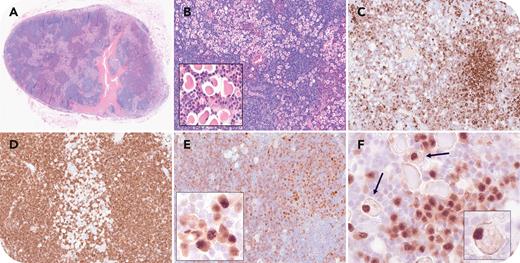
A 76-year-old woman underwent parotidectomy for squamous cell carcinoma. An adjacent lymph node revealed a vaguely nodular lymphoid infiltrate (panel A; hematoxylin and eosin [H&E] stain, original magnification ×20). Atypical plasmacytoid cells and histiocytes, both containing crystalline immunoglobulin inclusions, surrounded the lymphoid nodules (panel B; H&E stain, original magnification ×100 [inset; original magnification ×400]), and were expanded in the medullary cords. Lymphoid cells were positive for CD20 (panel C; original magnification ×200) with dimmer expression in the plasmacytoid component. Both cell types were CD5+ (panel D; original magnification ×200) and cyclin D1+ (panel E; original magnification ×200 [inset highlighting cyclin D1+ plasma cells; original magnification ×400]). Cells were negative for SOX11, CD56, CD10, and BCL6. MUM1 highlighted the plasmacytoid cells (panel F; original magnification ×400), which contained immunoglobulin (Ig) inclusions (panel F, arrows and inset; original magnification ×500). Plasmacytoid cells stained for IgA-κ but negative for Ig-λ, IgD, IgG, and IgM. Molecular studies were positive for a B-cell clone. Next-generation sequencing identified a CCND1::IGHJ3 fusion and mutation in BIRC3; MYD88 was wild-type.
The findings indicate involvement by mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), CD5/cyclin D1+, associated with an IgA-restricted plasma cell population, also positive for cyclin D1. The expression of IgA heavy chain is an atypical feature because most cases of MCL express IgM. The absence of SOX11 expression has been reported in MCL showing plasma cell differentiation, a feature that facilitates plasma cell differentiation.
For additional images, visit the ASH Image Bank, a reference and teaching tool that is continually updated with new atlas and case study images. For more information, visit https://imagebank.hematology.org.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal