Cryo-EM structure of the type I antiphospholipid antibody POmAb bound to the region R90-Y93 of kringle-1 of prothrombin is described.
By forcing prothrombin to open, type I antibodies prolong the clotting time with a new mechanism of action, acting as an anticoagulant.
Visual Abstract
Antiprothrombin antibodies are found in antiphospholipid patients, but how they interact with prothrombin remains elusive. Prothrombin adopts closed and open forms. We recently discovered type I and type II antibodies and proposed that type I recognizes the open form. In this study, we report the discovery and structural and functional characterization in human plasma of a type I antibody, POmAb (prothrombin open monoclonal antibody). Using surface plasmon resonance and single-molecule spectroscopy, we show that POmAb interacts with kringle-1 of prothrombin, shifting the equilibrium toward the open form. Using single-particle cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we establish that the epitope targeted by POmAb is in kringle-1, comprising an extended binding interface centered at residues R90-Y93. The 3.2-Å cryo-EM structure of the complex reveals that the epitope overlaps with the position occupied by the protease domain of prothrombin in the closed state, explaining the exclusive binding of POmAb to the open form. In human plasma, POmAb prolongs phospholipid-initiated and diluted Russell’s viper venom clotting time, which could be partly rescued by excess phospholipids, indicating POmAb is an anticoagulant but exerts a weak lupus anticoagulant effect. These studies reveal the structural basis of prothrombin recognition by a type I antiphospholipid antibody and uncover an exciting new strategy to achieve anticoagulation in human plasma.
Introduction
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by vascular thromboses in the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies.1-3 A prominent target of antiphospholipid antibodies is the clotting factor prothrombin.4-7 Prothrombin is the precursor of thrombin,8,9 which is essential for blood clot formation. Past studies have suggested a role of kringle domains,5,10,11 but how antiprothrombin (anti-PT) interacts with prothrombin remains poorly understood.
Recently, we discovered that prothrombin adopts closed and open forms at equilibrium12,13 and showed that these forms can be recognized by anti-PT antibodies using different mechanisms.14 Moreover, we identified 2 types of anti-PT antibodies,14 type I and type II, and proposed that type I recognizes the open form, whereas type II recognizes both forms. This study reports the discovery and structural and functional characterization of POmAb (prothrombin open monoclonal antibody), a type I anti-PT antiphospholipid antibody.
Study design
BALB/c mouse immunization experiments were performed with human fragment-1. Screening of clones and binding specificity was performed using an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), in which each protein of interest was immobilized into Nunc MAXISORP plates at 0.5 μg/well and binding was detected using 1:10 000 dilution of horseradish peroxidase–conjugated anti-mouse IgG (γ-chain specific) antibody. The cDNA of light and heavy chains of POmAb were cloned into pcDNA 3.4 as a mouse IgG1. The antibody was recombinantly produced in CHO cells and purified using protein A, followed by size exclusion chromatography. Prothrombin variants and fragments were produced as described previously.14,15 Binding affinities were measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) on a BIAcore-S200 instrument using a CM5 sensor chip in which antibodies were immobilized using N-hydroxysuccinimide/1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (NHS/EDC) chemistry. Titrations were performed by injecting increasing concentrations of prothrombin, prothrombin fragments, and prothrombin variants at a 25 μL/min flow rate. Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) measurements of freely diffusing prothrombin molecules labeled at residues 101 and 478 with the FRET pair Alexa555/Alexa647 were performed with a confocal microscope, MicroTime 200, equipped with pulsed interleaved excitation, as reported in previous publications.13,15,16 Phospholipid-binding experiments were performed by SPR, as described previously.14,17 Fab of POmAb in complex with prothrombin was purified on size exclusion chromatography. The complex (0.33 mg/mL) was applied onto 300-mesh Quantifoil 2/2 holey grids before plunge freezing in liquid ethane on an FEI Vitrobot Mark IV. Grids were loaded onto a Titan Krios G3 cryogenic transmission electron microscope operating at 300 kV and equipped with an FEI Falcon IV direct electron detector. Screening and data collection were performed at a pixel size of 1.081 Å, using a dose of 62.2 e−/Å2 across 40 frames, using a set defocus range of −1 to −2.4 μm. Micrographs were imported and processed using cryoSPARC.18 Activated partial thromboplastin time was measured using the CEPHEN APTT kit on an ST4 semiautomated coagulometer. Dilute Russell’s viper venom time was measured using the HEMOCLOT LA-S and LA-C kits on an ST4 semiautomated coagulometer. Prothrombin activation was monitored using a colorimetric assay that continuously reports the amount of thrombin that is generated on cleavage by the prothrombinase complex.13,19 Prothrombin activation was also monitored by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, as detailed elsewhere.13,19 More details are available in the supplemental Information (available on the Blood website).
Results and discussion
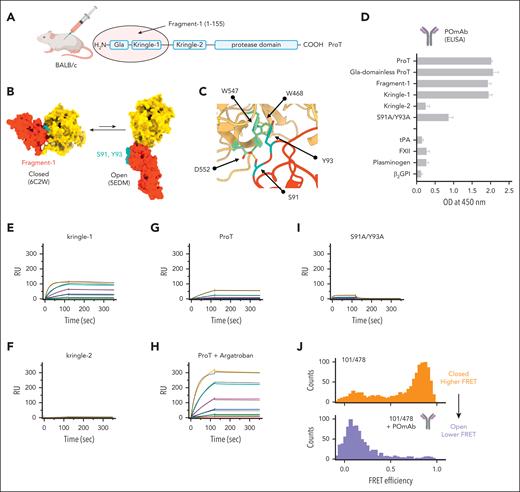
Guided by our recent findings,14,16 we conducted research on available antibodies and created new ones by immunizing mice with fragment-1 of human prothrombin (Figure 1A). Antibodies were tested by ELISA against fragment-1, prothrombin, gla-domainless prothrombin, kringle-1, kringle-2, and the prothrombin variant S91A/Y93A, which carries 2 mutations in kringle-1, S91A and Y93A. Residues S91 and Y93 constitute an ideal epitope for a type I antibody. They are exposed in the open but hidden in the closed form (Figure 1B), where they interact with residues W468, W547, and D552 of the protease domain (Figure 1C).12,15
Discovery and biochemical characterization of POmAb. (A) Human prothrombin (Uniprot entry: P00734) is made of 4 domains, which are connected by 3 linkers. Fragment-1, comprising residues 1-155, was injected into BALB/c mice for immunization experiments. (B) Conformational equilibrium of prothrombin (ProT), showing large relocation of fragment-1 (red) relative to the protease domain (yellow) as prothrombin transitions from closed to open forms and strategic location of residues S91 and Y93 in kringle-1 (cyan). (C) Closed-up view of the interface between kringle-1 (red) and protease domain (yellow) that forms in closed prothrombin, highlighting key interactions (yellow lines) of residues S91 and Y93 in kringle-1 (cyan) with residues W468, W547, and D552 (green) of the protease domain. (D) Characterization of POmAb by ELISA. POmAb was incubated with specified proteins, and binding was detected with an anti-mouse γ-specific IgG antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase and TMB (3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine) substrate. Each binding experiment was independently repeated a minimum of 3 times. (E-I) Surface plasmon resonance experiments. Shown are reference-subtracted real-time association and dissociation profiles resulting from flowing kringle-1 (0-1000 nM) (E), kringle-2 (0-1000 nM) (F), prothrombin (0-1000 nM) (G), prothrombin (0-1000 nM) with 200 μM argatroban (H), and prothrombin variant S91A/Y93A (0-2000 nM) (I) onto immobilized POmAb. Fit is shown in black. Rate constants obtained by fitting the sensograms are reported in supplemental Table 1. (J) FRET histograms of prothrombin labeled at residues 101 in kringle-1 and 478 in the serine protease domain in the absence (orange; top) and presence of 500 nM POmAb (purple; bottom). β2GPI, β2-glycoprotein I; FXII, factor XII; RU, resonance units; tPA, tissue-type plasminogen activator.
Discovery and biochemical characterization of POmAb. (A) Human prothrombin (Uniprot entry: P00734) is made of 4 domains, which are connected by 3 linkers. Fragment-1, comprising residues 1-155, was injected into BALB/c mice for immunization experiments. (B) Conformational equilibrium of prothrombin (ProT), showing large relocation of fragment-1 (red) relative to the protease domain (yellow) as prothrombin transitions from closed to open forms and strategic location of residues S91 and Y93 in kringle-1 (cyan). (C) Closed-up view of the interface between kringle-1 (red) and protease domain (yellow) that forms in closed prothrombin, highlighting key interactions (yellow lines) of residues S91 and Y93 in kringle-1 (cyan) with residues W468, W547, and D552 (green) of the protease domain. (D) Characterization of POmAb by ELISA. POmAb was incubated with specified proteins, and binding was detected with an anti-mouse γ-specific IgG antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase and TMB (3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine) substrate. Each binding experiment was independently repeated a minimum of 3 times. (E-I) Surface plasmon resonance experiments. Shown are reference-subtracted real-time association and dissociation profiles resulting from flowing kringle-1 (0-1000 nM) (E), kringle-2 (0-1000 nM) (F), prothrombin (0-1000 nM) (G), prothrombin (0-1000 nM) with 200 μM argatroban (H), and prothrombin variant S91A/Y93A (0-2000 nM) (I) onto immobilized POmAb. Fit is shown in black. Rate constants obtained by fitting the sensograms are reported in supplemental Table 1. (J) FRET histograms of prothrombin labeled at residues 101 in kringle-1 and 478 in the serine protease domain in the absence (orange; top) and presence of 500 nM POmAb (purple; bottom). β2GPI, β2-glycoprotein I; FXII, factor XII; RU, resonance units; tPA, tissue-type plasminogen activator.
One antibody, which we named POmAb, reacted well against fragment-1, prothrombin, gla-domainless prothrombin, and kringle-1 but showed a significantly reduced binding activity for the variant S91A/Y93A (Figure 1D). It also failed to interact with kringle-2 and plasma proteins containing analogous kringle domains (namely, plasminogen, tissue plasminogen activator, and factor XII), as well as β2-glycoprotein I, a major antigen of antiphospholipid antibodies in APS1,20 (Figure 1D). This indicates that POmAb is specific for kringle-1 of prothrombin.
After recombinantly expressing POmAb (supplemental Figure 1), we used SPR to confirm results obtained by ELISA and determine affinity toward kringle-1. We found that POmAb binds kringle-1 with high affinity (dissociation constant [Kd] = 5.3 nM) (Figure 1E, supplemental Table 1), and, as expected, it fails to bind kringle-2 (Figure 1F). We next investigated whether POmAb prefers the open form. To this end, we repeated SPR experiments using prothrombin in the absence (Figure 1G) and presence of the active site ligand argatroban (Figure 1H). We previously showed that argatroban shifts the conformation of closed prothrombin to the open form, resulting in kringle-1 exposure.12,15 SPR documented that, in the presence of argatroban, POmAb binds significantly faster to open prothrombin, with on and off rates similar to those of kringle-1 (supplemental Table 1). This indicates that the epitope recognized by POmAb preexists, is available in the open form, but is inaccessible in the closed form. SPR also confirmed that the binding of POmAb to the variant S91A/Y93A was reduced because of a faster dissociation rate (Figure 1I). Without residues S91 and Y93, the antibody rapidly binds to prothrombin but cannot remain bound to it.
To confirm that POmAb binds the open form, we performed single-molecule FRET experiments using the FRET pair 101-478 (Figure 1J). In the unbound form, 101-478 shows high FRET, which is a signature of the closed form.12,13,15 However, on the addition of POmAb, the FRET signal quantitatively shifted toward lower FRET. This indicates that POmAb interacts with kringle-1 only when prothrombin is open, shifting the equilibrium toward this form.
To visualize the binding interface, we solved the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the Fab fragment of POmAb bound to prothrombin (Figure 2). Two-dimensional classification showed particles containing the Fab region of POmAb and a small portion of prothrombin, not the entire molecule (supplemental Figure 2). This indicates that on binding, prothrombin remains flexible, except for the region bound by or adjacent to the Fab. In keeping with this interpretation, the density map displayed unequivocal density for the POmAb Fab constant (heavy and light) and variable (heavy [VH] and light [VL]) domains and for kringle-1, with some weak density for the Gla domain (supplemental Figure 3). In contrast, no density was found for kringle-2 and the protease domain.
Cryo-EM structure of POmAb bound to prothrombin. (A) Fab fragment of POmAb comprising heavy (purple; heavy [HC] and VH) and light (violet; light [LC] and VL) chains bound to kringle-1 (cyan). (B) Interacting surfaces of kringle-1 (top) and Fab (bottom) colored according to the electrostatic potential (blue = electropositive, red = electronegative). Note how residue R90 in kringle-1 is attracted by residue D314 of the antibody, resulting in electrostatic complementarity. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions are mediated by Y93 in kringle-1 and a cluster of tyrosine residues (Y92, Y248, Y250, and Y274), and in the antibody, they provide additional binding energy. (C) Zoom-in of the binding interface between kringle-1 (cyan) and POmAb (purple). Shown are energetically favorable interactions between the 2 proteins. Antibody residues are shown in wheat. (D) Crystal structure of the closed form of prothrombin solved at 4.1-Å resolution (6C2W.pdb; yellow) overlayed on the 3.2-Å cryo-EM structure of the POmAb/kringle-1 complex shows how the protease domain clashes against the antibody. Binding of the protease domain and POmAb to residues R90-Y93 of kringle-1 is mutually exclusive.
Cryo-EM structure of POmAb bound to prothrombin. (A) Fab fragment of POmAb comprising heavy (purple; heavy [HC] and VH) and light (violet; light [LC] and VL) chains bound to kringle-1 (cyan). (B) Interacting surfaces of kringle-1 (top) and Fab (bottom) colored according to the electrostatic potential (blue = electropositive, red = electronegative). Note how residue R90 in kringle-1 is attracted by residue D314 of the antibody, resulting in electrostatic complementarity. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions are mediated by Y93 in kringle-1 and a cluster of tyrosine residues (Y92, Y248, Y250, and Y274), and in the antibody, they provide additional binding energy. (C) Zoom-in of the binding interface between kringle-1 (cyan) and POmAb (purple). Shown are energetically favorable interactions between the 2 proteins. Antibody residues are shown in wheat. (D) Crystal structure of the closed form of prothrombin solved at 4.1-Å resolution (6C2W.pdb; yellow) overlayed on the 3.2-Å cryo-EM structure of the POmAb/kringle-1 complex shows how the protease domain clashes against the antibody. Binding of the protease domain and POmAb to residues R90-Y93 of kringle-1 is mutually exclusive.
The structure was solved at a nominal resolution of 3.2 Å (supplemental Table 2), with high resolution at the binding interface approaching 2.7 Å (supplemental Figure 2). Analysis of the de novo model built in the density revealed that the interface is centered around residues R90-Y93 of kringle-1 (Figure 2A) and stabilized by electrostatic interactions (Figure 2B), with a buried surface area of ≈850 Å2. Most complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) participate in forming the binding interface. Key interactions occur between residues E111 in kringle-1 with Y92 and Y274 of the antibody and R90 with D314 in the CDR3 loop of the POmAb VH domain (Figure 2C). Residue Y93 of kringle-1 engages in hydrogen bonding with residue N54 in the CDR2 loop of the POmAb VL domain, whereas S91 interacts with Q318 in the CDR3 loop of the POmAb VH domain, explaining why substitution of these residues to alanine results in loss of binding. The complete list of the intermolecular contacts is in supplemental Table 3. Superposition of the cryo-EM structure of POmAb bound to kringle-1 with the X-ray crystal structure of the closed form of prothrombin15 reveals why POmAb cannot bind with this conformation (Figure 2D, supplemental Figure 4). By interacting with kringle-1, the antibody clashes against the protease domain, forcing prothrombin to remain open.
Some antibodies against prothrombin (ie, anti-phosphatidylserine/prothrombin antibodies [aPS/PT]) strongly correlate with lupus anticoagulant (LA).6,21-25 LA is a laboratory test that indicates a phospholipid-dependent prolongation of clotting time, which is rescued by additional phospholipids. LA is believed to occur because of antibody-mediated dimerization of prothrombin, which competes with the binding of clotting factors for phospholipid surfaces.24-26 Consistent with this knowledge and our previous results,14 we found that IgG of POmAb increased the binding of prothrombin wild type to negatively charged liposomes (Figure 3A) but not the variant S91A/Y93A, which weakly binds to it. This effect was not seen with the Fab fragment, which, unlike IgG, is monovalent. However, both IgG and Fab resulted in a dose-dependent prolongation of the clotting time initiated by the activator cephalin (Figure 3B). Furthermore, the IgG prolonged the dilute Russell’s viper venom time, but this effect was only partly corrected by adding excess phospholipids (Figure 3C). This indicates that POmAb is an anticoagulant in human plasma but produces a modest LA phenomenon. To verify that the prolongation was because of specific prothrombin binding, we used prothrombin-deficient plasma supplemented with either prothrombin wild type or the variant S91A/Y93A. As expected, this effect was only present with prothrombin wild type but not with the variant S91A/Y93A (Figure 3D).
POmAb exerts an anticoagulant effect in human plasma by forcing prothrombin (PT) to open. (A) Antibody-stimulated binding of prothrombin wild type (WT; 250 nM; red) and variant S91A/Y93A (250 nM; blue) to negatively charged liposomes (POPC:POPS 80:20) monitored by SPR. IgG and Fab POmAb were used at 2.5 μg/mL. Values of fold increase were determined using the formula: RUIgG/Fab/RUfree at 115 seconds. The horizontal dotted line set at y = 1.0 indicates there is no effect of the treatment. Raw data are shown in supplemental Figure 7. (B) Activated partial thromboplastin time of human plasma measured at increasing concentrations of POmAb IgG (blue) and Fab (red) (0-5 μM). (C) Dilute Russell’s viper venom time expressed as normalized LA ratio, as per manufacturer’s instructions. Shown are normal control (CTRL) plasma (negative [-ve] CTRL), LA-control plasma (positive [+ve] CTRL), and normal control plasma supplemented with 1 μM POmAb. The horizontal dotted line set at y = 1.2 indicates the threshold provided by the manufacturer for considering a specimen LA positive (above threshold) or negative (below threshold). (D) Clotting time measured prothrombin-deficient plasma supplemented with prothrombin wild type or the variant S91A/Y93A. (E) Continuous assay monitoring of the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin by prothrombinase complex. The assay started with the addition of 2.5 pM factor Xa to 25 nM prothrombin that was preincubated for 20 minutes with 20 μM phospholipids, 2 nM cofactor Va, and increasing concentrations of Fab (0-2 μM). The release of p-nitroaniline on hydrolysis of FPF (H-D-Phe-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide) was monitored at 405 nm.19 (F) Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the conversion of prothrombin (1.25 μM) to thrombin by the prothrombinase complex (0.2 nM factor Xa, 20 μM phospholipids, and 10 nM cofactor Va) in the absence and presence of 1.5 μM Fab POmAb, which shows as 2 bands at 25 kDa because of the presence of reducing agent. The disappearance of PT (72-kDa band) is slower in the presence of Fab and is linked to lower accumulation of B-chain (28 kDa) and A-chain (6 kDa), which are signatures of thrombin. Moreover, in the presence of Fab, there is significantly more accumulation of a band at 50 kDa (black arrow), compatible with cleavage at R155 and the formation of prethrombin-1.9,19 (G) Proposed mechanism of action of POmAb resulting in anticoagulation. Note that prothrombin circulates mostly in closed form. Our SPR data with Fab in A suggest that, on binding to phospholipids, prothrombin does spontaneously open. Thus, it requires POmAb to decisively shift the equilibrium toward the open form.∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, not significant; PTC, prothrombinase complex.
POmAb exerts an anticoagulant effect in human plasma by forcing prothrombin (PT) to open. (A) Antibody-stimulated binding of prothrombin wild type (WT; 250 nM; red) and variant S91A/Y93A (250 nM; blue) to negatively charged liposomes (POPC:POPS 80:20) monitored by SPR. IgG and Fab POmAb were used at 2.5 μg/mL. Values of fold increase were determined using the formula: RUIgG/Fab/RUfree at 115 seconds. The horizontal dotted line set at y = 1.0 indicates there is no effect of the treatment. Raw data are shown in supplemental Figure 7. (B) Activated partial thromboplastin time of human plasma measured at increasing concentrations of POmAb IgG (blue) and Fab (red) (0-5 μM). (C) Dilute Russell’s viper venom time expressed as normalized LA ratio, as per manufacturer’s instructions. Shown are normal control (CTRL) plasma (negative [-ve] CTRL), LA-control plasma (positive [+ve] CTRL), and normal control plasma supplemented with 1 μM POmAb. The horizontal dotted line set at y = 1.2 indicates the threshold provided by the manufacturer for considering a specimen LA positive (above threshold) or negative (below threshold). (D) Clotting time measured prothrombin-deficient plasma supplemented with prothrombin wild type or the variant S91A/Y93A. (E) Continuous assay monitoring of the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin by prothrombinase complex. The assay started with the addition of 2.5 pM factor Xa to 25 nM prothrombin that was preincubated for 20 minutes with 20 μM phospholipids, 2 nM cofactor Va, and increasing concentrations of Fab (0-2 μM). The release of p-nitroaniline on hydrolysis of FPF (H-D-Phe-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide) was monitored at 405 nm.19 (F) Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the conversion of prothrombin (1.25 μM) to thrombin by the prothrombinase complex (0.2 nM factor Xa, 20 μM phospholipids, and 10 nM cofactor Va) in the absence and presence of 1.5 μM Fab POmAb, which shows as 2 bands at 25 kDa because of the presence of reducing agent. The disappearance of PT (72-kDa band) is slower in the presence of Fab and is linked to lower accumulation of B-chain (28 kDa) and A-chain (6 kDa), which are signatures of thrombin. Moreover, in the presence of Fab, there is significantly more accumulation of a band at 50 kDa (black arrow), compatible with cleavage at R155 and the formation of prethrombin-1.9,19 (G) Proposed mechanism of action of POmAb resulting in anticoagulation. Note that prothrombin circulates mostly in closed form. Our SPR data with Fab in A suggest that, on binding to phospholipids, prothrombin does spontaneously open. Thus, it requires POmAb to decisively shift the equilibrium toward the open form.∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, not significant; PTC, prothrombinase complex.
The discovery that Fab of POmAb has an anticoagulant effect similar to that of the whole IgG is intriguing. It shows that the mechanism resulting in the prolongation of clotting time is more complex than just sequestration of phospholipids. To investigate this further, we monitored prothrombin conversion to thrombin in vitro using purified components. In a continuous kinetic assay,15 we found that Fab POmAb inhibited prothrombin conversion to thrombin by prothrombinase in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3E). However, inhibition never reached completion, even when excess Fab POmAb was used compared with prothrombin. Prothrombin is cleaved by factor Xa at residues R155, R271, and R320 to generate thrombin.9,12,15,27 Gel-electrophoresis experiments in Figure 3F confirmed the inhibitory effect of Fab POmAb and showed an altered activation pathway, with more cleavage at R155. Thus, Fab of POmAb lowers thrombin generation by modulating prothrombin conformation rather than blocking its interaction with prothrombinase (Figure 3G). This novel mechanism of action may result in a new class of anticoagulants.
Our data suggest that a significant portion of the anticoagulant effect of IgG POmAb stems from stabilization of the open form. To test if this model applies to other type I antibodies, we identified a new monoclonal antibody, 5B10. Like POmAb, 5B10 binds kringle-1. But unlike POmAb, 5B10 is insensitive to the mutations S91A and Y93A. Despite binding a different epitope, 5B10 stabilized the open form, resulted in mild anticoagulation in human plasma, and produced a weak LA effect, just like POmAb (supplemental Figure 5). POmAb and 5B10 emerge from this study as promising tools to investigate the role of type I antibodies and prothrombin dynamics in vitro and in vivo.
A final comment goes to the role of type I antibodies as contributors to LA. Although we found type I antibodies while screening for subpopulations of aPS/PT in thrombotic patients with APS who were positive for LA,14 our data with POmAb and 5B10 suggest that type I antibodies are minor contributors to LA. This implies that antibodies other than type I play a greater role in this test. New findings with the monoclonal anti–kringle-2 antibody AHP, shown in supplemental Figure 6, support this view. Unlike POmAb and 5B10, AHP binds closed and open forms of prothrombin with similar affinity and produces a strong LA effect. These findings reveal fundamental differences between different subtypes of anti-PT antibodies, provide new insights into the mechanism underlying LA in patients with APS, and set the stage for future mechanistic studies.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants R01 HL150146 (N.P.) and R35 HL135775 (R.F.) from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; a grant from the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences (JIT839 [N.P.]), which is, in part, supported by the NIH, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; Clinical and Translational Science Award grant UL1 TR002345; and the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Saint Louis University. B.S. and K.B. are supported by the Washington University Center for Cellular Imaging, which is funded, in part, by Washington University School of Medicine, Children’s Discovery Institute of Washington University, and St. Louis Children’s Hospital (CDI-CORE-2015-505 and CDI-CORE-2019-813), the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital (3770), Washington University Diabetes Research Center (DK020579), and the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine (CA091842).
Authorship
Contribution: N.P. designed the research; S.K. and N.P. performed the research and solved the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure; B.S. and K.B. collected cryo-EM data and helped solve the structure; N.P. wrote the manuscript; S.K., N.P., R.F., and V.P. analyzed and interpreted the data and edited the manuscript; and all authors reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.P. and R.F. are pursuing a provisional patent application for type I anti-PT antibodies and their antibody fragments for use in composition, diagnostics, and clinical applications. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Nicola Pozzi, Edward A. Doisy Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, 1100 South Grand Blvd, St. Louis, MO 63104; email: nicola.pozzi@health.slu.edu.
References
Author notes
All data are contained in the article. Map files and structural coordinates have been deposited in publicly available databanks.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


![Cryo-EM structure of POmAb bound to prothrombin. (A) Fab fragment of POmAb comprising heavy (purple; heavy [HC] and VH) and light (violet; light [LC] and VL) chains bound to kringle-1 (cyan). (B) Interacting surfaces of kringle-1 (top) and Fab (bottom) colored according to the electrostatic potential (blue = electropositive, red = electronegative). Note how residue R90 in kringle-1 is attracted by residue D314 of the antibody, resulting in electrostatic complementarity. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions are mediated by Y93 in kringle-1 and a cluster of tyrosine residues (Y92, Y248, Y250, and Y274), and in the antibody, they provide additional binding energy. (C) Zoom-in of the binding interface between kringle-1 (cyan) and POmAb (purple). Shown are energetically favorable interactions between the 2 proteins. Antibody residues are shown in wheat. (D) Crystal structure of the closed form of prothrombin solved at 4.1-Å resolution (6C2W.pdb; yellow) overlayed on the 3.2-Å cryo-EM structure of the POmAb/kringle-1 complex shows how the protease domain clashes against the antibody. Binding of the protease domain and POmAb to residues R90-Y93 of kringle-1 is mutually exclusive.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/19/10.1182_blood.2023022942/2/m_blood_bld-2023-022942-gr2.jpeg?Expires=1765115856&Signature=qFcBSfCO0siaYwoJnokGOY9tim5YNNp5ekSzpcsLOM6YIf8qbywJxfp3g78iXaOwkrTfsXfZGu6l46S92l2qeW~E5-LNqy7LoAoHDrvrl~MbccVJ3Uc5EZYeni2tfAtJvx~7BumNK~yfuUpXSEjos4gaPuAP5BGCK2nSaiqKvrSNHS30DZtswE02s-n95D7XUctu68~ki1eSonXCnbl4pTxKDkw9JpKbN6NbE9tXQ3mbtNaw23ddOgLAvDrP~y72Rk8umR7H7wr~rPNGF8R0kElS1wz8C4m5OG0N-96G~xxtFnz7ouT6LWn3ZvdsCTYj7KKqeKhAHVMyIzbjU7eOUQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![POmAb exerts an anticoagulant effect in human plasma by forcing prothrombin (PT) to open. (A) Antibody-stimulated binding of prothrombin wild type (WT; 250 nM; red) and variant S91A/Y93A (250 nM; blue) to negatively charged liposomes (POPC:POPS 80:20) monitored by SPR. IgG and Fab POmAb were used at 2.5 μg/mL. Values of fold increase were determined using the formula: RUIgG/Fab/RUfree at 115 seconds. The horizontal dotted line set at y = 1.0 indicates there is no effect of the treatment. Raw data are shown in supplemental Figure 7. (B) Activated partial thromboplastin time of human plasma measured at increasing concentrations of POmAb IgG (blue) and Fab (red) (0-5 μM). (C) Dilute Russell’s viper venom time expressed as normalized LA ratio, as per manufacturer’s instructions. Shown are normal control (CTRL) plasma (negative [-ve] CTRL), LA-control plasma (positive [+ve] CTRL), and normal control plasma supplemented with 1 μM POmAb. The horizontal dotted line set at y = 1.2 indicates the threshold provided by the manufacturer for considering a specimen LA positive (above threshold) or negative (below threshold). (D) Clotting time measured prothrombin-deficient plasma supplemented with prothrombin wild type or the variant S91A/Y93A. (E) Continuous assay monitoring of the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin by prothrombinase complex. The assay started with the addition of 2.5 pM factor Xa to 25 nM prothrombin that was preincubated for 20 minutes with 20 μM phospholipids, 2 nM cofactor Va, and increasing concentrations of Fab (0-2 μM). The release of p-nitroaniline on hydrolysis of FPF (H-D-Phe-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide) was monitored at 405 nm.19 (F) Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the conversion of prothrombin (1.25 μM) to thrombin by the prothrombinase complex (0.2 nM factor Xa, 20 μM phospholipids, and 10 nM cofactor Va) in the absence and presence of 1.5 μM Fab POmAb, which shows as 2 bands at 25 kDa because of the presence of reducing agent. The disappearance of PT (72-kDa band) is slower in the presence of Fab and is linked to lower accumulation of B-chain (28 kDa) and A-chain (6 kDa), which are signatures of thrombin. Moreover, in the presence of Fab, there is significantly more accumulation of a band at 50 kDa (black arrow), compatible with cleavage at R155 and the formation of prethrombin-1.9,19 (G) Proposed mechanism of action of POmAb resulting in anticoagulation. Note that prothrombin circulates mostly in closed form. Our SPR data with Fab in A suggest that, on binding to phospholipids, prothrombin does spontaneously open. Thus, it requires POmAb to decisively shift the equilibrium toward the open form.∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, not significant; PTC, prothrombinase complex.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/19/10.1182_blood.2023022942/2/m_blood_bld-2023-022942-gr3.jpeg?Expires=1765115856&Signature=rfYsJC4OXm21p-eE~Y4-Kxd12V3dCYtWel4od7TVniGOu1Y8zkPZIQcQeNhXi~~fsU-DsPc~EX7rEWnluOEDNSkpVQEHZtHHwaLlHj-xV8s-0uKgkJdOj4mMM21rrVPAUEK4Ol9y9uqXUDwfNCJGR9Vp3eFOrZEMCq3Z5192dDcOzMZbPs-RKLGrUFctZUrGb5NJypoeCFf8TbXs0~EqGNAYCQJhqf9ZNCfknQk3I2JAkQWamtZzqvqOuoPaccUYGvD9ttLnAh9fEhHNI0IwxanK6WoIc8ne8wlLgIa0X1ndUy1aTaTqw8hM3rnLoXyRmGCzohPMZpB5InvMkWNCeA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal