Abstract
Although the genetic landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been broadly profiled by large-scale sequencing studies performed over the past decade, the molecular basis of the transformation of CLL into aggressive lymphoma, or Richter syndrome (RS), has remained incompletely characterized. Recent advances in computational methods of clonal deconvolution, as well as extensive sample collection efforts in this rapidly progressive malignancy, have now enabled comprehensive analysis of paired CLL and RS samples and have led to multiple new studies investigating the genetic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic origins of RS. In parallel, new genetically engineered and xenograft mouse models have provided the opportunity for gleaning fresh biological and mechanistic insights into RS development and stepwise evolution from antecedent CLL. Altogether, these studies have defined RS driver lesions and CLL risk lesions and identified pathways dysregulated in transformation. Moreover, unique molecular subtypes of RS have been revealed, including a disease marked by profound genomic instability with chromothripsis/chromoplexy and whole genome duplication. Novel profiling approaches, including single-cell DNA and transcriptome sequencing of RS biopsy specimens and cell-free DNA profiling of patient plasma, demonstrate promise for the timely identification of RS clones and may translate to noninvasive identification and early diagnosis of RS. This review summarizes the recent scientific advances in RS and supports the integrated study of human genomics with mouse modeling to provide an advanced understanding of the biological underpinnings of transformation. These recent studies have major implications for much-needed novel therapeutic strategies for this still largely incurable malignancy.
Introduction
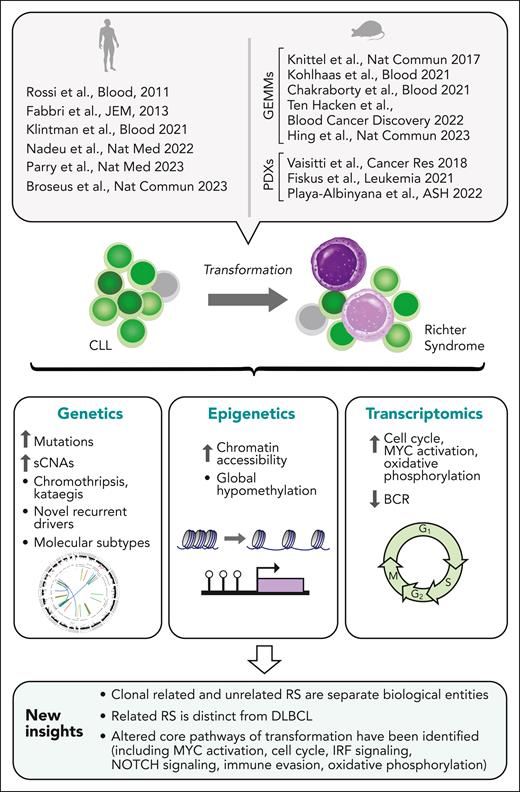
Clonal evolution is a fundamental property of cancers, driving disease progression, relapse, and therapeutic resistance across malignancies.1-3 The transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) into an aggressive lymphoma, or Richter syndrome (RS), is an extreme example of clonal evolution manifesting in a histologic change to high-grade malignancy.2 Despite recent therapeutic advances in the management of CLL, transformation to RS remains associated with a dismal prognosis.2,4 RS most commonly manifests as an aggressive malignancy with a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) histology,2 yet it is associated with inferior survival compared with de novo DLBCL, and limited prior studies have suggested key differences between these lymphomas despite shared histologic appearance.5-7 RS is also distinct from aggressive CLL manifesting with increased appearance of proliferation centers in secondary lymphoid organs.8,9 Older studies of human RS genetics previously identified certain RS-risk lesions (eg, TP53 and CDKN2A/B loss, activating NOTCH1 mutations, MYC amplifications)5-7 but a more systematic understanding of the genetic, epigenetic, and transcriptomic profile of RS has been achievable only recently owing to: (1) collaborative efforts to attain sufficiently powered collections of biospecimens, (2) advances in genomic profiling, including studies performed at single-cell resolution, and (3) novel disease modeling (Figure 1).
New understanding of RS. Insights into the biology of RS gained by recent large-scale studies profiling the genetic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic features of RS, and by the generation of mouse GEMM and PDX models highly reflective of human RS. GEMM, genetically engineered mouse model; PDX, patient-derived xenograft.
New understanding of RS. Insights into the biology of RS gained by recent large-scale studies profiling the genetic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic features of RS, and by the generation of mouse GEMM and PDX models highly reflective of human RS. GEMM, genetically engineered mouse model; PDX, patient-derived xenograft.
Here, we review these major developments. Overall, these studies have revealed key mechanisms and pathways of transformation and underscored the distinct biology of RS. Novel approaches to address the challenge of analyzing RS are surveyed, providing new paths for discovering the basis for stepwise evolution to a transformed state, the potential for early and noninvasive detection of transformation in patients with CLL, and new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to combat this devastating disease.
Mapping clonal evolution to RS
Identification of RS-specific driver lesions
The comprehensive understanding of RS drivers has been limited both by sample availability in this aggressive malignancy (occurring only in ∼2%-10% patients with CLL)2 and by challenges posed in computational analysis and clonal deconvolution. Still, a limited number of RS-risk factors have long been appreciated, including unmutated immunoglobulin status (UM-CLL), NOTCH1 and TP53 alterations, CDKN2A/B loss,2,5-7 BCR subset #8 configuration, and complex karyotype.10,11 In studies performed almost a decade ago, examination of the immunoglobulin gene heavy variable (IGHV) locus identified that RS could arise as clonally related to the antecedent CLL or occur as a clonally unrelated malignancy, the latter of which has been associated with a more favorable prognosis similar to de novo DLBCL.7,12 Over the last year, 3 new large-scale analyses of paired RS and CLL samples, largely of DLBCL histology, have been conducted at the exome and genome-wide scale, which in aggregate exceed 100 individuals.13-15 Together, these studies provide hitherto unparalleled insight into drivers of RS transformation and reconstruct the evolutionary history of CLL evolving to RS.13-15 Furthermore, the increasing availability of large data sets of genetically characterized CLL16 and DLBCL17,18 have provided comparator cohorts which has facilitated the ability to define molecular features unique to RS.
Fresh insights from recent large-scale genomic studies
Application of advanced computational technologies to reconstruct phylogenies and trace CLL clones moving toward RS14,15 have by now yielded numerous insights regarding the genetic events that define the histologic switch. First, these studies have demonstrated that the majority of RS is indeed clonally related to the antecedent CLL, as established through detailed clone tracing from whole exomes and genomes,13-15 IGHV sequencing13-15,19 and even from single-cell mitochondrial barcoding.20 These genome-wide approaches definitively established the existence of clonally unrelated RS,15 revealing lack of a common early cell progenitor with CLL due to the absence of shared somatic genetic events. Second, increased genomic complexity was found to define the observed shift in histology across these newer studies. Transformation to RS was marked by an increased burden of somatic mutations and copy number alterations (sCNAs),13-15 kataegis and chromothripsis/chromoplexy, a greater fraction of genome altered and numerous structural variants.13-15 Whole genome doubling (WGD) was also identified in 15.5% of RS.15 Third, these studies have led to the discovery of the hallmark pathways and drivers affected by transformation (Figure 2). Consistent with older reports, highly prevalent alterations were detected in TP53 (63% sCNA, 55% sCNV), CDKN2A/B (sCNA 19%), and the NOTCH1 (40.3% NOTCH1, 11.5% SPEN) and MYC pathways (ie, 11.5% MGA mutation, 21.2% MGA deletion, 15.4% and MYC amplification) (Table 1).5-7,13-15,21 In these more recent studies, additional somatic nucleotide variants (sSNV) and sCNA events were found to affect DNA damage, MAPK13 and chromatin regulation, and NFκB pathways.14 Statistically significant alterations specific to RS were newly identified, including frequent mutations in IRF2BP2 (13.5%, and sSNVs in CCND3, DNMT3A, TET2, and SRSF1 in addition to numerous recurrent focal sCNAs.15 Other key insights included the loss of epigenetic disease drivers (eg, EZH2/KMT2C, SETD2, ARID1A) and the MYC negative regulator MGA, both as mutational loss and sCNA loss, as key events toward RS progression (Figure 2A).14,15 Altogether, the identified events highlight the common genetically altered pathways leading to RS development, which include epigenetics/chromatin regulation, splicing, MYC activation, NFκB signaling, immune evasion, inflammation, translation, antiapoptotic signaling, DNA damage response, and cell cycle (Figure 2B). Fourth, RS was revealed to comprise multiple molecular subtypes.15 Nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) clustering of RS somatic mutations revealed 5 distinct RS subtypes, each defined by a constellation of driver alterations15 and supported by paired transcriptome analysis, including 2 subtypes with lower fraction of genome altered and more favorable prognosis: Tri12/NOTCH16 and a previously unrecognized RS class marked by SF3B1/EGR2 mutations.15TP53 mutation–associated subtypes (including a mut-NOTCH1-IRF2BP2, a WT NOTCH1, and WGD-RS subtypes) were associated with worse prognosis. Of note, WGD-RS contained the highest proportion of RS evolving from cases with mutated immunoglobulin status (M-CLL), suggesting this as a common trajectory by which M-CLL undergoes histologic transformation. Fifth, numerous mutational processes have now been linked to RS that were not previously commonly observed in analyses of CLL16 beyond the contributions of signatures encompassing aging and AID. This included DNA mismatch repair,13,15 reactive oxygen species,14,15 prior therapy-related signatures,14,15 a novel RS signature (SBS-RT), and signatures previously recognized in DLBCL.14 Further work is needed to define the functional impact of uncovered drivers and conclusively identify the transforming defining events. Certainly, increasing cohort size will increase power to identify recurrent driver events and their impact on prognosis.16
Genetic lesions and affected cellular pathways of RS. (A) Recurrent driver lesions and impacted B-cell pathways in RS. Image partially created with BioRender software. (B) Timing of major RS pathway alterations in the evolution of CLL toward RS. CNG, copy number gain; CNL, copy number loss; GOF, gain of function mutations; LOF, loss of function mutations.
Genetic lesions and affected cellular pathways of RS. (A) Recurrent driver lesions and impacted B-cell pathways in RS. Image partially created with BioRender software. (B) Timing of major RS pathway alterations in the evolution of CLL toward RS. CNG, copy number gain; CNL, copy number loss; GOF, gain of function mutations; LOF, loss of function mutations.
Frequency of recurrent driver events in RS
| . | Percent in discovery cohort (n = 52) . | Percent in total cohort (n = 97) . | Pathway impacted (focal events only) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| del(17p) | 63.5 | 52.6 | DNA damage |
| TP53 | 55.8 | 43.3 | DNA damage |
| NOTCH1 | 40.4 | 39.2 | NOTCH signaling |
| del(13q14.2) | 25.0 | 29.9 | |
| del(9p21.3)[CDKN2A/B] | 19.2 | 27.8 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| del(9p) | 26.9 | 24.7 | |
| SF3B1 | 19.2 | 21.6 | RNA splicing |
| del(1p) | 23.1 | 20.6 | |
| IRF2BP2 | 13.5 | 19.6 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| Tri(12) | 15.4 | 19.6 | |
| del(6q) | 19.2 | 18.6 | |
| del(9q) | 23.1 | 18.6 | |
| del(15q15.1)[MGA] | 21.2 | 17.5 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| amp(1q23.1) | 23.1 | 16.5 | Antiapoptotic signaling |
| del(11q22.3)[ATM] | 15.4 | 15.5 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| del(7q36.2)[EZH2, KMT2C] | 11.5 | 15.5 | Chromatin remodeling |
| WGD | 17.3 | 15.5 | |
| amp(7p) | 15.4 | 15.5 | |
| del(14q32.11) | 19.2 | 13.4 | |
| amp(8q24.21)[MYC] | 15.4 | 13.4 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| del(2q37.1) | 15.4 | 12.4 | |
| del(8q12.1) | 11.5 | 12.4 | |
| XPO1 | 9.6 | 12.4 | Nuclear export |
| EGR2 | 11.5 | 11.3 | B-cell transcription |
| MGA | 11.5 | 11.3 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| PIM1 | 9.6 | 11.3 | |
| SPEN | 11.5 | 10.3 | NOTCH signaling/B-cell transcription |
| del(16q12.1) | 11.5 | 9.3 | |
| del(3p21.32)[SETD2] | 7.7 | 9.3 | Chromatin remodeling |
| amp(13q31.2) | 11.5 | 9.3 | |
| KRAS | 11.5 | 9.3 | BCR signaling |
| MYC | 5.8 | 9.3 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| amp(11q23.1)[POU2AF1] | 7.7 | 9.3 | B-cell transcription |
| del(10q) | 5.8 | 9.3 | Inflammatory signaling |
| ATM | 5.8 | 8.2 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| BRAF | 5.8 | 8.2 | BCR signaling |
| del(12p13.2) | 5.8 | 8.2 | |
| del(19p13.3) | 7.7 | 8.2 | |
| del(1p35.3)[ARID1A] | 5.8 | 8.2 | Chromatin remodeling |
| del(1q42.13) | 7.7 | 8.2 | |
| amp(16q23.2)[IRF8] | 7.7 | 8.2 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| del(18q22.2) | 7.7 | 7.2 | |
| DNMT3A | 7.7 | 7.2 | DNA methylation |
| amp(7q21.2)[CDK6] | 11.5 | 7.2 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| amp(9p24.1)[PD-L1/PD-L2] | 7.7 | 7.2 | Immune evasion |
| IRF8 | 7.7 | 7.2 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| CARD11 | 7.7 | 6.2 | BCR signaling |
| del(8p21.3) | 7.7 | 5.2 | |
| HIST1H1E | 7.7 | 5.2 | Chromatin-histone |
| SRSF1 | 5.8 | 5.2 | RNA splicing |
| MYD88 | 1.9 | 5.2 | Inflammatory signaling |
| PRDM1 | 3.8 | 5.2 | B-cell transcription |
| del(13q14.2) [RB1] | 7.7 | 5.2 | DNA damage |
| TET2 | 5.8 | 5.1 | DNA methylation |
| B2M | 5.8 | 4.1 | Immune evasion |
| CCND3 | 1.9 | 4.1 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| CHD2 | 5.8 | 4.1 | Chromatin remodeling |
| amp(19p13.2) | 7.7 | 4.1 | |
| amp(6p22.1)[IRF4] | 5.8 | 4.1 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| GNB1 | 5.8 | 4.1 | BCR signaling |
| TBL1XR1 | 5.8 | 4.1 | RNA processing |
| ZC3H18 | 5.8 | 4.1 | RNA processing |
| amp(18q21.33) | 1.9 | 3.1 | |
| HIST1H2AC | 3.8 | 3.1 | Chromatin-histone |
| EZH2 | 5.8 | 3.1 | Chromatin remodeling |
| NFKBIE | 5.8 | 3.1 | Inflammatory signaling |
| . | Percent in discovery cohort (n = 52) . | Percent in total cohort (n = 97) . | Pathway impacted (focal events only) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| del(17p) | 63.5 | 52.6 | DNA damage |
| TP53 | 55.8 | 43.3 | DNA damage |
| NOTCH1 | 40.4 | 39.2 | NOTCH signaling |
| del(13q14.2) | 25.0 | 29.9 | |
| del(9p21.3)[CDKN2A/B] | 19.2 | 27.8 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| del(9p) | 26.9 | 24.7 | |
| SF3B1 | 19.2 | 21.6 | RNA splicing |
| del(1p) | 23.1 | 20.6 | |
| IRF2BP2 | 13.5 | 19.6 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| Tri(12) | 15.4 | 19.6 | |
| del(6q) | 19.2 | 18.6 | |
| del(9q) | 23.1 | 18.6 | |
| del(15q15.1)[MGA] | 21.2 | 17.5 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| amp(1q23.1) | 23.1 | 16.5 | Antiapoptotic signaling |
| del(11q22.3)[ATM] | 15.4 | 15.5 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| del(7q36.2)[EZH2, KMT2C] | 11.5 | 15.5 | Chromatin remodeling |
| WGD | 17.3 | 15.5 | |
| amp(7p) | 15.4 | 15.5 | |
| del(14q32.11) | 19.2 | 13.4 | |
| amp(8q24.21)[MYC] | 15.4 | 13.4 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| del(2q37.1) | 15.4 | 12.4 | |
| del(8q12.1) | 11.5 | 12.4 | |
| XPO1 | 9.6 | 12.4 | Nuclear export |
| EGR2 | 11.5 | 11.3 | B-cell transcription |
| MGA | 11.5 | 11.3 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| PIM1 | 9.6 | 11.3 | |
| SPEN | 11.5 | 10.3 | NOTCH signaling/B-cell transcription |
| del(16q12.1) | 11.5 | 9.3 | |
| del(3p21.32)[SETD2] | 7.7 | 9.3 | Chromatin remodeling |
| amp(13q31.2) | 11.5 | 9.3 | |
| KRAS | 11.5 | 9.3 | BCR signaling |
| MYC | 5.8 | 9.3 | B-cell transcription-MYC activation |
| amp(11q23.1)[POU2AF1] | 7.7 | 9.3 | B-cell transcription |
| del(10q) | 5.8 | 9.3 | Inflammatory signaling |
| ATM | 5.8 | 8.2 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| BRAF | 5.8 | 8.2 | BCR signaling |
| del(12p13.2) | 5.8 | 8.2 | |
| del(19p13.3) | 7.7 | 8.2 | |
| del(1p35.3)[ARID1A] | 5.8 | 8.2 | Chromatin remodeling |
| del(1q42.13) | 7.7 | 8.2 | |
| amp(16q23.2)[IRF8] | 7.7 | 8.2 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| del(18q22.2) | 7.7 | 7.2 | |
| DNMT3A | 7.7 | 7.2 | DNA methylation |
| amp(7q21.2)[CDK6] | 11.5 | 7.2 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| amp(9p24.1)[PD-L1/PD-L2] | 7.7 | 7.2 | Immune evasion |
| IRF8 | 7.7 | 7.2 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| CARD11 | 7.7 | 6.2 | BCR signaling |
| del(8p21.3) | 7.7 | 5.2 | |
| HIST1H1E | 7.7 | 5.2 | Chromatin-histone |
| SRSF1 | 5.8 | 5.2 | RNA splicing |
| MYD88 | 1.9 | 5.2 | Inflammatory signaling |
| PRDM1 | 3.8 | 5.2 | B-cell transcription |
| del(13q14.2) [RB1] | 7.7 | 5.2 | DNA damage |
| TET2 | 5.8 | 5.1 | DNA methylation |
| B2M | 5.8 | 4.1 | Immune evasion |
| CCND3 | 1.9 | 4.1 | Cell cycle/DNA damage |
| CHD2 | 5.8 | 4.1 | Chromatin remodeling |
| amp(19p13.2) | 7.7 | 4.1 | |
| amp(6p22.1)[IRF4] | 5.8 | 4.1 | B-cell transcription-inflammation |
| GNB1 | 5.8 | 4.1 | BCR signaling |
| TBL1XR1 | 5.8 | 4.1 | RNA processing |
| ZC3H18 | 5.8 | 4.1 | RNA processing |
| amp(18q21.33) | 1.9 | 3.1 | |
| HIST1H2AC | 3.8 | 3.1 | Chromatin-histone |
| EZH2 | 5.8 | 3.1 | Chromatin remodeling |
| NFKBIE | 5.8 | 3.1 | Inflammatory signaling |
Data from Parry et al, Evolutionary history of transformation from chronic lymphocytic leukemia to Richter syndrome. Nat Med. 2023;29(1):158-169,15 with permission from Springer Nature.
Dysregulated pathways of RS: integrating epigenetics and transcriptomics
The affected cellular pathways of RS appear to converge on a limited set of pathways, namely aberrant cell cycle (E2F targets, G2M checkpoints), MYC targets, MTORC1 signaling, oxidative phosphorylation, and DNA repair.14,15,19 In addition, transcriptomic analysis of CLL and RS showed a comparative decrease in BCR signaling in RS.14,15,19 However, RS is likely not entirely BCR-independent, as highlighted by clinical observations of response to Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibition22,23 and functional studies explored below in recent mouse models. Furthermore, increased RS oxidative phosphorylation was functionally validated with in vitro cellular respiration experiments in primary CLL and RS cells.14 In parallel, global hypomethylation appears to be a defining feature of RS14,19 in 2 genome-wide methylation studies. Examination of 6 paired CLL and RS samples showed the observed methylation pattern largely reflected the CLL cell of origin (M-CLL vs UM-CLL).14 Interestingly, this CLL-like methylation imprint was retained in clonally related RS cases and absent from clonally unrelated RS in the integrative analysis of 58 RS cases, 25 of which had paired CLL, along with CLL, DLBCL, and normal B cells.19 Differentially methylated regions between RS and CLL have been linked to NOTCH and Wnt pathways and to immune pathways, including the PD-1 immune checkpoint.19 Transformation to RS resulted in markedly altered chromatin accessibility and activation in the analysis of 6 patients with RS by ATAC-seq and/or H3K27acetylation profiling, with newly opening binding sites to transcription factors impacting core pathways of oxidative phosphorylation, cell cycle, mTOR, MYC, and interferon regulatory factor (IRF) signaling.14 These pathways were unique to RS and not previously identified in CLL epigenome analyses.16,24 Combined with the observed epigenetic driver alterations in RS14,15 and downregulation of genes encoding chromatin remodelers,14 these findings altogether indicate common molecular pathways as central to the process of transformation and highlight the epigenome as a potential rich future area of RS investigation. Future epigenetic investigations may further inform RS disease risk subtypes and advance the understanding of the changes that occur in progression to transformation.
Clonally related RS is a lymphoma distinct from DLBCL
Emerging evidence now shows that clonally related RS has different genetics, epigenetics, and transcriptomics from de novo DLBCL, which supports observations from early RS genetic studies that RS represents a distinct disease entity.5-7,13-15 In contrast, these studies15,19 demonstrated that clonally unrelated RS has similar genetics, methylation, and expression to de novo DLBCL, which may explain its superior prognosis compared with clonally related RS.7 NMF clustering of RS and DLBCL genetic alterations15,17 show that related RS is largely distinct from DLBCL but most similar to cluster 2-DLBCL,17 which is marked by biallelic TP53 loss. Clonally unrelated RS clustered with de novo DLBCL, separately from RS, with membership across DLBCL subtypes.15 Integration of methylation and transcriptome data between RS and DLBCL19 further highlighted RS as a distinct lymphoma, with differentially methylated regions in target genes of Polycomb repressive complex 2, the epigenetic remodeling complex, which contains EZH2, and increased global hypomethylation in RS.19 Furthermore, methylation signatures allowed the separation of clonally related RS from DLBCL-like clonally unrelated RS, an association which was confirmed by subsequent hierarchical clustering of RS transcriptomes and IGHV analyses.19 The clonally related RS signature showed comparative enrichment in NOTCH1, PI3K, and BCR pathways.19 Interestingly, this clonally related RS signature could be subsequently detected in a subset of ABC-DLBCLs across large, sequenced cohorts of DLBCL,18 enriched in unclassified and N1 subsets of DLBCL, and associated with CD5+ immunohistochemistry analysis status and poor overall survival. IRF2BP2 mutations and NOTCH1 alterations are key features of N1-DLBCL,18 suggesting shared transcriptomic and molecular genetic features between RS and the adverse-risk subtype of N1-DLBCL.15,18,19
At present, the existing data do not definitively define the RS cell of origin. Whether RS arises from proliferative lymphoid tissue microenvironments, stem-like CLL cells, or a dormant early CLL clone, remains unknown. Recent patient xenograft models25 suggest that the RS cell of origin is preexisting and contained within the circulating CLL pool, recapitulating the concept of RS-seeding cell highlighted in human studies.14 Genomic profiling has highlighted that RS arising from M-CLL occurs through distinct mechanisms, such as through WGD and rapid genomic instability.15 These insights support the notion that the molecular evolutionary routes of transformation may depend on the characteristics of the originating CLL cell. Future multiomic integrative approaches that examine RS evolution across lymphoid compartments will provide additional insight into the cellular origin and compartments of RS and how they differ compared with CLL and DLBCL subsets and subtypes.
Immune microenvironment of RS
The tumor microenvironment of CLL has long been understood to play a crucial role in CLL initiation and progression.26 Although immune checkpoint blockade has not demonstrated major clinical activity for CLL, several clinical studies have documented response rates of 40% to 65% to anti-PD1 treatment in patients with RS,27-29 and there is hope generated by recent investigations of bispecific antibodies and engineered cellular therapies.30 These observations thus motivate further study of the immune microenvironment and cellular interactions in RS.
Several key observations regarding the immune microenvironment of RS have been observed through immunohistochemistry analysis. These include the detection of an increase in FOXP3+ T-regulatory cells and CD163+ macrophages in the RS lymph node.31 In addition, surface PD-1 staining has been identified on clonally related RS malignant B cells, whereas it is generally not observed in DLBCL or CLL outside of the weak expression in proliferation centers.32,33 Interestingly, dysregulated methylation surrounding the PD-1 locus may underlie this protein expression change.19 The T-cell repertoire may shift with transformation as well, with reduced peripheral blood T-cell receptor clonality reported in RS as compared with CLL, which raises interesting questions about whether this altered T-cell receptor repertoire promotes or may instead constrain RS.31
Although PD-1 checkpoint blockade has shown some promise in RS, the mechanisms underlying the basis for this response remain incompletely elucidated. Genetic features of RS may contribute to this response (ie, increased neoantigen load, PD-L1/L2 amplification, or B2M loss),15 as well as altered immune expression pathways of the tumor (ie, PD-1 expression).31-33 Given the typical admixture of tumor and immune populations within a biopsy specimen, resolving the contribution of diverse cell populations to gene expression is challenging, but single-cell technologies are now enabling more precise immune profiling.34 Recently, single-cell RNA-seq profiling of bone marrow resident T-cell populations in RS highlighted key differences in immune cell composition compared with normal marrow, including increased cytotoxic and T-regulatory populations.35 Checkpoint blockade responders showed increased CD8 effector/effector memory (E/EM) populations, which were marked by the transcription factor ZNF683, and which displayed preserved cytotoxicity and intermediate exhaustion.35 This population displayed homology to T-cell clusters seen in solid tumor studies, and functional analyses showed it to regulate pathways of cytotoxicity and T-cell activation, suggesting that key exploitable immune populations can be identified and targeted by immune-based therapies in RS (Figure 3). Furthermore, more in-depth characterization of the key immune and stromal cell changes between the CLL and RS immune microenvironment will likely be possible in the future with advances in single-cell approaches and spatial profiling techniques.
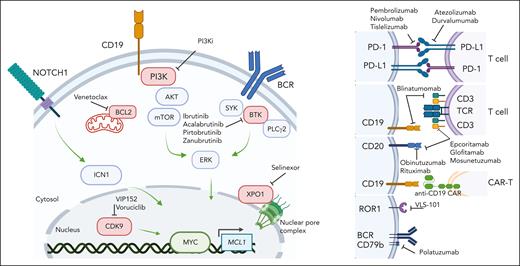
Investigational therapeutic landscape of RS. Small molecule targeted agents and immune therapeutics currently in open or recently completed clinical trials for RS. Image created with BioRender software.
Investigational therapeutic landscape of RS. Small molecule targeted agents and immune therapeutics currently in open or recently completed clinical trials for RS. Image created with BioRender software.
The evolving treatment landscape for RS: targeted agents and immune therapies
Given the poor response rates of RS to traditional chemoimmunotherapy approaches, clinical trials are favored for RS treatment, as reflected by consensus guidelines.2,30,36 New understanding of the molecular basis of RS and transforming mechanisms highlights potential promise toward the identification of therapeutic vulnerabilities, many of which are already being exploited in clinical investigation, as new therapies are desperately needed in this refractory malignancy (summary of agents in registered clinical trials in Figure 3). In addition to checkpoint blockade approaches (ie, PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade), active areas of clinical investigation include combination therapies of novel agents (BTKi, BCL-2i, PI3Ki, and XPOi) with or without chemotherapy. Recently completed studies of venetoclax + REPOCH in RS37 and ibrutinib + R-CHOP in N1 DLBCL38 showed promising response rates and suggested that despite transcriptional changes in BCR signaling and oxidative phosphorylation in RS, RS cells display partial or synergistic sensitivity to novel agents when combined with chemotherapy backbones. Other ongoing registered or recent studies are also examining other targeted agents (ie, CDK9 inhibition), bispecific antibodies (ie, CD3/CD20 or CD19/CD3), antibody-drug conjugates (eg, VLS-101 against ROR1, polatuzumab against the BCR coreceptor CD79b), noncovalent BTKi, and CAR T-cell approaches.30 The combination of parallel evolving clinical and associated laboratory investigations will likely dramatically shift the management of RS in the upcoming decade.
Modeling RS in vivo: insights into disease biology and therapeutic vulnerabilities
Genetically engineered mice provide evidence for RS drivers
Although human studies have provided important insight into the genetic basis of transformation, mechanistic biology remains largely unexplored because of the limited availability of primary patient material and the lack of RS-derived cell lines. Genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) reflective of human genetics and the disease progression from indolent CLL are now increasingly available. To date, most reported models have relied on the Eμ-TCL1 background, which is recognized to reflect an aggressive variant of CLL and is thus not faithful to the indolent nature of the parental human malignancy.39 Nonetheless, these studies have provided functional insight into the relevance of selected genetic drivers and/or signaling pathways in RS transformation, including loss or Trp53 or Atm,40 MYC overexpression,41 and aberrant expression of the protein arginine methyltransferase.42
Recent introduction of combinatorial lesions through CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing onto a del(13q) background provides proof-of-concept that coselection of multiple CLL drivers (in particular Trp53, the MYC negative regulator Mga and the chromatin remodeler Chd2) can drive lymphoma transformation.43 These models uniquely recapitulate clonally related RS transformation from antecedent indolent CLL, with remarkable histologic (ABC-DLBCL-like histology), transcriptomic (shared transcriptional signatures with human RS), genetic (clonal selection upon transformation, high degree of chromosomal instability in RS), and functional (aberrant MYC/PI3K signaling) similarity to human disease.14,15,19,43 Aberrant activation of the MYC/PI3K axis in transforming disease, linked to diminished expression of protein phosphatases (eg, PTEN), is further associated with increased RS sensitivity to MYC/PI3K/mTOR signaling inhibition in these models.43 Other mouse models have provided insight into the impact of individual RS driver lesions. For example, consistent with the prevalence DNMT3A loss in ∼5% RS cases, loss of Dnmt3a associated with increased NOTCH signaling6 proving the relevance of this lesion in predisposing CLL cells to transformation in another B-cell restricted CLL model.44,45
The role of BCR signaling and microenvironment in RS
The presence of BCR stereotyped subset #8 receptors is a recognized risk factor for RS,10 implying chronic autoantigenic stimulation as a predisposing factor for transformation, and patients with RS have shown some degree of response to both covalent and noncovalent BTK inhibitor therapy.22,23 Despite these observations, the role of antigen-dependent BCR signaling in RS remains controversial, with conflicting observations in human and mouse model studies. Nadeu et al demonstrated diminished BCR signaling both at the transcriptional and functional level (ie, through Ca2+ signaling-based assays) in RS compared with antecedent CLL,14 whereas IgM stimulation together with loss of the CDKN2A/B cell cycle regulators were shown to be essential to RS transformation in TCL1 mice,46 and depletion of surface IgM via CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing was detrimental to human RS cellular survival in NOD scid gamma–based xenografts.47 Because 70% of RS arise from pregerminal center U-CLLs, BCR competence would be expected to be a characteristic feature of these cells, similar to CLL cases carrying unmutated immunoglobulins,48 but this aspect remains to be explored in a larger number of human primary RS. It also remains to be evaluated whether autonomous BCR signaling, typical of CLL,49 characterizes patients at increased risk of transformation. Interestingly, loss of the anergy regulator NFAT2 in mice led to transformation into RS,48 supporting the potential relevance for antigen-dependent BCR signaling in the transforming disease.
Although most CLL signaling pathways [eg, BCR, NOTCH, and toll-like receptors (TLR)] converge on MYC activation, the relevance of these individual signaling axes in shaping immune-microenvironmental crosstalk still remains to be defined. In the report by Kohlhaas et al,50 NOTCH signaling hyperactivation mediated by AKT constitutive activation in TCL1-based crosses was associated to increased interaction of the transforming clone with DLL1-overexpressing CD4+ T cells, thus providing a link between presence of selected molecular changes and microenvironment reprogramming. In line with the known relevance of monocyte/macrophages in mediating CLL progression in vivo in mouse models, TLR inhibition via IRAK4i therapy reduced macrophages and delayed RS cell engraftment in immune-deficient mice.47 Additional studies have started exploring microenvironmental characteristics in mouse models, with preliminary analyses pointing to a high degree of CD8+ T-cell exhaustion and an abundance of PD1+ tumor-associated macrophages associated with transformed disease, with possible implications for response/resistance to CPB.51
Harnessing xenograft and GEMM models to understand therapeutic vulnerabilities of RS
The high proliferative activity of primary RS cells has facilitated the development of xenograft models more consistently than for CLL25,52,53 and has allowed the robust assessment of novel therapeutic modalities, including the combination of PI3K inhibition via duvelisib with BCL2 inhibition by venetoclax,54 anti-ROR1 monoclonal antibodies,55 anti-CD37 immunotoxins,56 or BET-PROTACs alone or combined with ibrutinib or venetoclax52 (Figure 3). Although these are valuable models for the preclinical evaluation of therapeutics, particularly those requiring the presence of human antigens, such as bispecifics or immunotoxins, the lack of fully functional T, B, and natural killer cells characterizing the NOD scid gamma strain used to generate these models limits the ability to interrogate immune-related changes underlying response and resistance to therapy. More complex disease models, including those using “humanized” strains (eg, animals carrying human immune cellular components), are thus necessary to extend the applicability of these platforms to the testing of immune-targeting agents. In parallel, many of these targetable pathways and agents are being investigated in RS clinical trials, with potential knowledge to be gained from the cooperative study of patient-derived samples and mouse models (xenografts and GEMMs) in upcoming years.
Toward early detection, improved diagnosis
Novel single-cell insights into RS origin
The application of single-cell technologies to examine RS diagnosis biopsies has identified intermediate or “in-transition” populations by sCNA profiles, thus providing insight into stepwise genomic disorder and transcriptional shifts of transformation within a lymph node or marrow microenvironment.15 Nadeu et al reported the detection of alterations first linked to RS clones in whole-genome sequencing at low frequency in 5 of 9 patients with CLL examined,14 a finding supported by single-cell DNA sequencing.14 In further examination of these serial patient samples through single-cell RNA sequencing, some pre-RS cells displayed a transcriptional and sCNA profile similar to the eventually diagnosed RS.14 This early seeding of RS clones, appearing up to 19 years before RS diagnosis,14 opens many areas of future scientific study into the origin of RS, including the questions of whether patients who go on to develop RS can be identified early in the course of CLL and whether these novel single-cell technologies could be leveraged to improve early detection and diagnosis of RS (Figure 4). In addition, these findings raise questions as to whether small RS-like subclones may exist frequently in patients with CLL, whether a failure of immune surveillance, therapeutic pressure, or additional genetic or epigenetic events subsequently trigger the eventual emergence of transformation and inspire future laboratory-based investigations into these open questions.
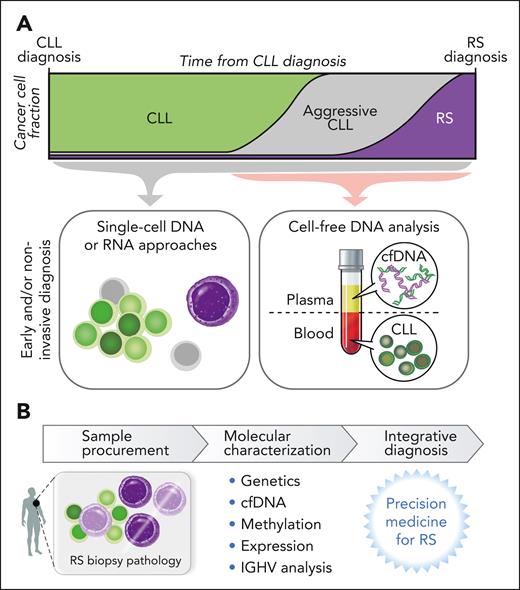
Translational potential of RS investigation. (A) Examination of single cells and/or plasma offers opportunity for early detection of RS clones or RS molecular changes, which may translate to enable early or noninvasive diagnosis. (B) The potential of molecular characterization along with traditional histopathology assessment to refine RS diagnosis.
Translational potential of RS investigation. (A) Examination of single cells and/or plasma offers opportunity for early detection of RS clones or RS molecular changes, which may translate to enable early or noninvasive diagnosis. (B) The potential of molecular characterization along with traditional histopathology assessment to refine RS diagnosis.
Noninvasive diagnosis
Examination of plasma-derived cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has a strong focus in lymphoma, particularly surrounding diagnosis, classification, and treatment monitoring.57 Examination of cfDNA in RS poses unique challenges because plasma in patients with RS contains both cfDNA shed from RS lymph nodes as well as circulating CLL disease (Figure 4). Prior publications suggested that RS changes and nodal CLL evolution were detectable in plasma.58 In a recent analysis of serial plasma samples from 24 patients, RS changes were indeed detected in the cfDNA of patients with RS as sCNAs in ultra-low pass whole genome sequencing that were often absent from the concurrently sampled CLL.15 Furthermore, exome sequencing of cfDNA samples could detect RS mutations not harbored by the CLL cells.15 Thus, cfDNA may be a rich future area of study in RS given the challenges of RS biopsy-based diagnosis and may even help lead to early noninvasive recognition of RS.
Conclusions
Traditionally, the diagnosis of RS has relied upon expert pathological assessment of an adequate tissue biopsy. However, studies have suggested the misdiagnosis rate may be as high as 20%.9 Furthermore, biopsy targeting and clinical tissue sampling remain a limitation, and PET-based assessments are not always predictive of transformation, especially in relapsed/refractory disease.59 Therefore, there is a real opportunity to incorporate molecular diagnostics, along with clinical information, to augment expert pathology assessment. Identification of RS genetic changes may further help clinicians and pathologists identify patients with RS, or at risk for RS. In addition, IGHV sequencing, which has the ability to distinguish clonally related and clonally unrelated RS, has challenges given the need for adequate CLL and RS samples that can be concurrently analyzed to assess for the same IGHV sequence. Therefore, the recent identification of defining genetic, methylation, and transcriptomic features of clonally related RS holds promise for potential translation to enable proper identification of clonally unrelated and related RS independent of CLL and RS DNA admixture and without the need for the initial CLL sample. Given the superior prognosis of clonally unrelated RS, this has implications for therapy decisions, such as consolidation approaches and allogeneic stem cell transplant.60,61 Recent scientific advances have made major progress into unlocking the underlying basis of RS, including the identification of molecular pathways of transformation that converge in common pathways of NOTCH1, DNA damage, IRF signaling, MYC signaling, MTORC1 signaling, chromatin modification, cell cycle, and PI3K signaling. These recent data give hope that further understanding the dysregulated processes underlying transformation may lead to a better understanding of targetable alterations and therapeutic vulnerabilities, as well as maximizing strategies to innovate upon existing diagnostic and detection approaches. Integration of genetics, transcriptomics, and methylation, as well as an advanced understanding of the RS tumor microenvironment and deeper mechanistic studies in mouse models, may highlight factors underlying response and resistance to investigational therapies and provide further insight into novel treatment strategies in RS.
Acknowledgments
E.M.P. acknowledges support from National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI) grant K08CA270085. E.t.H. is a scholar of the American Society of Hematology. C.J.W. acknowledges support from NIH/NCI grants P01 CA206978 and 1U10CA180861-01.
Authorship
Contribution: All authors wrote this manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.J.W. and E.M.P. are named as inventors on US provisional patent application serial number 63/244,625, filed on 15 September 2021 and US provisional patent application serial number 63/291,213, filed on 17 December 2021, both of which are entitled “Diagnosis and Prognosis of Richter’s Syndrome”; C.J.W. receives funding support from Pharmacyclics and holds equity in BioNTech, Inc. E.t.H. declares no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Catherine J. Wu, Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 450 Brookline Ave, Dana Building, Room DA-520, Boston MA 02115; e-mail: cwu@partners.org.
References
Author notes
∗E.M.P. and E.t.H. contributed equally to this article.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal