Key Points
For most adults with sickle cell disease, haploidentical BMT with thiotepa + PTCy is now a widely available curative option with excellent outcomes.
For children, haploidentical BMT with thiotepa + PTCy requires additional strategies to decrease graft failure rates.
Visual Abstract
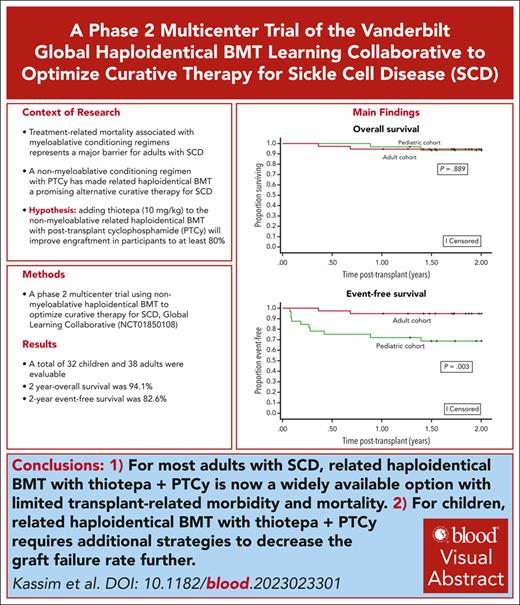
In the setting of a learning collaborative, we conducted an international multicenter phase 2 clinical trial testing the hypothesis that nonmyeloablative–related haploidentical bone marrow transplant (BMT) with thiotepa and posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) will result in 2-year event-free survival (no graft failure or death) of at least 80%. A total of 70 participants were evaluable based on the conditioning protocol. Graft failure occurred in 8 of 70 (11.4%) and only in participants aged <18 years; all had autologous reconstitution. After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, the 2-year Kaplan-Meier–based probability of event-free survival was 82.6%. The 2-year overall survival was 94.1%, with no difference between children and adult participants. After excluding participants with graft failure (n = 8), participants with engraftment had median whole blood donor chimerism values at days +180 and +365 after transplant of 100% (n = 58), respectively, and 96.6% (57/59) were off immunosuppression 1 year after transplant. The 1-year grade 3 to 4 acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) rate was 10%, and the 2-year moderate–severe chronic GVHD rate was 10%. Five participants (7.1%) died from infectious complications. We demonstrate that nonmyeloablative haploidentical BMT with thiotepa and PTCy is a readily available curative therapy for most adults, even those with organ damage, compared to the more expensive myeloablative gene therapy and gene editing. Additional strategies are required for children to decrease graft failure rates. The trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01850108.
Medscape Continuing Medical Education online

In support of improving patient care, this activity has been planned and implemented by Medscape, LLC and the American Society of Hematology. Medscape, LLC is jointly accredited with commendation by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education for the healthcare team.
Medscape, LLC designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
Successful completion of this CME activity, which includes participation in the evaluation component, enables the participant to earn up to 1.0 MOC points in the American Board of Internal Medicine's (ABIM) Maintenance of Certification (MOC) program. Participants will earn MOC points equivalent to the amount of CME credits claimed for the activity. It is the CME activity provider's responsibility to submit participant completion information to ACCME for the purpose of granting ABIM MOC credit.
All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test with a 75% minimum passing score and complete the evaluation at https://www.medscape.org/journal/blood; and (4) view/print certificate. For CME questions, see page 2677.
Disclosures
CCME questions author Laurie Barclay, freelance writer and reviewer, Medscape, LLC, declares no competing financial interests.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this activity, participants will:
Describe event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) treated with nonmyeloablative related haploidentical bone marrow transplantation (haplo-BMT) with thiotepa and posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy), based on an international, multicenter, phase 2 clinical trial with 70 evaluable participants
Determine graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) rate, infections, and associated factors in patients with SCD treated with nonmyeloablative-related haplo-BMT with thiotepa and PTCy, based on an international multicenter phase 2 clinical trial with 70 evaluable participants
Identify clinical implications of EFS, OS, and GVHD in patients with SCD treated with nonmyeloablative-related haplo-BMT with thiotepa and PTCy, based on an international multicenter phase 2 clinical trial with 70 evaluable participants
Release date: June 20, 2024; Expiration date: June 20, 2025
Introduction
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is characterized by painful vaso-occlusive episodes, acute and chronic organ injury, resulting in a poor quality of life and a significantly reduced life expectancy for adults in low-middle and high-income countries.1 Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the only established curative therapy for SCD. However, 2 major barriers have prohibited the widespread adoption of curative therapy in SCD: the very limited donor pool availability and treatment-related mortality associated with myeloablative conditioning regimens for adults with SCD.2 Common SCD–related organ complications associated with death in adults with SCD are stroke and progressive heart, lung, and kidney disease,3-6 probably rendering many adult patients with such complications ineligible for the recently approved myeloablative gene therapy options, due to concerns for increased treatment-related mortality.2,7
Nonmyeloablative conditioning regimens have made haploidentical bone marrow transplant (BMT) a promising alternative curative therapy in SCD.8 To reduce transplant-related toxicity and mortality, particularly for adults with SCD, nonmyeloablative or reduced intensity conditioning regimens have been developed. However, an important limitation of haploidentical BMT with the nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen as developed at Johns Hopkins was a graft failure rate of 40%.9
In 2012, we developed the multicenter Vanderbilt Global Haploidentical BMT Learning Collaborative to optimize curative therapy for SCD. The group tested the hypothesis that adding thiotepa to the nonmyeloablative–related haploidentical BMT with posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) will improve engraftment in participants to at least 80%.9 We initially demonstrated durable engraftment in 14 of 15 participants (93%, including 2 with previous graft failure) and a 100% overall survival after a median follow-up of 13.3 months.10 We present the final results of our phase 2 study (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01850108).
Methods
Study design
In an international multicenter learning collaborative context, we used a prospective, phase 2 study of related nonmyeloablative haploidentical BMT with thiotepa for children and adults with SCD. Site investigators determined their research governance approval for the trial. Eight sites had informed consent and assent for participating in the phase 2 clinical trial. According to local institutional governance following the Declaration of Helsinki, informed consent was obtained from parents or participants aged >16 years, and assent was obtained from younger participants, before enrollment. One site offered the treatment as the best available care in the clinical trial setting with the approval of the local institutional review board. All sites had institutional approval for sharing data with Vanderbilt University Medical Center. An independent data safety monitoring committee (DSMC) assessed the safety and clinical trial futility results.
Learning collaborative model and study setting
We used the collaborative learning model of the Institute for Healthcare Improvement.11 This approach, which has achieved results in prior research programs, was focused on improving clinical outcomes in SCD.12,13 The following strategy was undertaken in the learning collaborative: (1) regularly scheduled meetings to discuss participants and trial updates (initially weekly for ∼5 years, then biweekly, and in the last year monthly); (2) local institutional review board approval; (3) a memorandum of understanding between investigators to work collaboratively; (4) collection of minimal and accurate data; (5) agreement to follow the protocol as listed in clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01850108; (6) signed data user agreement with the investigator and Vanderbilt University School of Medicine; (7) electronic verification of the primary outcome measures (per protocol) after the completion of the trial; and (8) a spirit of collaboration.
Participants
The inclusion criteria were participants aged 1 to 70 years who were diagnosed with SCD, lack a human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–matched sibling donor, but have a suitable and available related haploidentical donor (first- and second-degree relatives) willing to donate bone marrow (BM) and have good performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score, 0 or 1; Karnofsky Performance Scale score, ≥70).14 Additional inclusions were site-specific.
Treatment
The first 5 participants treated using the Johns Hopkins protocol9 had SCD (n = 3) and transfusion-dependent thalassemia (n = 2). The DSMC met after 3 (2 with SCD) of the initial 5 participants treated with this protocol without thiotepa had graft failure, suggesting protocol modification to reduce graft failure on 22 August 2014. Thiotepa (10 mg/kg) was added to the regimen which consisted of ATG, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation (200 cGy) with PTCy as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood website). The consortium elected to focus only on children and adults with SCD after 2014. All participants were analyzed based on the same conditioning regimen. Evaluable participants were only those who received the conditioning regimen as listed in clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01850108.
Donors and grafts
BM stem cells were harvested from consenting first- and second-degree relatives who (1) shared at least 1 HLA haplotype with the participant, (2) did not have SCD or other hemoglobinopathies, and (3) were in good health. Potential donors were initially typed at the HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C loci at the intermediate- or high-resolution level. HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 alleles were typed at a high-resolution level. Haplotypes were determined based on family studies whenever possible.15 The donors of the initial 9 participants were primed with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) at 10 mg/kg per day for 5 consecutive days (days –5 to –1). The consortium members elected to stop priming with G-CSF because it did not result in higher BM harvests than expected without G-CSF priming. The target total nucleated cell dose was 2.5 × 108/kg to 4.0 × 108/kg of the recipient’s ideal body weight, with the volume not to exceed 20 mL/kg donor’s weight once the minimal target dose was reached and infused on day 0.16 Donors with sickle cell trait were not excluded. When more than 1 donor was available, the selection priority included: a donor age <40 years, a donor with the fewest HLA allele mismatches, full match > minor > major ABO mismatch, cytomegalovirus-matched donor-recipient pairs, and those with the least donor–specific anti-HLA antibodies.17 BM was unmanipulated except in major ABO–incompatible grafts or when graft volume was >20 mL/kg per recipient body weight, which were red blood cells and/or plasma depleted.
Peri-BMT supportive care
Hemoglobin S level was maintained at <30% within 7 days before commencing the conditioning regimen, while iron chelation therapy was discontinued at least 24 hours before the start of conditioning. The minimum hemoglobin level after transplant until engraftment was 9 g/dL. Other supportive care measures were site-specific with no protocol-based expectations. Institutional supportive measures included but were not limited to surveillance for cytomegalovirus (CMV), adenovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation, treatment of viral reactivations or infections, strict blood pressure control, seizure prophylaxis for the duration of immunosuppressive therapy, maintenance of platelet count >50 × 109/L, and antifungal prophylaxis through day +100. We do not define a uniform viral surveillance strategy nor a common definition of CMV, adenovirus, or Epstein-Barr virus reactivation.
Definitions of donor-recipient chimerism, graft failure, GVHD, and neutrophil and platelet recovery
Donor-recipient chimerism studies were measured by polymerase chain reaction analysis of the variable number of nucleotide tandem repeats unique to donors or recipients on total peripheral blood mononuclear cells and isolated CD3+ T cells on days +30, +60, +90, +180, and +365, and 2 years after transplant. Some centers could not perform T-cell chimerism due to financial constraints. Primary graft failure was defined as the presence of <5% donor cells as assessed by peripheral blood chimerism (of any lineage) at day +30. Secondary graft failure was defined as the presence of <5% donor cells as assessed by peripheral blood chimerism (of any lineage), with prior evidence of ≥5% donor cells with autologous reconstitution and standard SCD medical care afterward. Diagnosis and grading of acute and chronic GVHD were done following established criteria.18,19 Neutrophil recovery was defined as the first 3 days of neutrophil counts of ≥0.5 ×109/L. Platelet recovery was defined as platelet count ≥50 ×109/L after transplant with at least 7 days without a platelet transfusion.
Study objectives and end points
We hypothesized that a nonmyeloablative–related haploidentical BMT with thiotepa and PTCy would result in a 2-year event-free survival (no graft failure or death) of at least 80%. Secondary objectives were the estimation of overall survival, engraftment rate, chimerism values, and incidences of acute and chronic GVHD. Unacceptable toxicity is defined as the probability of graft failure or death exceeding 20% (event-free survival, <80%).
Statistical analysis
Only evaluable participants who received the protocol’s conditioning regimen were included. Baseline patient characteristics were summarized with median and interquartile range (IQR) or mean with standard deviation for continuous variables, depending on data distribution, and with count and percentage for categorical variables. Event-free survival and overall survival were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, with median survival and its 95% confidence interval (CI). The trial-stopping rule was based on the probability of graft failure, which was modeled using a Bayesian Beta-Binomial model with a very weak prior distribution, Beta (0.2, 0.8). For the dependent transplantation outcomes of acute and chronic GVHD, the incidence was calculated in the presence of their competing risks (graft failure or death). The probability of graft failure and death was estimated at each interim assessment, and if the data indicated that unacceptable toxicity is highly likely (event-free survival, <80%), then accrual would be halted, and safety data reviewed. Graft failure occurred in the first 2 of 3 participants treated without thiotepa. Although the stopping rule boundary was not crossed, the DSMC requested a safety review, and accrual was halted, resulting in a protocol modification with the addition of thiotepa. Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS version 29.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY) and Stata version 15.0 (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX).
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the institutional review board of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; St Mary's Hospital, Imperial College, London, United Kingdom; Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris, France; Amsterdam University Medical Centers, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Atrium Health Levine Children's Hospital, Charlotte, NC; Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant and Cell Therapy Program, University of Gainesville, Gainesville, FL; Pediatric Hematology Oncology and Blood and Marrow Transplantation, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; King Faisal Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; and King Abdulaziz Medical City, Ministry of National GuardHealth Affairs, Riyadh/King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, Riyadh/King Saud Bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Results
Participant and donor characteristics
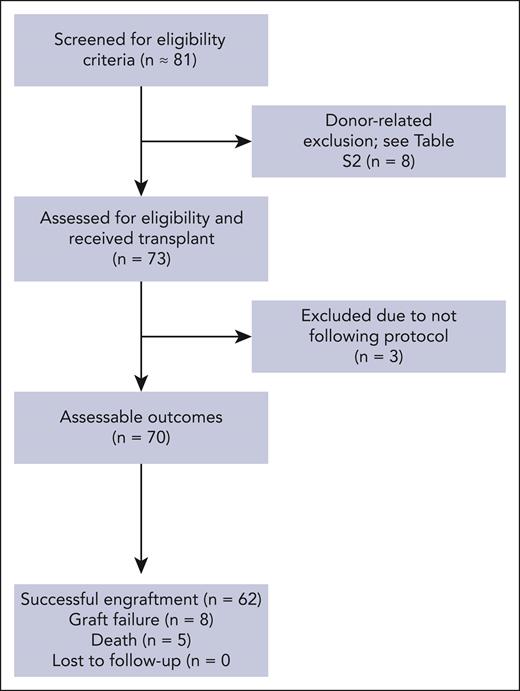
We report the final results of participants with a follow-up period of at least 1 year enrolled in the trial from 8 August 2014 to 1 March 2022. The median follow-up time was 2.4 years (IQR, 1.5-3.9), based on the time of graft failure or death on 1 March 2023. A total of 81 participants from 8 sites and 3 continents (North America, Europe, and Asia) were screened, and 73 (90.1%) underwent BMT. Eight participants screened did not proceed to transplant due to donor-related barriers (supplemental Table 1). Pretransplant occurrence of SCD–related organ damage is summarized in supplemental Table 2. Recipient and donor characteristics are summarized in Table 1. After signing the informed consent, 3 participants were not evaluable because of following reasons: (1) received peripheral blood stem cells in addition to BM stem cells owing to low BM harvest yield (n = 1); (2) donor being HLA-identical on HLA review (n = 1); and (3) receiving alternative immunosuppression (n = 1; Figure 1). A total of 70 participants were included in the final analyses.
Characteristics of study participants
| Variable . | Total (n = 70) . | Pediatric (n = 32) <18 y . | Adult (n = 38) ≥18 y . | P value∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at transplant, median (IQR), y | 19.1 (14.1-25.0) | 13.8 (8.0-16.0) | 24.9 (20.4-31.3) | NA |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 31 (44.3) | 14 (43.8) | 17 (44.7) | .934 |
| SCD genotype (SS and Sβ0-thalassemia), n (%) | 68 (97.1) | 32 (100.0) | 36 (94.7) | .234† |
| Follow-up time, median (IQR), y | 2.4 (1.5-3.9) | 2.2 (0.5-3.8) | 3.1 (1.7-4.7) | .088 |
| Transplantation indication, n (%)‡ | ||||
| Stroke (overt and silent infarcts) | 37 (52.9) | 21 (65.6) | 16 (42.1) | .050 |
| Acute chest syndrome | 36 (51.4) | 13 (40.6) | 23 (60.5) | .097 |
| Osteonecrosis | 7 (10.0) | 3 (9.4) | 4 (10.5) | 1.000† |
| Sickle nephropathy | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | 1.000† |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 4 (5.7) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (10.5) | .120† |
| Alloimmunization | 16 (22.9) | 5 (15.6) | 11 (28.9) | .186 |
| Donor characteristics | ||||
| Donor age, mean (SD) | 34.4 (12.1) | 36.8 (10.9) | 32.4 (12.8) | .127 |
| Donor sex, male, n (%) | 33 (47.1) | 16 (50.0) | 17 (44.7) | .660 |
| Donor relationship, n (%) | .003† | |||
| Mother | 19 (27.1) | 13 (40.6) | 6 (15.8) | |
| Father | 15 (21.4) | 10 (31.2) | 5 (13.2) | |
| Sibling | 33 (47.1) | 9 (28.1) | 24 (63.2) | |
| Other | 3 (4.3) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.9) | |
| Sickle cell trait (AS) | 56 (80.0) | 30 (93.8) | 26 (68.4) | .008 |
| Donor/recipient sex match, n (%) | .473 | |||
| Sex-matched transplant | 36 (51.4) | 14 (43.8) | 22 (57.9) | |
| Female donor, male recipient | 16 (22.9) | 8 (25.0) | 8 (21.1) | |
| Male donor, female recipient | 18 (25.7) | 10 (31.3) | 8 (2115) | |
| ABO incompatibility, n (%), (n = 68) | .586† | |||
| No incompatibility | 52 (76.5) | 22 (73.3) | 30 (79.0) | |
| Minor incompatibility | 10 (14.7) | 4 (13.3) | 6 (15.8) | |
| Major incompatibility | 6 (8.8) | 4 (13.3) | 2 (5.3) | |
| CMV serostatus, n (%) | .134† | |||
| CMV-seronegative recipient and donor | 4 (5.7) | 2 (6.3) | 2 (5.3) | |
| CMV-seropositive recipient and donor | 47 (67.1) | 19 (59.4) | 28 (73.7) | |
| CMV-seronegative recipient and CMV- seropositive donor | 14 (20.0) | 10 (31.3) | 4 (10.5) | |
| CMV-seropositive recipient and CMV-seronegative donor | 5 (7.1) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (10.5) | |
| Degree of HLA match, n (%) | .008† | |||
| 5/10 | 24 (34.3) | 7 (21.9) | 17 (44.7) | |
| 6/10 | 11 (15.7) | 4 (12.5) | 7 (18.4) | |
| 7/10 | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | |
| 8/10 | 2 (2.9) | 1 (3.1) | 1 (2.6) | |
| 9/10 | 2 (2.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.3) | |
| 6/12 | 22 (31.4) | 16 (50.0) | 6 (15.8) | |
| 7/12 | 4 (5.7) | 1 (3.1) | 3 (7.9) | |
| 8/12 | 3 (4.3) | 3 (9.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 9/12 | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | |
| DSA positive, n (%) | 7 (10.0) | 6 (21.9) | 0 (0.0) | .003† |
| TNC dose (108/kg), median (IQR) | 5.9 (3.6-8.7) | 5.7 (2.8-8.6) | 6.4 (3.8-9.1) | .361 |
| CD34+ cell dose (106/kg), median (IQR) | 4.1 (2.5-5.9) | 4.2 (2.7-7.5) | 3.8 (2.4-5.6) | .275 |
| Graft source, n (%) | .166† | |||
| BM | 61 (87.1) | 30 (93.8) | 31 (81.6) | |
| Primed BM | 9 (12.9) | 2 (6.3) | 7 (18.4) |
| Variable . | Total (n = 70) . | Pediatric (n = 32) <18 y . | Adult (n = 38) ≥18 y . | P value∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at transplant, median (IQR), y | 19.1 (14.1-25.0) | 13.8 (8.0-16.0) | 24.9 (20.4-31.3) | NA |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 31 (44.3) | 14 (43.8) | 17 (44.7) | .934 |
| SCD genotype (SS and Sβ0-thalassemia), n (%) | 68 (97.1) | 32 (100.0) | 36 (94.7) | .234† |
| Follow-up time, median (IQR), y | 2.4 (1.5-3.9) | 2.2 (0.5-3.8) | 3.1 (1.7-4.7) | .088 |
| Transplantation indication, n (%)‡ | ||||
| Stroke (overt and silent infarcts) | 37 (52.9) | 21 (65.6) | 16 (42.1) | .050 |
| Acute chest syndrome | 36 (51.4) | 13 (40.6) | 23 (60.5) | .097 |
| Osteonecrosis | 7 (10.0) | 3 (9.4) | 4 (10.5) | 1.000† |
| Sickle nephropathy | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | 1.000† |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 4 (5.7) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (10.5) | .120† |
| Alloimmunization | 16 (22.9) | 5 (15.6) | 11 (28.9) | .186 |
| Donor characteristics | ||||
| Donor age, mean (SD) | 34.4 (12.1) | 36.8 (10.9) | 32.4 (12.8) | .127 |
| Donor sex, male, n (%) | 33 (47.1) | 16 (50.0) | 17 (44.7) | .660 |
| Donor relationship, n (%) | .003† | |||
| Mother | 19 (27.1) | 13 (40.6) | 6 (15.8) | |
| Father | 15 (21.4) | 10 (31.2) | 5 (13.2) | |
| Sibling | 33 (47.1) | 9 (28.1) | 24 (63.2) | |
| Other | 3 (4.3) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.9) | |
| Sickle cell trait (AS) | 56 (80.0) | 30 (93.8) | 26 (68.4) | .008 |
| Donor/recipient sex match, n (%) | .473 | |||
| Sex-matched transplant | 36 (51.4) | 14 (43.8) | 22 (57.9) | |
| Female donor, male recipient | 16 (22.9) | 8 (25.0) | 8 (21.1) | |
| Male donor, female recipient | 18 (25.7) | 10 (31.3) | 8 (2115) | |
| ABO incompatibility, n (%), (n = 68) | .586† | |||
| No incompatibility | 52 (76.5) | 22 (73.3) | 30 (79.0) | |
| Minor incompatibility | 10 (14.7) | 4 (13.3) | 6 (15.8) | |
| Major incompatibility | 6 (8.8) | 4 (13.3) | 2 (5.3) | |
| CMV serostatus, n (%) | .134† | |||
| CMV-seronegative recipient and donor | 4 (5.7) | 2 (6.3) | 2 (5.3) | |
| CMV-seropositive recipient and donor | 47 (67.1) | 19 (59.4) | 28 (73.7) | |
| CMV-seronegative recipient and CMV- seropositive donor | 14 (20.0) | 10 (31.3) | 4 (10.5) | |
| CMV-seropositive recipient and CMV-seronegative donor | 5 (7.1) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (10.5) | |
| Degree of HLA match, n (%) | .008† | |||
| 5/10 | 24 (34.3) | 7 (21.9) | 17 (44.7) | |
| 6/10 | 11 (15.7) | 4 (12.5) | 7 (18.4) | |
| 7/10 | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | |
| 8/10 | 2 (2.9) | 1 (3.1) | 1 (2.6) | |
| 9/10 | 2 (2.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.3) | |
| 6/12 | 22 (31.4) | 16 (50.0) | 6 (15.8) | |
| 7/12 | 4 (5.7) | 1 (3.1) | 3 (7.9) | |
| 8/12 | 3 (4.3) | 3 (9.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 9/12 | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | |
| DSA positive, n (%) | 7 (10.0) | 6 (21.9) | 0 (0.0) | .003† |
| TNC dose (108/kg), median (IQR) | 5.9 (3.6-8.7) | 5.7 (2.8-8.6) | 6.4 (3.8-9.1) | .361 |
| CD34+ cell dose (106/kg), median (IQR) | 4.1 (2.5-5.9) | 4.2 (2.7-7.5) | 3.8 (2.4-5.6) | .275 |
| Graft source, n (%) | .166† | |||
| BM | 61 (87.1) | 30 (93.8) | 31 (81.6) | |
| Primed BM | 9 (12.9) | 2 (6.3) | 7 (18.4) |
A summary depicting the clinical characteristics of 70 evaluable participants who received the conditioning regimen as per protocol, and their donors.
CMV, cytomegalovirus; DSA, donor-specific antigens; SD, standard deviation; TNC, total nucleated cell dose.
χ2 test for the count, t test for mean, or Mann-Whitney test for the median, unless otherwise indicated.
Fisher exact test.
Some patients had >1 indication.
Screening and inclusion for haploidentical BMT with thiotepa and PTCy for SCD.
Donor–specific anti-HLA antibodies were assayed in all recipients; 7 patients had donor–specific anti-HLA antibodies, all with a mean fluorescence intensity <3000.15 The median total nucleated cell dose administered was 5.9 × 108 cells/kg (IQR, 3.6-8.7).
Event-free survival
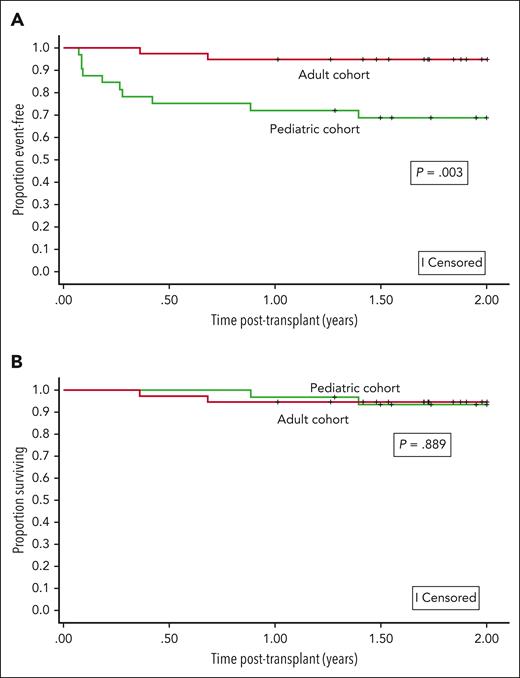
The Kaplan-Meier–based probability of event-free survival at 1 and 2 years was 84.3% (95% CI, 73.4-91.0) and 82.6% (95% CI, 71.4-89.7), respectively. Event-free survival differed by age group (age <18 years or >18 years) at 1 year (P = .007) and 2 years (P = .003) (Figure 2A).
Event-free and overall survival. (A) The 2-year event-free survival probabilities after nonmyeloablative haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with thiotepa and posttransplant cyclophosphamide were significantly higher in adults than in children with SCD. The event-free survival probabilities at 2 years for children and adults were 68.4% (95% CI: 49.1-81.6) and 94.7% (95% CI: 80.6-98.7), respectively. (B) The 2-year overall survival probabilities after nonmyeloablative haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with thiotepa and posttransplant cyclophosphamide were comparable between adults and children with SCD. The overall survival probabilities at 2 years for children and adults were 93.6% (95% CI: 76.9-98.3) and 94.7% (95% CI: 80.6-98.7), respectively.
Event-free and overall survival. (A) The 2-year event-free survival probabilities after nonmyeloablative haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with thiotepa and posttransplant cyclophosphamide were significantly higher in adults than in children with SCD. The event-free survival probabilities at 2 years for children and adults were 68.4% (95% CI: 49.1-81.6) and 94.7% (95% CI: 80.6-98.7), respectively. (B) The 2-year overall survival probabilities after nonmyeloablative haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with thiotepa and posttransplant cyclophosphamide were comparable between adults and children with SCD. The overall survival probabilities at 2 years for children and adults were 93.6% (95% CI: 76.9-98.3) and 94.7% (95% CI: 80.6-98.7), respectively.
The Kaplan-Meier–based probability of overall survival at 1 and 2 years was 95.7% (95% CI, 87.3-98.6) and 94.1% (95% CI, 84.9-97.7), respectively (Figure 2B). A post hoc Kaplan-Meier–based survival analysis stratified by age was completed based on the observation that all graft failures occurred in participants aged <18 years.
No differences in overall survival between the age groups were seen at 1 year (P = .650) or 2 years (P = .889). Five participants (7.1%) died, all due to infections (Table 2). The total number of person-years in the cohort was 234.4. There were 105.8 and 128.6 person-years for the children and adults, respectively. The overall death incidence rate was 2.13 deaths per 100 person-years (95% CI, 0.69-4.98), with rates by age group as follows: <18 years, 1.89 deaths per 100 person-years (95% CI, 0.21-6.83); >18 years, 2.33 deaths per 100 person-years (95% CI, 0.47-6.81). The incidence rate ratio for deaths in children to adults was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.07-7.08; P = .818).
The cause of death in 7.1% of participants in the trial
| Age at BMT, y . | Sex, recipient/donor . | Days posttransplant . | Cause of death . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40.2 | Female/female | 1265 | Primary cause of death: cardio-respiratory failure Secondary cause of death: presumed COVID-19 infection |
| 1.3 | Female/female | 323 | Primary cause of death: disseminated adenovirus infection Secondary cause of death: MAS, GI GVHD, and multiorgan failure |
| 5.3 | Female/female | 509 | Primary cause of death: Pneumococcal sepsis Secondary cause of death: ARDS, ischemia, and necrosis in all extremities requiring extensive plastic surgery, and multiorgan failure |
| 18.7 | Female/female | 132 | Primary cause of death: disseminated adenovirus infection Secondary cause of death: multiorgan failure |
| 36.0 | Female/female | 248 | Primary cause of death: respiratory failure and worsening pulmonary HTN Secondary cause of death: poor graft function (platelet and RBC); CMV reactivation, TA-TMA, PRES, and acute acute-on on-chronic renal failure; recurrent GI bleeding; recurrent C. diff and salmonella infections; BK virus cystitis; right internal jugular vein thrombosis |
| Age at BMT, y . | Sex, recipient/donor . | Days posttransplant . | Cause of death . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40.2 | Female/female | 1265 | Primary cause of death: cardio-respiratory failure Secondary cause of death: presumed COVID-19 infection |
| 1.3 | Female/female | 323 | Primary cause of death: disseminated adenovirus infection Secondary cause of death: MAS, GI GVHD, and multiorgan failure |
| 5.3 | Female/female | 509 | Primary cause of death: Pneumococcal sepsis Secondary cause of death: ARDS, ischemia, and necrosis in all extremities requiring extensive plastic surgery, and multiorgan failure |
| 18.7 | Female/female | 132 | Primary cause of death: disseminated adenovirus infection Secondary cause of death: multiorgan failure |
| 36.0 | Female/female | 248 | Primary cause of death: respiratory failure and worsening pulmonary HTN Secondary cause of death: poor graft function (platelet and RBC); CMV reactivation, TA-TMA, PRES, and acute acute-on on-chronic renal failure; recurrent GI bleeding; recurrent C. diff and salmonella infections; BK virus cystitis; right internal jugular vein thrombosis |
A total of 5 of 70 participants died due to infections.
ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; C. diff, Clostridioides difficile; CMV, cytomegalovirus; GI, gastrointestinal; MAS, macrophage activation syndrome; PRES, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; RBC, red blood cell; TA-TMA, transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy.
Primary and secondary graft failure
Graft failure occurred in 8 of 70 participants (11.4%), with 4 primary and 4 secondary graft failures (Table 3). All graft failures were in participants aged <18 years (referred to as children in this manuscript), and all had autologous reconstitution and were alive at the time of last follow-up. A post hoc analysis showed that the graft failure rate was higher in participants aged <18 years than participants aged >18 years (P = .001). All secondary graft failures occurred within 180 days after transplant.
Characteristics of participants with graft failure
| Type of graft failure . | Days posttransplant . | Recipient age (y) . | Donor age (y) . | Sex (D/R) . | TNC cell dose × 108/kg . | DSA . | ABO mismatch . | CMV serostatus (D/R) . | CMV reactivation . | Comments . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | 31 | 8.2 | 39 | Female/female | 10.5 | No | None | Positive/negative | No | Discontinued sirolimus for suspected allergy at d +21, treated with high-dose steroids; later developed hypertension and PRES |
| Primary | 26 | 3.8 | 40 | Male/male | 5.6 | No | Major | Negative/positive | Yes | Parainfluenza < d +30 posttransplant |
| Primary | 31 | 16.0 | 38 | Female/male | 3.1 | No | None | Positive/positive | Yes | CMV viremia, MRSA bacteremia Died on d +411 of fungemia after the second transplant |
| Primary | 33 | 5.4 | 31 | Female/female | 5.1 | No | None | Positive/negative | Yes | HSV stomatitis, CMV viremia, Enterobacter bacteremia |
| Secondary | 87 | 15.1 | 35 | Female/male | 4.5 | No | None | Positive/negative | No | None |
| Secondary | 153 | 15.2 | 42 | Female/male | 1.3 | No | Major | Positive/negative | No | Invasive fungal infection (chest), CNS bacteremia, EBV viremia |
| Secondary | 67 | 6.0 | 45 | Male/male | 7.0 | No | None | Positive/negative | No | MRSA, urine BK virus cystitis |
| Secondary | 97 | 14.8 | 16 | Male/male | 23.5 | No | None | Positive/positive | Yes | CMV viremia |
| Type of graft failure . | Days posttransplant . | Recipient age (y) . | Donor age (y) . | Sex (D/R) . | TNC cell dose × 108/kg . | DSA . | ABO mismatch . | CMV serostatus (D/R) . | CMV reactivation . | Comments . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | 31 | 8.2 | 39 | Female/female | 10.5 | No | None | Positive/negative | No | Discontinued sirolimus for suspected allergy at d +21, treated with high-dose steroids; later developed hypertension and PRES |
| Primary | 26 | 3.8 | 40 | Male/male | 5.6 | No | Major | Negative/positive | Yes | Parainfluenza < d +30 posttransplant |
| Primary | 31 | 16.0 | 38 | Female/male | 3.1 | No | None | Positive/positive | Yes | CMV viremia, MRSA bacteremia Died on d +411 of fungemia after the second transplant |
| Primary | 33 | 5.4 | 31 | Female/female | 5.1 | No | None | Positive/negative | Yes | HSV stomatitis, CMV viremia, Enterobacter bacteremia |
| Secondary | 87 | 15.1 | 35 | Female/male | 4.5 | No | None | Positive/negative | No | None |
| Secondary | 153 | 15.2 | 42 | Female/male | 1.3 | No | Major | Positive/negative | No | Invasive fungal infection (chest), CNS bacteremia, EBV viremia |
| Secondary | 67 | 6.0 | 45 | Male/male | 7.0 | No | None | Positive/negative | No | MRSA, urine BK virus cystitis |
| Secondary | 97 | 14.8 | 16 | Male/male | 23.5 | No | None | Positive/positive | Yes | CMV viremia |
Graft failure occurred in 8 of the 70 study participants; 4 experienced primary graft failures, and 4 experienced secondary graft failures.
CMV, cytomegalovirus; CNS, coagulase-negative staphylococci; D/R, donor/recipient; DSA, donor-specific antibody; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; HSV, herpes simplex virus; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PRES, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; TNC, total nucleated cell.
After excluding participants with graft failure (n = 8), participants who engrafted had median whole blood donor chimerism values at day +180 and day +365 after transplant of 100.0% (IQR, 99.8%-100.0%; n = 59) and 100.0% (IQR, 100.0%-100.0%; n = 58), respectively (Table 4). For participants with available T-cell chimerism, values at day +180 and day +365 after transplant were 100.0% (IQR, 99.0%-100.0%; n = 49) and 100% (IQR, 100.0%-100.0%; n = 42), respectively. Among fully engrafted participants, 57 of 59 (96.6%) were off immunosuppression at day +365 after transplant. Among fully engrafted participants whose donors had sickle cell trait, hemoglobin S was <50% and was undetectable in participants with a normal hemoglobin A donor at 6 months after transplant.
Cellular recovery and chimerism in engrafted patients
| Variable∗ . | Total (n = 62) . | Pediatric (n = 24) <18 y . | Adult (n = 38) ≥18 y . | P value† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platelet recovery, d (n = 60) | 32.5 (27.0-40.8) | 32.0 (27.0 - 52.0) | 33.0 (27.0-38.5) | .523 |
| Neutrophil recovery, d (n = 62) | 20.5 (18.0-24.0) | 20.0 (17.2-22.8) | 21.0 (18.0-24.2) | .372 |
| Day +30 chimerism (%) | ||||
| Whole blood (n = 60) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 99.0 (98.8-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | <.001 |
| CD3+ (n = 58) | 100.0 (97.4-100.0) | 98.0 (93.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | <.001 |
| Day +180 chimerism (%) | ||||
| Whole blood (n = 59) | 100.0 (99.8-100.0) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | .161 |
| CD3+ (n = 49) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (97.0-100.0) | 100.0 (99.2-100.0) | .470 |
| Day +365 chimerism (%) | ||||
| Whole blood (n = 58) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | .685 |
| CD3+ (n = 42) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | .187 |
| Variable∗ . | Total (n = 62) . | Pediatric (n = 24) <18 y . | Adult (n = 38) ≥18 y . | P value† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platelet recovery, d (n = 60) | 32.5 (27.0-40.8) | 32.0 (27.0 - 52.0) | 33.0 (27.0-38.5) | .523 |
| Neutrophil recovery, d (n = 62) | 20.5 (18.0-24.0) | 20.0 (17.2-22.8) | 21.0 (18.0-24.2) | .372 |
| Day +30 chimerism (%) | ||||
| Whole blood (n = 60) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 99.0 (98.8-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | <.001 |
| CD3+ (n = 58) | 100.0 (97.4-100.0) | 98.0 (93.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | <.001 |
| Day +180 chimerism (%) | ||||
| Whole blood (n = 59) | 100.0 (99.8-100.0) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | .161 |
| CD3+ (n = 49) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (97.0-100.0) | 100.0 (99.2-100.0) | .470 |
| Day +365 chimerism (%) | ||||
| Whole blood (n = 58) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | .685 |
| CD3+ (n = 42) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | 100.0 (99.0-100.0) | 100.0 (100.0-100.0) | .187 |
The 62 participants who did not experience graft failure had median whole blood donor chimerism values at day +180 and day +365 after transplant of 100.0%.
Median (interquartile range).
Mann-Whitney test.
Most participants were at risk for CMV reactivation; 67.1% were recipient and donor CMV-seropositive, 20.0% were recipient CMV-seronegative with CMV-seropositive donors, and 7.1% of the recipients were seropositive and the donor seronegative. The univariate analyses revealed that being at risk of CMV reactivation was not associated with graft failure (P = 1.00). Graft failure was also not associated with donor age (P = .722), degree of HLA-mismatch (P = .715), donor-recipient sex-mismatch (P = .710), total nucleated cell dose (P = .625), or ABO mismatch (P = .458). We did not conduct a multivariate analysis for graft failure because of the small number of events and the unanticipated results that graft failure only occurred in children.
GVHD rate
The 1-year rate of grades 3 to 4 acute GVHD was 10.0% (95% CI, 4.6-18.6) with no differences between children and adults (12.5% [95% CI, 4.4-27] vs 7.9% [95% CI, 2.3-19.6], respectively; P = .52). The 2-year incidence of moderate-severe chronic GVHD was 10.0% (95% CI, 4.6-18.6), which was significantly higher in children than in adults (18.8% [95% CI, 8.2-34.6] vs 2.6% [95% CI, 0.3-11.6], respectively; P = .025). One participant with grade 4 acute gastrointestinal GVHD required additional immunosuppressive therapy and was off immunosuppression at day +365. Two participants continued immunosuppression beyond day +365. One participant with biopsy–proven grade 1 acute gastrointestinal GVHD remained on immunosuppressive therapy until day +833. The second participant with chronic GVHD of skin and eyes remained on immunosuppressive therapy until day +573. No association was found between cell dose and the presence of grades 3 to 4 acute (P = .506) or moderate/severe chronic GVHD (P = .631).
Discussion
To our knowledge, we completed the first multicenter, international phase 2 trial of a nonmyeloablative haploidentical BMT with thiotepa and PTCy to cure children and adults with SCD. At least 90% of the children and adults with SCD had related eligible haploidentical donors, making our protocol immediately available for most individuals with SCD living in middle-high income countries that have a preexisting BMT unit. The results of our trial support our hypothesis of event-free survival of at least 80%, which was 82.6% after 2 years. The overall survival rates at 1 and 2 years were 95.7% and 94.1%, respectively, with no difference between children and adults.
Our treatment protocol was based on the extensive preclinical and early clinical research conducted at Johns Hopkins, demonstrating the potential for haploidentical transplant being a viable option for patients with hematologic malignancies initially16 and subsequently in individuals with severe hemoglobinopathies.9 A significant limitation of the Johns Hopkins haploidentical protocol for severe hemoglobinopathies was the presence of graft failure in 40% of the participants. Investigators at the initial 2 sites (Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris, France and Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN) initially elected to replicate the Johns Hopkins protocol regimen. Primary graft failure occurred in 3 of the first 5 participants (60%). We therefore elected to add a new agent, thiotepa (10 mg/kg), to the conditioning regimen, which resulted in significantly improved engraftment and event-free survival.10
The overall survival in this trial was comparable with that of a matched related myeloablative pediatric SCD BMT outcomes in a large multicenter French study, ∼95%.20 In 2 contemporary pediatric cohorts, the incidence death rate for children with SCD receiving medical care at a quaternary medical center in the United States and a national registry in France was 0.15 deaths per 100-person years.20,21 In comparison, in this trial, the incidence rate of death in children with SCD was 1.67 deaths per 100-person years, an 11-fold (1.67/0.15) increase when compared with the standard care. The mortality rates in children receiving maximal medical therapy vs the current haploidentical protocol suggest that when the primary focus is only on vital status over a 2-year period, the risk-benefit ratio tilts toward receiving maximum medical therapy at a comprehensive SCD center over haploidentical BMT. Our trial design was unable to include other potential transplant benefits such as quality of life, primary, and secondary stroke prevention.
In a contemporary cohort of adults with SCD in the United States, the death incidence rate is age-dependent.21 Among adults with SCD, those aged 18 to 36 years and >36 years have death incidence rates of 2.36 (95% CI, 1.57-3.42) and 4.72 (95% CI, 2.70-7.67) deaths per 100 person-years, respectively.21 The rate of death in the adults participating in this trial was 2.31 deaths per 100 person-years (95% CI, 0.46-6.75). The mortality rates in adults with SCD receiving medical therapy vs the current haploidentical protocol suggest that when the primary focus is only on vital status over 2 years, the risk-benefit ratio tilts toward our haploidentical BMT protocol over maximum medical therapy. For adults, our trial design was unable to address whether transplant exacerbated or attenuated the trajectory of heart, lung, and kidney disease, the major organs associated with death in adults.3,5,6
Our curative nonmyeloablative haploidentical therapy protocol therapy has 3 significant advantages compared with the current myeloablative gene therapy and gene editing treatment trials (supplemental Table 3).22,23 First, none of the adults in our phase 2 trial were excluded from the trial because of stroke or severe preexisting heart, lung, and kidney disease (supplemental Table 4).24 Second, the current relative cost of haploidentical transplant is anticipated to be approximately one-fifth of the cost for the curative myeloablative gene therapy and gene editing trials (estimated $432 157 vs minimally estimated $2.1 million).25,26 Third, our haploidentical protocol is readily available for children and adults with SCD living in middle- and high-income countries because of the familiarity of now routine haploidentical transplant protocol with PTCy. Furthermore, in Africa, where at least 70% of the world’s children with SCD are born, emerging African BM transplant centers may easily follow the protocol. We postulate that the costs, local expertise, the availability of these emerging curative therapies (nonmyeloablative haploidentical, myeloablative gene therapy, and gene editing), and the immediate, intermediate, and long-term health effects of these various curative regimens will influence the personal and health care system (the payor) decisions as to which curative therapy will be used.27
The results of our trial showed all participants designated as being cured had 100% full donor engraftment, and 97% were off immunosuppression at 1 year. The importance of a therapeutic goal of full donor engraftment is underscored by the recent observations that the goal of stable mixed chimerism after nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for SCD carries the risk of graft failure, which is associated with an increased incidence of myeloid malignancies.28-30 As expected, our low incidence of acute and chronic GVHD is similar to previous outcomes using nonmyeloablative haploidentical BMT with PTCy.8 The incidence of chronic GVHD in our trial was especially low in adult participants.
Unexpectedly, in our trial, all 8 graft failures (25%) occurred in participants aged <18 years. Importantly, none of the graft failures were associated with death, all had autologous reconstitution of their BM, and participants received a second haploidentical BMT; however, we did not include the outcomes of the second transplants in this consortium because our focus was on the first transplant. To improve the engraftment rate in children, the consortium was unwilling to add azathioprine preconditioning to the protocol because early results of adding a preconditioning regimen of azathioprine 3mg/kg per day and hydroxyurea 30 mg/kg per day to the current protocol demonstrated an increased risk of macrophage activation syndrome and were associated with an unacceptably high risk of death in children at 13.6% (3/22).31 Our protocol did not evaluate whether increasing the total body irradiation (TBI) dose from 200 cGy to 400 cGy might result in better engraftment in children with SCD compared with thiotepa alone. Preliminary results with a few participants of both approaches studied separately were comparable.10,32 Other strategies that may decrease graft failure in children with SCD that require systematic evaluation in a clinical trial setting include using higher dose total marrow irradiation instead of TBI to reduce overall organ toxicity/damage.33-35
Importantly, all 5 deaths in this trial were related to infectious complications, underlining the need for a better understanding of the kinetics of immune reconstitution and improving supportive care after nonmyeloablative haploidentical BMT. Unexpectedly, all deaths occurred in female recipients. Given that sex has not been a risk factor for death, further evaluation is warranted to understand whether this was a chance occurrence or other factors contributed to this pattern.
Most haploidentical transplant trials in individuals with SCD using PTCy are small, single-institution studies, with varying conditioning and stem cell source modifications.36-39 Bolanos-Meade et al sought to improve the main problem of primary graft failure noted in their initial report in 20129 by increasing the dose of TBI in their original nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen to 400 cGy from 200 cGy in transplant-eligible patients with severe hemoglobinopathies in a phase 2 study.32 Of the 17 participants enrolled, including both children and adults (median age, 16 years; range, 6-31), 12 (71%) had SCD, and 5 (29%) had transfusion-dependent thalassemia. A total of 13 (76%) developed full donor myeloid engraftment, with 3 (18%) having mixed chimerism and 1 (6%) having primary graft failure. These single-center haploidentical trials do not provide sufficient evidence to consider as standard therapy.
The phase 2 multicenter SCD haploidentical trial, sponsored by the National Institute of Health Blood Marrow Transplant–Clinical Transplant Network 1507 protocol, has recently been completed. This haploidentical transplant protocol also includes thiotepa and PTCy; however, the trial includes hydroxyurea preconditioning at 30 mg/kg per day from 70 days through 10 days before the transplant, regular blood transfusion to keep the hemoglobin S levels <30% and the hemoglobin levels >9.0 g/dL prior to the start of transplant conditioning. The recent results of the adult stratum of this multicenter trial, presented at the 2023 American Society for Hematology meeting, are similar to the adult stratum in our trial. The combined favorable results of the 2 adult haploidentical transplant protocols with thiotepa and PTCy with 80 participants provide the most robust evidence to date that this strategy is a readily available curative therapy for adults with SCD in a preexisting BMT program.40
A novel component of our trial was the use of the learning collaborative to initiate the trial, a process that we have used when addressing the clinical utility of regular blood transfusion for the secondary prevention of overt and silent strokes.41 The strength of the learning collaborative included keeping the primary outcome measures (graft failure and death) simple and verifiable. The intangible benefits include improved BMT supportive care measures for children and adults by sharing experiences during the initially weekly and now monthly meetings. A unique aspect of this clinical trial was that no site investigator received any funding to conduct this phase 2 trial.
A significant limitation of the learning collaborative was that some investigators elected not to follow the agreed-upon protocol due to local site investigators’ preferences, an option typically not permitted in a funded controlled trial (supplemental Table 4). Another limitation was the heterogeneity in the CMV prophylaxis, surveillance, and treatment. Further work is required to address this potentially modifiable risk factor of graft failure, particularly in children. Although our SCD curative therapy, to our knowledge, is by far the largest curative trial to date, with 70 evaluable participants with a median follow-up for ∼2 years, it is too short of an interval to know the full range of treatment-related morbidity and mortality. A long-term health-effects study is planned to address the late health effects of our haploidentical transplant protocol.
In a multicenter, international learning collaborative, we demonstrate that nonmyeloablative haploidentical BMT with thiotepa and PTCy is now a therapeutic curative option for adults with SCD in middle-high income BMT centers when compared with the less available, more restrictive adult entry criteria, and expensive myeloablative gene therapy and gene editing trials. For children, additional modifications in the conditioning regimens are required to decrease graft failure that is not associated with death.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by an intramural grant from the Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Stem Cell Transplantation at the Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the endowed chair funds from the Department of Pediatrics, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. Afolabi philanthropic funds supported data coordinator K.L.W. and the statistical analysis by M.R. Additionally, several hospital clinical research program grants supported local activities. Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) provided funding for the cost of the clinical studies.
GBT was not a cosponsor of either study.
Authorship
Contribution: A.A.K. and M.R.D. designed the trial; A.A.K., E.N., and M.R.D. wrote the drafts of the manuscript; J.d.l.F., K.L.W., A.S., R.V.G., C.B., B.P.S., B.H., M.J.E., R.H., N.D., F.A., M. Alzahrani, H.G.R., K.G., J.A.C., M. Aljurf, M.E., B.A., A.D.A., and E.D. reviewed and edited the manuscript; A.A.K., E.N., J.d.l.F., A.S., R.V.G., C.B., B.P.S., B.H., M.J.E., R.H., N.D., F.A., M. Alzahrani, H.G.R., K.G., J.A.C., M. Aljurf, M.E., B.A., A.D.A., and E.D enrolled and cared for participants; and M.R. completed the statistical analysis and reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: E.N. declares research funding, consultancy and speaker’s bureau fees from Novartis; and speaker’s bureau fee from Vertex. M. Alzahrani serves on the advisory boards for Novartis, Kite-Glead, MSD, and Amgen; and received an honorarium from Kite-Glead. M.E. declares research support from Global Blood Therapeutics and Pfizer. M.R.D. and his institution sponsored 2 externally funded research investigator-initiated projects (M.R.D. did not receive any compensation for the conduct of these 2 investigator-initiated observational studies); M.R.D. served as medical advisor in developing the CTX001 Early Economic Model; consulted for the Forma Pharmaceutical company about sickle cell disease in 2021 and 2022; and served on the steering committee for a Novartis-sponsored phase 2 trial to prevent priapism in men with sickle cell disease. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Adetola A. Kassim, Vanderbilt-Meharry Center of Excellence in Sickle Cell Disease, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, 3903 The Vanderbilt Clinic, 1301 Medical Center Dr, Nashville, TN 37232; email: adetola.kassim@vumc.org; and Michael R. DeBaun, Vanderbilt-Meharry Center of Excellence in Sickle Cell Disease Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, 2200 Children’s Way, 11206DOT, Nashville, TN 37232; email: m.debaun@vumc.org.
References
Author notes
Fully anonymized data may be shared upon request from any qualified investigator with an approved study and data transfer agreement between Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the institution. Please see the Resource Sharing Plan included in the supplemental file for additional details.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal