Key Points
Contemporary trials no longer demonstrate the previous benefits conferred by vincristine-steroid pulses during maintenance for B-cell ALL.
Decreasing or removing pulses likely does not affect survival or risk of relapse but is associated with reduced toxicity.
Abstract
The benefit associated with the incorporation of vincristine-corticosteroid pulses in maintenance therapy for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is unclear, particularly in the context of modern intensive therapy. This systematic review and meta-analysis examined the impact of reducing the frequency of vincristine-steroid pulses during maintenance for pediatric patients newly diagnosed with B-cell ALL. Two authors reviewed all eligible studies identified through a comprehensive search, extracted data from 25 publications (12 513 patients), and assessed the risk of bias. We created historical and contemporary subgroups; the latter included trials providing both a version of Protocol III from the early Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster trials and eliminating routine prophylactic cranial radiation. Meta-analysis of event-free survival data suggested no benefit between more frequent or less frequent pulses in contemporary trials (hazard ratio [HR], 0.96; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-1.09), which differed significantly from historical trials (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68-0.91; P = .04). We found no significant impact of reduced pulse frequency on overall survival or relapse risk. There was however increased odds of grade 3+ nonhepatic toxicity in the high-pulse frequency group (odds ratio, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.12-1.52). This systematic review suggests that the previous benefit conferred by frequent pulses of vincristine-steroids in maintenance therapy for pediatric B-cell ALL in historical trials no longer applies in contemporary trials but is associated with toxicity. These results will help guide the development of the next phase of clinical trials in the field of pediatric ALL and question the continued use of pulses in maintenance among patients not in clinical trials, particularly those experiencing toxicity.
Introduction
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common childhood cancer, with most of them comprising B-cell lineage disease.1 With improvements in supportive care, identification of high-risk features, such as minimal residual disease or specific molecular or genetic markers, and subsequent risk stratification, cure rates have continued to improve and now exceed 90%.2,3 As such, current trials focus not only on increasing cure rates further but also on decreasing toxicity and late effects of therapy without sacrificing the outcomes.
ALL treatment comprises intensive induction and postinduction phases, followed by a prolonged maintenance or continuation phase. Maintenance consists of continuous exposure to antimetabolite therapy;4,5 nonadherence to this therapy has been associated with an increased risk of relapse.6-8 However, there remains significant controversy as to whether additional agents are required throughout maintenance. Historically, “reinduction” was provided to patients receiving “pulses” of vincristine (VCR) and corticosteroids, which interrupted antimetabolite therapy; the duration of these pulses has shortened over time and, now, typically involves 5 or 7 days of corticosteroids with 1 or 2 doses of VCR per pulse.
Two systematic reviews with individual patient data meta-analysis have previously addressed the use of VCR-steroid pulses in maintenance therapy.9,10 In a Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Collaborative Group (CALLCG) publication from 1996,9 5 trials were combined that collected patient data between 1970 and 1990 and showed clear benefit of the addition of pulses compared with no pulses, reducing the odds of an event by 29% ± 8%. The follow-up review conducted by CALLCG in 201010 included 20 comparative studies that assembled patient data between 1965 and 2002, with 15 of them contributing individual patient data; again, the benefit of pulses showed a significant reduction in the overall event rate (odds ratio [OR], 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.73-0.92), particularly in studies that used prednisone, as opposed to dexamethasone. However, a large cooperative European clinical trial, I-BFM-SG-ALL IR 95,11 included in the second CALLCG review demonstrated no benefit of the addition of pulses during maintenance, and subsequently, treatment strategies diverged around the world. Significant heterogeneity persists in how often and how many pulses are provided, if any; in fact, several clinical trials have compared different frequencies and amounts of pulses in maintenance, which have not previously been assessed in meta-analysis. This includes 2 large, recently published trials12,13 that did not demonstrate any improvement in event-free survival (EFS) with changes in the frequency or amount of pulses during maintenance.
Thus, an updated systematic review that considers contemporary trials involving patients since 2002 and expands the intended comparison beyond pulses vs no pulses to consider changes in pulse frequency or volume between the treatment arms is warranted. With the ongoing evolution in therapeutic strategies and risk stratification for pediatric B-cell ALL, it is possible that the previous benefit of VCR and steroid pulses in maintenance is no longer applicable. This review aims to quantify the impact of reducing the frequency of VCR-steroid pulses during maintenance therapy in pediatric patients newly diagnosed with B-cell ALL. We also aim to determine whether this impact differed between historical and modern treatment regimens.
Methods
Eligibility criteria
We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in either peer-reviewed journals, previous systematic reviews, or abstract forms as well as those provided directly by the study authors identified during our initial search. No restrictions were placed with respect to the language or date of publication. We included trials that assessed the outcomes of pediatric patients (ages 1-18 years) newly diagnosed with B-cell ALL. Trials which did not specify an immunophenotype or where >75% of patients were of B-cell lineage were also included. Trials specifically for patients with relapsed leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, infant ALL (below 1 year), Philadelphia chromosome–positive ALL, T-cell ALL, Burkitt (L3) leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, or Down syndrome were excluded.
We included all trials that assessed EFS or overall survival (OS) as the primary outcome and compared 2 or more forms of maintenance or continuation therapy where both arms provided an antimetabolite chemotherapy (6–mercaptopurine and/or methotrexate) backbone with at least 1 of the arms providing intermittent VCR-steroid pulses. All frequencies, types, and doses of steroids (dexamethasone and prednisone) were included. We were interested in assessing outcomes in trials that compared higher vs lower frequencies of pulses, with no restrictions or requirements on the actual number of pulses or frequency in either arm; it was possible that a frequency of once every 4 weeks could be considered high frequency in 1 trial (when compared with once every 12 weeks) and low frequency in another (when compared with once every 3 weeks). Trials in which pulses were halted early in 1 arm compared with the other or had no pulses in 1 arm were also included. Although some studies that included intensification with additional chemotherapy agents during maintenance (eg, intermediate-dose methotrexate,14-17 cyclophosphamide and intermediate- or high-dose cytarabine,13,16-19 or etoposide/teniposide16,17,19) met our prespecified inclusion criteria, a post hoc decision was made to exclude these trials, allowing for more direct evidence of the impact of changing the VCR-steroid pulse frequency. Trials that focused on the late effects of therapy more than 5 years after treatment were excluded. Secondary trial publications focusing on toxicity or quality of life data were included, provided that survival data were available in an alternate publication.
Search strategy and selection criteria
We conducted our electronic search in several databases, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL, supplemented with searches in the online European Union and National Institutes of Health clinical trial databases, recent abstracts, conference proceedings, and manual searches through reference lists of previous systematic reviews. The study authors were contacted for clarification, if required. All searches were performed from the date of database inception to 13 February 2022. An example search is shown in supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website. Two independent reviewers (L.G., S.B.) examined the studies at all screening stages; in cases of disagreement, consensus was achieved through discussion. The full inclusion and exclusion criteria used during abstract and full text screening are listed in supplemental Table 2.
Data extraction and outcome definition
Data were extracted using a form template and spreadsheet developed by an author with content expertise (L.G.), following piloting by both the extractors (L.G., S.B.). The study authors were contacted to request any missing data; however, no missing data were provided. Additional missing data were sought using secondary references or previous systematic reviews, if those were available.
We gathered information about the study design, trial dates, and eligibility criteria/population included in each trial with details about the risk stratification applied and proportions of patients with B-lineage disease or central nervous system involvement (classified as CNS2 or CNS3 per standard definitions13 or as presence/absence of CNS leukemia in older trials). Participant-level data were collected according to randomized arm, when possible, including risk group, age, white blood cell count, race, and sex; insufficient data about leukemia biology were available for meaningful inclusion. We also collected treatment details, including specifics of dose and frequency of VCR-steroid pulses, duration of maintenance therapy, and other drugs provided during maintenance (supplemental Tables 3-4).
We recorded estimations of EFS (range, 3- to 8-year: mode, 5-year) and OS determined using life table analysis or Kaplan-Meier curves with associated CIs or log-rank statistics (P value) for comparing the trial arms. Data stratified based on sex, risk group, and/or receipt cranial radiation were recorded, if available. When not provided, the EFS was estimated using the count data of the events. Using the best available data, hazard ratios (HRs) with standard errors were calculated for EFS and OS in accordance with the methods described by Tierney et al.20
ORs were calculated for overall and isolated CNS relapses and any available toxicities. In recent papers, grading of toxicity based on the common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) has been frequently reported; in such studies, any severe toxicity (grade 3 or higher) was recorded. In older publications, we recorded any reported toxicity, which in most cases corresponded to grade 3 or higher when compared with those based on the CTCAE criteria. To estimate overall toxicity, the rates of any reported events were combined to provide a measure of overall toxicity. Quality of life data were also sought.
Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias for each included study was assessed based on individual and overall outcomes using the Cochrane risk of bias tool (RoB version 2.0), applying the effect of assigned intervention21 for randomized studies. Traffic light plots and summary tables were created online, using RobVis package.22
Statistics and analysis
Data were summarized in tabular form to assess patterns and possibilities for meta-analysis. Apart from the tabulation, no formal narrative synthesis methods or plots were used. Studies were combined for meta-analysis, and forest plots generated using RevMan version 5.4 (The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020). We used the generic inverse variance method to pool the results for all time-to-event data (EFS and OS), with HRs as the principal summary measure. We used the Mantel-Haenszel method to pool dichotomous event data relative to those of patients at risk to calculate and combine the ORs. Both the HRs and ORs were reported with associated 95% CIs. A random effects model was used in all cases; fixed effect models were considered in cases with very low event rates but did not substantially change the results.
Overall statistical heterogeneity and that between subgroups were assessed using χ2 (threshold set at P = .1) and I2 statistics.23,24 A funnel plot was generated for any meta-analysis containing at least 10 studies, to assess for potential reporting bias. The quality and certainty of the evidence for all outcomes with sufficient data were assessed using the recommended strategies developed by the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) working group.25 The GRADEpro GDT software (McMaster University & Evidence Prime Inc, 2021) was used to summarize the findings. We chose a minimally important threshold of 5%, corresponding to the consensus opinion of a clinically significant change in EFS, which was used for power calculations in all recent trials.
To assess the potential impact of anticipated clinical heterogeneity, we planned subgroup analyses based on the variation in treatment approach over time, risk stratification group, and overall risk of bias. Trials were categorized as historical vs contemporary, the latter defined as treatment that included a delayed intensification or reintensification phase based on Protocol III from early Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster (BFM) trials26,27 and avoidance of prophylactic cranial radiation in all except the patients who were at highest risk (eg, CNS3 at diagnosis). We also examined the impact of cumulative corticosteroid exposure, measured using dexamethasone equivalents. Additional subgrouping based on demographic features was considered but was ultimately not feasible. We performed sensitivity analyses to determine the impact of categorizing 1 study28 as either historical or contemporary.
Results
Search results
We identified 5999 records that underwent title and abstract screening, after the removal of 1564 duplicates (Figure 1). We excluded 5676 studies, leaving 323 studies for full-text review. We were unable to retrieve the full text of 6 records; additionally, 2 records were unavailable, but primary data were captured via an alternative publication. During the full text screening, 282 additional studies were excluded, primarily because of incorrect intervention or study design. The 8 records described in supplemental Table 5 were excluded post hoc13-19,30 because they either included additional or incorrect chemotherapy comparator(s) or data was unavailable.
Description of included studies and interventions
A total of 25 publications met the criteria for inclusion, representing 2 prior systematic reviews,9,10 2 ongoing trials without published data,31-33 and 16 randomized controlled trials.11-13,26,28,34-48 Data were available for a total of 12 513 patients, with 6269 randomized to receive low pulse frequency and 6244 randomized to receive high pulse frequency. Immunophenotype was not reported in 7 of the 8 historical trials (76.25% of patients); in contemporary trials, 91.6% of patients were of B-cell lineage, 4.8% were of T-cell lineage, and 3.7% were of unreported lineage. Further details of the patients in the included trials are presented in supplemental Table 3.
Significant variations in pulse dosing, frequency, and steroid type were present in the low- and high-frequency arms among the included trials (Table 1). All trials used between 1.5 and 2.0 mg/m2 per week of VCR and either between 40 and 100 mg/m2 per day of prednisone (40 mg/m2 per day was the most common dosage) or 6 mg/m2 per day of dexamethasone. Most of the trials compared 1 arm receiving VCR-steroid pulses with the other receiving none, including 2 ongoing trials, which are nearing completion (Table 2). In 2 RCTs, both arms received pulses at different frequencies: 4 vs 6 weeks,14 4 vs 12 weeks among standard-risk patients,12 and 12 vs 16 weeks among low-risk patients.45 And lastly, 2 RCTs compared early discontinuation of VCR-steroid pulses vs continuation.
Characteristics of included studies
| . | Number of studies (%) . | Number of patients (%) . |
|---|---|---|
| All trials | 16 | 12 513 |
| Years the study opened | ||
| 1965-1979 | 8 (50.0) | 1540 (12.3) |
| 1980-1994 | 2 (12.5) | 932 (7.4) |
| 1995-2009 | 4 (25.0) | 4151 (33.2) |
| 2010-present | 2 (12.5) | 5890 (47.1) |
| Era of therapy | ||
| Historical | 10 (62.5) | 2383 (19.0) |
| Contemporary | 6 (37.5) | 10 130 (81.0) |
| Geographic region | ||
| North America | 6 (37.5) | 4869 (38.9) |
| Europe and Russia | 7 (43.8) | 4627 (37.0) |
| Latin America | 2 (12.5) | 94 (0.8) |
| Asia | 1 (0.6) | 2923 (23.4) |
| Steroid used | ||
| Dexamethasone | 6 (37.5) | 9831 (78.6) |
| Prednisone∗ | 11 (68.8) | 2682 (21.4) |
| VCR doses per pulse | ||
| 1 | 10 (62.5) | 11 896 (95.1) |
| 2 | 2 (12.5) | 94 (0.8) |
| 3 or 4 | 4 (25.0) | 523 (4.2) |
| Duration of pulse | ||
| 5 to 7 d | 9 (56.3) | 11 749 (93.9) |
| 14 to 15 d | 5 (31.3) | 534 (4.3) |
| 28 d | 2 (12.5) | 230 (1.8) |
| Randomization | ||
| Every 4 to 14 wk vs none | 12 (75.0) | 5789 (46.3) |
| Stopping vs continuing beyond 1 y | 2 (12.5) | 2955 (23.6) |
| Higher vs lower frequency | 2 (12.5) | 3769 (30.1) |
| . | Number of studies (%) . | Number of patients (%) . |
|---|---|---|
| All trials | 16 | 12 513 |
| Years the study opened | ||
| 1965-1979 | 8 (50.0) | 1540 (12.3) |
| 1980-1994 | 2 (12.5) | 932 (7.4) |
| 1995-2009 | 4 (25.0) | 4151 (33.2) |
| 2010-present | 2 (12.5) | 5890 (47.1) |
| Era of therapy | ||
| Historical | 10 (62.5) | 2383 (19.0) |
| Contemporary | 6 (37.5) | 10 130 (81.0) |
| Geographic region | ||
| North America | 6 (37.5) | 4869 (38.9) |
| Europe and Russia | 7 (43.8) | 4627 (37.0) |
| Latin America | 2 (12.5) | 94 (0.8) |
| Asia | 1 (0.6) | 2923 (23.4) |
| Steroid used | ||
| Dexamethasone | 6 (37.5) | 9831 (78.6) |
| Prednisone∗ | 11 (68.8) | 2682 (21.4) |
| VCR doses per pulse | ||
| 1 | 10 (62.5) | 11 896 (95.1) |
| 2 | 2 (12.5) | 94 (0.8) |
| 3 or 4 | 4 (25.0) | 523 (4.2) |
| Duration of pulse | ||
| 5 to 7 d | 9 (56.3) | 11 749 (93.9) |
| 14 to 15 d | 5 (31.3) | 534 (4.3) |
| 28 d | 2 (12.5) | 230 (1.8) |
| Randomization | ||
| Every 4 to 14 wk vs none | 12 (75.0) | 5789 (46.3) |
| Stopping vs continuing beyond 1 y | 2 (12.5) | 2955 (23.6) |
| Higher vs lower frequency | 2 (12.5) | 3769 (30.1) |
Includes prednisone, prednisolone, and methylprednisolone.
Treatment and randomization summary of included studies
| Study ID . | Trial dates . | Reference . | Trial entry criteria (y) . | Risk stratification . | VCR dosage . | Steroid dosage . | Pulse randomization (# analyzed/arm) . | Approximate duration of maintenance or treatment . | EFS (95% CI; %) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical therapy | |||||||||
| SWOG 663/664/ALinC | 1965-1967 | Fernbach et al 1975,34 CALLCG 201010 | Age <15 | — | 2 mg/m2 per wk ×4 | Prednisone 60 mg/m2 per d × 28 d | q 12 wk (44) vs none (56) | Tx: Until relapse | — |
| St. Jude 7 | 1970-1972 | Aur et al 1973,35 CALLCG 201010 | Age <20 | — | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×3 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 15 d | q 12 wk × 10 (47) vs none (47) | Tx: 2.5 y | 29.8 (20.6-39) |
| HIVH D74 | 1974-1977 | Ortega 198636 | Age <15 | — | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×2 | Prednisolone 40 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 12 wk × 12 (32) vs none (30) | Tx: 3 y | — |
| DCLSG ALL 3 | 1975-1979 | Van der Does-Van den Berg et al 1998,46 197537 | Age <15 | Standard risk | 2 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 7 wk × 14 (79) vs none (68) | Tx: 2 y | 43 (37-49) vs 41 (25-47) |
| CCG 141A 2 | 1978-1979 | Bleyer et al 1983,38 CALLCG 201010 | Age <21 | Nonlow risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 4 wk (150) vs none (151) | Tx: 3 vs 5 y (randomized) | 66.9 (61.6-72.2) |
| CCG 161 | 1978-1983 | Bleyer et al 199139 | Age 36 | Low risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 4 wk (302) vs none (303) | Tx: 2 vs 3 y (randomized) | 76.6 vs 63.9 (P = .003) |
| BFM-79 | 1979-1981 | Henze et al 1981,40 Riehm 199026 | Age <18 | Nonhigh risk | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×3 | Prednisone 50 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 14 wk × 3 (103) vs none (96) | Mx: 16-18 mo | 76 vs 71 (P = .44) |
| INEN-7902 | 1979-1983 | CALLCG 201010 | — | High risk (unable to confirm) | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×2 | Prednisone 100 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 8 wk ×4 +/−q 12 wk × 8 (15 vs 17) | Tx: 3 y | 9.1 (0.7-17.5) |
| PETHEMA ALL-84SR | 1984-1989 | CALLCG 201010 | Age <15 | Standard risk (unable to confirm) | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×4 | Prednisolone 40 mg/m2 per d × 28 d | q 4 wk × 4 (69) vs none (61) | Tx: 2 y | 55.2 (42.3-68.1) |
| ALL-MB 91 | 1995-2002 | Karachunskiy et al 200828 | Age <18 | All risk groups | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 8 wk (358) vs none (355) | Mx: 18 mo | 67 (64-70) vs 68 (65-71) |
| Contemporary therapy | |||||||||
| CCG-1891 | 1990-1993 | Lange et al 200241 | Age 1-9 | Standard risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 3 wk (397) vs q 4 wk (405) | Mx: 2 y (F), 3 y (M) | 77 (75-79) vs 76 (75-77) |
| I-BFM-SG- ALL IR 95 | 1995-2000 | Conter et al 2007,11 Burger et al 200542 | Age <18 | Intermediate risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 10 wk × 6 (1325) vs none (1293) | Mx: 18 mo | 79.8 (77.4-82.2) vs 79.2 (76.8-81.6) |
| AIEOP-ALL-95 | 1995-2000 | Arico et al 2008,48 200343 | Age <18 | Intermediate risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 10 wk × 6 (187) vs none (222) | Mx: 18 mo | 84.9 (79.8-90) vs 82.2 (76.9-87.5) |
| EORTC 58951 | 1999-2002 | De Moerloose et al 201044 | Age <18 | Standard & high risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 60 mg/m2 per d vs dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 10 wk × 6 (167) vs none (163) | Mx: 18 mo | 90.6 (86.5-94.7) vs 82.8 (77.3-88.3) |
| COG AALL 0932 | 2010-2018 | Schore et al 202045 | Age 1-10 + WBC <50, low-risk features | Low risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d ×5 vs 7 d | q 12 wk (302) vs q 16 wk (301) | Mx: 2.5 y vs 2 y (F)/3 y (M) | 98.5 (96.7-100) vs 98.8 (97.2-100) |
| 2010-2018 | Angiolillo et al 202112 | Age 1-10 + WBC <50 | Standard risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 4 wk (1186) vs q 12 wk (1178) | Mx: 2 y (F) /3 y (M) | 94.1 (92.2-96.0) vs 95.1 (93.3-96.9) | |
| CCCG ALL 2015 | 2015-2020 | Yang et al 202113 | Age 0-18; LR: low-risk features | Low risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 4 wk × 1 y then q 8 wk × 7 (1442) vs stop (1481) | Tx: 2.5 y | 90.3 (88.4-92.2) vs 90.2 (88.2-92.2) |
| Study ID . | Trial dates . | Reference . | Trial entry criteria (y) . | Risk stratification . | VCR dosage . | Steroid dosage . | Pulse randomization (# analyzed/arm) . | Approximate duration of maintenance or treatment . | EFS (95% CI; %) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical therapy | |||||||||
| SWOG 663/664/ALinC | 1965-1967 | Fernbach et al 1975,34 CALLCG 201010 | Age <15 | — | 2 mg/m2 per wk ×4 | Prednisone 60 mg/m2 per d × 28 d | q 12 wk (44) vs none (56) | Tx: Until relapse | — |
| St. Jude 7 | 1970-1972 | Aur et al 1973,35 CALLCG 201010 | Age <20 | — | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×3 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 15 d | q 12 wk × 10 (47) vs none (47) | Tx: 2.5 y | 29.8 (20.6-39) |
| HIVH D74 | 1974-1977 | Ortega 198636 | Age <15 | — | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×2 | Prednisolone 40 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 12 wk × 12 (32) vs none (30) | Tx: 3 y | — |
| DCLSG ALL 3 | 1975-1979 | Van der Does-Van den Berg et al 1998,46 197537 | Age <15 | Standard risk | 2 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 7 wk × 14 (79) vs none (68) | Tx: 2 y | 43 (37-49) vs 41 (25-47) |
| CCG 141A 2 | 1978-1979 | Bleyer et al 1983,38 CALLCG 201010 | Age <21 | Nonlow risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 4 wk (150) vs none (151) | Tx: 3 vs 5 y (randomized) | 66.9 (61.6-72.2) |
| CCG 161 | 1978-1983 | Bleyer et al 199139 | Age 36 | Low risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 4 wk (302) vs none (303) | Tx: 2 vs 3 y (randomized) | 76.6 vs 63.9 (P = .003) |
| BFM-79 | 1979-1981 | Henze et al 1981,40 Riehm 199026 | Age <18 | Nonhigh risk | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×3 | Prednisone 50 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 14 wk × 3 (103) vs none (96) | Mx: 16-18 mo | 76 vs 71 (P = .44) |
| INEN-7902 | 1979-1983 | CALLCG 201010 | — | High risk (unable to confirm) | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×2 | Prednisone 100 mg/m2 per d × 14 d | q 8 wk ×4 +/−q 12 wk × 8 (15 vs 17) | Tx: 3 y | 9.1 (0.7-17.5) |
| PETHEMA ALL-84SR | 1984-1989 | CALLCG 201010 | Age <15 | Standard risk (unable to confirm) | 1.5 mg/m2 per wk ×4 | Prednisolone 40 mg/m2 per d × 28 d | q 4 wk × 4 (69) vs none (61) | Tx: 2 y | 55.2 (42.3-68.1) |
| ALL-MB 91 | 1995-2002 | Karachunskiy et al 200828 | Age <18 | All risk groups | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 8 wk (358) vs none (355) | Mx: 18 mo | 67 (64-70) vs 68 (65-71) |
| Contemporary therapy | |||||||||
| CCG-1891 | 1990-1993 | Lange et al 200241 | Age 1-9 | Standard risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 40 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 3 wk (397) vs q 4 wk (405) | Mx: 2 y (F), 3 y (M) | 77 (75-79) vs 76 (75-77) |
| I-BFM-SG- ALL IR 95 | 1995-2000 | Conter et al 2007,11 Burger et al 200542 | Age <18 | Intermediate risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 10 wk × 6 (1325) vs none (1293) | Mx: 18 mo | 79.8 (77.4-82.2) vs 79.2 (76.8-81.6) |
| AIEOP-ALL-95 | 1995-2000 | Arico et al 2008,48 200343 | Age <18 | Intermediate risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 10 wk × 6 (187) vs none (222) | Mx: 18 mo | 84.9 (79.8-90) vs 82.2 (76.9-87.5) |
| EORTC 58951 | 1999-2002 | De Moerloose et al 201044 | Age <18 | Standard & high risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Prednisone 60 mg/m2 per d vs dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 10 wk × 6 (167) vs none (163) | Mx: 18 mo | 90.6 (86.5-94.7) vs 82.8 (77.3-88.3) |
| COG AALL 0932 | 2010-2018 | Schore et al 202045 | Age 1-10 + WBC <50, low-risk features | Low risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d ×5 vs 7 d | q 12 wk (302) vs q 16 wk (301) | Mx: 2.5 y vs 2 y (F)/3 y (M) | 98.5 (96.7-100) vs 98.8 (97.2-100) |
| 2010-2018 | Angiolillo et al 202112 | Age 1-10 + WBC <50 | Standard risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 5 d | q 4 wk (1186) vs q 12 wk (1178) | Mx: 2 y (F) /3 y (M) | 94.1 (92.2-96.0) vs 95.1 (93.3-96.9) | |
| CCCG ALL 2015 | 2015-2020 | Yang et al 202113 | Age 0-18; LR: low-risk features | Low risk | 1.5 mg/m2 | Dexamethasone 6 mg/m2 per d × 7 d | q 4 wk × 1 y then q 8 wk × 7 (1442) vs stop (1481) | Tx: 2.5 y | 90.3 (88.4-92.2) vs 90.2 (88.2-92.2) |
F, female; LR, low risk; M, male; Mx, maintainance; Tx, treatment; q, every; WBC, white blood cell.
Assessment of study quality
Using the RoB 2.0 tool for RCTs, no trial was rated as having an overall low risk of bias. Most trials published in 1995 or earlier had major lapses in reporting details surrounding randomization, deviations, and missed outcome data, resulting in an overall high risk of bias in 6 out of 11 trials available for review. Trials published in the last 20 years were more robust, with only minor concerns identified, most of which were related to a lack of blinding in all trials, leading to the potential for risk of bias in deviations from the trial context or the lack of a prespecified data analysis plan. Traffic light plots and justification for bias assessment are provided in supplemental Materials (supplemental Table 6; supplemental Figure 1).
Impact of pulses on EFS and OS
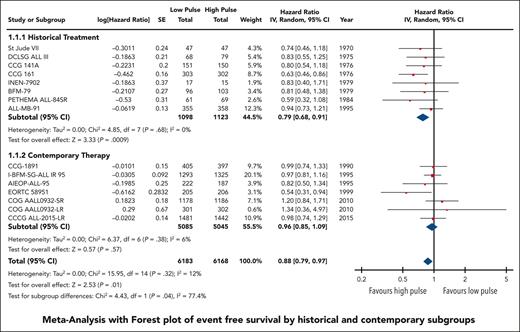
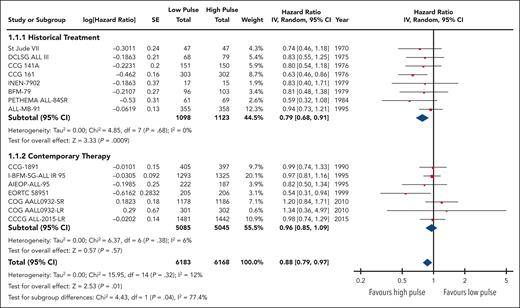
EFS data were available and pooled for meta-analysis from 14 trials encompassing 6183 children with low pulse frequency and 6168 with high pulse frequency. Data for 4 of these trials were extracted solely from previous systematic reviews because either the primary references were not provided or publications were not available for review. Although data from NOPHO 2000 were not available according to randomized arm; personal communication from study authors revealed that there was no difference between arms.30 When all trials were pooled together, the HR was 0.88 (95% CI, 0.79-0.97), favoring higher-frequency over lower-frequency pulses (Figure 1); however, the overall quality of the evidence was rated as very low because of very serious concerns regarding risk of bias and imprecision. Although there was minimal overall statistical heterogeneity (I2 = 12%), the known clinical heterogeneity in the treatment strategies justified our planned subgroup analyses.
We grouped all included trials into historical and contemporary subgroups as described earlier; there was a significant difference in HRs between these 2 subgroups (P = .04; Figure 2). Historical therapy approaches favored high pulse frequency (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68-0.91), whereas contemporary approaches suggested no benefit of high or low pulse frequency (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.85-1.09). Sensitivity analysis placing ALL-MB-91 in the contemporary rather than historical subgroup did not significantly impact the results. Additional subgroup analysis according to risk stratification did not demonstrate any benefit of high pulse frequency among trials involving patients who were at low and standard/intermediate risk; the remaining trials favored higher-frequency pulses but were confounded by the era of treatment. Separating trials by risk of bias assessment did not provide any additional insights (supplemental Figure 2).
The HR for the contemporary subgroup corresponded to an absolute reduction in EFS of 0.3% (range, from an increase by 0.6% to a decrease by 1.6%) if the baseline EFS was taken to be 98%, as was reported by Schore et al for patients at low risk,45 or an absolute reduction in EFS of 1.3% (range, from an increase by 2.7% to a decrease by 1.3%) if the baseline risk was taken to be 80%, as was reported by Yang et al for patients at high risk;13 neither of these represent a statistically significant change from baseline risk. When considered in isolation, the quality of this evidence was rated as moderate because of concerns about the risk of bias.
Data regarding OS were available in 5 RCTs,11-13,28,44 representing 9029 patients (4512 receiving low pulse frequency and 4517 receiving high pulse frequency). No benefit to high pulse frequency was observed (HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.78-1.16; supplemental Figure 3). Statistical heterogeneity was low (I2 = 0%), and the overall quality of the evidence was rated as low, because of serious concerns about the risk of bias and imprecision.
Impact of pulses on relapse risk
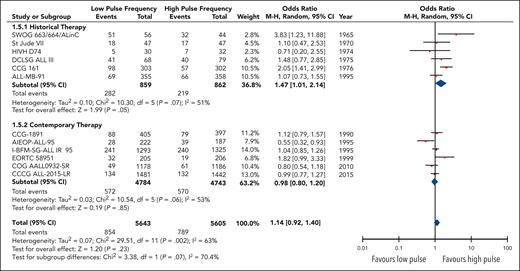
Twelve studies reported the overall rates of relapse encompassing 11 248 patients. Although no statistical benefit on the risk of relapse with higher pulse frequency was observed (OR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.72-1.08), heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 63%) and remained moderate within each subgroup (Figure 3). Regardless, there was a significant difference24 (P = .07) in the odds of a relapse event occurring in high-frequency arms between the contemporary therapy subgroup (OR, 1.02; 95% CI; 0.83-1.25) and the historical therapy subgroup (OR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.47-0.99).
Forest plot of overall relapses based on historical and contemporary subgroups.
Forest plot of overall relapses based on historical and contemporary subgroups.
Among 10 trials with data on isolated CNS relapse, the risk of such relapses did not differ between lower- and higher-frequency pulses (OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.71-1.37); this did not differ between historical and contemporary studies (P = .63; supplemental Figure 4). Overall, the quality of evidence for total and isolated relapses was rated as low, using the GRADE criteria, primarily because of the high risk of bias in several older trials.
Impact of pulses on nonhepatic toxicity
The reporting of the toxicity data was inconsistent across the included trials. Five trials reported selected toxic events both independently11,41,44 and as pooled rates of serious adverse events graded per the CTCAE criteria.12,13 The specific independent toxicities that were pooled for this analysis (supplemental Table 7) included rates of osteonecrosis, severe infections, peripheral neuropathy, need for platelet or blood transfusion, admission to hospital, and/or fever-neutropenia episodes. Hepatic toxicity was excluded from the meta-analysis because the rates reported separately in historical trials exceeded other toxicity rates and were not included in the pooled reports of serious adverse events in contemporary trials. Several trials reported deaths in complete remission and/or infectious related deaths that were not included in the meta-analysis because the reported data were not consistently separated by randomized intervention.
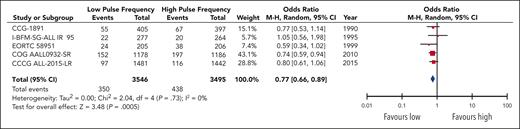
Overall, the pooled data encompassing 7041 patients in 5 trials demonstrated an increased odds of significant (grade 3+) nonhepatic events in the high-pulse-frequency group (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.12-1.52; Figure 4). This corresponded to an absolute increase in the number of toxic events for the high-pulse-frequency arm by 33 (range, 13-54) per 1000 patients compared with the baseline risk in the low-pulse-frequency arm. Toxicity data were also pooled separately for both osteonecrosis and peripheral neuropathy events, because they were intimately associated with the use of VCR and steroids (supplemental Figure 5).
Two trials reported osteonecrosis in separate publications: 9 of 409 patients in AIEOP-ALL-9543 (2 before maintenance therapy) and 25 of 1046 patients in I-BFM-SG-ALL IR 95 developed osteonecrosis;42 neither of these publications separated the data based on the randomized arm. The pooled effect estimate for osteonecrosis events in 3 trials12,13,44 did not show a statistically significant difference between higher and lower pulses (OR, 1.64-0.61; 95% CI, 0.86-3.09; P = .13), although the confidence intervals were wide. For peripheral neuropathy, the pooled results of 4 trials11-13,41 demonstrated a significant increase in the odds of an event in the high-pulse-frequency arm (OR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.11-2.38), corresponding to an absolute increase in events of 13 (range, 2-28) per 1000 patients in the high-pulse-frequency arm. The quality of evidence for all toxicity outcomes was rated down to moderate, because of risk of bias.
Discussion
This systematic review found that in childhood ALL, the survival benefit associated with including VCR-steroid pulses in maintenance therapy was restricted to historical trials that lacked the intensified premaintenance therapy characterizing more contemporary protocols. When analyses were restricted to such contemporary trials, a higher pulse frequency was not associated with EFS or overall relapse risk. However, a higher pulse frequency was associated with increased toxicity rates.
Since the publication of I-BFM-SG-ALL IR-95,11 which demonstrated no significant difference between those who received pulses and those who did not (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.81-1.15), VCR-steroid pulses have been eliminated in many European countries where BFM protocols are used routinely. In contrast, the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) protocols primarily used across North America have continued to include VCR-steroid pulses, although these have been reduced from every 4 weeks to every 12 weeks in the current open standard- and high-risk trials (AALL 1731/2). This is based on results from the BFM trials and more recent publications of COG AALL 0932,12,45 in which a reduction in pulse frequency did not affect survival outcomes. In parts of Asia and elsewhere, protocols are based on a Total Therapy approach from St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, where intensification during maintenance therapy is provided using not only VCR-steroid pulses but also additional chemotherapy,13,49 particularly for patients at intermediate and high risk, which makes direct comparison with patients treated with BFM-based therapy more difficult. This feature made data for high-risk patients enrolled in CCCG ALL-201513 ineligible for inclusion in our meta-analysis, though there was no significant difference in EFS outcomes between control and experimental arms for all the risk stratification groups (low-risk: HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.74-1.29; intermediate/high-risk: HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.79-1.24).
An important finding of our review was the increased grade 3+ toxicity associated with higher pulse frequencies. The impact of treatment on long-term morbidity,50-52 including major impacts on mental health and health-related quality of life,47,53-55 for pediatric patients with ALL is well established. Among children enrolled in COG AALL0932, there was a high incidence of a decrease in the physical and emotional quality of life compared with that among the general public.47 Some of this impact may be related to the need for frequent trips or admissions to the hospital for the treatment of their disease or potential complications. Moreover, the potential for serious illness and even death exists even with minor immunosuppressive therapy during maintenance, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.56 Previous attempts at limiting the length of maintenance therapy to less than ∼2 years have not been successful, although it may be possible in certain biologic subgroups.56,57 Eliminating and reducing the amount of chemotherapy provided for maintenance is, thus, of great appeal, especially because of the known acute and long-term toxicities associated with VCR and steroids.58
Several cautions exist when generalizing our results to the full population of pediatric ALL. Firstly, this analysis is unable to identify the components of therapy in contemporary trials that contribute the most to our findings. Although several factors are likely to be involved, increased cumulative chemotherapy exposure through the inclusion of a delayed intensification (or similar) phase or increased corticosteroids is a probable contributor. Secondly, a significant proportion of patients, particularly in historical trials, did not have a reported immunophenotype, although a substantial majority of such patients are likely to have B-lineage disease. Thirdly, individual outcome data for patients with specific cytogenetic and molecular aberrations were unavailable. It is possible that a higher pulse frequency may continue to be beneficial for patients with higher-risk features (eg, IZKF1 mutations).59,60 Fourthly, our results may not be applicable to specific low- and middle-income countries where intensification of premaintenance therapy is not possible because of excessive treatment-related toxicity. Finally, our results are most generalizable to low- and intermediate/standard-risk patients. We did not find any trials involving high-risk patients that met our eligibility criteria.
Additional limitations include missing data and primary publications for review; a few older studies were included solely because of their presence in previous reviews, and independent confirmation of data or risk of bias assessment was not possible. Some assumptions and data manipulation steps were required to complete the meta-analysis; however, this was mainly required in older trials that contributed minimal weight, limiting the effect. The quality of the evidence according to the GRADE criteria was also variable (ranging from very low- to moderate-quality; supplemental Figure 6), although the most robust data came from contemporary trials with the least amount of bias. Therefore, we can be relatively more confident in the quality of the data for this subgroup. Although we did not find any significant impact of publication bias, its existence cannot be ruled out.
We conclude that the benefit associated with frequent pulses of VCR and steroids in maintenance therapy for pediatric B-cell ALL in historical trials no longer exists in modern therapy using contemporary protocols, although the risk of increased toxicity remains. Thus, these results support the omission of pulses during pediatric ALL maintenance therapy in the next phase of clinical trials, particularly for patients at low and standard risk in high-resource settings, and call into question the continued use of pulses for patients not enrolled in clinical trials.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Gabriela Ines Villanueva and Sergei Reznikov for their help with translation of articles in Spanish and Russian, respectively, during screening.
L.G. and S.B. are graduate students at the McMaster University. This work was completed in partial fulfillment of the course requirements for their degrees.
Authorship
Contribution: L.G. designed and wrote the review protocol, coconducted the search, screened potentially eligible studies, assessed risk of bias, extracted and analyzed data, including meta-analysis, interpreted results, generated the figures/tables, and wrote and edited the manuscript, including compiling the references; S.B. contributed to finalizing the review protocol, coconducted the search, screened potentially eligible studies, assessed risk of bias, extracted data, and contributed toward the analysis of the data and the first draft of the figures and manuscript; F.F. provided mentorship and feedback throughout the design of the review protocol and after preliminary analysis was conducted; L.T. reviewed and edited the manuscript with respect to statistical methodology; M.L.L., D.T.T., and E.A.R. reviewed and provided feedback on the final manuscript; and S.G. contributed to finalizing data analysis, in particular subgroup analysis, and editing of the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.L.L. has the Aldarra Foundation endowed chair of pediatric cancer research by Bill and June Boeing founders. E.A.R. is a professor at KiDS of New York University (NYU) Foundation by NYU Langone Health. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Louise Guolla, Department of Pediatrics, McMaster University (Rm 3N27), 1280 Main St W, Hamilton, ON, Canada L8S 4K1; e-mail: guollal@mcmaster.ca.
References
Author notes
Presented in abstract form at the 64th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, New Orleans, LA, 10 December 2022.
All data sets generated and/or analyzed during this study were retrieved or estimated from the primary publications referenced in this article. The extracted data used in the meta-analysis are available on request from the corresponding author, Louise Guolla (guollal@mcmaster.ca).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal