Key Points
Proximity proteomics and siRNA subscreens in endothelial cells reveal proteins associated with regulated actomyosin expulsion of VWF.
PAK2 and septin hetero-oligomeric complexes are required for actomyosin ring function and effective VWF release.
Abstract
In response to tissue injury, within seconds the ultra-large glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) is released from endothelial storage organelles (Weibel−Palade bodies) into the lumen of the blood vasculature, where it leads to the recruitment of platelets. The marked size of VWF multimers represents an unprecedented burden on the secretory machinery of endothelial cells (ECs). ECs have evolved mechanisms to overcome this, most notably an actomyosin ring that forms, contracts, and squeezes out its unwieldy cargo. Inhibiting the formation or function of these structures represents a novel therapeutic target for thrombotic pathologies, although characterizing proteins associated with such a dynamic process has been challenging. We have combined APEX2 proximity labeling with an innovative dual loss-of-function screen to identify proteins associated with actomyosin ring function. We show that p21 activated kinase 2 (PAK2) recruits septin hetero-oligomers, a molecular interaction that forms a ring around exocytic sites. This cascade of events controls actomyosin ring function, aiding efficient exocytic release. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of PAK2 or septins led to inefficient release of VWF and a failure to form platelet-catching strings. This new molecular mechanism offers additional therapeutic targets for the control of thrombotic disease and is highly relevant to other secretory systems that employ exocytic actomyosin machinery.
Introduction
The endothelial response to injury or infection is rapid. Within seconds, rod-shaped storage organelles (Weibel-Palade bodies [WPB]) containing premade proinflammatory and prohemostatic proteins are trafficked to the cell surface and exocytose their content into the vascular lumen.1,2 The primary cargo of WPB is the ultra-large, prohemostatic glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF).3 Upon exocytosis, VWF multimers unfurl to produce (up to) 1-mm−long strings revealing multiple binding sites for platelets4; this kickstarts the hemostatic response.
Failure to secrete properly processed VWF, because of mutation or defects in cellular machinery associated with WPB formation, results in the most common inherited bleeding disorder (von Willebrand disease).5 However, excess circulating VWF (due to the absence of the VWF-cleaving enzyme ADAMTS13) results in multiple microvascular occlusions (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura).6 More generally, lower levels of VWF are protective for cardiovascular disease,7 whereas higher levels are associated with an increased risk.7,8 Controlling VWF release is therefore a therapeutic strategy for limiting disease pathology.
The biophysical properties of VWF impose an obstacle to efficient secretion. Endothelial cells have evolved processes to enable regulated secretion.1 One such specialization is the recruitment of actin and myosin to form a ring around the secretory granule.9,10 The contraction of these actomyosin structures promotes granule compression, and the resulting force extrudes content apically. Despite their critical physiological role, very little is known about the molecular underpinnings of secretory actomyosin structures. The characterization of such machinery represents a significant challenge because of their small, transient, and dynamic nature and is further complicated by the background of other diverse, pleiotropic actin structures.
Actomyosin ring function occurs in discrete phases and is essential for unfurling platelet-catching VWF strings across the cell surface.1 Ring recruitment is initiated by upstream signaling that promotes de novo nucleation1,11 or rearrangement of actin filaments.12 This is followed by contraction and, finally, disassembly. Actomyosin rings are important to squeeze out ultra-large VWF multimers13 in a process that typically lasts ∼20 seconds.1 So far, non-muscle myosin II (NMII) isoforms have been associated with actin ring contraction in endothelial cells. Recently, myosin Vc has been implicated in stabilizing the actomyosin ring,11 and in other secretory systems additional myosins help recruit actin and organize contraction.14,15
Although the actomyosin ring is essential for controlling the hemostatic output of WPB, the copackaged cargo that supports an inflammatory response (eg, P-selectin) is not affected. Thus, loss of the actomyosin ring has little effect on recruitment of leukocytes.16 Targeting the function of the actomyosin ring provides a novel therapeutic target to control hemostasis while avoiding the risk of immunocompromising patients.17
Here, we used proximity proteomics, biochemical assays, high-throughput, and high-resolution imaging to perform the first unbiased screen of actomyosin ring machinery required for regulated secretion in human primary cells. Our approach reveals the functional “blueprints” of specialized exocytic machinery and describes novel roles in VWF secretion and actomyosin ring regulation for p21 activated kinase 2 (PAK2) and the septin cytoskeleton.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (PromoCell) were cultured as described previously, in the absence of antibiotics.18
Plasmids for transient transfection
eGFP-SEPT6 was a gift from M. Way (Francis Crick Institute, London, United Kingdom). GFP-VWF19 was a gift from J. Voorberg and J.A. Van Mourik (Sanquin Research Laboratory, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). P-selectin lumenal domain mCherry was previously cloned in our laboratory.1 LifeAct-GFP was a gift from B. Baum (University College London, London, United Kingdom). APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a was synthesized by GeneArt (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
APEX-2 proteomics
Four 15-cm plates of confluent HUVECs were required for each proteomics condition analyzed. HUVECs were nucleofected with APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a or buffer alone and seeded into 15-cm plates. Transfected HUVECs were incubated overnight with 7 μM heme to encourage effective folding of APEX2. Mock and APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a−transfected cells were fed with 500 μM biotin tyramide (Iris Biotech) (30 minutes, 37°C). HUVECs were untreated or stimulated with 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) or histamine/adrenaline/3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (HAI). After 10 minutes, the culture medium was replaced with M199 supplemented with 1 mM hydrogen peroxide. After 1 minute, the biotinylation reaction was stopped by 3 washes in stop solution (phosphate-buffered saline [PBS], 10 mM sodium azide, 10 mM ascorbate, and 5 mM Trolox). HUVECs were lysed in RIPA buffer with 10 mM sodium azide and protease inhibitors. Lysates centrifuged (21 000g, 15 minutes, 4°C) and protein concentration determined (Pierce 660 nm, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Protein lysate from each condition was saved for confirmatory immunoblotting. A 1.8-mg quantity of lysate was added to 250 μL high-capacity neutravidin beads (Life Technologies) in low-binding tubes (Life Technologies) and incubated overnight at 4°C. The beads were washed (25 mM ammonium bicarbonate) before centrifugation and storage at −80°C.
Mass spectrometry
Analysis of protein samples by mass spectrometry was performed as previously described.20 The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium21 via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD036983 and 10.6019/PXD036983. As a community resource, full lists of significant proteins identified can be found in supplemental Tables 1-3 (available on the Blood website).
VWF release assay
VWF release assays and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were performed as described previously.1
Near-infrared fluorescence dot blot quantification of VWF
This approach was modified from Vora et al (supplemental Figure 1).22 A standard curve was prepared by serially diluting human plasma and 3 μL of standard or sample was pipetted onto nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham). The next day, the membrane was blocked for 30 minutes in 3% bovine serum albumin PBS before the addition of rabbit anti-VWF antibody (Dako), followed by a biotin-conjugated mouse anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen). Finally, the membrane was incubated with streptavidin IRDye 800CW (Licor). The membrane was washed 3 times with PBS (0.2% Tween-20) between steps. The fluorescence signal was detected using Azure C600 (Azure Biosystems). Samples were analyzed by densitometry using Image Studio (Licor).
Accel siRNA screen
A total of 96 Accel siRNAs targeting actin-binding proteins (including control) were made to order (Dharmacon). Lists of targets and accession numbers are in the supplementary materials (supplemental Table 4).
siRNA knockdown of single targets
siRNA oligonucleotides targeting SEPT7 (Cat: L-011607-00-0005) and PAK2 (Cat: L-003597-00-0005) were purchased from Dharmacon (Horizon) as SMART pools and as 4 independent oligos. SEPT2 (Cat: AM16704), SEPT7 (Cat: AM16704), and SEPT9 (Cat: AM16704) siRNA were purchased from Ambion. A quantity of 300 picomol siRNA was transfected over 2 rounds using an AMAXA nucleofector. Control siRNA firefly luciferase was made by Eurofins Genomics (sequence 5' cgu-acg-cgg-aau-acu-ucg 3').
Exit site size screen
HUVECs were transfected using Accel siRNA reagents (Horizon) as per the manufacturer’s protocol, and VWF exit size analysis was performed using high-content confocal microscopy.16
Immunofluorescence and immunoblotting
Immunofluorescence and immunoblotting were carried out as previously described.1
GFP TRAP
Cells were nucleofected with plasmid DNA and seeded into 10-cm plates. Forty-eight hours later, cell lysates were collected and processed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Chromotek).
Live-cell imaging of HUVECs
For imaging septin dynamics, cells were transfected with eGFP-SEPT6 and P.sel.lum.mCherry and seeded into 4-compartment cell-viewing dishes. Forty-eight hours later, cells were stimulated with PMA (100 ng/mL) and images acquired using a Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope. The same procedure was followed for imaging actin dynamics except that LifeAct-GFP was used in combination with P.sel.lum.mCherry and cells were imaged 24 hours after nucleofection. For inhibitor studies, cells were pre-incubated in 1 μM of FRAX486 or 50 μM forchlorfenuron (FCF) for at least 30 minutes.
VWF multimer gel
VWF multimer gels were performed as described previously.23
VWF string assay
siRNA-transfected HUVECs (3 × 104 cells) were seeded into Ibidi IV0.4 flow chambers (Cat: 80606). The next day, HUVEC were washed in Hanks balanced salt solution (Cat: 14065056) and left untreated or stimulated with PMA (100 ng/mL) in Hanks balanced salt solution for 20 minutes. Using a syringe pump, HUVECs were subject to shear stress at 5 dynes/cm2 for 5 minutes before being fixed with 4% PFA under gradually declining shear values.
In vivo VWF secretion assay
All in vivo procedures were conducted using 8- to 12-week-old mice in accordance with the institutional Animal Welfare Ethical Review Body (AWERB) and United Kingdom Home Office guidelines.
Male C57BL/6 mice (Charles River, UK) were housed under controlled environmental conditions (12-hour light/dark cycles at ambient temperature and humidity) on a standard chow diet. In vivo VWF secretion assay was performed as described elsewhere,24,25 with the following exception: 1.5 hours prior to starting, FRAX486 or equivalent dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was administered IV in 100 μL saline.
Additional methods are described in the supplemental Methods.
Results
Rab27a-APEX2 proximity proteomics reveals novel WPB-associated proteins associated with VWF release
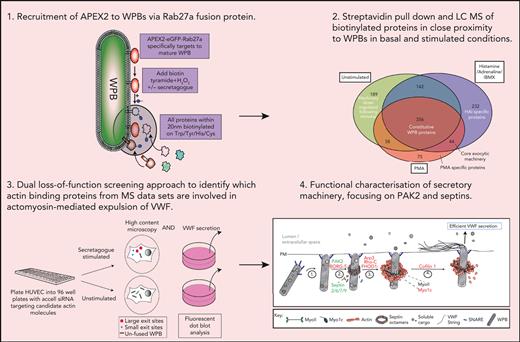
We targeted APEX226,27 to the WPB surface by fusing it to Rab27a (Figure 1A-C), a protein resident on mature WPBs23,28 even at the point of fusion.29 This construct selectively targets to WPBs, and proximal proteins are labeled with biotin following a short, 60-second labeling period (Figure 1D). To monitor how proximal proteins change during fusion with the plasma membrane, the protocol was performed with unstimulated HUVECs, HUVECs stimulated with PMA, or a combination of HAI. These treatments increase regulated release of VWF and effectively recruit the actomyosin ring during WPB exocytosis.16 By using agents with discrete stimulatory mechanisms, the resulting data allowed precise analysis of the proximal proteins likely to represent core exocytic machinery.
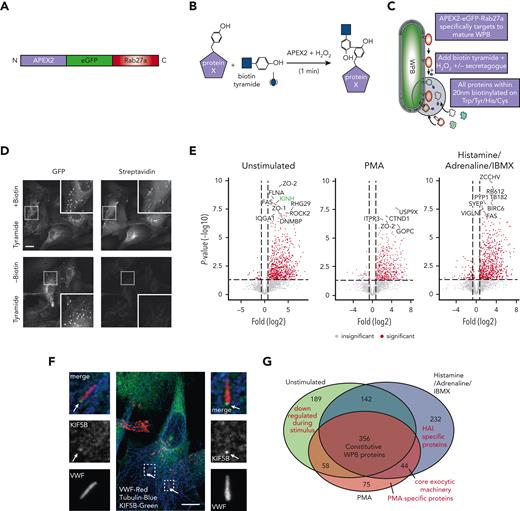
Proximity proteomics reveals novel WPB-associated machinery. (A) Schematic representation of the APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a construct used to transfect HUVECs. (B) Biotinylation reaction catalyzed following the addition of hydrogen peroxide and biotin tyramide. (C) The APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a construct is recruited to mature WPBs, allowing spatiotemporally-specific biotin labeling on nearby proteins. The addition of stimulants allows detection of proteins with putative roles in basal and regulated granule release. (D) Confocal LSM of HUVECs in the presence or absence of biotin tyramide. Biotinylated proteins are detected using AF647-conjugated streptavidin and colocalized with the enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)−tagged fusion protein. (E) Scatter graphs depicting the most significant (paired t test) and upregulated proteins as compared to mock-transfected control HUVECs in unstimulated, PMA-stimulated, and HAI-stimulated cells. Kinesin-1 heavy chain (KINH) (green) was used to validate the data set. (F) IF analyses of HUVECs illustrate KIF5B (KINH) localizing to one end of WPBs under resting conditions. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) Venn diagram of mass spectrometry data sets illustrates the number of proteins in close proximity to WPBs under all conditions, exclusively under basal conditions or following stimulation. (H) Heat map depiction of the average normalized spectral counts of the 44 stimulation-associated proteins in mock and APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a groups (in the presence or absence of PMA/HAI). (I) Myosin-1c (green) is present at points of WPB fusion in PMA-stimulated HUVECs. Scale bar, 10 μm.
Proximity proteomics reveals novel WPB-associated machinery. (A) Schematic representation of the APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a construct used to transfect HUVECs. (B) Biotinylation reaction catalyzed following the addition of hydrogen peroxide and biotin tyramide. (C) The APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a construct is recruited to mature WPBs, allowing spatiotemporally-specific biotin labeling on nearby proteins. The addition of stimulants allows detection of proteins with putative roles in basal and regulated granule release. (D) Confocal LSM of HUVECs in the presence or absence of biotin tyramide. Biotinylated proteins are detected using AF647-conjugated streptavidin and colocalized with the enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)−tagged fusion protein. (E) Scatter graphs depicting the most significant (paired t test) and upregulated proteins as compared to mock-transfected control HUVECs in unstimulated, PMA-stimulated, and HAI-stimulated cells. Kinesin-1 heavy chain (KINH) (green) was used to validate the data set. (F) IF analyses of HUVECs illustrate KIF5B (KINH) localizing to one end of WPBs under resting conditions. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) Venn diagram of mass spectrometry data sets illustrates the number of proteins in close proximity to WPBs under all conditions, exclusively under basal conditions or following stimulation. (H) Heat map depiction of the average normalized spectral counts of the 44 stimulation-associated proteins in mock and APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a groups (in the presence or absence of PMA/HAI). (I) Myosin-1c (green) is present at points of WPB fusion in PMA-stimulated HUVECs. Scale bar, 10 μm.
We identified 745 (basal), 533 (PMA), and 774 (HAI) proteins found to be enriched in comparison to mock-transfected cells. The log fold increase in peptide counts was plotted against each biotinylated protein’s statistical significance (-log10) (Figure 1E) to reveal a hierarchal view of molecules in close proximity to Rab27a before and after stimulation. Of note, the identity of previously unknown kinesin motor proteins responsible for plus end microtubule-based movement were revealed. Kinesins were differentially enriched in unstimulated (KINH) and stimulated (KIF11) conditions, suggesting independent roles in WPB dynamics. KIF5B (KINH) (Figure 1E) was highly enriched and statistically significant in the unstimulated mass spectrometry data set (P < .05, Mock vs APEX2-eGFP-Rab27a). Supporting this, KIF5B was localized at 1 end of WPBs in unstimulated conditions by immunofluorescence (IF) (Figure 1F). Displaying the proteomic data as a Venn diagram illustrated the proportional constituents of the data set (Figure 1G), where 232 proteins have putative roles specifically in response to HAI, and 75 proteins in response to PMA, with 44 overlapping proteins. We hypothesize that these 44 WPB-associated proteins present in both stimulated conditions are representative of core exocytic machinery (Figure 1H). This list includes proteins already associated with WPB secretion, such as STXBP3,30 PI4KA,31 and exocyst.32 Intriguingly, this data set included the unconventional myosin-1c (Myo1c) but not NMII isoforms. Consistent with this, Myo1c was localized to sites of WPB fusion by IF (Figure 1I). Our proximity proteomic approach provides a valuable resource comparing basal and stimulation specific WPB effector proteins. It also represents a starting point to discover actin-specific exocytic machinery controlling VWF release.
Morphometric and secretory screen identifies actin-binding proteins that regulate WPB exocytic mode
The proximity labeling approach generated a list of candidates that are likely to be involved in many aspects of WPB function. We analyzed the functional role of candidates specifically associated with actin remodeling. The spatial proximity of WPBs to cortical actin networks resulted in actin-binding proteins being detected in both unstimulated and stimulated conditions, and preliminary analysis of hits revealed that they were not always associated with exocytic actomyosin ring function. To verify their involvement and to identify the strongest candidates for further analysis, we adopted a loss-of-function approach by performing 2 additional siRNA screens (Figure 2A). The first measured the stimulated secretion of VWF using a high-throughput immunoblotting technique (supplemental Figure 1). The second used a high-content imaging approach monitoring actomyosin ring recruitment by the size, number, and localization of fusion sites. Larger fusion sites are associated with the actomyosin ring, whereas smaller sites represent actomyosin ring-independent release.16 This dual screening approach determines the candidate proteins that are required for secretion and that directly affect actomyosin ring function. We expanded our screen, where possible, to include selected protein isoforms. Using 2 different secretagogues (PMA and HAI), we generated a scatter plot that demonstrated the effects of silencing actin-binding proteins on VWF release and actomyosin ring function. This displays those proteins for which VWF secretion and exit site size were reduced from the control (Figure 2B-D; supplemental Figure 2). Distinct groupings of proteins were apparent: a small Rho GTPase (RhoC) that typically functions upstream of actin nucleation; the p21-activated kinase (PAK2), a kinase that links Rho GTPases to cytoskeletal reorganization33; a group of proteins involved in actin nucleation, including the formins FHOD1/334; and the actin-related protein (Arp) complex (we also noted members of the septin cytoskeletal family and their regulating proteins, Cdc42 effector proteins 1 and 335); and finally, the actin-severing protein, cofilin 1 (Figure 2C-D). This short list of proteins likely maps to the discrete phases of the actomyosin ring lifetime, providing a fundamental starting point for the generation of a mechanistic model.
Dual siRNA subscreen identifies which actin-binding proteins play a role in VWF release. (A) Schematic representation of the loss-of-function screening approach used. HUVECs were transfected with siRNA-targeting proteins (and their associated effectors) identified through proximity proteomics. Transfected cells were stimulated with PMA or HAI and either fixed in the presence of an anti-VWF antibody for analysis by confocal LSM to quantify WPB exit site size or the supernatants were collected for quantification of VWF release by fluorescent dot blot. (B) A scatter plot was generated that depicted only the proteins whose reduction in expression led to a decrease in VWF release or proportion of exit sites less than 2 μm2 in comparison to control siRNA. The targets with most prominent effect from each protein class have been annotated. The effect of depletion of shortlisted candidates on (C) PMA-stimulated and (D) HAI-stimulated VWF release. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005 (one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Dunnett multiple comparison).
Dual siRNA subscreen identifies which actin-binding proteins play a role in VWF release. (A) Schematic representation of the loss-of-function screening approach used. HUVECs were transfected with siRNA-targeting proteins (and their associated effectors) identified through proximity proteomics. Transfected cells were stimulated with PMA or HAI and either fixed in the presence of an anti-VWF antibody for analysis by confocal LSM to quantify WPB exit site size or the supernatants were collected for quantification of VWF release by fluorescent dot blot. (B) A scatter plot was generated that depicted only the proteins whose reduction in expression led to a decrease in VWF release or proportion of exit sites less than 2 μm2 in comparison to control siRNA. The targets with most prominent effect from each protein class have been annotated. The effect of depletion of shortlisted candidates on (C) PMA-stimulated and (D) HAI-stimulated VWF release. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005 (one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Dunnett multiple comparison).
Signaling associated with VWF release
The PAK family of serine threonine kinases are effector proteins of the Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac.36 PAKs have reported roles in secretory processes37,38 via the kinase catalytic domain at the C-terminus that interacts with actin regulators: myosin II regulatory light chains (MLC) via MLCK39 and cofilin via LIM Kinase (LIMK).40 Moreover, a kinase-independent function has been described through interaction with the guanine nucleotide exchange factor β-PIX at the N-terminal domain41 (supplemental Figure 3A).
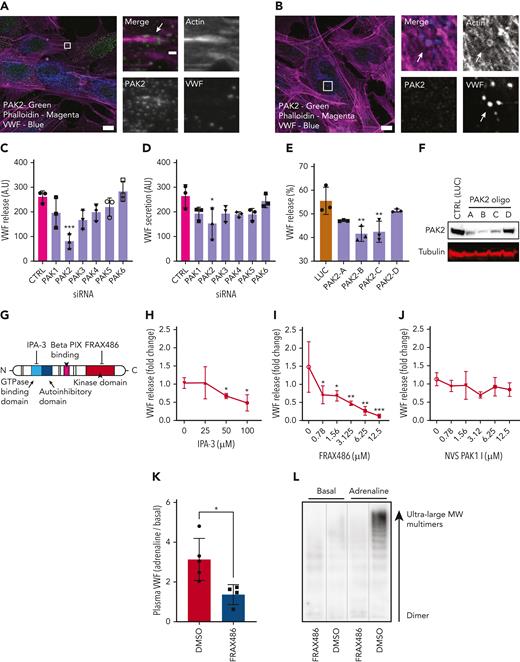
IF analyses showed that PAK2 was localized as puncta present throughout the cytoplasm and at the end of dorsal stress fibers (Figure 3A). However, it was not detectable on the actomyosin ring (Figure 3B). From the screening data, only silencing of the PAK2 isoform reduced VWF release in response to both PMA (P < .005) and HAI (P < .05) (Figure 3C-D), consistent with a dose-dependent effect of gene silencing on PAK2 expression and VWF release (PAK2 oligo B and C, P < .01) (Figure 3E-F). Taken together, this indicates a potential signaling role upstream of VWF release.
PAK2 signaling regulates VWF release from endothelial cells. (A) Confocal analysis localizes PAK2 (green) to the cytoplasm and at the end of dorsal actin stress fibers (magenta) in HUVECs. (B) PAK2 (green) is not present on the actin ring (magenta) that forms at exocytosis (inset). Scale bars, 10 μm (full size) and 1 μm (inset); brightness and contrast increased for clarity. (C-D) The effect of siRNA depletion of the 6 PAK isoforms on (C) PMA-stimulated and (D) HAI-stimulated VWF secretion. (E) PAK2 depletion reduced PMA stimulated VWF release in a dose-dependent fashion. HUVECs were independently transfected with 4 different siRNA oligonucleotides targeting PAK2. VWF secretion was determined by fluorescent dot blot and PAK2 protein abundance determined by western blotting. (F) Western blotting of HUVEC lysate detected as single band at the estimated size of 61 kDa. (G) Schematic representation of PAK2 structure and targets for pharmacological inhibition. (H) Pharmacological inhibition of the autoregulatory domain of PAK2 with 25 to 50 μM IPA-3 prevents VWF release. (I) Targeting the catalytic kinase domain of PAK2 with FRAX486 inhibits VWF release (0.78-12.5 μM). (J) The specific PAK1 inhibitor NVS PAK1.1 has no effect on VWF release at 12.5 μM. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparison). (K-L) Effect of FRAX486 administration on adrenaline-stimulated VWF secretion in vivo. C57 black WT mice were administered FRAX486 or an equivalent volume of DMSO. Tail vein bleeds were performed to assess basal VWF levels. Intraperitoneal injection of adrenaline (0.5 mg/kg) was used to stimulate VWF secretion from the murine vasculature (DMSO, n = 5; FRAX486, n = 4). After 30 minutes, mice were sacrificed and the plasma was isolated. Plasma VWF levels and multimer composition were assessed by near-infrared dot blot (K) and multimer gel (L). MW, molecular weight. ∗P < .05.
PAK2 signaling regulates VWF release from endothelial cells. (A) Confocal analysis localizes PAK2 (green) to the cytoplasm and at the end of dorsal actin stress fibers (magenta) in HUVECs. (B) PAK2 (green) is not present on the actin ring (magenta) that forms at exocytosis (inset). Scale bars, 10 μm (full size) and 1 μm (inset); brightness and contrast increased for clarity. (C-D) The effect of siRNA depletion of the 6 PAK isoforms on (C) PMA-stimulated and (D) HAI-stimulated VWF secretion. (E) PAK2 depletion reduced PMA stimulated VWF release in a dose-dependent fashion. HUVECs were independently transfected with 4 different siRNA oligonucleotides targeting PAK2. VWF secretion was determined by fluorescent dot blot and PAK2 protein abundance determined by western blotting. (F) Western blotting of HUVEC lysate detected as single band at the estimated size of 61 kDa. (G) Schematic representation of PAK2 structure and targets for pharmacological inhibition. (H) Pharmacological inhibition of the autoregulatory domain of PAK2 with 25 to 50 μM IPA-3 prevents VWF release. (I) Targeting the catalytic kinase domain of PAK2 with FRAX486 inhibits VWF release (0.78-12.5 μM). (J) The specific PAK1 inhibitor NVS PAK1.1 has no effect on VWF release at 12.5 μM. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparison). (K-L) Effect of FRAX486 administration on adrenaline-stimulated VWF secretion in vivo. C57 black WT mice were administered FRAX486 or an equivalent volume of DMSO. Tail vein bleeds were performed to assess basal VWF levels. Intraperitoneal injection of adrenaline (0.5 mg/kg) was used to stimulate VWF secretion from the murine vasculature (DMSO, n = 5; FRAX486, n = 4). After 30 minutes, mice were sacrificed and the plasma was isolated. Plasma VWF levels and multimer composition were assessed by near-infrared dot blot (K) and multimer gel (L). MW, molecular weight. ∗P < .05.
We used the pan PAK1-3 inhibitor IPA-3, which targets the autoregulatory domain of PAK2,42 and FRAX48643, which inhibits kinase activity (Figure 3G). IPA-3 (Figure 3H) and FRAX486 (Figure 3I) both inhibited VWF release from endothelial cells. By contrast, the PAK1 inhibitor NVS PAK1 144 displayed no significant effect on VWF secretion (Figure 3J). These pharmacological strategies show that PAK2 is essential for VWF secretion, and this is dependent on both its N-terminal regulatory and the C-terminal catalytic domains. We subsequently assessed whether PAK inhibition with FRAX486 was sufficient to inhibit cAMP-induced VWF secretion in vivo. Administration of adrenaline (0.5 mg/kg) resulted in an increase in plasma VWF levels of ∼213% (Figure 3K). VWF multimer gel indicated that this VWF was composed of high-molecular weight VWF multimers (Figure 3L). Intravenous administration of FRAX486 (2 × 10−4 mg/kg) reduced adrenaline-stimulated VWF secretion in vivo (Figure 3K).
Using siRNA and immunoblotting, we concluded that regulation of cofilin activity and ERK1/2 signaling (supplemental Figure 3) do not explain the pronounced effect of PAK2 inhibition on VWF release. PAK inhibits MLCK,39,45 but does not play this role in VWF release, as the MLCK inhibitor (ML-7) increases the time taken for VWF release.1 We therefore hypothesized that PAK2 controls another cytoskeleton component identified by our screen, namely, the septins. There is a precedence for this, as PAK homologues in yeast46-48 and pathogenic fungi49 act as regulators of septin biology.
Septin rings are recruited to fused WPBs during exocytosis
Septins are enigmatic cytoskeletal GTPases that regulate microtubules and actomyosin.50,51 Septins comprise 4 subfamilies, each containing 1 or more paralogs. Independent septin subunits incorporate into hetero-oligomers to form higher-order structures, including filaments, rings, and gauzes50,52,53 (Figure 4A); however, as the sole member in its subfamily, septin 7 (SEPT7) is essential for hetero-oligomerization and thus is crucial to the formation of higher-order assemblies, including rings.
Septin rings are recruited to WPBs post fusion in an actin-independent but PAK2-dependent process. (A) To form higher-order structures such as rings, septin (SEPT) monomers from different subfamilies (eg, SEPT2/6/7/9) must form hetero-oligomers (6mers or 8mers). (B) SEPT7 is recruited to WPBs following stimulation. IF analyses of SEPT7 (green), VWF (blue), and actin (magenta) in HUVEC cultures stimulated with the presence or absence 100 ng/mL PMA and/or 1 μM CCE. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Schematic representation of the approach used to image septins in live endothelial cells. GFP-tagged SEPT6 interacts with endogenous SEPT7 upon ring formation. (D) GFP pull-down of control GFP and eGFP-SEPT6−transfected cells detects the association of the eGFP-SEPT6 transgene product with endogenous SEPT2 and SEPT7. Beta tubulin was absent in both eGFP control and eGFP-SEPT6 pull-down samples. ∗Cross-reactivity. (E) Confocal microscopy of fixed HUVECs transfected with P.sel.lum.mCherry (magenta) and eGFP-SEPT6 (green) and probed for SEPT7 (red) by IF. Images show that eGFP-SEPT6 is incorporated into rings that are positive for SEPT7 staining. Scale bars, 10 μm. (F) SEPT9 is localized to fused WPBs following stimulation with PMA. (G) Live cell imaging of PMA (100 ng/mL)−stimulated HUVECs indicates that SEPT6-eGFP rings form post fusion. Brightness and contrast increased for clarity. †WPB fusion. ∗Septin ring formation; 0.5- to 6-μm Z stacks acquired every 5 seconds for 10 minutes. Scale bars, 1 μm. (H) HUVECs were transfected with LUC control (left panel) or PAK2-targeted siRNA (right panel) and probed for SEPT7 (green), VWF (blue), and actin (magenta). Scale bar, 10 μm. (I) Quantification of the number of SEPT7 associated with VWF as a proportion of the total number of rounded (fused) WPBs. A total of 15 images per condition from three independent experiments (ratio paired t test). ∗∗∗P < .005.
Septin rings are recruited to WPBs post fusion in an actin-independent but PAK2-dependent process. (A) To form higher-order structures such as rings, septin (SEPT) monomers from different subfamilies (eg, SEPT2/6/7/9) must form hetero-oligomers (6mers or 8mers). (B) SEPT7 is recruited to WPBs following stimulation. IF analyses of SEPT7 (green), VWF (blue), and actin (magenta) in HUVEC cultures stimulated with the presence or absence 100 ng/mL PMA and/or 1 μM CCE. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Schematic representation of the approach used to image septins in live endothelial cells. GFP-tagged SEPT6 interacts with endogenous SEPT7 upon ring formation. (D) GFP pull-down of control GFP and eGFP-SEPT6−transfected cells detects the association of the eGFP-SEPT6 transgene product with endogenous SEPT2 and SEPT7. Beta tubulin was absent in both eGFP control and eGFP-SEPT6 pull-down samples. ∗Cross-reactivity. (E) Confocal microscopy of fixed HUVECs transfected with P.sel.lum.mCherry (magenta) and eGFP-SEPT6 (green) and probed for SEPT7 (red) by IF. Images show that eGFP-SEPT6 is incorporated into rings that are positive for SEPT7 staining. Scale bars, 10 μm. (F) SEPT9 is localized to fused WPBs following stimulation with PMA. (G) Live cell imaging of PMA (100 ng/mL)−stimulated HUVECs indicates that SEPT6-eGFP rings form post fusion. Brightness and contrast increased for clarity. †WPB fusion. ∗Septin ring formation; 0.5- to 6-μm Z stacks acquired every 5 seconds for 10 minutes. Scale bars, 1 μm. (H) HUVECs were transfected with LUC control (left panel) or PAK2-targeted siRNA (right panel) and probed for SEPT7 (green), VWF (blue), and actin (magenta). Scale bar, 10 μm. (I) Quantification of the number of SEPT7 associated with VWF as a proportion of the total number of rounded (fused) WPBs. A total of 15 images per condition from three independent experiments (ratio paired t test). ∗∗∗P < .005.
To determine the role of SEPT7 in WPB exocytosis, we analyzed the localization of SEPT7 following PMA stimulation using IF and confocal microscopy. Under resting conditions, SEPT7 was present on actin stress fibers and was not localized with rod-shaped WPBs (Figure 4B, top left panel). Following stimulation, WPBs fuse with the plasma membrane, resulting in a change in granule pH from acidic to neutral and an associated change in morphology (rod-shaped to circular). Following PMA stimulation, SEPT7 rings were observed encapsulating fused WPBs (Figure 4B, top right panel). Phalloidin costaining indicated that septin and actin rings are mutually exclusive. Treatment of cells with an inhibitor of actin polymerization, cytochalasin E (CCE), resulted in an increase in the total number of septin rings (Figure 4B, bottom left panel). This increase in septin rings reflects the release of septins normally associated with actin polymers.52 However, the number of septin rings associated with fused WPB following stimulation remained the same (Figure 4B, bottom right panel). This demonstrated that fusion leads to the recruitment of septin rings, and that is independent of actin polymerization.
To image septin dynamics in real time, we transfected HUVECs with a plasmid encoding an eGFP-tagged SEPT6 subunit (Figure 4C). Pull down of eGFP-SEPT6 compared to control revealed incorporation of the tagged protein into endogenous hetero-oligomer complexes containing both SEPT2 and SEPT7 (Figure 4D). IF analysis indicated the fusion-protein colocalized with SEPT7 in filaments and rings (Figure 4E). SEPT9 was also localized to fused WPBs, indicating that exocytic septin rings are octamers (2/6/7/9) (Figure 4F). siRNA-mediated silencing of individual septin paralogues inhibited VWF release, demonstrating that they are not functionally redundant, and suggested a role for filamentous hetero-oligomers (supplemental Figure 2A-B). In contrast, high-content imaging of VWF exit sites revealed a trend towards increased size in cells depleted for SEPT6 family members (supplemental Figure 2C-D), consistent with the view that SEPT6 family members can replace one another.53
We optimized eGFP-SEPT6 expression to visualize dynamic endogenous septin structures (supplemental Figure 4A-D). Using mCherry-tagged lumenal domain of P-selectin (P.sel.lum.mCherry) as a marker for WPB fusion, live cell imaging showed that septin ring formation follows collapse of the rod-shaped structure, indicating a role independent of membrane fusion (Figure 4G). Septin ring formation can be imaged in the presence of CCE at exocytic sites post fusion (supplemental Figure 4E). Strikingly, siRNA-mediated depletion of PAK2 reduced the proportion of fused WPBs that recruited a SEPT7 ring (P < .005, luciferase (LUC) 22.5% [±5.7 SEM] vs PAK2 12% [±2.9 SEM]) (Figure 4H-I). Taken together, septin rings form post fusion, independently of actin, and this process requires PAK2.
Pharmacological regulation and siRNA-mediated silencing SEPT7 alters actomyosin ring dynamics
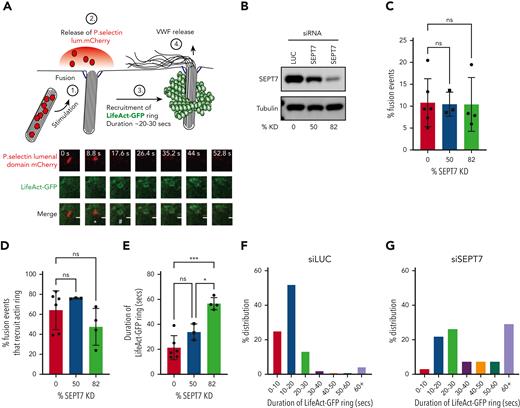
We next used a live cell imaging approach in combination with SEPT7 depletion to estimate the recruitment and kinetics of the actin ring. This assay monitored changes in WPB morphology, loss of P.sel.lum.mCherry signal, and recruitment of LifeAct-GFP (Figure 5A). Using 2 independent siRNAs targeting SEPT7, we could achieve knockdown (KD) of target proteins of approximately 50% and 82% (Figure 5B). No significant differences in the number of WPB fusion events were detected when SEPT7 KD cells were compared to cells nucleofected with LUC-targeted siRNA (Figure 5C). In all, 64.2% ± 7.2% of fusion events in control transfected cells (LUC) recruited an actin ring. No statistical differences were detected when compared to either SEPT7 siRNA-treated groups (75% ± 0.25% and 45% ± 8.9%) (Figure 5D). We did, however, determine more pronounced differences in actin ring kinetics. Actin ring formation is a tightly regulated process that lasts ∼20 seconds under stimulated conditions.1 We observed a dose-dependent increase in actin ring duration in SEPT7-depleted HUVECs. SEPT7 KD significantly (P < .005) increased the average lifetime of the actin ring by ∼165% (LUC 21.3 ± 13.5 seconds vs SEPT7 56.6 ± 2.1 seconds) (Figure 5E). This was also illustrated by percentage changes in the distribution frequency of the duration of LifeAct-GFP signal (Figure 5F and G). Taken together, these data suggest that septin SEPT7 is dispensable for actin ring formation but plays critical roles in regulating ring kinetics.
siRNA-mediated depletion of SEPT7 perturbs actin ring kinetics during WPB exocytosis. (A) WPB fusion was quantified by change in morphology (rod>round) and loss of mCherry signal, whereas actin ring recruitment was assessed by the presence or absence of LifeAct-GFP signal. White asterisk (∗) indicates change in morphology from rod>round. Number sign (#) indicates recruitment of LifeAct GFP ring. HUVECs were co-transfected (2 rounds) with either 300 pM LUC or independent SEPT7-targeted siRNAs and both LifeAct-GFP and p.sel.lum.mCherry. (B) Western blotting was used to determine KD efficiencies of approximately 50% and 82% (averaged from 3 independent experiments). (C) SEPT7 knockdown did not affect vesicle fusion. (D) Quantification of actin ring formation as a percentage of total fusion events. (D-E) Quantification of the duration of the “lifetime” of actin ring (LifeAct-GFP signal) in control and SEPT7 KD cells. ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005. One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple-comparison test. Frequency distribution (%) of actin ring duration in luciferase siRNA (F) and SEPT7 siRNA-treated cells (84% KD efficiency) (G). Cell numbers for live cell imaging. LUC control, 46 cells; SEPT7, 25 cells (50% KD), and SEPT7, 30 cells (82% KD).
siRNA-mediated depletion of SEPT7 perturbs actin ring kinetics during WPB exocytosis. (A) WPB fusion was quantified by change in morphology (rod>round) and loss of mCherry signal, whereas actin ring recruitment was assessed by the presence or absence of LifeAct-GFP signal. White asterisk (∗) indicates change in morphology from rod>round. Number sign (#) indicates recruitment of LifeAct GFP ring. HUVECs were co-transfected (2 rounds) with either 300 pM LUC or independent SEPT7-targeted siRNAs and both LifeAct-GFP and p.sel.lum.mCherry. (B) Western blotting was used to determine KD efficiencies of approximately 50% and 82% (averaged from 3 independent experiments). (C) SEPT7 knockdown did not affect vesicle fusion. (D) Quantification of actin ring formation as a percentage of total fusion events. (D-E) Quantification of the duration of the “lifetime” of actin ring (LifeAct-GFP signal) in control and SEPT7 KD cells. ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005. One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple-comparison test. Frequency distribution (%) of actin ring duration in luciferase siRNA (F) and SEPT7 siRNA-treated cells (84% KD efficiency) (G). Cell numbers for live cell imaging. LUC control, 46 cells; SEPT7, 25 cells (50% KD), and SEPT7, 30 cells (82% KD).
The septin inhibitor FCF54 and inhibitor of the p21-activated kinases were used here to further address our model using an alternative approach. Pre-incubation with FCF inhibited PMA-stimulated VWF release in a dose-dependent fashion (supplemental Figure 5A). FRAX486 significantly reduced the number of fusion events, as compared to PMA-stimulated controls (PMA 6.5 ± 1.2/cell vs FRAX486+PMA 2.8 ± 0.76/cell, P < .05) (supplemental Figure 5B). In all, 74% ± 14.3% of PMA, 54% ± 11.2% of FRAX-486+PMA, and 63% ± 10.4% of FCF+PMA-stimulated fusion events recruited the actin ring (supplemental Figure 5C). A greater effect was seen in actin ring kinetics. In this case, we observed a significant increase in mean duration (lifetime) following inhibition of septins. Specifically, the average actin ring lifetime of PMA-stimulated cells was 21 ± 1.2 seconds, which increased to 32.5 ± 5.9 seconds and 33.1 ± 6.1 seconds following exposure to suboptimal concentrations of FRAX486 (1 μM) or FCF (50 μM), respectively (supplemental Figure 5D-E).
SEPT7 depletion perturbs the release of VWF strings
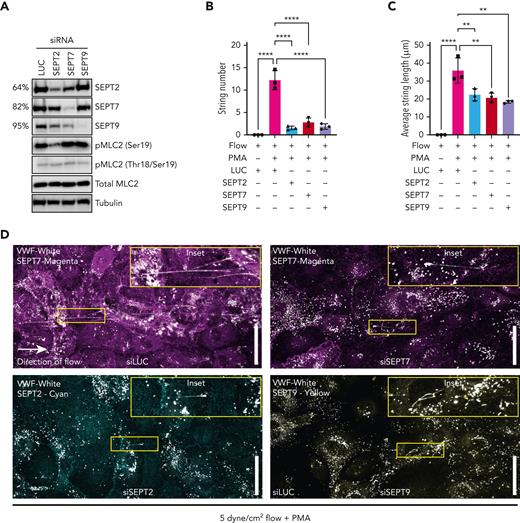
Physiological shear stress in the venous vasculature ranges from 2.5 to 20 dynes/cm2 55 and aids the unfurling of secreted VWF into long strings that anchor to the endothelial cell surface, providing self-association and platelet-binding sites.18,56 We therefore set out to test the effect of septin depletion on VWF string formation under flow conditions. We first confirmed KD efficiencies of septin targeting siRNAs. KD of SEPT2, SEPT7, and SEPT9 resulted in a 64%, 82% and 95% target protein depletion, respectively (Figure 6A; supplemental Figure 6). Previous studies suggest that septins provide a scaffold for myosin and their activators to allow maximal contractile responses.57,58 We next assessed the activation state of myosin light chain 2 (MLC2). SEPT2 depletion reduced global phosphorylation levels of MLC2 at Ser19 by approximately 39% (Figure 6A). VWF strings were not detectable when unstimulated HUVEC were exposed to 5-dyne/cm2 shear values for 5 minutes. Pre-exposure to PMA resulted in the formation of VWF strings under flow, which ranged from 5 to 200 μm in length (Figure 6B,D). Depletion of SEPT2, SEPT7, or SEPT9 significantly inhibited the number and lengths of VWF strings formed under the same conditions. Most striking was the effect on the number of VWF strings secreted (strings per field of view: PMA 12.2 ± 1.0, SEPT2 1.5 ± 0.2, SEPT7 2.8 ± 0.5, SEPT9 1.8 ± 0.3) (Figure 6C-D). We noted the same phenotype under static conditions (supplemental Figure 6).
Septin depletion reduces efficiency of VWF string release. HUVECs were depleted of SEPT2, SEPT7, and SEPT9 using siRNA and VWF string secretion under flow assessed by immunofluorescence. (A) Western blotting confirmed effective target protein depletion in HUVECs treated with 300 pM SEPT2/7/ siRNA. MLC2 phosphorylation at ser19 was reduced in SEPT2 KD cells. (B) Depletion of SEPT/7/9 inhibited VWF string formation in HUVECs exposed to 5 dynes/cm2. (C) On average, SEPT2/7/9 depletion resulted in shorter VWF strings bound to the endothelial cell surface. Data presented as mean from each independent experiment (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. (D) Confocal microscopy images (0.5 μm Z stacks) were acquired using identical settings. Scale bar, 50 μm. Representative immunofluorescence images of septin and VWF staining in siLUC (top left panel), siSEPT7 (top right panel), siSEPT2 (bottom left panel), and siSEPT9 (bottom right panel) treated HUVECs.
Septin depletion reduces efficiency of VWF string release. HUVECs were depleted of SEPT2, SEPT7, and SEPT9 using siRNA and VWF string secretion under flow assessed by immunofluorescence. (A) Western blotting confirmed effective target protein depletion in HUVECs treated with 300 pM SEPT2/7/ siRNA. MLC2 phosphorylation at ser19 was reduced in SEPT2 KD cells. (B) Depletion of SEPT/7/9 inhibited VWF string formation in HUVECs exposed to 5 dynes/cm2. (C) On average, SEPT2/7/9 depletion resulted in shorter VWF strings bound to the endothelial cell surface. Data presented as mean from each independent experiment (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. (D) Confocal microscopy images (0.5 μm Z stacks) were acquired using identical settings. Scale bar, 50 μm. Representative immunofluorescence images of septin and VWF staining in siLUC (top left panel), siSEPT7 (top right panel), siSEPT2 (bottom left panel), and siSEPT9 (bottom right panel) treated HUVECs.
Discussion
The proximity labeling approach used here complements and extends previous proteomic work,59 providing data as to how proximal proteins change during the process of exocytosis. We took advantage of the rapid labeling time of APEX-2 and compared unstimulated and stimulated cells, thus defining a pool of proteins constitutively associated with WPB and those that are recruited following stimulation. PMA and HAI stimulation result in different WPB proximal proteins presumably reflecting differences in downstream signaling; alternative stimuli such as thrombin or vasopressin will likely also exhibit signal-specific differences. However, the list of 44 overlapping proteins that were specifically enriched in both HAI- and PMA-stimulated cells are likely candidates for core exocytic machinery (including previously characterized exocytic machinery alongside novel candidates). It should be noted that we used HUVECs as a cellular system for proximity proteomics, and thus we cannot rule out differences compared to other endothelial subtypes.
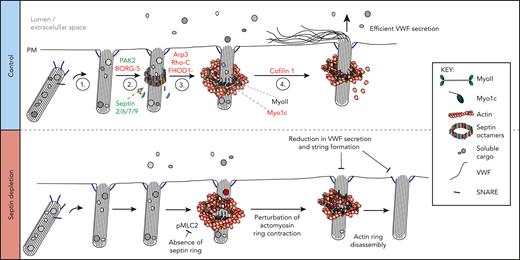
The actin-binding protein subscreens provided functional validation of the mass spectrometry hits, identifying proteins with a direct role in actomyosin ring function. We revealed a new structural component of the WPB exocytic machinery—a septin ring that forms post fusion that controls the dynamics of the actin ring—and generated a putative working model of actomyosin ring function (Figure 7).
Schematic representation of a working model depicting machinery associated with actomyosin-dependent expulsion of VWF from endothelial cells. (1) Upon stimulation, WPBs are trafficked to the cell surface where fusion with the plasma membrane occurs. (2) Septin rings are recruited to fused WPBs (independently of actin), where they likely transfer myosins (eg, NMII or Myo1C) or their activators. This process is PAK2 dependent. (3) Actin rings are formed by rearrangement of cortical actin or de novo nucleation. Possible candidates from our screen include FHOD1 and Arp3. Actin ring formation itself could displace the septin ring. (4) The actin ring contracts/compresses with the aid of NMII and cofilin 1. Myo1c may play a role in tethering actin to the WPB membrane. Proteins in red and green were identified through proximity proteomics and loss of function screening approaches. Proteins in black were identified through previous research. (Bottom panel) Disrupting the formation of the septin ring during WPB exocytosis results in prolonged actin ring dynamics as well as an inhibition of VWF secretion and string formation. SEPT2 depletion reduces the phosphorylation status of MLC2. This results in actin rings contracting more slowly or failing to contract before being disassembled. Interfering with actin ring formation or function results in less efficient VWF secretion.
Schematic representation of a working model depicting machinery associated with actomyosin-dependent expulsion of VWF from endothelial cells. (1) Upon stimulation, WPBs are trafficked to the cell surface where fusion with the plasma membrane occurs. (2) Septin rings are recruited to fused WPBs (independently of actin), where they likely transfer myosins (eg, NMII or Myo1C) or their activators. This process is PAK2 dependent. (3) Actin rings are formed by rearrangement of cortical actin or de novo nucleation. Possible candidates from our screen include FHOD1 and Arp3. Actin ring formation itself could displace the septin ring. (4) The actin ring contracts/compresses with the aid of NMII and cofilin 1. Myo1c may play a role in tethering actin to the WPB membrane. Proteins in red and green were identified through proximity proteomics and loss of function screening approaches. Proteins in black were identified through previous research. (Bottom panel) Disrupting the formation of the septin ring during WPB exocytosis results in prolonged actin ring dynamics as well as an inhibition of VWF secretion and string formation. SEPT2 depletion reduces the phosphorylation status of MLC2. This results in actin rings contracting more slowly or failing to contract before being disassembled. Interfering with actin ring formation or function results in less efficient VWF secretion.
Strikingly, the greatest effects on VWF secretion were observed following PAK2 inhibition. PAKs regulate exocytosis in platelets,60 pancreatic acinar cells, and beta cells.37,38 We demonstrate that PAK2 is essential for regulated secretion of VWF from endothelial cells. PAK homologues in yeast (Ste20 and Cla4)46-48 and the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae (Chm1)49 have previously been reported to regulate septin biology. Cla4 phosphorylates cdc10 (SEPT7-like protein in yeast) in vitro and loss of Cla4 perturbs septin collar formation.46 Similarly, in Magnaporthe oryzae, Chm1 mutant cells do not form septin or actin rings at the appressorium, which is an appendage that pierces the rice plant leaf cuticle in a force-driven process.49 Using the PAK2 target consensus sequence (K/R)-R-X-S,61,62 we noted 2 potential target sites within SEPT1 (Ser253) and SEPT9 (Ser434). Previous studies in yeast have shown that phospho-serine residues within these regions (N-terminal of SUE) are positive regulators of septin ring formation.63 In our study, we show that septin rings formed at exocytosis in a PAK2-dependent process, representing the first link between PAK2 and septins in a mammalian system.
Mammalian septins have been described as the “fourth component of the cytoskeleton”64; they play key roles in maintaining junctional integrity,65-67 membrane dynamics,68 and recruiting components of the contractile ring used in cytokinesis.57,69 Our findings represent the first description of a role for septins in actomyosin-mediated secretion.
We observed SEPT2/6/7/9 rings encapsulating WPBs during exocytosis, independently of actin polymerization. Septins play a role in vesicle tethering and fusion with the PM via association with the exocyst complex70 and SNAREs71,72; however, the timing of septin ring recruitment (post fusion) makes these trafficking roles unlikely. Depletion of the core septin subunit (SEPT7) did not affect WPB fusion but inhibited septin ring formation, resulting in actomyosin rings that persist for longer with delayed kinetics. This might reflect either a slower contraction of the actin ring or a failure to contract before subsequent disassembly. Either way, this phenotype results in a failure for VWF to be secreted as platelet-catching strings. We previously performed ultrastructural analyses of WPB fusion events using dual-color confocal microscopy and correlative electron microscopy. This illustrated that inhibiting the actomyosin ring through exposure to CCE resulted in a failure of VWF to extend past open fusion pores.1
Our results demonstrate that inhibition of septin function did not reduce the efficiency of actin recruitment; instead, we conclude that septins are responsible for the transfer or activation of myosin isoforms to facilitate efficient actomyosin contractility. In support of this, SEPT7-depleted cells phenocopy the effect of blebbistatin,1 and depletion of SEPT2 reduced MLC2 phosphorylation. This supports our hypotheses that the actomyosin ring is required for a force-driven process that aids the release of ultra-large VWF multimers, and that septins support this process through the transfer or activation of myosin isoforms.
Here we have used a proximity proteomics approach to identify WPB-associated machinery and have determined how this changes dynamically during exocytosis. Furthermore, we performed the first unbiased screen of actomyosin exocytic machinery using loss-of-function approaches assessing VWF exit site size and secretion. Combined, these approaches have enabled elucidation of an essential signaling pathway associated with VWF release in vitro and in vivo, as well as a novel role for septins in actomyosin-regulated exocytosis. This machinery can be pharmacologically inhibited and thus represents new drug targets for thrombotic pathologies. Overall, our results are of fundamental and clinical importance for understanding how endothelial cells control hemostasis, and also, more generally, how actomyosin coats control regulated secretion.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank their funders and collaborators.
This work was funded by the British Heart Foundation (BHF) (grant: PG/19/60/34585) and supported by the CMR Advanced Bio-Imaging Facility, which has been established through generous funds from the Wellcome Trust, the BHF, Barts Charity, and Queen Mary University of London. T.P.M. was funded by a Barts Charity Project grant (MGU05434). Research in the Mostowy laboratory is supported by a European Research Council Consolidator grant (772853—ENTRAPMENT) and Wellcome Trust Senior Research Fellowship (206444/Z/17/Z).
Authorship
Contribution: T.D.N., S.E.-M., C.L.R., and S.M. developed the methodology; C.L.R., S.E.-M., T.D.N., J.J.M., T.P.M., D.L.-M., and K.B.K. performed the investigation; T.D.N. supervised the study; S.E.M. and T.D.N. wrote the original draft; and all authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Thomas D. Nightingale, Centre for Microvascular Research, William Harvey Research Institute, Charterhouse Square, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, London EC1M 6BQ, United Kingdom; e-mail: t.nightingale@qmul.ac.uk.
References
Author notes
∗S.E.-M. and C.L.R. contributed equally to this work.
Mass spectrometry data are available via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD036983 and 10.6019/PXD036983. For other original data and constructs, please contact t.nightingale@qmul.ac.uk.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


![Dual siRNA subscreen identifies which actin-binding proteins play a role in VWF release. (A) Schematic representation of the loss-of-function screening approach used. HUVECs were transfected with siRNA-targeting proteins (and their associated effectors) identified through proximity proteomics. Transfected cells were stimulated with PMA or HAI and either fixed in the presence of an anti-VWF antibody for analysis by confocal LSM to quantify WPB exit site size or the supernatants were collected for quantification of VWF release by fluorescent dot blot. (B) A scatter plot was generated that depicted only the proteins whose reduction in expression led to a decrease in VWF release or proportion of exit sites less than 2 μm2 in comparison to control siRNA. The targets with most prominent effect from each protein class have been annotated. The effect of depletion of shortlisted candidates on (C) PMA-stimulated and (D) HAI-stimulated VWF release. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005 (one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Dunnett multiple comparison).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/141/8/10.1182_blood.2022017419/8/m_blood_bld-2022-017419-gr2.jpeg?Expires=1769121128&Signature=F16AOmsePgo5VzKNXbviknXit7gCLCjPQEBg1EARBrz70qZdT8Bcc8P2fWYSVKqMuTt8sKgBpM0H1~bjKrKdtHCek~P0a3MfMAUu7tI0n6C7baZpWZKnWIfOcMvvHHz11UQv9SaQ2bUrtQDLxgXBgH-R6yruHN9hyPa3jyox6ShAHLw0sx7BepvK1m0Ix878DYJ1wKCFiI6tD8x4KN6tZljWXdeJD9XWU2Qf9LyH-pfslYQqiIJq9GendCTQtcivDK6SNqvIz3qBHE-wIVA-E68pLLfG5bvnpM-6vtV-rd4UjmFzeMIY8KD4FPckbO5DhZs5kJ7wFSz3b~7sV-q7HQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal