfere with DNA repair. In MM cells, the loss of DIS3 prevents the clearance of these RNAs at ssDNA breaks, preventing the binding of BRCA1 and RAD51, ultimately leading to DSBs. Accordingly, cancer cells of a patient presenting with DIS3 mutations present an increased mutational burden. Additionally, as part of the interferon-mediated antiviral response, in MM cells, these hybrids elicit a strong overexpression of proinflammatory interferon, suggesting that cells with inactivated DIS3 may become more immunogenic (see further). Of interest, the depletion of another gene in MM leads to a robust accumulation of DNA-RNA hybrids. This gene is AATF/Che-1, an RNA-binding protein essential for transcription, whose loss also increases interferon in MM cells.79
Another gene frequently lost or mutated in MM is the histone demethylase KDM6A.80 Although data in MM are lacking, evidence associates the loss of KDM6A with increased DNA damage. In acute leukemia, KDM6A is associated with the expression of DNA repair genes, and KDM6A loss prevents DNA repair.81 Mechanistically, in Drosophila, it has been shown that KDM6A physically interacts with p53 and that both are recruited to the ku80 promoter and control ku80 expression.82 Further analyses are required to confirm a role for KDM6A in aiding DNA repair in MM.
Furthermore, the apoptotic pathways elicited by DNA damage are affected in MM. Besides the limited role of p53, as outlined earlier, there is another pathway frequently deregulated in MM as well as in other blood cancers, which interferes with DNA damage–induced apoptosis. This pathway is centered on the ABL1 kinase, which usually resides in the cytoplasm but upon DNA damage, relocates to the nucleus, where it pairs up with the Hippo pathway coactivator YAP183 to trigger cell death.13 A subset of patients with MM presents focal homozygous deletions encompassing the YAP1 locus, thus disrupting this proapoptotic path. In other hematological cancer cells as well as in the cases of MM in which the YAP1 genetic locus is intact, YAP1 presents exceedingly low levels of expression, when compared with in healthy plasma cells. As a consequence, ABL1 is kept outside of the nucleus, thus preventing apoptosis. It is noteworthy that YAP1 acts as an oncogene in epithelial cancers, in which it is frequently amplified and/or overexpressed and pairs with different partners to orchestrate an entirely different, protumorigenic program.83
Finally, several of these genes are concurrently mutated in MM samples,84 as, for example, MMSET in the t(4:14) translocation and DIS3 or the translocation t(14;16) that activates the oncogene MAF with mutations in ATM and DIS3. It is tempting to speculate that these co-occurenc may compensate for and cooperate for DNA repair and DNA damage to overcome the potential liabilities arising from each genetic lesion.
Nononcogene addictions and DNA damage in MM
Besides genetically altered oncogenes and tumor suppressors as causative of cancer, there is increasing recognition that several cellular physiological processes are exploited by cancer cells for their own survival. This phenomenon has been dubbed “nononcogene addiction,”85,86 referring to the reliance of cancer cells on normal cellular functions that are not targeted by genetic lesions but are essential for cancer survival. These cellular responses include various networks that are activated in conditions of stress; for example, mitotic, metabolic, proteotoxic, and oxidative stresses. Notably, several of these cellular responses are linked to DNA damage and repair, through replicative stress or other means. In MM, 2 stress responses exert a prominent role, the proteotoxic and the oxidative pathways, which, in turn, may elicit DNA damage (Figure 1).
Proteotoxic stress and its role on DNA damage
Antibody production remains a defining feature of plasma cells. Indeed, treatment with proteasome inhibitors rarely, if ever, leads to the abrogation of the immunoglobulin production, suggesting that the synthesis of immunoglobulins is central to MM identity and survival despite the severe stretch on MM physiology.87 Indeed, the proteasome of MM cells is strongly activated and strained by this persistent protein overload.88,89 On this premise rests the use of proteasome inhibitors in MM, which remains a cornerstone treatment of this disease. Interestingly, a strong link has been identified between the activity of the proteasome and DNA repair. Albeit assessed mostly with inhibitors, the proteasome strongly fosters HR pathway–dependent repair.90 Additionally, hampering the proteasome led to reduced monoubiquitination of FANCD2, the formation of 53BP1 foci, and the recruitment of various DNA damage response players at DNA damage sites, including ATM, NBS1, BRCA1, FANCD2, and RAD51.91 In all, these data suggest that in MM cells, the activation of the proteasome contributes to protect the DNA from damage, boosting HR repair and providing an unexpected aid for the survival of MM cells.
ROS production and DNA damage
As mentioned, oncogenes such as MYC, RAS, and BRAF increase the production of ROS.56,92 Indeed, MM cells present increased levels of ROS.93 ROS could provoke DNA damage directly92,94 or enhance replicative stress because of oxidized nucleotides.45,95 The ROS-induced induction of replicative stress appears context dependent.47 For example, Cottini et al demonstrated, in MM, how MYC induces DNA damage both through replicative stress and through ROS. Notably, in this cellular system, MYC-induced ROS production does not elicit replicative stress.50 Interestingly, the proteasome blunts the generation of ROS in MM,96 confirming the widespread prosurvival role of the proteasome in MM biology, tempering both ROS production and DNA damage. Furthermore, it has recently been shown that the FGF/FGFR axis reduces ROS production in MM, because FGF inhibition triggers ROS-induced DNA damage.97
Exploiting DNA damage in MM
Attesting for the central role of DNA damage in MM, melphalan has been the first effective therapy introduced to treat MM, with the first report published in 1958.98 As a matter of fact, this year marks the 65th year of the use of this drug to treat patients with MM; before then, there was no effective treatment for MM, and since then, melphalan has remained the mainstay treatment for MM.99,100 Melphalan is a nitrogen mustard, bifunctional alkylating agent, which also induces intrastrand and interstrand DNA crosslinks in a manner that is not cell cycle specific,22,28,101 and is, therefore, effective also in slow-proliferating MM cells. Other alkylating agents, such as cyclophosphamide, have been proven effective in treating MM.18 The main reason by which melphalan has emerged as the main DNA-damaging compound, still extensively used to treat MM, is because of its pharmacokinetic properties and its oral route of administration,18 which could be pivotal in killing slow-growing myeloma cells.18-20 After its introduction in the clinic, it was found that adding corticosteroids provided an advantage with respect to melphalan alone, but no other combinations were more effective than melphalan alone,102 so the melphalan-plus-prednisone therapy has remained at the center of MM therapy for decades.4 Intriguingly, mechanisms of resistance to melphalan leverage upon the empowerment of DNA repair pathways,28 including the HR pathway, nucleotide excision repair,103 and base excision repair through the HR pathway.104 In 1 example, NF-κB increases the expression of the Fanconi/BRCA1 pathway, thus overcoming melphalan-induced DNA damage in MM cells.105 Additionally, the microenvironment surrounding MM cells may drive not only DNA damage itself in cancer cells but also resistance to DNA damage–inducing chemotherapies.28,106
Synthetic lethality opportunities
The introduction of the concept of synthetic lethality in cancer treatment seems to have been adapted particularly well in DNA-damage treatments.107 The most well-known example is the use of poly-(adenosine 5′-diphosphate–ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors in BRCA1/2-mutated cancers, the so-called “brca-ness.”22,24 In this setting, the most accredited mechanism posits that the lack of BRCA1/2, essential for the HR pathway response, interferes with the repair of broken replication forks, leading to ssDNA nicks. PARP, which mends these breaks, then becomes indispensable to the proper repair of DNA and ultimately for cell survival. Therefore, PARP inhibitors could be exploited in any condition in which the HR pathway is hampered. As a matter of fact, combination therapies that merge PARP inhibition with pharmacological or genetic inhibition of MM-relevant targets may provide novel, fruitful avenues to treat MM. Among the possible examples, MYC overexpression is associated with enhanced sensitivity to PARP inhibition.108 Additionally, DIS3 loss, impairing the ability of BRCA1 to reach DSBs, enhances the sensitivity to PARP inhibitors.77 Moreover, KDM6A inactivation, associated with PARP inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia,81 could also potentially be leveraged in MM.
More broadly, following this synthetic lethal paradigm, any vulnerability that is specific to cancer cells could be exploited, interfering with ≥2 pathways that are specifically required by cancer cells to survive. Such vulnerabilities may stem from the mutational landscape or phenotypic features of MM cells, in combination with compounds that, for example, elicit DNA damage or interfere with DNA repair.22,24 For instance, YAP1 is under the control of a serine-threonine kinase, STK4. Inactivation of STK4 restores YAP1 levels, triggering cell death in vitro and in vivo after exposure of MM cells to DNA-damaging agents.13 An intriguing alternative may be represented by YAP1 activators, which have shown a similar activity on MM cells.109
In addition, replicative stress itself lends itself to be exploited in synthetic lethal approaches.49 In particular, targeting ATR, the central relay untying stalled forks, which solves replicative stress, has become an enticing and very effective target in cancer in general,24 and in MM specifically,48,50 alone or in combination with DNA-damaging agents. ATR is very rarely mutated in cancer, mostly because it exerts an essential role for relinquishing cancer cells from fork stalling, and ultimately from replicative stress; thus, it is an ideal target to pursue.
The nononcogene addictions defining MM cells, such as the proteotoxic stress, could also be seized to increase DNA damage and MM cell demise. For example, because proteasome inhibition interferes mostly with HR and BRCA1, as mentioned earlier,90,91 the combined inhibition of the proteasome along with PARP leads to DNA damage–centered apoptosis.110 Accordingly, compounds that increase ROS production, such as piperlongumine, increase apoptosis in MM cells, alone, or, in an intriguing twist, in combination with ATR inhibitors.50
Immune therapy and DNA-damaging agents
Immune therapy is revolutionizing the treatment of cancers, although its application, especially in some tumor types, remains limited.46,111,112 Even in MM, the impact of immune therapies has insofar not been profound.113 This is especially true for immune-checkpoint blockers, antibodies that inhibit the immune-suppressive molecules PD-1, PD-L1, LAG3, or CTLA4 on the cancer cell surface, thus unleashing tumor-specific CD8+ T cells. MM cells are endowed with high levels of PD-L1, yet these treatments have shown limited efficacy in this disease. The wise combination of DNA-damaging compounds with immune-based therapies may overcome this limited efficacy. Chemotherapy has long been considered associated with immune depression, yet at this point, several studies in epithelial and solid cancers have demonstrated a paradoxical synergy between immune-checkpoint blockers and DNA-damaging therapies.112 Faulty repair of DNA could generate neoantigens on the MM cell surface, which could be targeted by the immune system. However, it is becoming increasingly clear that these results are likely not related to the generation of neoantigens on the cancer cell surface, which would require more time but by other mechanisms. For example, the generation of DNA fragments after treatment with DNA-damaging agents could lead to their spilling into the cytoplasm in which they become immunogenic, mimicking viral infection. Once this phenomenon occurs, primitive pathogen pattern recognition receptors are engaged, for example, cGAS-STING, eliciting an immune response. Besides ssDNA breaks and DSBs, DNA-RNA–hybrid accumulation triggers this response that, in MM, could emerge, for example, from DIS3 loss77 or AATF/Che-1 inactivation,79 as described earlier. It is then tempting to speculate that also in MM, an old drug, melphalan, could unleash the full power of immune therapy in MM.
Concluding remarks
After all these years, seizing DNA damage to induce MM cell death remains as essential as ever. Moreover, new potential approaches glimmers in the future. Novel, more effective derivatives of melphalan have been proposed.114 Synthetic, lethal approaches, built upon DNA-damaging agents and exploiting the genetic and phenotypic features of MM cells, promise to deliver new opportunities. A new chapter is about to be opened, which combines DNA-damaging therapies with immune therapies. Rooted in the genetic and biology of the disease, it appears that the therapeutic exploitation of DNA damage remains as central as ever, also in the myeloma future.
Acknowledgments
The author is thankful for, and apologizes to, the authors whose work could not be included in this review because of space constraints. The author thanks all the members of the Tonon laboratory for their discussions and support.
This work was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (IG grant ID: 17109).
Authorship
Contribution: G.T. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Giovanni Tonon, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Via Olgettina 60, 20132 Milan, Italy; email: tonon.giovanni@hsr.it.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal