Hematological malignancies express high levels of CLEC2D, the inhibitory ligand for CD161.
Fully human CD161 mAbs enhance T-cell– and natural killer cell–mediated immunity.
Visual Abstract
The CD161 inhibitory receptor is highly upregulated by tumor-infiltrating T cells in multiple human solid tumor types, and its ligand, CLEC2D, is expressed by both tumor cells and infiltrating myeloid cells. Here, we assessed the role of the CD161 receptor in hematological malignancies. Systematic analysis of CLEC2D expression using the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia revealed that CLEC2D messenger RNA was most abundant in hematological malignancies, including B-cell and T-cell lymphomas as well as lymphocytic and myelogenous leukemias. CLEC2D protein was detected by flow cytometry on a panel of cell lines representing a diverse set of hematological malignancies. We, therefore, used yeast display to generate a panel of high-affinity, fully human CD161 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that blocked CLEC2D binding. These mAbs were specific for CD161 and had a similar affinity for human and nonhuman primate CD161, a property relevant for clinical translation. A high-affinity CD161 mAb enhanced key aspects of T-cell function, including cytotoxicity, cytokine production, and proliferation, against B-cell lines originating from patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and Burkitt lymphoma. In humanized mouse models, this CD161 mAb enhanced T-cell–mediated immunity, resulting in a significant survival benefit. Single cell RNA-seq data demonstrated that CD161 mAb treatment enhanced expression of cytotoxicity genes by CD4 T cells as well as a tissue-residency program by CD4 and CD8 T cells that is associated with favorable survival outcomes in multiple human cancer types. These fully human mAbs, thus, represent potential immunotherapy agents for hematological malignancies.
Introduction
Targeting of the most widely studied T-cell inhibitory receptors, PD-1 and CTLA-4, has led to remarkable clinical responses in some cancer types, but other cancer types remain largely refractory to immune checkpoint blockade.1-3 It is, therefore, important to discover alternative pathways responsible for escape from tumor immunity. CD161 (NKR-P1A) was initially shown to inhibit natural killer (NK) cell–mediated cytotoxicity of tumor cells, and CLEC2D (alternatively named lectin-like transcript 1; LLT1) was identified as its ligand.4,5 CD161 and CLE2D are type 2 transmembrane, disulfide-linked homodimers with C-type lectin extracellular (EC) domains.6,7 We recently demonstrated that CD161 was highly upregulated by tumor-infiltrating CD8 and CD4 T cells in glioblastoma and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-mutant gliomas, with >90% of infiltrating CD8 T cells expressing this inhibitory receptor. Single cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) analysis demonstrated broad expression of KLRB1 (encoding CD161 protein) among CD8 and CD4 T cells but minimal expression by FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in multiple solid tumors, including non–small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and melanoma.8,9 ScRNA-seq analysis of hepatocellular cancer showed that KLRB1 was more highly expressed in relapsed than in primary tumors, and CD161+ CD8 T cells were present at a higher density in relapsed tumors.10,KLRB1 was also upregulated by chimeric antigen receptor T cells repetitively stimulated with tumor cells in an in vitro model of T-cell exhaustion, along with multiple other genes encoding NK cell receptors.11 These data indicate that CD161 represents a potential therapeutic target for human tumors by enhancing the antitumor function of both T cells and NK cells. Engagement of both T and NK cells is an attractive approach because tumors frequently escape the cytotoxic action of CD8 T cells by downregulation or loss of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) expression. MHC-I deficient tumors can be targeted by NK cells.12
Several lines of evidence support a potential role of the CD161-CLEC2D pathway in hematological malignancies. CLEC2D was shown to be upregulated after activation of dendritic cells and B cells with toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands,13,14 and CLEC2D expression was also induced in B cells after Epstein-Barr virus infection.15 Immunohistochemistry analysis demonstrated high-level expression of CLEC2D by germinal-center B cells; CLEC2D was also expressed in multiple B-cell malignancies, including Burkitt lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).16 Furthermore, a recent study demonstrated that high frequencies of T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains and CD161-expressing CD4 T cells were associated with subsequent relapse from acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) after bone marrow transplantation.17 In this study, we developed a panel of fully human CD161-blocking monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and used these mAbs to investigate the functional role of the CD161-CLEC2D pathway in inhibiting T-cell function in hematological malignancies.
Materials and methods
Generation of human CD161 mAbs by yeast display
A human single-chain variable fragment yeast library with a diversity of 109 clones was generated as previously described.18-20 Initial selection was performed with 3 rounds of negative and positive selection on 10-fold diversity at each round using Biotin-Binder Dynabeads (Thermo). Negative selection was performed against Dynabeads and then human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1)-Fc–coated Dynabeads. Subsequently, positive selection was performed with CD161-Ig–coated Dynabeads in the presence of soluble human IgG1-Fc (1 μM). The enriched populations were incubated with chicken anti-cMyc antibody (Exalpha) and biotinylated CD161-Ig (1 μM), followed by fluorophore-conjugated goat anti–chicken secondary antibody and streptavidin (Thermo). Cells were sorted using a BD FACSAria II. Affinity maturation was performed as previously described.19,20
Cytotoxicity assays with tumor cells and T cells
NY-ESO-1 T-cell receptor–positive (TCR+) CD161+ T cells were first incubated with CD161 or isotype control antibodies for 2 to 16 hours at the indicated antibody concentration, before coculture with NY-ESO-1–expressing tumor cells at the indicated effector-to-target ratios. For cytotoxicity assays, after 4 hours in coculture, Precision Count Beads (BioLegend) were added at a 1:1 ratio to tumor cells, followed by incubation with CellEvent caspase-3/7 (ThermoFisher Scientific) and Zombie dye. Cells were then stained for CD19 and CD3 before flow cytometric analysis. Percentage of tumor killing was calculated by counting cleaved caspase-3/7+ cells (early apoptosis) among CD19+ CD3neg tumor cells. For T-cell proliferation assays, NY-ESO-1 TCR+ CD161+ T cells were prestained with CellTrace Violet (CTV) proliferation dye (Life Technologies) before coculture. T-cell proliferation was quantified using FlowJo Proliferation package based on CTV dilution.
Humanized mouse models of advanced leukemia and lymphoma
NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ NSG mice obtained from The Jackson Laboratory were housed in pathogen-free conditions, and experiments were performed in compliance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (protocol 08-049). Healthy naïve female mice (6-10 weeks) were injected IV with 2.5 × 105 NY-ESO-1+ Raji tumor cells or 1 × 106 NY-ESO-1+ NALM-1 tumor cells. Tumor burden was monitored by bioluminescence in vivo imaging. Mice were injected subcutaneously with D-luciferin (150 mg/kg; Perkin Elmer) and imaged after 8 minutes. Mice were randomized to treatment groups based on average signal intensity (photons per second) in the hind limbs (day 5 for Raji model and day 21 for NALM-1 model) to ensure equal disease burden across groups. Mice were then IV injected with NY-ESO-1-TCR+ CD161+ T cells at the indicated cell doses. Bioluminescence was performed weekly, and signal intensity was quantitated as photons per second over the entire body. Mice were monitored daily and euthanized upon reaching predetermined clinical endpoints.
Additional materials and methods are included in the supplemental Materials, available on the Blood website.
Results
Generation of human CD161 mAbs by yeast display
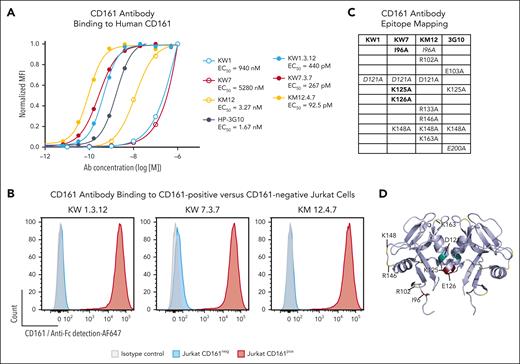
We screened a human single-chain variable fragment yeast display library with a diversity of 109 clones to generate mAbs that block the CD161-CLEC2D interaction.18 After enrichment using magnetic beads and flow cytometry, we identified 3 unique clones termed KW1, KW7, and KM12 that bound to the soluble CD161-Ig fusion protein. A minimum of 3 rounds of affinity maturation were performed on individual clones to enhance affinity for CD161. When expressed as human IgG1 mAbs, all 3 parental clones and their affinity-matured versions bound to CD161+ Jurkat cells but not to CD161– parental cells (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 1A). The affinity-matured clones showed half-maximal binding to human and cynomolgus CD161 at picomolar concentrations (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1B). The Fc regions of these CD161 mAbs–contained mutations (L234A, L235A, and P329G) known to prevent binding to activating Fc receptors, including complement activation or antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.21
Generation of human mAbs specific for CD161. (A) Parental and affinity-matured CD161 mAbs were incubated with Jurkat cells expressing human CD161 at the indicated mAb concentrations. Cell surface–bound antibodies were then quantified with a fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody and normalized to CD161 surface expression. HP-3G10 (3G10) is a commercially available murine CD161 mAb. (B) Affinity-matured CD161 mAbs were incubated with CD161+ or CD161– Jurkat cells, and bound mAbs were detected with a fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody. (C) Alanine mutants of CD161 were generated for charged and neighboring residues, and these mutants were transiently expressed in 293F cells. Parental antibodies were titrated as in panel A, and the change in mean fluorescence intensity (at mAb concentration of 100 nM) was used to identify mutations that affected CD161 antibody binding. Mutations with a reduction in binding of ≥80% (bold), 60% to 80% (italic), and 40% to 60% (nonstylized) are indicated for each antibody. (D) Epitope residues listed in panel C are mapped on the CLEC2D crystal structure (Protein Data Bank 5MGS); teal, KW1; maroon, KW7; and yellow, KM12. Representative results of 2 independent experiments. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
Generation of human mAbs specific for CD161. (A) Parental and affinity-matured CD161 mAbs were incubated with Jurkat cells expressing human CD161 at the indicated mAb concentrations. Cell surface–bound antibodies were then quantified with a fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody and normalized to CD161 surface expression. HP-3G10 (3G10) is a commercially available murine CD161 mAb. (B) Affinity-matured CD161 mAbs were incubated with CD161+ or CD161– Jurkat cells, and bound mAbs were detected with a fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody. (C) Alanine mutants of CD161 were generated for charged and neighboring residues, and these mutants were transiently expressed in 293F cells. Parental antibodies were titrated as in panel A, and the change in mean fluorescence intensity (at mAb concentration of 100 nM) was used to identify mutations that affected CD161 antibody binding. Mutations with a reduction in binding of ≥80% (bold), 60% to 80% (italic), and 40% to 60% (nonstylized) are indicated for each antibody. (D) Epitope residues listed in panel C are mapped on the CLEC2D crystal structure (Protein Data Bank 5MGS); teal, KW1; maroon, KW7; and yellow, KM12. Representative results of 2 independent experiments. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
Both CD161 and CLEC2D are disulfide-linked homodimers, and the crystal structure helped identify 2 CLEC2D binding sites on the CD161 homodimer.6 We generated CD161 mutants in which several charged (and neighboring) residues were mutated to alanine and identified mutations on CD161 that reduced or abolished binding by these mAbs. A mutation in a surface-exposed loop of CD161 (K148A) interfered with CD161 binding by mAbs KW7 and KM12, and this CD161 residue was in close vicinity to the CLEC2D binding interface (S129 and Q154). Several mutations located close to the CD161 dimerization interface also interfered with mAb binding, potentially due to contributions of some of these residues to the binding interface of these mAbs and/or alterations in the conformation of the CD161 EC domain (Figure 1C-D; supplemental Figure 1C). These mutagenesis data provided further evidence for the specificity of the generated mAbs. However, not all residues in the CD161 EC domain were mutated, resulting in incomplete definition of the binding epitopes, in particular for mAb KW1.
Inhibition of CLEC2D binding by CD161 mAbs
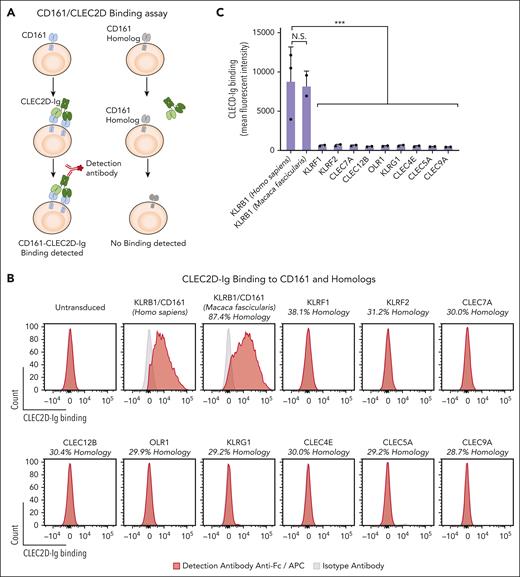
We next developed a CLEC2D-Ig fusion protein to evaluate the ability of these human mAbs to compete for CLEC2D binding to CD161. The CLEC2D crystal structure demonstrated proximity between the N-terminus of the first CLEC2D EC domain and the C-terminus of the second CLEC2D EC domain in the homodimer. Taking advantage of their proximity, we designed a CLEC2D homodimer by linking the 2 copies of the CLEC2D EC domain through a short flexible linker. An Fc domain was attached to the C-terminus of the second CLEC2D chain to generate a bivalent CLEC2D fusion protein in which each Fc chain carried a CLEC2D homodimer (supplemental Figure 2A-B). Bivalent CLEC2D-Ig resulted in strong labeling of CD161+ but not CD161– Jurkat cells (Figure 2A-B). We then used this CLEC2D-Ig fusion protein to investigate whether CLEC2D selectively binds to CD161 or potentially to other C-type lectins with significant sequence homology. We identified 9 human C-type lectins with sequence identity to the CD161 EC binding domain ranging from 38.1% to 28.7% (Figure 2B). We also included the cynomolgus primate (Macaca fascicularis) CD161 that shared 87.4% sequence identity with human CD161. We expressed these proteins in Jurkat cells, which coexpressed ZsGreen fluorescent protein (supplemental Figure 2C). Bivalent CLEC2D-Ig bound with a high degree of specificity to human and cynomolgus CD161 but not to any of the tested human CD161 homologs. These results confirmed that a CD161-blocking mAb would be a specific therapeutic approach to target the CD161-CLEC2D pathway. We also used this panel of transfectants to test the specificity of CD161 mAbs. CD161-blocking mAb KW7.3.7 bound selectively to CD161 but none of the tested homologous C-type lectins (Figure 2D). CD161 mAbs showed similar dose-dependent binding to human or cynomolgus CD161, a property relevant for future testing (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1B). Neither human CLEC2D-Ig nor human CD161-blocking mAb KW7.3.7 bound to primary murine NK or T cells (Figure 2E-F) or to a 3T3 transfectant expressing murine NKR-P1B (supplemental Figure 3A-C).
Specific antibody binding to CD161 but not other C-type lectins with significant sequence homology. Jurkat cells were lentivirally transduced with complementary DNAs (cDNAs) encoding human (Homo sapiens) or nonhuman primate (Macaca fascicularis) CD161 (KLRB1 gene) or other human C-type lectins with significant sequence homology to CD161. (A) Assay for assessing CLEC2D-Ig binding to CD161 and other C-type lectins. (B) Analysis of bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding to the indicated panel of transfectants. Each cell line was incubated with CLEC2D-Ig, and binding was detected with anti-Fc/APC–conjugated antibody. Percent of sequence identity to the extracellular domain of human CD161 is indicated for each homolog. (C) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of CLEC2D-Ig bound to the panel of transfectants (combined data for 2 independent assays). (D) CD161 antibody binding to CD161 or other C-type lectin receptors. Each cell line was incubated with CD161 mAb KW7.3.7, and binding was detected with anti-Fc/APC–conjugated antibody. (E) Binding of human bivalent CLEC2D-Ig to murine C57BL/6 NK cells (NK1.1+ CD49b+ CD3– [left]) and T cells (CD3+ NK1.1– [right]). (F) CD161 antibody binding to murine C57BL/6 NK cells (left) and T cells (right). Representative results from at least 2 independent experiments (B-F). Unpaired t test: ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells.
Specific antibody binding to CD161 but not other C-type lectins with significant sequence homology. Jurkat cells were lentivirally transduced with complementary DNAs (cDNAs) encoding human (Homo sapiens) or nonhuman primate (Macaca fascicularis) CD161 (KLRB1 gene) or other human C-type lectins with significant sequence homology to CD161. (A) Assay for assessing CLEC2D-Ig binding to CD161 and other C-type lectins. (B) Analysis of bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding to the indicated panel of transfectants. Each cell line was incubated with CLEC2D-Ig, and binding was detected with anti-Fc/APC–conjugated antibody. Percent of sequence identity to the extracellular domain of human CD161 is indicated for each homolog. (C) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of CLEC2D-Ig bound to the panel of transfectants (combined data for 2 independent assays). (D) CD161 antibody binding to CD161 or other C-type lectin receptors. Each cell line was incubated with CD161 mAb KW7.3.7, and binding was detected with anti-Fc/APC–conjugated antibody. (E) Binding of human bivalent CLEC2D-Ig to murine C57BL/6 NK cells (NK1.1+ CD49b+ CD3– [left]) and T cells (CD3+ NK1.1– [right]). (F) CD161 antibody binding to murine C57BL/6 NK cells (left) and T cells (right). Representative results from at least 2 independent experiments (B-F). Unpaired t test: ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells.
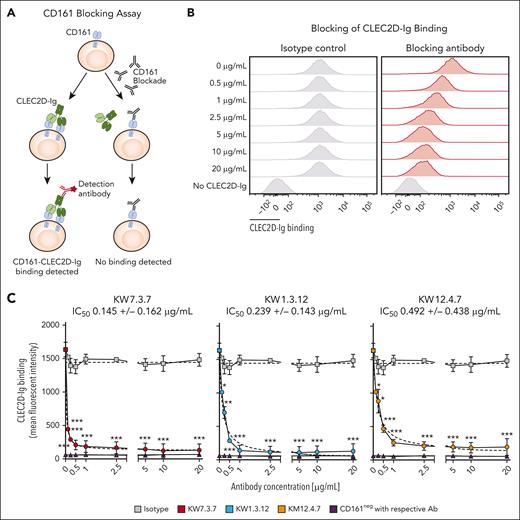
We next used the bivalent CLEC2D-Ig fusion protein to evaluate whether the human CD161 mAbs inhibited ligand binding. We set up a competition assay in which CD161+ Jurkat cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of CD161 or control mAbs and probed for binding to CLEC2D-Ig (Figure 3A-C). These experiments demonstrated strong dose-dependent inhibition of bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding by the 3 human CD161 mAbs but not the control mAb (Figure 3B-C). It is important to note that the measured half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (range, 0.145-0.492 μg/mL) did not measure mAb affinities because of the avidity effect contributing to bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding.
CD161 mAbs block CLEC2D binding. (A) Approach for measuring competition of bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding to cell surface CD161. Jurkat cells expressing human CD161 were incubated with CLEC2D-Ig and increasing concentrations of isotype control or CD161-blocking mAbs. Cell surface–bound CLEC2D-Ig was then quantified with a fluorophore-conjugated secondary mAb. (B) CD161+ Jurkat cells were incubated with CLEC2D-Ig in the presence of increasing concentrations of CD161 blocking mAbs (clones KW7.3.7, KW1.3.12, and KM12.4.7) or an isotype control mAb. Bound CLEC2D-Ig was quantified by flow cytometry. (C) Mean fluorescence intensity of bound CLEC2D-Ig fitted to nonlinear dose-response curve (calculated by least squares regression method and shown in dashed line); calculated half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) are listed for each antibody. Representative results of >3 independent experiments. Unpaired t test at each antibody concentration compared with isotype control; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
CD161 mAbs block CLEC2D binding. (A) Approach for measuring competition of bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding to cell surface CD161. Jurkat cells expressing human CD161 were incubated with CLEC2D-Ig and increasing concentrations of isotype control or CD161-blocking mAbs. Cell surface–bound CLEC2D-Ig was then quantified with a fluorophore-conjugated secondary mAb. (B) CD161+ Jurkat cells were incubated with CLEC2D-Ig in the presence of increasing concentrations of CD161 blocking mAbs (clones KW7.3.7, KW1.3.12, and KM12.4.7) or an isotype control mAb. Bound CLEC2D-Ig was quantified by flow cytometry. (C) Mean fluorescence intensity of bound CLEC2D-Ig fitted to nonlinear dose-response curve (calculated by least squares regression method and shown in dashed line); calculated half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) are listed for each antibody. Representative results of >3 independent experiments. Unpaired t test at each antibody concentration compared with isotype control; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
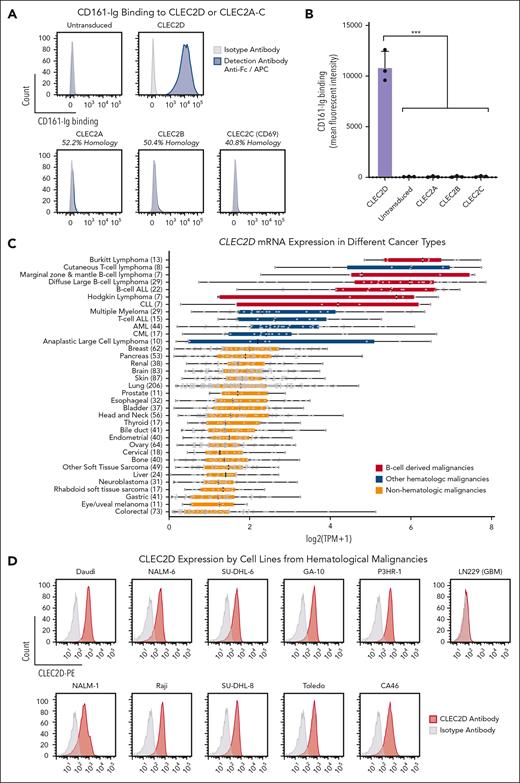
We next generated a bivalent CD161-Ig fusion protein using the same design (supplemental Figure 2A). We used this fusion protein to investigate whether CD161 only binds to CLEC2D or potentially also to other CLEC2 family members with homologous EC domains (sequence identity, 40.8%-52.2%). These experiments demonstrated strong binding of bivalent CD161-Ig to CLEC2D but no detectable binding to CLEC2A, B, or C (Figure 4A-B). These data confirmed that a CD161-blocking mAb could selectively target its interaction with CLEC2D.
CLEC2D is highly expressed in hematological malignancies and binds with a high degree of specificity to CD161. (A-B) LN229 cells that lacked expression of CLEC2D or related C-type lectins were lentivirally transduced with complementary DNAs encoding human CLEC2D or other CLEC2 family members. Soluble bivalent CD161-Fc was incubated with transduced cells, and binding was quantified with a fluorophore-conjugated anti-Fc antibody. (A) Analysis of CD161-Fc binding to CLEC2D and other members of the CLEC2 family (CLEC2A-C). Percent sequence identity to the extracellular domain of human CLEC2D is indicated for each homolog. Representative assay of 3 independent experiments. (B) Mean fluorescence intensity of bound CD161-Fc to the panel of CLEC2A-D transfectants (combined data from 2 independent assays). (C) CLEC2D mRNA expression by a diverse panel of cancer cell lines from the Broad Institute Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. The number of individual cell lines is indicated for each cancer type. B-cell malignancies (red) and other hematological malignancies (blue) are highlighted. (D) CLEC2D surface expression by a panel of cell lines from hematological malignancies; isotype control Ab staining is indicated in gray. Glioblastoma cell line LN229 (no CLEC2D expression) used as negative control. Representative results of 3 independent experiments. Unpaired t test comparison to CLEC2D mean fluorescence intensity; ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
CLEC2D is highly expressed in hematological malignancies and binds with a high degree of specificity to CD161. (A-B) LN229 cells that lacked expression of CLEC2D or related C-type lectins were lentivirally transduced with complementary DNAs encoding human CLEC2D or other CLEC2 family members. Soluble bivalent CD161-Fc was incubated with transduced cells, and binding was quantified with a fluorophore-conjugated anti-Fc antibody. (A) Analysis of CD161-Fc binding to CLEC2D and other members of the CLEC2 family (CLEC2A-C). Percent sequence identity to the extracellular domain of human CLEC2D is indicated for each homolog. Representative assay of 3 independent experiments. (B) Mean fluorescence intensity of bound CD161-Fc to the panel of CLEC2A-D transfectants (combined data from 2 independent assays). (C) CLEC2D mRNA expression by a diverse panel of cancer cell lines from the Broad Institute Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. The number of individual cell lines is indicated for each cancer type. B-cell malignancies (red) and other hematological malignancies (blue) are highlighted. (D) CLEC2D surface expression by a panel of cell lines from hematological malignancies; isotype control Ab staining is indicated in gray. Glioblastoma cell line LN229 (no CLEC2D expression) used as negative control. Representative results of 3 independent experiments. Unpaired t test comparison to CLEC2D mean fluorescence intensity; ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
CLEC2D is highly expressed in hematological malignancies
We used publicly available RNA-seq data from 1339 cancer lines in the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia, including 208 lines from hematological malignancies and 1131 lines from solid tumors to identify cancer types with high CLEC2D messenger RNA (mRNA) expression (Figure 4C).22 This data set demonstrated significantly higher CLEC2D transcript levels in hematological malignancies than in solid tumors. Furthermore, cell lines from B-cell–derived malignancies showed the highest mean CLEC2D mRNA levels. We confirmed CLEC2D cell surface protein expression in a panel of cell lines from hematological malignancies (Figure 4D) that were used for functional experiments. No labeling by this CLEC2D mAb was detected by the LN229 glioblastoma cell line that was negative for CLEC2D at the mRNA level. Treatment with a TLR9 agonist (CpG oligodeoxynucleotide) resulted in upregulation of CLEC2D expression (supplemental Figure 4A-B) but also has pleiotropic effects on malignant cells, including upregulation of costimulatory receptors.14
CD161 blockade enhances T-cell activation and cytotoxicity in vitro
We next evaluated the functional consequences of CD161 inhibition using cocultures of primary human CD161+ T cells and cell lines representing human hematological malignancies (NALM-1/chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), Toledo/DLBCL, and Raji/Burkitt lymphoma). We cocultured tumor cell lines with primary human T cells engineered to express the 1G4 NY-ESO-1–specific TCR (supplemental Figure 5A-F). Tumor cell lines were lentivirally transduced to express HLA-A∗02:01 (if not endogenously expressed) and the NY-ESO-1 protein for recognition by the NY-ESO-1 TCR (supplemental Figure 5G-H).
An important aspect in the design of these experiments was to isolate primary T cells from healthy donors that naturally expressed the CD161 receptor. CD161 is expressed by effector-memory CD4 and CD8 T cells as well as mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells.23,24 We sorted CD161+ T cells that did not have MAIT TCR (identified by TCR-Vα7.2 staining) because MAIT cells have innate immune features that are not characteristic of tumor-infiltrating T cells.25 In our healthy donor population, CD161+ T cells comprised 21.7 ± 8.8% of CD4+ MAIT− and 9.7 ± 6.5% of CD8+ MAIT− T cells (supplemental Figure 5E). Sorted CD161+ T cells were electroporated with Cas9 protein with bound TRAC guide RNA and a single-stranded DNA template for integration into the TRAC locus by homology-directed repair (supplemental Figure 5B). This template encoded the entire NY-ESO-1 TCRβ chain but only part of the TCRα chain to ensure that NY-ESO-1 TCR expression required correct in-frame integration into the TRAC locus.26 NY-ESO-1 TCR+ T cells were sorted using a hemagglutinin (HA)-epitope tag on the N-terminus of the mature TCRα chain. In vitro activation conditions were critical for the expansion of CD161+ T cells. Effector-memory T cells have a lower threshold for TCR activation than naïve T cells, and use of CD3/CD28 Dynabeads resulted in overstimulation and poor expansion. Rather, stimulation with low concentrations of plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 mAbs enabled substantial expansion of these cells and maintenance of CD161 expression (supplemental Figure 6A-B).
We tested 3 different cytokine conditions for expansion of CD161+ T cells, including interleukin-2 (IL-2) alone, IL-7/IL-15, or IL-7/IL-15/IL-21 (supplemental Figure 6C-E). All 3 cytokine conditions enabled expansion of CD161+ T cells, with larger total cell numbers in both IL-7/IL-15 and IL-7/IL-15/IL-21 conditions. Importantly, IL-2–supplemented cultures contained a larger percentage of CD161+ cells among both CD8 and CD4 T cells (supplemental Figure 6F-G). NY-ESO-1 TCR+–edited T cells that expanded under these cytokine conditions showed a similar capacity to kill tumor cells (supplemental Figure 6H-I). Subsequent experiments were performed with T cells expanded with low dose CD3/CD28 in the presence of IL-2. A limitation of this approach was that total T cells rather than only CD8 T cells were used for the generation of NY-ESO-1 TCR+ T cells, because depletion of CD4 T cells would have introduced further complexity into this challenging workflow and negatively affected CD8 T-cell yield. Therefore, we carefully examined CD8 T cells in the in vivo experiments using both flow cytometry and scRNA-seq readouts.
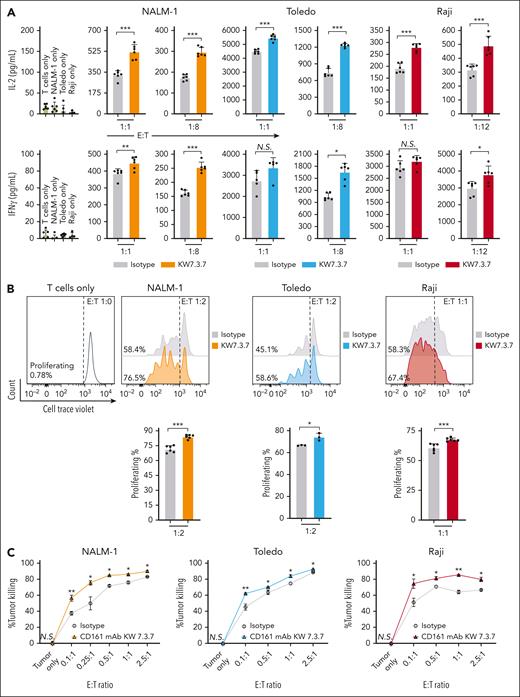
CD161+ T cells that expressed the NY-ESO-1 TCR were then cocultured with NALM-1 (CML), Toledo (DLBCL), or Raji (Burkitt lymphoma) cells that expressed endogenous CLEC2D and the tumor antigen NY-ESO-1. The KW7.3.7 mAb was selected for these experiments based on its specificity for CD161 and high-level expression in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. CD161 blockade was found to significantly increase the secretion of IL-2 and interferon gamma by T cells cocultured with tumor cells. The CD161 mAb also enhanced T-cell proliferation as determined by CTV dye dilution in labeled T cells (Figure 5A-B). Importantly, CD161 inhibition enhanced the cytotoxic activity of NY-ESO-1 TCR–expressing T cells against leukemia and lymphoma cell lines in 4-hour assays using cleaved caspase-3/7 in tumor cells as a readout (Figure 5C). We further tested the relevance of the CLEC2D ligand in T-cell–mediated cytotoxicity and observed that inactivation of the CLEC2D gene in tumor cells also resulted in more efficient killing by T cells (Figure 5D-F). Finally, we also evaluated this CD161 blocking mAb in the context of NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity. We found that CD161 blockade enhanced killing of Daudi cells (MHC-I deficient due to B2M mutation) by primary human NK cells (Figure 5G). Coculture assays with CpG oligonucleotide–pretreated tumor cells showed no further enhancement of cytotoxicity (supplemental Figure 4C-D). These data demonstrated that targeting of the CD161 receptor with a fully human mAb enhanced multiple important aspects of antitumor T-cell and NK cell function.
CD161 blockade enhances T-cell function. Primary human CD161+ T cells expressing a NY-ESO-1 TCR were cocultured with cell lines from hematological malignancies (NALM-1, Toledo, and Raji cells) expressing NY-ESO-1 antigen at the indicated effector-to-target (E:T) ratio and treated with isotype control or CD161 blocking mAbs (clone KW7.3.7). (A) After 72 hours in culture, IL-2 and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) in the supernatant was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (B) Impact of CD161 inhibition on T-cell proliferation. T cells were prestained with CTV proliferation dye before coculture assay, and T-cell proliferation was determined at 96 hours based on CTV dilution by flow cytometry. The percentage of proliferating T cells is indicated. (C) T-cell–mediated cytotoxicity against NALM-1, Toledo, or Raji cells was assessed in the presence of CD161 blocking or isotype control mAbs. Specific tumor cell killing was determined after 4 hours of coculture at the indicated E:T ratios by flow cytometric detection of cleaved caspase-3/7 and the use of counting beads. (D-E) Inactivation of the CLEC2D gene in tumor cell lines by CRISPR/Cas9; quantification of CLEC2D surface expression (D) and CLEC2D editing efficiency (E) (Synthego interference of CRISPR edits [ICE]analysis). (F) T-cell cytotoxicity against the CLEC2D knockout or wild-type tumor cell lines. (G) NK cell cytotoxicity activity against Daudi cells (naturally B2M mutant). Representative results from 2 independent experiments. Unpaired t test, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001 NS, not significant; WT, wild type.
CD161 blockade enhances T-cell function. Primary human CD161+ T cells expressing a NY-ESO-1 TCR were cocultured with cell lines from hematological malignancies (NALM-1, Toledo, and Raji cells) expressing NY-ESO-1 antigen at the indicated effector-to-target (E:T) ratio and treated with isotype control or CD161 blocking mAbs (clone KW7.3.7). (A) After 72 hours in culture, IL-2 and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) in the supernatant was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (B) Impact of CD161 inhibition on T-cell proliferation. T cells were prestained with CTV proliferation dye before coculture assay, and T-cell proliferation was determined at 96 hours based on CTV dilution by flow cytometry. The percentage of proliferating T cells is indicated. (C) T-cell–mediated cytotoxicity against NALM-1, Toledo, or Raji cells was assessed in the presence of CD161 blocking or isotype control mAbs. Specific tumor cell killing was determined after 4 hours of coculture at the indicated E:T ratios by flow cytometric detection of cleaved caspase-3/7 and the use of counting beads. (D-E) Inactivation of the CLEC2D gene in tumor cell lines by CRISPR/Cas9; quantification of CLEC2D surface expression (D) and CLEC2D editing efficiency (E) (Synthego interference of CRISPR edits [ICE]analysis). (F) T-cell cytotoxicity against the CLEC2D knockout or wild-type tumor cell lines. (G) NK cell cytotoxicity activity against Daudi cells (naturally B2M mutant). Representative results from 2 independent experiments. Unpaired t test, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001 NS, not significant; WT, wild type.
To test whether the CD161 mAb had a direct effect on T-cell activation, we stimulated CD161+ T cells with control or CD161 mAb in the presence of CD3 and CD28 mAb. Treatment with immobilized or soluble CD161 mAb showed no direct effect on T-cell activation measured by the expression of early T-cell activation markers CD25 and CD69 (supplemental Figure 7A-B). These data confirmed that CD161 mAb only blocks CLEC2D binding to the CD161 receptor but is otherwise biologically inert.
CD161 blockade improves survival in mouse models of leukemia and lymphoma
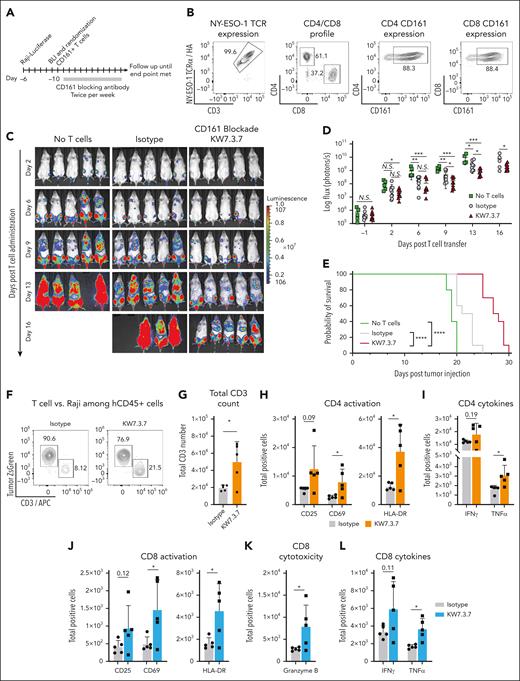
We aimed to model advanced human disease for which therapeutic interventions are most urgently needed. NSG mice were IV injected with NY-ESO-1+ luciferase-positive Raji or NALM-1 tumor cells at the indicated cell doses. These tumor models recapitulated advanced human disease with rapid engraftment into the bone marrow, spleen, and liver. Raji and NALM-1 cell expansion was serially monitored by in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Once tumor cells had engrafted (day 5 in Raji model and day 10 in NALM-1 model), mice were randomized to treatment groups based on bioluminescence flux in the hind limbs (photons per second) to ensure similar tumor burden among treatment groups. Engineered NY-ESO-1 TCR+ CD161+ T cells were then IV injected at the indicated cell doses, and mice were treated twice weekly with CD161 or isotype control mAbs (5 mg/kg; Figure 6A-E). Treatment with the CD161 mAb significantly prolonged survival in this aggressive model compared with treatment with control mAb (Figure 6E). Mice engrafted with NALM-1 tumor cells survived past day 35 after T-cell transfer and were euthanized for end point analysis. Residual tumor burden was significantly lower in CD161 mAb–treated mice (supplemental Figure 8). Flow cytometric analysis 7 days after T-cell transfer demonstrated that CD161 mAb treatment enhanced T-cell infiltration as well as activation of both CD8 and CD4 T cells (CD69 and HLA-DR activation markers). Furthermore, total numbers of granzyme B+ CD8 T cells as well as tumor necrosis factor α–positive CD8 and CD4 T cells were significantly higher in the CD161 mAb treatment group (Figure 6F-L).
CD161 blockade enhances T-cell–mediated tumor clearance in a humanized mouse model. (A) Experimental design. NSG mice were injected IV with 2.5 × 105 NY-ESO-1+ Luciferase-positive ZsGreen+ Raji cells. Tumor engraftment was monitored by bioluminescence imaging. Five days after tumor cell injection, mice were randomized to treatment groups to ensure similar tumor burden. On day 6, a total of 1.5 × 106 NY-ESO-1 TCR+ CD8 T cells (4 × 106 total T cells) were injected IV, and mice were treated twice per week with 5 mg/kg of CD161 (KW7.3.7) or isotype control mAbs. (B) T-cell profile before adoptive transfer. NY-ESO-1 TCR expression, CD4/CD8 ratio, and CD161 expression were measured by flow cytometry. (C) Disease progression after T-cell administration was quantified by bioluminescence imaging, and total flux was quantified. (D-E) Impact of CD161 blockade on tumor burden quantified by bioluminescence (D) and overall survival (E). Panels A-E show representative assay of 2 independent repeats. (F-L) Analysis of T cells in the bone marrow on day 13 after tumor cell injection (day 7 after T-cell administration). (F) Percentage of Raji cells (ZsGreen) vs CD3+ T cells in both treatment groups. (G-L) Flow cytometry analysis of total human CD3+ T cells (G), activation markers expressed by CD4+ T cells (H), and CD8+ T cells (J), IFN-γ and tumor necrosis factor TNFα–positive (TNFα)+ CD4 (I) and CD8 (L) T cells, and granzyme B+ CD8 T cells (K). Panels F-L analyses were performed once with 5 mice per group. Each data point represents a biological replicate (individual mouse); Unpaired t test, ∗P < .5; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells; BLI, bioluminescence.
CD161 blockade enhances T-cell–mediated tumor clearance in a humanized mouse model. (A) Experimental design. NSG mice were injected IV with 2.5 × 105 NY-ESO-1+ Luciferase-positive ZsGreen+ Raji cells. Tumor engraftment was monitored by bioluminescence imaging. Five days after tumor cell injection, mice were randomized to treatment groups to ensure similar tumor burden. On day 6, a total of 1.5 × 106 NY-ESO-1 TCR+ CD8 T cells (4 × 106 total T cells) were injected IV, and mice were treated twice per week with 5 mg/kg of CD161 (KW7.3.7) or isotype control mAbs. (B) T-cell profile before adoptive transfer. NY-ESO-1 TCR expression, CD4/CD8 ratio, and CD161 expression were measured by flow cytometry. (C) Disease progression after T-cell administration was quantified by bioluminescence imaging, and total flux was quantified. (D-E) Impact of CD161 blockade on tumor burden quantified by bioluminescence (D) and overall survival (E). Panels A-E show representative assay of 2 independent repeats. (F-L) Analysis of T cells in the bone marrow on day 13 after tumor cell injection (day 7 after T-cell administration). (F) Percentage of Raji cells (ZsGreen) vs CD3+ T cells in both treatment groups. (G-L) Flow cytometry analysis of total human CD3+ T cells (G), activation markers expressed by CD4+ T cells (H), and CD8+ T cells (J), IFN-γ and tumor necrosis factor TNFα–positive (TNFα)+ CD4 (I) and CD8 (L) T cells, and granzyme B+ CD8 T cells (K). Panels F-L analyses were performed once with 5 mice per group. Each data point represents a biological replicate (individual mouse); Unpaired t test, ∗P < .5; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells; BLI, bioluminescence.
CD161 blockade enhances tissue-residency program of tumor-infiltrating T cells
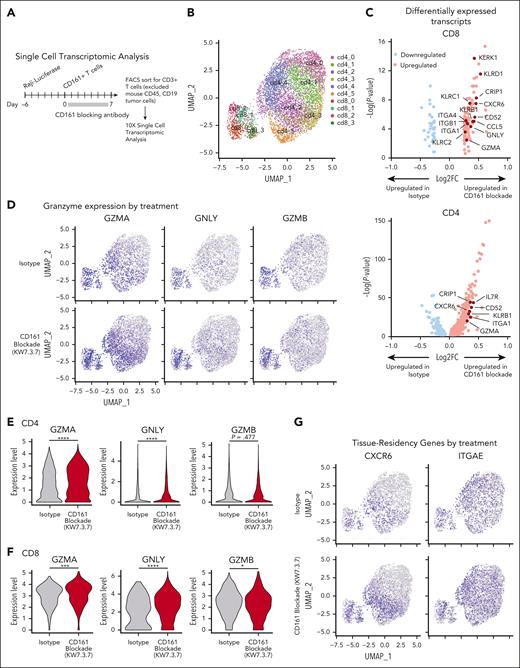
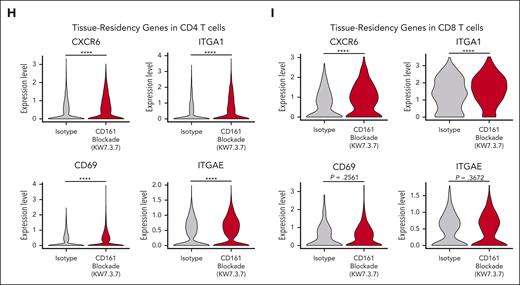
We performed scRNA-seq analysis of tumor-infiltrating T cells (Raji model 7 days after T-cell transfer). T cells from 5 mice were labeled with DNA-barcoded antibodies (hashtagging) and sorted by flow cytometry (Figure 7A; supplemental Figure 9A). Six clusters of CD4 T cells and 4 clusters of CD8 T cells were identified in this data set (Figure 7B). The KLRB1 gene encoding CD161 was expressed at a higher level in CD4 and CD8+ T cells from CD161 vs control mAb–treated mice (supplemental Figure 9B-C). Differential expression analysis on the CD4+ and CD8+ populations was performed separately to identify transcripts upregulated and downregulated in CD161 mAb–treated mice (Figure 7C). In both CD4 and CD8 T cells, cytotoxicity genes, including GZMA and GNLY, were expressed at a higher level by cells from CD161 mAb–treated mice (Figure 7D-F). Interestingly, multiple genes representing markers of tissue residency were overexpressed by T cells from CD161 mAb–treated mice, including CXCR6 and ITGA1 (CD4 and CD8 T cells) as well as CD69 and ITGAE (CD4 T cells; Figure 7G-I; supplemental Figure 9C). Recent studies have demonstrated that tissue-resident memory T cells are associated with longer survival in multiple cancers and response to immune checkpoint blockade.27-30 These findings were validated by flow cytometric staining of key markers (Figure 6; supplemental Figure 9E-H). Furthermore, treatment with CD161 mAb led to upregulation of a subset of NK cell genes, including KLRD1, KLRC1, KLRC2, and KLRK1, and this functional state has been associated with enhanced cytotoxicity (Figure 7B-C).9 Pathway analysis identified programs that were upregulated in both CD4 and CD8 T cells from CD161 mAb vs control mAb–treated mice, including allograft rejection, oxidative phosphorylation, and ribosomal protein synthesis (supplemental Figure 9D). These analyses demonstrated that CD161 blockade improved key aspects of T-cell function.
Single-cell analysis of tumor-infiltrating T cells. (A) Experimental design. NSG mice were injected IV with 2.5 × 105 NY-ESO-1+ Raji cells, followed by IV injection of 3 × 106NY-ESO-1 TCR+ CD161+ cells on day 6 (n = 5 mice per treatment group) and treatment with either CD161 mAb or isotype control. On day 13, cells were isolated from bone marrow of both hind limbs, and fluorescence-activated cell sorted on live CD3+ T cells (human CD45+, human CD19–, ZsGreen–, and mouse CD45–). Cells were analyzed by scRNA-seq using the 10X Genomics platform. (B) Identification of CD4 and CD8 T-cell clusters across all samples (n = 5 mice per treatment cohort). (C) Differentially expressed transcripts in CD8 (left) and CD4 (right) T cells in CD161 mAb–treated vs isotype–treated mice. Only transcripts expressed in >10% CD4 or CD8 T cells with an adjusted P value < .05 are shown (supplemental Tables 1 and 2). (D) Distribution of granzyme A (GZMA), granulysin (GNLY), and granzyme B (GZMB) expression in isotype control (top) vs CD161 mAb (bottom) treatment groups. (E-F) Violin plots showing expression of GZMA, GNLY, and GZMB in CD4+ (E) and CD8+ (F) T-cell clusters. Values trimmed at 2% and 98% for plotting. (G) Distribution of C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 6 (CXCR6) and integrin subunit alpha E (ITGAE) expression in isotype control (top) vs CD161 mAb (bottom) treatment groups. (H-I) Violin plots showing differential expression of tissue-residency markers (CXCR6, ITGA1, CD69, and ITGAE) in CD4 (H) and CD8 (I) T cells in CD161 vs isotype control treatment groups. Data from 1 scRNA-seq experiment with hashtagged cells from 5 mice per treatment group. Two-sided unpaired Wilcoxon rank sum test, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. UMAP, uniform manifold approximation and projection.
Single-cell analysis of tumor-infiltrating T cells. (A) Experimental design. NSG mice were injected IV with 2.5 × 105 NY-ESO-1+ Raji cells, followed by IV injection of 3 × 106NY-ESO-1 TCR+ CD161+ cells on day 6 (n = 5 mice per treatment group) and treatment with either CD161 mAb or isotype control. On day 13, cells were isolated from bone marrow of both hind limbs, and fluorescence-activated cell sorted on live CD3+ T cells (human CD45+, human CD19–, ZsGreen–, and mouse CD45–). Cells were analyzed by scRNA-seq using the 10X Genomics platform. (B) Identification of CD4 and CD8 T-cell clusters across all samples (n = 5 mice per treatment cohort). (C) Differentially expressed transcripts in CD8 (left) and CD4 (right) T cells in CD161 mAb–treated vs isotype–treated mice. Only transcripts expressed in >10% CD4 or CD8 T cells with an adjusted P value < .05 are shown (supplemental Tables 1 and 2). (D) Distribution of granzyme A (GZMA), granulysin (GNLY), and granzyme B (GZMB) expression in isotype control (top) vs CD161 mAb (bottom) treatment groups. (E-F) Violin plots showing expression of GZMA, GNLY, and GZMB in CD4+ (E) and CD8+ (F) T-cell clusters. Values trimmed at 2% and 98% for plotting. (G) Distribution of C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 6 (CXCR6) and integrin subunit alpha E (ITGAE) expression in isotype control (top) vs CD161 mAb (bottom) treatment groups. (H-I) Violin plots showing differential expression of tissue-residency markers (CXCR6, ITGA1, CD69, and ITGAE) in CD4 (H) and CD8 (I) T cells in CD161 vs isotype control treatment groups. Data from 1 scRNA-seq experiment with hashtagged cells from 5 mice per treatment group. Two-sided unpaired Wilcoxon rank sum test, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. UMAP, uniform manifold approximation and projection.
In vivo induction of CD161 expression
We previously demonstrated that CD161 was highly upregulated by glioblastoma-infiltrating T cells compared with circulating T cells.9 We, therefore, examined whether CD161 may be expressed by T cells in the tumor microenvironment and whether CD161 upregulation required tumor antigen recognition. We engrafted NSG mice with NALM-1 cells that did or did not express the NY-ESO-1 antigen (NY-ESO-1+ vs wild-type NALM-1) and transferred CD161– NY-ESO-1 TCR+ T cells. CD161 upregulation was only observed when NALM-1 tumor cells expressed the NY-ESO-1 antigen, indicating that upregulation was dependent on antigen recognition by the TCR (supplemental Figure 10A-E). CD161 expression was observed in both bone marrow and spleen, and it increased over time in both CD8 and CD4 T-cell populations. CD161+ T cells expressed higher levels of the CD69 activation marker as well as higher levels of the PD-1 and CD39 T-cell exhaustion markers typically upregulated on T cells by repetitive TCR stimulation (supplemental Figure 10F-G). The rapid proliferation of tumor cells in NSG mice even at limiting cell doses and the timeframe of CD161 upregulation precluded the use of CD161– T cells in therapy experiments. Nevertheless, these data demonstrated that TCR stimulation induced upregulation of the CD161 inhibitory receptor. Induction of CD161 expression was not observed in vitro after CD3/CD28 antibody stimulation, suggesting that multiple signals from the tumor microenvironment, in concert with TCR signaling, resulted in induction of CD161 expression.
Discussion
Here, we report the generation and characterization of fully human CD161 mAbs that inhibited binding of the CLEC2D ligand and, thereby, substantially enhanced the function of both CD4 and CD8 T cells against a diverse set of hematological malignancies. These mAbs showed selective binding to CD161, but not related C-type lectin receptors, and iterative cycles of mutagenesis and selection yielded high-affinity mAbs. CD161 blockade enhanced antitumor immunity in humanized mouse models, and ex vivo analysis demonstrated enhanced functionality of infiltrating CD4 and CD8 T cells. ScRNA-seq analysis demonstrated that CD161 mAb treatment enhanced key pathways within tumor-infiltrating T cells, including cytotoxicity and tissue-residency as well as protein synthesis (ribosome) and metabolic programs (oxidative phosphorylation).
Previous studies demonstrated that the KLRB1 gene encoding CD161 is broadly expressed by tumor-infiltrating CD4 and CD8 T-cell populations as well as NK cells.9,10,31,KLRB1 expressing T cells from human solid tumors expressed an effector/effector-memory program rather than a terminal exhaustion program.9 These results were consistent with analysis of circulating virus-specific memory T cells in which CD161+ cells had higher cytotoxic activity than CD161– T cells.23,24 Expression of KLRB1 by multiple immune-effector cells populations, specifically CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and NK cells, offers the potential for multipronged immune attack. The fully human CD161 mAbs reported here enhance key aspects of CD4 and CD8 T-cell function, including proliferation, cytokine production, and cytotoxicity. This fully human CD161 mAb also enhances NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells, consistent with prior studies using a murine CD161 blocking mAb.4,5 Engagement of multiple effector cell populations is particularly relevant in hematological malignancies because of well-documented immune evasion mechanisms. For example, 50% of DLBCL cases were found to lack surface expression of MHC-I proteins due to somatic mutations in B2M or other genes in the MHC-I pathway. Furthermore, 70% of MHC-I+ cases harbored monoallelic genetic alterations.32 DLBCL with molecular alterations in the MHC-I pathway had higher mutational burden and inferred neoantigen load, consistent with escape from CD8 T-cell–mediated attack. We recently demonstrated that a coordinated immune attack by CD4 T cells and NK cells induced by a cancer vaccine provided a substantial survival benefit even in a mouse model of MHC-I–deficient tumors. Interestingly, CD4 T cells were found to be essential for the recruitment of NK cells, which acted as the major effector cell population.12
Why is the CLEC2D gene expressed at the highest level in hematological malignancies? CLEC2D expression is strongly induced by B-cell activation through the B-cell receptor, CD40, and TLRs, and high-level CLEC2D expression has been documented in germinal-center B cells.13,15 B-cell malignancies that originate from germinal-center B cells or represent an activated B-cell state, therefore, show high-level CLEC2D expression at the mRNA and protein level.16 Activation signals, including TLR ligands, also induce CLEC2D expression in myeloid cells, providing an explanation for CLEC2D expression by malignant cells representing the myeloid lineage (AML and CML). Finally, CLEC2D is also expressed by activated T cells, accounting for its expression in T-cell lymphomas.13,15 CLEC2D binding by the CD161 receptor may, therefore, inhibit T-cell function not only during direct interactions with tumor cells but also during interactions with immunosuppressive cell populations within the tumor microenvironment.
The CD161 mAbs reported here were selected for properties that enable rapid clinical translation. We envision several therapeutic applications in hematological malignancies including combination therapies that could further enhance the function of both T cells and NK cells.33 Of interest is combination therapy with ibrutinib, an inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase, which inhibits signaling by the B-cell receptor pathway.34 Ibrutinib also markedly increases CD4 and CD8 T-cell numbers in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia through inhibition of IL-2 inducible kinase signaling in T cells.35
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Animal Facility for bioluminescence imaging services. The authors thank members of the Wucherpfennig lab for their scientific discussions and support.
This work was supported by the Bridge Project, a partnership between the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at MIT and the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center (K.W.W., M.L.S., and K.D.W.), an accelerator fund from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants R01 CA238039, R01 CA251599, R01 CA234018, P01 CA163222 and P01 CA236749 (K.W.W.), and the Ludwig Center at Harvard Medical School (K.W.W.). K.W.W. is a codirector of the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The study was also supported by the American Society of Hematology Research Training Award for Fellows, and Pedals for Pediatrics (F.A.C.); a postdoctoral fellowship from the American Cancer Society (PF-17-042-01-LIB) and the NIH education loan repayment program funded by NIH/NCI (L30 CA231679-01) (N.D.M.); and a Cancer Research Institute Irvington Postdoctoral Fellowship (CRI4489) (X.N.).
Authorship
Contribution: B.H.K. and K.D.W. developed mAbs; F.A.C., O.K., B.H.K., N.D.M., K.D.W., and K.W.W. designed experiments; O.K., F.A.C., B.H.K., H.W., A.M.L., X.N., and J.P. conducted experiments; S.Z., F.A.C., O.K., B.H.K., X.C., G.-C.Y., M.L.S., K.D.W., and K.W.W. analyzed data; and F.A.C. and K.W.W. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: K.W.W. serves on the scientific advisory boards of TScan Therapeutics, SQZ Biotech, Bisou Bioscience Company, DEM BioPharma, Solu Therapeutics, and Nextechinvest; and receives sponsored research funding from Novartis. K.W.W., M.L.S., and K.D.W. are cofounders, stockholders, and advisory board members of Immunitas Therapeutics, a biotech company. N.D.M. served as a scientific adviser to Immunitas Therapeutics; and since 4 October 2021, is a stockholder and an employee of Asher Biotherapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Kai W. Wucherpfennig, Cancer Immunology and Virology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 450 Brookline Ave, Boston, MA 02215; email: kai_wucherpfennig@dfci.harvard.edu; and K. Dane Wittrup, Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at MIT, Cambridge, MA 02141; email: wittrup@mit.edu.
References
Author notes
F.A.C., B.H.K., O.K., and S.Z. contributed equally to this work.
ScRNA-seq data are deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (accession number GSE220200).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


![Specific antibody binding to CD161 but not other C-type lectins with significant sequence homology. Jurkat cells were lentivirally transduced with complementary DNAs (cDNAs) encoding human (Homo sapiens) or nonhuman primate (Macaca fascicularis) CD161 (KLRB1 gene) or other human C-type lectins with significant sequence homology to CD161. (A) Assay for assessing CLEC2D-Ig binding to CD161 and other C-type lectins. (B) Analysis of bivalent CLEC2D-Ig binding to the indicated panel of transfectants. Each cell line was incubated with CLEC2D-Ig, and binding was detected with anti-Fc/APC–conjugated antibody. Percent of sequence identity to the extracellular domain of human CD161 is indicated for each homolog. (C) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of CLEC2D-Ig bound to the panel of transfectants (combined data for 2 independent assays). (D) CD161 antibody binding to CD161 or other C-type lectin receptors. Each cell line was incubated with CD161 mAb KW7.3.7, and binding was detected with anti-Fc/APC–conjugated antibody. (E) Binding of human bivalent CLEC2D-Ig to murine C57BL/6 NK cells (NK1.1+ CD49b+ CD3– [left]) and T cells (CD3+ NK1.1– [right]). (F) CD161 antibody binding to murine C57BL/6 NK cells (left) and T cells (right). Representative results from at least 2 independent experiments (B-F). Unpaired t test: ∗∗∗P < .001. APC, antigen presenting cells.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/12/10.1182_blood.2023022882/2/m_blood_bld-2023-022882-gr2df.jpeg?Expires=1763468908&Signature=HBNDZ5Ytoqw0ODF9Y9comIu-jhUULIka0YL6de3tQpkWD565yOLkoXUHCvxIlUttshHZk7RfFiejT82m6Upusb9vD8kN1jOFKybvrIziFqyWilCJZuR4aCa2si6Q~vyTkyGfRPndzoE0VEGRWwF99X7dcc1pbjH7zgUYWOFixI40r~5PnUleSzUO4jgUuUQzq8toH8sUci0dUD2U22Q7MfaJn0r~j9n3NOIFcm4Xd5J7x0FB1B8CwfpiG0d-uwL942-F7bIZAGuZlgXsfGtV~MItS7sgRcNHmHlxY2W5BkMIh2P-bmd9uuIg6VZAS~jySBsfXmW-eCQs2pWpNQNU2g__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![CD161 blockade enhances T-cell function. Primary human CD161+ T cells expressing a NY-ESO-1 TCR were cocultured with cell lines from hematological malignancies (NALM-1, Toledo, and Raji cells) expressing NY-ESO-1 antigen at the indicated effector-to-target (E:T) ratio and treated with isotype control or CD161 blocking mAbs (clone KW7.3.7). (A) After 72 hours in culture, IL-2 and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) in the supernatant was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (B) Impact of CD161 inhibition on T-cell proliferation. T cells were prestained with CTV proliferation dye before coculture assay, and T-cell proliferation was determined at 96 hours based on CTV dilution by flow cytometry. The percentage of proliferating T cells is indicated. (C) T-cell–mediated cytotoxicity against NALM-1, Toledo, or Raji cells was assessed in the presence of CD161 blocking or isotype control mAbs. Specific tumor cell killing was determined after 4 hours of coculture at the indicated E:T ratios by flow cytometric detection of cleaved caspase-3/7 and the use of counting beads. (D-E) Inactivation of the CLEC2D gene in tumor cell lines by CRISPR/Cas9; quantification of CLEC2D surface expression (D) and CLEC2D editing efficiency (E) (Synthego interference of CRISPR edits [ICE]analysis). (F) T-cell cytotoxicity against the CLEC2D knockout or wild-type tumor cell lines. (G) NK cell cytotoxicity activity against Daudi cells (naturally B2M mutant). Representative results from 2 independent experiments. Unpaired t test, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001 NS, not significant; WT, wild type.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/12/10.1182_blood.2023022882/2/m_blood_bld-2023-022882-gr5dg.jpeg?Expires=1763468908&Signature=SoXHICcJE05fhGXF0TImH6z0b5l~CB2~fmW~ueyVntYSlRetkewYwrARJ8xsHpgseZ~YTd0D4chLZI8WdMp86fknvC6lzBX0iHUoGo63Fk-LK~H3nWL0qDHkDMCK2bl-08R8LUmmp7nf-IYRg8yDI1g3l3yfnGhR9NqTafqcZjb~3GaiLiG30cc6XuFHHxkdkTk3KqnJ123BJp8qprfrWQXZkFRRYlUDWoGdpnLRmOAWlWzayzEYtqCzg9gdM2TG2gok7Rs0MmHmw2tvPiZwZVyKzmqJpgjKoo9b9bCZBl1bOvDYEGrZqRoG2NSygnHNtj3HXNdv19a7BtZTp8-udg__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal