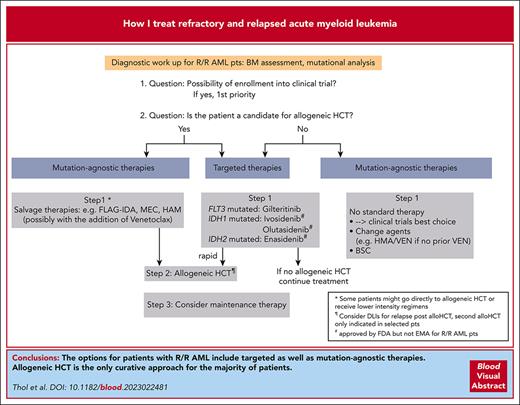
Visual Abstract
Most patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) develop refractory/relapsed (R/R) disease even in the presence of novel and targeted therapies. Given the biological complexity of the disease and differences in frontline treatments, there are therapies approved for only subgroups of R/R AML, and enrollment in clinical trials should be first priority. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is the only potentially curative strategy for most patients. Therapeutic approaches, including allogeneic HCT, triggered by the presence of measurable residual disease (MRD), have recently evolved to prevent overt hematologic relapse. Salvage therapy with chemotherapy or targeted therapy is frequently administered before HCT to reduce the leukemic burden. Gilteritinib is approved by the Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency for patients with relapsed FLT3 mutated AML, whereas targeted therapy for relapsed IDH1/2 mutated AML has only FDA approval. Patients who are R/R after azacitidine and venetoclax (AZA/VEN) have a dismal outcome. In this setting, even available targeted therapies show unsatisfactory results. Examples of ongoing developments include menin inhibitors, a targeted therapy for patients with mutated NPM1 or KMT2A rearrangements, antibodies targeting the macrophage immune checkpoint CD47, and triple combinations involving AZA/VEN. The latter cause significant myelosuppressive effects, which make it challenging to find the right schedule and dose.
Introduction
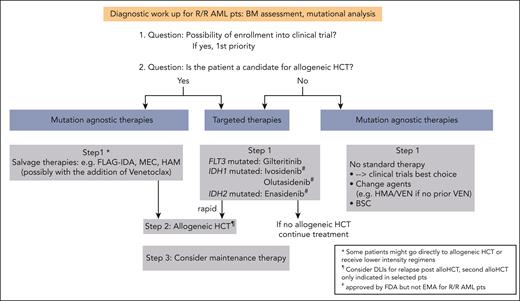
Despite considerable progress in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with the approval of novel drugs, relapse and refractory (R/R) disease remains a common clinical scenario with poor outcome.1,2 The 2022 European LeukemiaNet (ELN) recommendations provide response criteria for R/R disease based on not only hematologic criteria but also assessment of measurable residual disease (MRD), either by multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) or molecular assays (Table 1).3,4 When diagnosing a patient with R/R AML, a repeated mutational analysis is clearly warranted. Clonal evolution at the mutational level frequently occurs and can have direct therapeutic implications (see “Patient 1” and “Patient 2”; Figure 1).1,5-7 Among patients who received intensive therapy, the outcome is especially poor for those with a cytogenetic risk that is not favorable, FLT3 with internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD), higher age, previous allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), and early relapse (within the first 6 months).8,9 Therefore, our first priority is to enroll our patients with R/R AML into clinical trials (Figure 1). Because allogeneic HCT represents the only potentially curative treatment for most of the patients with R/R AML and rescues about one-third of them,3,10 we initiate a donor search for all patients eligible for transplant (if not already conducted at initial diagnosis) and perform allogeneic HCT once a donor is available. Given the poor prognosis of R/R AML (especially if not candidates for allogeneic HCT), we also focus on the quality of life and satisfactory symptom control. By describing 3 patients from our practice, we would like to illustrate our treatment decisions for this patient group.
Definitions of R/R AML according to the 2022 ELN recommendations
| Refractory disease | Failure to achieve CR, CRh, or CRi after |
| Two courses of intensive induction for intensively treated patients or | |
| A defined landmark (eg, 180 d) after starting nonintensive therapy | |
| Relapsed disease | After prior achievement of CR, CRh, or CRi |
| Increase of blasts to ≥5% | |
| Development of extramedullary disease | |
| Reappearance of blasts in the blood in at least 2 peripheral blood samples at least 1 wk apart | |
| MRD relapse | Conversion from MRD negativity to MRD positivity (independent of method) |
| Increase of MRD copy numbers ≥1 log10 between any 2 positive samples in patients with CR, CRh, or CRi in MRD detectable at low levels by qPCR |
| Refractory disease | Failure to achieve CR, CRh, or CRi after |
| Two courses of intensive induction for intensively treated patients or | |
| A defined landmark (eg, 180 d) after starting nonintensive therapy | |
| Relapsed disease | After prior achievement of CR, CRh, or CRi |
| Increase of blasts to ≥5% | |
| Development of extramedullary disease | |
| Reappearance of blasts in the blood in at least 2 peripheral blood samples at least 1 wk apart | |
| MRD relapse | Conversion from MRD negativity to MRD positivity (independent of method) |
| Increase of MRD copy numbers ≥1 log10 between any 2 positive samples in patients with CR, CRh, or CRi in MRD detectable at low levels by qPCR |
Proposed algorithm for the treatment of patients with R/R AML. alloHCT, allogeneic HCT; BSC, best supportive care; Pts, patients.
Proposed algorithm for the treatment of patients with R/R AML. alloHCT, allogeneic HCT; BSC, best supportive care; Pts, patients.
Patient 1
In 2020, a 52-year-old woman was diagnosed with AML with mutated NPM1. Further workup revealed a normal karyotype and comutations in FLT3 (FLT3-ITD with a low allelic ratio of 0.21) and TET2. The disease was classified as favorable risk according to the 2017 ELN classification.11 She was treated with “7 + 3” plus midostaurin12 and achieved a complete remission (CR). Given the good response and the favorable-risk profile, the patient received 3 cycles of intermediate-dose cytarabine, with midostaurin as consolidation treatment. MRD assessment for mutated NPM1 transcripts with real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was performed using the bone marrow and peripheral blood as recommended by the ELN MRD Working Party, and the patient achieved MRD negativity.3,4 However, 1 year after completing consolidation, the patient tested as MRD positive with >400 mutated NPM1 copies per ABL × 104 in the bone marrow and >600 mutated NPM1 copies per ABL × 104 in the peripheral blood.
Question
What does MRD relapse mean and how can we clinically react to prevent morphological relapse?
Treatment considerations
Technological advances in MRD detection, including standardization and consensus recommendations, now allow for the application of MRD assessment to routine clinical practice.4 Different technologies for MRD assessment are available.4,13 Both MFC and RT-qPCR are established methods for MRD detection in AML, the latter being applicable only to a few abnormalities (eg, mutated NPM1 and core-binding factor AML). Next-generation sequencing (NGS)–based MRD assessment has gained increasing interest. However, some challenges (including how to deal with markers for clonal hematopoiesis) remain, so this method is not established in routine practice.14-16 Following the ELN recommendations, we use RT-qPCR (for NPM1mut and core-binding factor leukemia) as well as MFC for other AML subtypes. NGS-based MRD analysis is rapidly evolving, but no clinical decisions should currently be based solely on results from NGS-based MRD measurement.4 Our patient showed 3 mutations at diagnosis (NPM1, FLT3-ITD, and TET2). NPM1 is a robust MRD marker and is rarely lost at relapse.17 RT-qPCR allows for the sensitive detection of very low levels of mutated NPM1 (10−4-10−5), making it an ideal MRD marker.4,17-19TET2 is frequently observed in remission samples and is rather a marker for clonal hematopoiesis, similar to DNMT3A and ASXL1 mutations.14 These mutations, called DTA mutations, should not be used as MRD markers.4 Beyond DTA, there are other mutations (eg, SRSF2, IDH2, JAK2, and TP53) that can be present in clonal hematopoiesis rather than residual AML. In contrast, FLT3-ITD is a good MRD marker with clinical relevance.20-22 After MRD positivity or an increase in MRD copy numbers ≥ 1log10 between any 2 positive samples is detected by RT-qPCR in patients with CR/CRh (CR with partial hematologic recovery)/CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi)-, results need to be rapidly confirmed in a consecutive sample. Although there is no approved therapy and no treatment standard for MRD relapse, we immediately search for a donor for all transplant-eligible patients. An example is NPM1-mutated AML, in which a rise in NPM1mut transcript levels strongly correlates with relapse.18 In an analysis of our study group, all patients (n = 36) with ≥200 NPM1mut per ABL × 104 during follow-up experienced relapse.17 This is supported by a recent randomized study in which a significant survival benefit was observed for MRD monitoring of mutated NPM1 and FLT3-ITD as compared with for the clinical observation.23 Thus, we recommend allogeneic HCT for all transplant-eligible patients when mutant transcript levels exceed 200 NPM1mut per ABL × 104 and with confirmatory analysis. Alternatively, there are ongoing clinical trials for patients who test positive for MRD, with the aim to reinduce molecular CR and prevent hematologic relapse. The therapeutic approaches include unselected or targeted therapies (eg, hypomethylating agents [HMAs], intensive chemotherapy, venetoclax, or FLT3 inhibitors; Table 2), immune-mediated cellular therapies (eg, natural killer-cell infusions), or vaccination against leukemic antigens (eg, WT1).
Early trial results in patients with molecular failure after firstline therapy
| Patient characteristics . | N . | Treatment . | MRD response . | Clinical outcome . | Reference . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPM1 MRD failure | 10 | AZA | 7 of 10 molecular response | CR sustained in 7 of 10, with median follow-up of 10 mo | 88 |
| RT-qPCR <1% or loss of donor chimerism | 53 (32 NPM1mut) | AZA | 36% MRDneg | 1 y RFS, 46% | 89 |
| NPM1 MRD failure | 33 | 20 chemotherapy/HMA ± HCT 13 direct HCT | 80% MRDneg (8/10 after chemotherapy only) | 2 y OS, 86% | 90 |
| NPM1 MRD relapse | 30 | 27 chemotherapy + HCT 3 direct HCT | 59% MRDneg (16/27 after chemotherapy only) | 2 y OS, 63% | 19 |
| NPM1 MRD failure or NPM1 MRD relapse | 5 7 | VEN + HMA/LDAC | 5 of 5 CR MRDneg 6 of 7 CR MRDneg | All responders had MRDneg during median follow-up of 12 mo | 91 |
| NPM1 MRD failure or NPM1 MRD relapse | 2 9 | VEN + AZA + HCT | 11 of 11 CR MRDneg (9/11 after VEN + AZA only) | CR sustained in 9/10 with median follow-up of 26 mo | 92 |
| MFC-MRD relapse | 16 | 7 HMA-based chemotherapy 9 direct HCT | 43% MRDneg (3/7 after chemotherapy only) | 5 y RFS, 31% 5 y OS, 45% | 93 |
| MRD relapse | 26 (20 NPM1mut) | VEN-LDAC | 54% MRDneg | 2 y EFS, 54% 2 y OS, 73% | 94 |
| Molecular MRD failure | 19 | VEN ± LDAC or HMA or other | 84% molecular remission | Median OS, 18.4 mo | 95 |
| MRD (NPM1 or other gene fusions) failure with baseline FLT3mut | 48 (39 NPM1mut) | 32 gilteritinib 8 quizartinib 8 sorafenib | 40% MRDneg | 2 y OS, 80% | 96 |
| Patient characteristics . | N . | Treatment . | MRD response . | Clinical outcome . | Reference . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPM1 MRD failure | 10 | AZA | 7 of 10 molecular response | CR sustained in 7 of 10, with median follow-up of 10 mo | 88 |
| RT-qPCR <1% or loss of donor chimerism | 53 (32 NPM1mut) | AZA | 36% MRDneg | 1 y RFS, 46% | 89 |
| NPM1 MRD failure | 33 | 20 chemotherapy/HMA ± HCT 13 direct HCT | 80% MRDneg (8/10 after chemotherapy only) | 2 y OS, 86% | 90 |
| NPM1 MRD relapse | 30 | 27 chemotherapy + HCT 3 direct HCT | 59% MRDneg (16/27 after chemotherapy only) | 2 y OS, 63% | 19 |
| NPM1 MRD failure or NPM1 MRD relapse | 5 7 | VEN + HMA/LDAC | 5 of 5 CR MRDneg 6 of 7 CR MRDneg | All responders had MRDneg during median follow-up of 12 mo | 91 |
| NPM1 MRD failure or NPM1 MRD relapse | 2 9 | VEN + AZA + HCT | 11 of 11 CR MRDneg (9/11 after VEN + AZA only) | CR sustained in 9/10 with median follow-up of 26 mo | 92 |
| MFC-MRD relapse | 16 | 7 HMA-based chemotherapy 9 direct HCT | 43% MRDneg (3/7 after chemotherapy only) | 5 y RFS, 31% 5 y OS, 45% | 93 |
| MRD relapse | 26 (20 NPM1mut) | VEN-LDAC | 54% MRDneg | 2 y EFS, 54% 2 y OS, 73% | 94 |
| Molecular MRD failure | 19 | VEN ± LDAC or HMA or other | 84% molecular remission | Median OS, 18.4 mo | 95 |
| MRD (NPM1 or other gene fusions) failure with baseline FLT3mut | 48 (39 NPM1mut) | 32 gilteritinib 8 quizartinib 8 sorafenib | 40% MRDneg | 2 y OS, 80% | 96 |
LDAC, low-dose cytarabine; MRDneg, negative MRD status; VEN, venetoclax.
Patient 1 (continued)
Already 4 weeks after detecting MRD, the patient developed a morphological relapse. At this time, the molecular analysis revealed NPM1, FLT3-ITD (with an increase in the allelic ratio to 2.7), and TET2 mutations as well as a novel mutation in NRAS. Treatment with gilteritinib monotherapy was initiated at 120 mg/d. After achieving CRi, allogeneic HCT from a matched unrelated donor was performed. Postallogeneic HCT management included treatment with sorafenib. Sorafenib as maintenance therapy after allogeneic HCT for FLT3-ITD–positive AML has been shown to increase overall survival (OS)24,25 and is described as a reasonable option in the 2022 ELN recommendations.3 The patient was in CR 180 days after allogeneic HCT.
Question
How does firstline therapy as well as the mutational profile influence our treatment options at relapse?
Treatment considerations
Clonal evolution is a common phenomenon at relapse. Thus, repeated molecular analysis is important to identify alterations in leukemic clones. In our patient, there was clonal evolution, with an increase in the ITD allelic ratio from 0.21 to 2.7 at the time of relapse, commonly resulting from copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity, as was in our patient. However, a high proportion of patients lose the FLT3-ITD clone in relapse after prior treatment with midostaurin, stressing the need for molecular testing at the time of relapse.6 Gilteritinib, a FLT3 inhibitor, is approved for FLT3-mutated R/R AML by both the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). It showed promising results in a phase 1/2 trial of R/R AML.26 Antileukemic activity was markedly enriched in patients with FLT3 mutations, paving the way for a randomized phase 3 study in FLT3-mutated R/R AML comparing gilteritinib monotherapy with conventional salvage therapy according to the physician’s choice.27 A total of 247 patients were randomized to the gilteritinib arm and 124 patients to salvage chemotherapy. Median OS was significantly longer in the gilteritinib arm (9.3 vs 5.6 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.49-0.83; P < .001). Rates of CR/CRh were significantly higher with gilteritinib (34.0% vs 15.3%). In an extended follow-up study 2 years after the primary analysis, the 2-year survival rates were 20.6% (95% confidence interval [CI], 15.8-26.0) in the gilteritinib arm vs 14.2% (95% CI, 8.3-21.6) in the standard arm.28 In this follow-up, 40 out of 64 patients who underwent allogeneic HCT received gilteritinib. Of these, 16 were alive 2 years after the transplant without relapse. However, these results also indicate that gilteritinib does not induce a long-term cure in most patients. Both trials were conducted before midostaurin became the standard of care in the frontline treatment of FLT3-mutated AML. As a consequence, in the phase 3 trial, only 5.7% of the patients had received midostaurin during frontline therapy, leaving the question of whether pretreatment with midostaurin affects the response to gilteritinib in relapse. A retrospective analysis compared the outcomes of patients who had received prior midostaurin or sorafenib treatment against the outcomes of those without.29 Although the remission duration was shorter with prior exposure to FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), a trend toward a longer median OS in the gilteritinib arm was again observed among patients with prior TKI exposure. Another FLT3 inhibitor, quizartinib, was not approved by the FDA and EMA because of concerns about the results of the phase 3 study.30 Our patient was treated with gilteritinib as a bridge to allogeneic HCT. Of note, she initially was not a candidate for allogeneic HCT because her disease was classified as favorable-risk AML according to 2017 ELN criteria (NPM1mut and FLT3-ITDlow) with molecular CR1. After allogeneic HCT, our patient was treated with sorafenib. Two randomized trials studied sorafenib as posttransplant maintenance therapy. In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 2 trial, 83 patients with FLT3-ITD–positive adult AML in CR received either placebo (n = 40) or sorafenib (n = 43).24 The 2-year relapse-free survival (RFS) rate was significantly higher in the sorafenib arm (85%) as compared with in the placebo arm (53.3%; P = .002). The strongest benefit was seen for those patients who tested MRD negative before transplant but MRD positive after transplant. Similarly, an open-label, multicenter phase 3 trial randomized 202 patients with FLT3-ITD–positive AML to sorafenib maintenance or to the control group.25 The 1-year cumulative incidence of relapse was 7% in patients receiving sorafenib vs 24.5% in patients not receiving the TKI,31 and in the extended follow-up, sorafenib was associated with an improved OS of 72% vs 55.9% at 60.4 months.25 The effect of 24 months of gilteritinib maintenance after allogeneic HCT was studied vs placebo in a randomized phase 3 trial in patients with FLT3-ITD–positive AML. In the whole cohort, gilteritinib maintenance failed to show a benefit for RFS (primary end point).32 However, a significant benefit was observed for RFS in those patients who had MRD-positive results either before or after transplant, whereas no difference was observed in patients who had MRD-negative results using an NGS-based MRD detection method (at a threshold of 10−6). This raises the question whether posttransplant maintenance with a TKI should be tailored according to the pretransplant or posttransplant MRD results.32
For fit patients without actionable targets, salvage chemotherapy is mostly used before allogeneic HCT, as recommended by ELN and NCCN,3,33 including FLAG-IDA (fludarabine, cytarabine, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and idarubicin); mitoxantrone, cytarabine, and etoposide34; cladribine, cytarabine, mitoxantrone, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; and high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone.35 CR rates are in the order of 40% to 60% for patients with a CR1 duration of 1 year or longer.34,35 Efforts to improve the response to the salvage regimens by combining them with novel agents, for example, venetoclax, are ongoing. Venetoclax is an oral, highly selective B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2 inhibitor with little efficacy as a single agent in AML36; however, it is synergistic with chemotherapy.37,38 FLAG-IDA has been tested in combination with venetoclax.39 The overall response rate (ORR) in patients with R/R AML was 75% in the phase 1B and 70% in the phase 2B trial as compared with 97% in those with newly diagnosed AML. Overall, the CR/CRi rate in R/R AML was 69%. Median OS was not reached in the phase 2 trial after 12 months. A total of 46% of patients with R/R AML proceeded to receive allogeneic HCT, resulting in a 1-year survival after transplant of 78%.39 Our single-center, retrospective study combining a 7-day course of venetoclax with FLA-IDA in R/R AML showed a significantly higher ORR in FLAVIDA compared with FLA-IDA only (78% vs 47%), whereas EFS and OS rates were similar, with 81% (FLAVIDA) and 79% (FLA-IDA) of patients proceeding to allogeneic HCT or donor-lymphocyte infusions (DLIs).40,41 Data from randomized trials are still lacking in this indication. Currently, a randomized phase 3 trial combining venetoclax with intensive chemotherapy is ongoing for firstline therapy (NCT04628026). Additionally, venetoclax with azacitidine (AZA) is also being evaluated as a bridge to transplantation.42-47 Menin inhibitors are novel therapies for patients with R/R AML with NPM1 mutations, such as “Patient 1,” or patients with KMT2A rearrangements, because both subgroups of leukemia rely on menin for proliferation and survival.48,49 Several menin inhibitors are in early clinical trials in R/R AML. In a phase 1 clinical trial, revumenib, a selective oral inhibitor of the menin-KMT2A interaction, was studied for 68 patients (of these, 56 with R/R AML), with 30% of patients achieving CR/CRh.50 Ziftomenib, an oral inhibitor of menin-KMT2A protein-protein interaction, was studied in a phase 1/2 study for patients who have R/R with NPM1-mutated or KMT2A-rearranged AML.51 In the preliminary report, CR and ORR rates were 30% and 40%, respectively, with a median duration of 8.2 months.51 Another possible target is E-selectin, whose expression is upregulated on the bone marrow endothelium by the release of proinflammatory signals through AML blasts, resulting in enhanced binding of leukemia to the endothelium. Uproleselan is an E-selectin antagonist that disrupts this cell adhesion. In a phase 1/2 study in R/R AML, the combination of uproleselan with intensive chemotherapy resulted in a 41% CR/CRi rate and a median OS of 8.8 months.52 Uproleselan is being evaluated in combination with intensive chemotherapy in a phase 3 trial for R/R AML (NCT03616470). For transplant-eligible patients, salvage therapy aims to reduce the leukemia burden before allogeneic HCT. This strategy is based on results showing that patients in CR (especially those having MRD-negative results) have a more favorable outcome after allogeneic HCT15 than patients with active disease.53 This is supported by a retrospective analysis between patients in MRD-positive morphologic remission and those with active disease at the time of allogeneic HCT.54 However, whether all patients with R/R AML benefit from salvage therapy with the attempt to induce CR beforeallogeneic HCT is not known and was studied in a recent phase 3 trial randomly assigning patients 1:1 to a remission induction strategy (RIST-arm) with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone and subsequent allogeneic HCT or to the disease control arm (DISC-arm) with watchful waiting after sequential conditioning and allogeneic HCT.55 The primary end point, CR on day 56 after allogeneic HCT, was achieved in 84.1% in the DISC-arm vs 81.3% in the RIST-arm. The 1-year leukemia-free survival from CR on day 56 was similar in both arms, as were the 1-year and 3-year OS from randomization. Further studies are needed to elucidate which molecular subgroups might benefit from salvage therapy before allogeneic HCT, especially because patients with FLT3-ITD–positive status were underrepresented in this trial. Furthermore, salvage therapy continues to play an important role for patients who are R/R and cannot undergo rapid allogeneic HCT (eg, ongoing donor search) or highly proliferative AML. In summary, our highest priority for patients with R/R AML is allogeneic HCT for all transplant-eligible patients.56
Patient 2
In 2021, a 75-year-old man with congestive heart disease received the diagnosis of AML not otherwise specified. Cytogenetic analysis revealed a trisomy 8, and mutational analysis showed mutations in IDH2, ASXL1, and NF1. He received combination therapy with azacitidine and venetoclax (AZA/VEN) and achieved a CRi after the first cycle. He was treated with an additional 12 cycles of AZA/VEN and took a “drug holiday” of 10 weeks at his personal request. At the time when he wanted to recommence therapy, the disease had recurred with 35% blasts on the blood smear. The mutational spectrum at this time showed positive results for all mutations present at diagnosis, with an additional mutation in TP53.
Question
What is the outlook of patients with R/R AML after treatment with AZA/VEN and what are their treatment options?
Treatment considerations
For patients unfit for intensive chemotherapy, treatment with the HMAs azacitidine (AZA) or decitabine plus venetoclax (VEN) has become the standard of care. Approval of this combination was based on the results of the placebo-controlled VIALE-A trial, in which a median OS of 14.7 months was observed in the AZA/VEN vs 9.6 months in the AZA + placebo arm (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.52-0.85; P < .001) at a median follow-up of 20.5 months.57 In an updated analysis with a median follow-up of 43.2 months, the survival curve for AZA/VEN-treated patients continued to decline, indicating that this combination is not curative for most patients.58 Virtually all patients will eventually relapse or become resistant while on treatment, even after a favorable initial response to treatment. However, in the subgroup of patients with NPM1-mutated AML, most patients achieve MRD negativity with a favorable outcome.59 Nevertheless, survival of patients relapsing after treatment with HMA/VEN is poor.60 In a retrospective study of 41 patients relapsing after HMA/VEN, the median OS was only 2.4 months.61-63 Salvage therapy did not lead to meaningful prolongation of survival as compared with no salvage therapy (2.9 vs 1.3 months), which is also our experience.61 If the performance status improves under initial therapy with HMA/VEN and the patient becomes eligible for allogeneic HCT, this treatment option should be considered before relapse occurs. At the time patients become R/R to HMA/VEN, they are likely to have acquired high-risk cytogenetic and molecular features (eg, mutations in TP53, FLT3, or N/KRAS) that further diminish the response rate to any therapy, including allogeneic HCT.63 For these patients, switching to other chemotherapy agents is not beneficial,63 and we aim to enroll them into clinical trials. At this point of time, a transparent discussion with the patient about what can or cannot be achieved with approved substances is mandatory. For many patients, the best supportive care and integration into palliative care services may be the preferred recommendations. Targeted therapy can be considered for those patients with actionable targets. Our patient harbored an IDH2 mutation at the time of diagnosis and relapse. For patients with IDH1 and IDH2 mutations, targeted therapy is available. Ivosidenib and olutasidenib as well as enasidenib are oral, selective inhibitors of mutant IDH1 and IDH2 enzymes, respectively (Table 3). These agents were approved by the FDA (but not by the EMA) based on phase 1/2 single-arm studies in patients with R/R IDH1/IDH2-mutated AML. Responses and survival were similar for all 3 inhibitors (ORR 42%, 48%, and 40% and median OS 8.8, 11.6, and 9.3 months for ivosidenib, olutasidenib, and enasidenib, respectively).64-67 However, the phase 3 trial of enasidenib vs conventional treatment options failed to show an OS benefit for heavily pretreated patients (6.5 months with enasidenib vs 6.2 months with standard therapy; HR, 0.86).67 Of note, the trials with ivosidenib and enasidenib were conducted outside the setting of failure to HMA/VEN because they were initiated before venetoclax became part of the standard of care. Therefore, the question arises: how do targeted therapies work in patients who have become R/R to HMA/VEN. In a multicenter retrospective cohort study, 22 patients with AML with FLT3 or IDH1/2 mutations (7 patients with FLT3-ITD, 2 patients with FLT3-TKD, 3 with IDH1, 7 with IDH2, and 3 patients with concomitant FLT3 and IDH mutations) were evaluated for response to salvage therapy after HMA/VEN frontline treatment.68 Patients received targeted therapy with gilteritinib (n = 11; of these, 3 patients in combination with HMA), sorafenib plus HMA (n = 1), ivosidenib (n = 2), olutasenib (n = 1), enasidenib (n = 7; of these, 3 patients in combination with HMA). The median OS after progression after HMA/VEN was only 4.4 months (5.6 months for patients with FLT3 mutation, 4.2 months for patients with IDH1/2 mutations). However, 5 out of 22 patients lived for more than 10 months, with a median OS of 11.5 months as compared with 3.3 months in nonresponders. Given the small number of patients in this retrospective analysis, the results need to be interpreted with caution. Importantly, for olutasidenib, a selective IDH1 inhibitor, the ORR in R/R AML was not different between patients who were venetoclax-naïve and patients with prior venetoclax exposure.66 Still, there is a very high medical need for novel treatments for patients relapsing after HMA/VEN as well as for those patients who are primary refractory to HMA/VEN (eg, a high percentage of patients with TP53 mutations). One of the possible approaches is antibodies targeting the macrophage immune checkpoint CD47.69 CD47 is a macrophage immune checkpoint that functions as a “do not eat me” signal on cancer cells. Inhibiting CD47 can promote the phagocytosis of leukemic cells.69 Magrolimab, a CD47 antibody, was studied in combination with AZA/VEN in R/R AML.70 Of note, only 2 out of 17 patients with prior VEN exposure showed a response (CRi) with a median OS of 3.1 months. Given these unsatisfactory results, additional patients who were R/R were not enrolled.70 Therefore, the prospect of patients who have relapsed or have become refractory to HMA/VEN remains dismal.
FDA/EMA approvals for R/R AML
| Agent . | FDA/EMA approval . | Age in study, y . | N . | ORR, % . | CR, % . | CRi, % . | Median survival, mo . | Reference . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ivosidenib | IDH1-mutated R/R AML/not authorized by EMA | 18-89 | 258 | 42 | 22 | 9 | 8.8 | 65 |
| Olutasidenib | IDH1-mutated R/R AML/not authorized by EMA | 32-87 | 153 | 48 | 32 | 10 | 11.6 | 66 |
| Enasidenib | IDH2-mutated R/R AML/not authorized by EMA | 19-100 | 109 | 40 | 19 | 7 | 9.3 | 64 |
| Gemtuzumab ozogamicin | CD33+ R/R AML as monotherapy/not authorized by EMA | 20-87 | 277 | 26 | 13 | 13 (CRp) | 4.9 | 97 |
| Gilteritinib | FLT3-mutated R/R AML | 20-84 | 247 | 54 | 21 | 26 | 9.3 | 27 |
| Agent . | FDA/EMA approval . | Age in study, y . | N . | ORR, % . | CR, % . | CRi, % . | Median survival, mo . | Reference . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ivosidenib | IDH1-mutated R/R AML/not authorized by EMA | 18-89 | 258 | 42 | 22 | 9 | 8.8 | 65 |
| Olutasidenib | IDH1-mutated R/R AML/not authorized by EMA | 32-87 | 153 | 48 | 32 | 10 | 11.6 | 66 |
| Enasidenib | IDH2-mutated R/R AML/not authorized by EMA | 19-100 | 109 | 40 | 19 | 7 | 9.3 | 64 |
| Gemtuzumab ozogamicin | CD33+ R/R AML as monotherapy/not authorized by EMA | 20-87 | 277 | 26 | 13 | 13 (CRp) | 4.9 | 97 |
| Gilteritinib | FLT3-mutated R/R AML | 20-84 | 247 | 54 | 21 | 26 | 9.3 | 27 |
CRp, CR with incomplete platelet recovery; IC, intensive chemotherapy; N, number of patients in the study.
Patient 3
In 2022, a 65-year-old man underwent a bone marrow biopsy when persistent pancytopenia was observed on routine blood analysis. A diagnostic workup revealed an AML with myelodysplasia-related changes. The bone marrow was hypocellular, with 20% blasts; cytogenetic analysis showed a complex karyotype; and molecular screening revealed mutations in TP53, DNMT3A, and NRAS. The patient had an ECOG (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group) performance status of 1 and no relevant comorbidities and was, therefore, considered eligible for intensive chemotherapy. After 1 cycle of CPX-351, the patient achieved a CR. Given the high-risk genetic profile, the patient underwent allogeneic HCT from a matched, unrelated donor. Unfortunately, the patient relapsed 5 months after allogeneic HCT.
Question
How could we prevent relapse after allogeneic HCT in this patient and what can we do if relapse occurs?
Treatment considerations
Allogeneic HCT in CR1 is generally recommended for fit patients with AML, if the predicted relapse rate exceeds 35% to 40%.3 In our patient 3, the relapse probability was especially high, given the fact that a TP53 mutation as well as a complex karyotype were identified. It was recently shown that allogeneic HCT improves OS in patients with TP53-mutated MDS as compared with non-HCT treatment.71 The survival benefit was independent of the allelic status of TP53.71 However, despite allogeneic HCT being the most effective consolidation therapy to prevent relapse, relapse still occurs in 45% to 55% of adverse-risk patients with AML, after allogeneic HCT72 being even higher in patients with mutated TP53.71 Outcome after posttransplant relapse is very poor, with a 2-year OS rate between 14% and 25% and few long-term cures.72 The prognosis is especially dismal for those patients with an early relapse after transplant (ie, in the first 6 months after allogeneic HCT).72 Thus, the quality of remission before HCT by choosing the best induction therapy is important. Randomized trials comparing intensive chemotherapy vs AZA/VEN as induction therapy are ongoing. Initial data from phase 1/2 trials suggested that magrolimab may be particularly active in high-risk AML, including TP53-mutated AML. However, the pivotal study comparing AZA/VEN vs AZA plus magrolimab in firstline therapy of AML with mutated TP53 was stopped prematurely because of futility. In addition, posttransplant efforts to prevent relapse are currently being evaluated. Trials with sorafenib and gilteritinib maintenance24,25,32 are examples of how preemptive maintenance therapy can reduce relapse rates in patients with FLT3-mutated AML. In a randomized phase 3 trial of azacitidine maintenance vs observation after allogeneic HCT, RFS was not improved with AZA maintenance.73 Other ongoing trials evaluate the utility of AZA/VEN maintenance therapy post allogeneic HCT (VIALE-T trial; NCT04161885) or oral azacitidine (CC-486; NCT04173533).74 Outside clinical trials, no standard therapy exists in this scenario. We aim to reduce immunosuppressive therapy as rapidly as possible and integrate DLIs into our therapeutic plan to evoke a graft-vs-leukemia effect. DLIs can be combined with other therapies, for example, intensive chemotherapy, azacitidine, targeted therapy, and so on, but require careful monitoring for the development of graft-versus-host disease.75 For a small fraction of patients, a second allogeneic HCT can be considered, for example, for younger patients with a late relapse without prior graft-versus-host disease. In a retrospective EBMT (European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation) registry study of 418 adult patients who relapsed after first allogeneic HCT, the 2-year OS was 26% in the second allogeneic HCT group (n = 137) as compared with 25% in the DLI group (n = 281). Similarly, 5-year OS was also not significantly different between both groups (19% with second allogeneic HCT and 15% with DLI).76 For us, these data support the use of DLIs whenever possible.
Future directions/perspective
To improve outcomes in R/R AML, triplet therapies are being studied, especially for older patients. Here, the triplet combination of AZA/VEN plus targeted therapy (eg, ivosidenib, enasidenib, and gilteritinib) or with other novel agents (eg, magrolimab, revumenib, and IMGN632) is being evaluated. One of the major challenges of triplet combinations is finding the right schedule and dose because these combinations have profound myelosuppressive effects. In a phase 1b/2 study, the combination of gilteritinib plus venetoclax resulted in a modified composite complete response rate (CR + CRi + CR with incomplete platelet recovery + morphological leukemia-free state) of 75% for patients with FLT3 mutations, irrespective of prior TKI treatment.77 The median duration of remission was 4.9 months. The triplet combination AZA/VEN plus gilteritinib yielded a response in 74% of patients (n = 14).78 The median OS was 5.8 months, and the 1-year OS rate was 27%. Similarly, in a phase 1b/2 study, ASTX727 (oral decitabine/cedazuridine) and venetoclax were combined with ivosidenib or enasidenib in 15 patients with IDH1/2-mutated R/R AML.79 The composite CR rate was 50% in the ivosidenib arm and 56% in the enasidenib arm. The highest response was observed in patients who are venetoclax-naïve. IMGN632, a CD123-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, was studied in a phase 1/2 trial in combination with AZA/VEN initially in 35 patients with R/R AML with an ORR of 55% and higher response rates in the higher intensity cohorts.80 In the continued study with 61 patients with R/R AML, the ORR was 62% and the continuous CR was 47% in patients with venetoclax-naïve patients, as compared with a ORR of 37% and a continuous CR of 11% after prior venetoclax exposure.81
A different approach are T-cell–based immunotherapies such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, bispecific T-cell engaging antibodies, or dual-affinity retargeting antibodies.82 The development of immunotherapies lags behind in AML because of the difficulty of finding the most suitable targets. Off-target effects, including myelosuppression, as well as unsatisfactory efficacy in early clinical trials, remain problematic. Furthermore, the long-term persistence of CAR T cells in vivo is challenging.83 Different lineage-restricted antigens such as CD33, CD123, CLL-1 (CLEC12A), and FLT3 are currently studied. Examples are bispecific T-cell engaging antibodies targeting CD33 (eg, AMV564 and AMG330), which showed only modest efficacy in AML.84 Flotetuzumab and vibecotamab are bispecific DART antibody–based molecules to CD3ε and CD123. Flotetuzumab was studied in a phase 1/2 study in 88 patients with R/R AML.85 The ORR was 30% among those patients (n = 30) treated with the phase 2 dose of the drug. Patients achieving CR/CRh showed a median OS of 10.2 months.85 The CAR T-cell development is also evolving in AML targeting CLL1 without significant myelotoxicity, with promising results in early-stage trials in pediatric AML.86,87
In summary, the options for patients with R/R AML are constantly evolving; however, a considerable amount of work is still necessary at the preclinical and clinical level before the outlook and the prognosis of these patients will significantly improve.
Acknowledgments
H.D. is supported by Collaborative Research Center SFB 1074 “Experimental models and clinical translation in leukemia” (Coordinating Investigator) and by research group FOR 2674 “Aging-related epigenetic remodeling in acute myeloid leukemia” (project A02), both funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Authorship
Contribution: F.T., H.D., and A.G. wrote the paper and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: F.T. serves in a consulting or advisory role with AbbVie, BMS/Celgene, Novartis, Astellas, Pfizer, and Jazz. H.D. serves in an advisory role for AbbVie, Agios, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Berlin-Chemie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GEMoaB, Gilead, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Syndax; and received research funding from AbbVie, Agios, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Kronos-Bio, and Novartis. A.G. declares no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Arnold Ganser, Department of Hematology, Hemostasis, Oncology, and Stem Cell Transplantation, Hannover Medical School, Carl-Neuberg-Str 1, D-30625 Hannover, Germany; email: ganser.arnold@mh-hannover.de.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal