Key Points
ERCC6L2 disease causes BMF that requires timely stem cell transplantation before progressing to a high-risk myeloid malignancy.
Frequent somatic TP53 mutation screening and BM examination are essential for surveillance of patients with ERCC6L2-related disease.
Abstract
Biallelic germ line excision repair cross-complementing 6 like 2 (ERCC6L2) variants strongly predispose to bone marrow failure (BMF) and myeloid malignancies, characterized by somatic TP53-mutated clones and erythroid predominance. We present a series of 52 subjects (35 families) with ERCC6L2 biallelic germ line variants collected retrospectively from 11 centers globally, with a follow-up of 1165 person-years. At initial investigations, 32 individuals were diagnosed with BMF and 15 with a hematological malignancy (HM). The subjects presented with 19 different variants of ERCC6L2, and we identified a founder mutation, c.1424delT, in Finnish patients. The median age of the subjects at baseline was 18 years (range, 2-65 years). Changes in the complete blood count were mild despite severe bone marrow (BM) hypoplasia and somatic TP53 mutations, with no significant difference between subjects with or without HMs. Signs of progressive disease included increasing TP53 variant allele frequency, dysplasia in megakaryocytes and/or erythroid lineage, and erythroid predominance in the BM morphology. The median age at the onset of HM was 37.0 years (95% CI, 31.5-42.5; range, 12-65 years). The overall survival (OS) at 3 years was 95% (95% CI, 85-100) and 19% (95% CI, 0-39) for patients with BMF and HM, respectively. Patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia with mutated TP53 undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation had a poor outcome with a 3-year OS of 28% (95% CI, 0-61). Our results demonstrated the importance of early recognition and active surveillance in patients with biallelic germ line ERCC6L2 variants.
Introduction
Excision repair cross-complementing 6 like 2 (ERCC6L2) is 1 of the most recently discovered genes associated with inherited bone marrow failure (BMF). The ERCC6L2 protein contributes to nucleotide excision repair and nonhomologous end joining.1-7 In addition, ERCC6L2-depleted cells have been shown to exhibit increased reactive oxygen species levels, and ERCC6L2 is suggested to play a role in mitochondrial function.1 Recessively inherited ERCC6L2 disease ranks highly among the drivers of BMF syndromes.4 Like most of the BMF-causing germ line gene defects, biallelic variants in ERCC6L2 also predispose patients to the development of myeloid malignancies.8 We previously reported that all ERCC6L2-driven hematological malignancies (HMs) harbor somatic TP53 mutations, and the somatic mutagenesis seems to occur already in the BMF phase.8 Concerningly, the TP53 mutations surreptitiously lead to a HM with extremely poor survival.9 In distinction from other BMFs with leukemia predisposition, acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs) stemming from ERCC6L2 disease seem to be restricted to erythroid lineage.8 The propensity for developing myeloid malignancy with TP53 mutations in ERCC6L2 disease renders it as a hematological disorder with extremely high-risk for morbidity and mortality.
Since the first depiction of patients with defective ERCC6L2, altogether 37 cases with biallelic germ line ERCC6L2 variants have been described in the literature (including 14 patients from Finland).1-4,8,10-15 In prior studies among Finnish patients, all cases have been homozygous for the variant ERCC6L2(NM_020207.7): c.1424delT (p.Ile475ThrfsTer36, rs768081343).8,10 Moreover, a 20-times-higher minor allele frequency (AF) of the variant in the Finnish population compared with that in the rest of the European population16 suggests an accumulation of ERCC6L2 disease because of genetic drift, as recognized by the Finnish disease heritage (FDH).17 Nevertheless, ERCC6L2 disease is not limited to Finland.
In this study, our multinational study group brought together the detailed clinical and molecular features of both novel and previously identified patients with ERCC6L2-related disease (n = 52). Our aim is to highlight the typical diagnostic clues and the course of ERCC6L2 disease, providing clinicians with a means for recognition and planning of interventions in a timely manner.
Methods
Study design
The study was approved by the Helsinki University Hospital Ethics Committee (#206/13/03/03/2016 and #303/13/03/01/2011) and the local institutional review boards. All study subjects provided written informed consent. A retrospective chart review was performed at 11 centers globally. Individuals with a genetic diagnosis of biallelic germ line variants in ERCC6L2 were included with no additional restrictions (n = 50). Two Finnish individuals died before genetic confirmation but were additionally considered in the study: 1 patient presented with severe aplastic anemia and the other had AML M6; they had 1 and 2 siblings with verified biallelic ERCC6L2 variants, respectively (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website). The investigators from multiple centers reviewed the medical records and pseudonymized the patient data. Bone marrow (BM) examinations, including defining the BM cellularity, were carried out in each participating center in accordance with the local practices (detailed original hematopathology reports were available for most Finnish patients; n = 19/23). The disease courses and treatment responses were reported as defined by the local treating physicians. Family pedigrees were studied whenever possible (n = 26/35 families). We performed a genealogical study to explore the possible founder effect of the variant ERCC6L2 c.1424delT in Finland in accordance with previously described criteria.18 We defined families as consanguineous if the parents were second cousins or closer.19
In this study, patients with a diagnosis of aplastic anemia or a mention of hypocellular BM were defined as having BMF. The diagnoses of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) were classified per the World Health Organization classification in 2016.20 The diagnosis of AML was reported per the standardized European LeukemiaNet 2022 criteria,21 and if of an erythroid root (AML M6), per morphological French-American-British classification. We considered a relative increase in the erythroid lineage of at least 50% of the total BM cells as an erythroid predominance. Individuals with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants but without a diagnosis of BMF, MDS, or AML were included in the statistical analyses if the result of a BM examination was available.
Statistical analyses
We evaluated differences in continuous variables using an unpaired t test and in categorical variables using the χ2 test. All tests were 2-tailed. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. We studied the overall survival (OS) probability and age of onset of HM by calculating Kaplan-Meier curves and compared them using the log-rank test. We used Cox proportional hazard models for hazard ratios. Initial contact with a hematologist was set as the first time point during follow-up. Death from any cause was defined as an event, and data of surviving patients were censored on the last day that they were known to be alive. Among the patients with an initial diagnosis of BMF, we observed only 2 deaths during the follow-up and, therefore, reported their mean survival time.
Results
Baseline characteristics of the subjects with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants
The study included 52 individuals with ERCC6L2 disease from 9 countries and 10 different ethnic groups (including 33 previously reported cases). Table 1 and Figure 1 summarize patient characteristics and ERCC6L2 mutation types. Of the 35 families, 12 (34%) were consanguineous. The median age at referral to a hematologist was 18 years. There was no change in the median age, even when individuals with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants but without a diagnosis of BMF, MDS, or AML were excluded. The most common initial diagnosis was BMF (n = 32; 62%). HM was diagnosed in every fourth individual at the first contact with a hematologist (MDS or AML, n = 14; T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [T-ALL], n = 1). The individual characteristics of the study subjects are presented in Table 2 and, in more detail, in supplemental Table 1. The median age at the time of diagnosis for BMF was significantly lower than that for HM (12.0 years and 29.0 years, respectively; P = .0007; Table 3). Genetic testing of the patients' families identified 5 siblings with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants without a previous diagnosis of hematological disease (Table 2; supplemental Table 1).
Summary of patient characteristics, n = 52
| Age at investigation | |
| Median, y (range) | 18 (2-65) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 32 (62) |
| Male | 20 (38) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |
| British Indian | 1 (2) |
| British Pakistani | 4 (8) |
| Druze | 1 (2) |
| East African | 3 (6) |
| Fijian Indian | 1 (2) |
| Finnish | 23 (44) |
| North African | 1 (2) |
| Puerto Rican | 1 (2) |
| Swedish | 2 (4) |
| White (not specified) | 15 (28) |
| Initial condition, n (%) | |
| Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 mutation without diagnosis of BMF, MDS, or AML | 5 (10) |
| BMF | 32 (62) |
| MDS | 9 (17) |
| MDS/AML∗ | 2 (4) |
| AML | 3 (6) |
| Other HM (ALL) | 1 (2) |
| ERCC6L2 genotype, n (%) | |
| Homozygous | 39 (75) |
| Compound heterozygous | 13 (25) |
| Individuals by ERCC6L2 mutation type, n (%) | |
| Biallelic frameshift | 29 (55) |
| Biallelic nonsense | 5 (10) |
| Biallelic splicing | 1 (2) |
| Biallelic exon deletion | 4 (8) |
| Biallelic missense | 4 (8) |
| Mixed | 9 (17) |
| Age at investigation | |
| Median, y (range) | 18 (2-65) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 32 (62) |
| Male | 20 (38) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |
| British Indian | 1 (2) |
| British Pakistani | 4 (8) |
| Druze | 1 (2) |
| East African | 3 (6) |
| Fijian Indian | 1 (2) |
| Finnish | 23 (44) |
| North African | 1 (2) |
| Puerto Rican | 1 (2) |
| Swedish | 2 (4) |
| White (not specified) | 15 (28) |
| Initial condition, n (%) | |
| Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 mutation without diagnosis of BMF, MDS, or AML | 5 (10) |
| BMF | 32 (62) |
| MDS | 9 (17) |
| MDS/AML∗ | 2 (4) |
| AML | 3 (6) |
| Other HM (ALL) | 1 (2) |
| ERCC6L2 genotype, n (%) | |
| Homozygous | 39 (75) |
| Compound heterozygous | 13 (25) |
| Individuals by ERCC6L2 mutation type, n (%) | |
| Biallelic frameshift | 29 (55) |
| Biallelic nonsense | 5 (10) |
| Biallelic splicing | 1 (2) |
| Biallelic exon deletion | 4 (8) |
| Biallelic missense | 4 (8) |
| Mixed | 9 (17) |
Per the ELN2022 classification.21
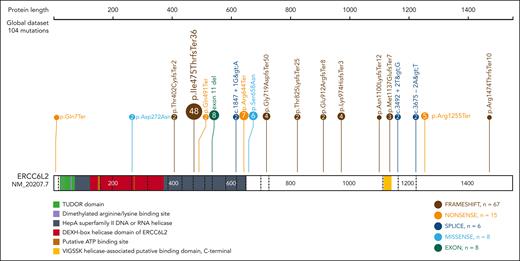
Germ line ERCC6L2 variants identified in study subjects. Various mutations are detected in ERCC6L2 (NM_20207.7). A Finnish founder mutation (p.Ile475ThrfsTer36) constitutes nearly half of the identified mutations. Figure created with ProteinPaint (proteinpaint.stjude.org).22
Germ line ERCC6L2 variants identified in study subjects. Various mutations are detected in ERCC6L2 (NM_20207.7). A Finnish founder mutation (p.Ile475ThrfsTer36) constitutes nearly half of the identified mutations. Figure created with ProteinPaint (proteinpaint.stjude.org).22
The individual characteristics of study subjects at initial investigations
| Patient ID . | Family ID . | Initial disease condition . | Age (y) . | ERCC6L2 genotype c.(NM_0202027.7) . | ERCC6L2 genotype p.(NP_064592.3) . | Somatic TP53 clones in BM or PB (NM_000546.6; VAF) . | Other somatic clones (VAF) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1∗ | EF1 | BMF | 2 | c.[3409_3410del]; [3763C>T] | p.[(Met1137GlufsTer7)];[(Arg1255Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP2∗ | EF2 | BMF | 5 | c.[1973G>A];[1973G>A] | p.[(Ser658Asn)];[(Ser658Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP3∗ | EF3 | BMF | 6 | c.[1930C>T];[1930C>T] | p.[(Arg644Ter)];[(Arg644Ter)] | Yes, variant N/A (4.8%) | No |
| EP4∗ | EF4 | BMF | 7 | c.[2156del];[3675-2A>T] | p.[(Gly719AspfsTer50)];[(?)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP5 | EF5 | BMF | 7 | c.[3492+2T>G];[3492+2T>G] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP6∗ | EF6 | BMF | 8 | c.[2734del];[2734del] | p.[(Glu912ArgfsTer8)]; [(Glu912ArgfsTer8)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP7∗ | EF7 | BMF | 8 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | Not detected initially, at age 15 y c.638G>T p.(Arg213Leu) (3%) | N/A |
| EP8∗ | EF8 | BMF | 8 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP9 | EF9 | BMF | 9 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | Not detected (latest screen at 10 y) | N/A |
| EP10∗ | EF7 | BMF | 9 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (1.5%) | N/A |
| EP11∗ | EF10 | BMF | 10 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.659A>G, p.(Tyr220Cys) (36%); c.725G>T, p.(Cys242Phe) (3%) | No |
| EP12 | EF11 | BMF | 11 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.723del, p.(Cys242AlafsTer5) (3%), c.376-2A>G (4.2%), c. 733G>A, p.(Gly245Ser) (41%) | TET2 c.4102T>C, p.(Phe1368Leu) (2%) |
| EP13 | EF12 | BMF | 11 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | Not detected (latest screen at 11 y) | No |
| EP14 | EF13 | BMF | 12 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.524G>A, p. (Arg175His)(7%) | N/A |
| EP15 | EF14 | BMF | 12 | c.[19C>T];[2156del] | p.[(Gln7Ter)];[(Gly719AspfsTer50)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP16∗ | EF2 | BMF | 12 | c.[1973G>A];[1973G>A] | p.[(Ser658Asn)];[(Ser658Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP17 | EF15 | BMF | 12 | c.[1930C>T];[1930C>T] | p.[(Arg644Ter)];[(Arg644Ter)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (18.7%) | No |
| EP18∗ | EF4 | BMF | 13 | c.[2156del];[3675-2A>T] | p.[(Gly719AspfsTer50)];[(?)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP19∗ | EF16 | BMF | 13 | c.[1930C>T];[1930C>T] | p.[(Arg644Ter)];[(Arg644Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP20∗ | EF17 | BMF | 14 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.646G>A, p.(Val216Met) (1.3%) | No |
| EP21∗ | EF18 | BMF | 17 | c.[2156del];[3300_3303del] | p.[(Gly719AspfsTer50)];[(Asn1100LysfsTer12)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP22∗ | EF19 | BMF | 18 | c.[1471C>T];[3796C>T] | p.[(Gln491Ter)];[(Arg1266Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP23∗ | EF20 | BMF | 20 | c.[1203_1206del];[1203_1206del] | p.[(Thr402CysfsTer2)];[(Thr402CysfsTer2)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP24 | EF21 | BMF | 20 | c.[1606_1751del];[1606_1751del] | p.[(Leu536GlyfsTer18)];[(Leu536GlyfsTer18)] | c.745A>T, p.(Arg249Trp) (15%); c.514G>T, p.(Val172Phe) (4%); c.737T>A, p.(Met246Lys) (2%) | No |
| EP25 | EF22 | BMF | 21 | c.[1606-141_1752-2788del];[1606-141_1752-2788del] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | c.569C>T, p.(Pro190Leu) (5%) | No |
| EP26 | EF23 | BMF | 24 | c.[1606-141_1752-2788del];[1606-141_1752-2788del] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | c.743G>A, p.(Arg248Gln) (35%) | No |
| EP27 | EF24 | BMF | 30 | c.[2474_2484delinsAAAG];[2474_2484delinsAAAG] | p.[(Thr825LysfsTer25)];[(Thr825LysfsTer25)] | Not detected | No |
| EP28 | EF25 | BMF | 32 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.713G>A, p.(Cys238Tyr), (19%) | N/A |
| EP29 | EF25 | BMF | 33 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.659A>G, p.(Tyr220Cys) (3%); later new clone c.716A>G p.(Asn239Ser) (5%) | No |
| EP30∗,† | EF26 | BMF | 34 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP31∗ | EF27 | BMF | 36 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (15%); c.818G>T, p.(Arg273Leu) (2.5%); c.814G>A, p.(Val272Met) (2%); later new clone c.41T>C, p.(Leu14Pro) (1.5%) | No |
| EP32∗ | EF17 | BMF | 57 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.743G>A, p.(Arg248Gln) (5%); c.830G>T, p.(Cys277Phe) (23%); c.843C>A, p.(Asp281Glu) (11%); later new clone c.528C>G, p.(Cys176Trp) (9%) | No |
| EP33∗ | EF28 | MDS | 12 | c.[2919_2923del];[2919_2923del] | p.[(Lys974HisfsTer3)];[(Lys974HisfsTer3)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP34 | EF29 | T-ALL | 12 | c.[1424del];[1930C>T] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Arg644Ter)] | c.730G>A, p.(Gly244Ser) (94%) | TET2 c.5860G>A (p.Ala1954Thr) (52.4%) |
| EP35∗ | EF19 | MDS | 21 | c.[1471C>T];[3796C>T] | p.[(Gln491Ter)];[(Arg1266Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP36∗ | EF30 | MDS | 22 | c.[814G>A];[814G>A] | p.[(Asp272Asn)];[(Asp272Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP37∗ | EF23 | MDS | 22 | c.[1606-141_1752-2788del];[1606-141_1752-2788del] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | Variant unknown (20%) | N/A |
| EP38∗ | EF31 | MDS-F | 25 | c.[4421_4422del];[1424del] | p.[(Arg1474ThrfsTer10)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (9%); c.818G>T, p.(Arg273Leu) (13%) | No |
| EP39 | EF32 | MDS | 29 | c.[1424del];[1847+1G>A] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(?)] | c.524G>A, p.Arg175His (27%); c.818G>A, p.(Arg273His) (5%) | No |
| EP40∗ | EF33 | MDS | 36 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.517G>A, p.(Val173Met)(72%) | No |
| EP41 | EF34 | MDS | 36 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.524G>A, p.(Arg175His) (6%) | NRAS c.38G>A p. (Gly13Asp) (2%); CBL c.1273_1281del p.(Gly425_Glu427del) (0.5%) |
| EP42∗,† | EF17 | MDS | 38 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP43∗ | EF33 | MDS/AML | 38 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.532C>G, p.(His178Asp) (35%) | No |
| EP44 | EF35 | MDS/AML | 40 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.817C>T, p.(Arg273Cys) (38%) | No |
| EP45 | EF32 | AML | 20 | c.[1424del];[1847+1G>A] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(?)] | IHC TP53+++ | NA |
| EP46∗ | EF17 | AML | 59 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.818G>T, p.(Arg273Leu) (VAF N/A) | N/A |
| EP47∗ | EF26 | AML | 65 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.577C>T, p.(His193Tyr); c.818G>A, p.(Arg273His) (VAF N/A) | N/A |
| EP48∗ | EF28 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 3 | c.[2919_2923del];[2919_2923del] | p.[(Lys974HisfsTer3)];[(Lys974HisfsTer3)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP49∗ | EF2 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 4 | c.[1973G>A];[1973G>A] | p.[(Ser658Asn)];[(Ser658Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP50∗ | EF1 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 11 | c.[3409_3410del];[3763C>T] | p.[(Met1137GlufsTer7)];[(Arg1255Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP51∗ | EF1 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 18 | c.[3409_3410del];[3763C>T] | p.[(Met1137GlufsTer7)];[(Arg1255Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP52 | EF35 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 41 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.490A>G, p.(Lys164Glu) (9%) | No |
| Patient ID . | Family ID . | Initial disease condition . | Age (y) . | ERCC6L2 genotype c.(NM_0202027.7) . | ERCC6L2 genotype p.(NP_064592.3) . | Somatic TP53 clones in BM or PB (NM_000546.6; VAF) . | Other somatic clones (VAF) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1∗ | EF1 | BMF | 2 | c.[3409_3410del]; [3763C>T] | p.[(Met1137GlufsTer7)];[(Arg1255Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP2∗ | EF2 | BMF | 5 | c.[1973G>A];[1973G>A] | p.[(Ser658Asn)];[(Ser658Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP3∗ | EF3 | BMF | 6 | c.[1930C>T];[1930C>T] | p.[(Arg644Ter)];[(Arg644Ter)] | Yes, variant N/A (4.8%) | No |
| EP4∗ | EF4 | BMF | 7 | c.[2156del];[3675-2A>T] | p.[(Gly719AspfsTer50)];[(?)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP5 | EF5 | BMF | 7 | c.[3492+2T>G];[3492+2T>G] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP6∗ | EF6 | BMF | 8 | c.[2734del];[2734del] | p.[(Glu912ArgfsTer8)]; [(Glu912ArgfsTer8)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP7∗ | EF7 | BMF | 8 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | Not detected initially, at age 15 y c.638G>T p.(Arg213Leu) (3%) | N/A |
| EP8∗ | EF8 | BMF | 8 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP9 | EF9 | BMF | 9 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | Not detected (latest screen at 10 y) | N/A |
| EP10∗ | EF7 | BMF | 9 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (1.5%) | N/A |
| EP11∗ | EF10 | BMF | 10 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.659A>G, p.(Tyr220Cys) (36%); c.725G>T, p.(Cys242Phe) (3%) | No |
| EP12 | EF11 | BMF | 11 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.723del, p.(Cys242AlafsTer5) (3%), c.376-2A>G (4.2%), c. 733G>A, p.(Gly245Ser) (41%) | TET2 c.4102T>C, p.(Phe1368Leu) (2%) |
| EP13 | EF12 | BMF | 11 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | Not detected (latest screen at 11 y) | No |
| EP14 | EF13 | BMF | 12 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.524G>A, p. (Arg175His)(7%) | N/A |
| EP15 | EF14 | BMF | 12 | c.[19C>T];[2156del] | p.[(Gln7Ter)];[(Gly719AspfsTer50)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP16∗ | EF2 | BMF | 12 | c.[1973G>A];[1973G>A] | p.[(Ser658Asn)];[(Ser658Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP17 | EF15 | BMF | 12 | c.[1930C>T];[1930C>T] | p.[(Arg644Ter)];[(Arg644Ter)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (18.7%) | No |
| EP18∗ | EF4 | BMF | 13 | c.[2156del];[3675-2A>T] | p.[(Gly719AspfsTer50)];[(?)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP19∗ | EF16 | BMF | 13 | c.[1930C>T];[1930C>T] | p.[(Arg644Ter)];[(Arg644Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP20∗ | EF17 | BMF | 14 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.646G>A, p.(Val216Met) (1.3%) | No |
| EP21∗ | EF18 | BMF | 17 | c.[2156del];[3300_3303del] | p.[(Gly719AspfsTer50)];[(Asn1100LysfsTer12)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP22∗ | EF19 | BMF | 18 | c.[1471C>T];[3796C>T] | p.[(Gln491Ter)];[(Arg1266Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP23∗ | EF20 | BMF | 20 | c.[1203_1206del];[1203_1206del] | p.[(Thr402CysfsTer2)];[(Thr402CysfsTer2)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP24 | EF21 | BMF | 20 | c.[1606_1751del];[1606_1751del] | p.[(Leu536GlyfsTer18)];[(Leu536GlyfsTer18)] | c.745A>T, p.(Arg249Trp) (15%); c.514G>T, p.(Val172Phe) (4%); c.737T>A, p.(Met246Lys) (2%) | No |
| EP25 | EF22 | BMF | 21 | c.[1606-141_1752-2788del];[1606-141_1752-2788del] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | c.569C>T, p.(Pro190Leu) (5%) | No |
| EP26 | EF23 | BMF | 24 | c.[1606-141_1752-2788del];[1606-141_1752-2788del] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | c.743G>A, p.(Arg248Gln) (35%) | No |
| EP27 | EF24 | BMF | 30 | c.[2474_2484delinsAAAG];[2474_2484delinsAAAG] | p.[(Thr825LysfsTer25)];[(Thr825LysfsTer25)] | Not detected | No |
| EP28 | EF25 | BMF | 32 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.713G>A, p.(Cys238Tyr), (19%) | N/A |
| EP29 | EF25 | BMF | 33 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.659A>G, p.(Tyr220Cys) (3%); later new clone c.716A>G p.(Asn239Ser) (5%) | No |
| EP30∗,† | EF26 | BMF | 34 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP31∗ | EF27 | BMF | 36 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (15%); c.818G>T, p.(Arg273Leu) (2.5%); c.814G>A, p.(Val272Met) (2%); later new clone c.41T>C, p.(Leu14Pro) (1.5%) | No |
| EP32∗ | EF17 | BMF | 57 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.743G>A, p.(Arg248Gln) (5%); c.830G>T, p.(Cys277Phe) (23%); c.843C>A, p.(Asp281Glu) (11%); later new clone c.528C>G, p.(Cys176Trp) (9%) | No |
| EP33∗ | EF28 | MDS | 12 | c.[2919_2923del];[2919_2923del] | p.[(Lys974HisfsTer3)];[(Lys974HisfsTer3)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP34 | EF29 | T-ALL | 12 | c.[1424del];[1930C>T] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Arg644Ter)] | c.730G>A, p.(Gly244Ser) (94%) | TET2 c.5860G>A (p.Ala1954Thr) (52.4%) |
| EP35∗ | EF19 | MDS | 21 | c.[1471C>T];[3796C>T] | p.[(Gln491Ter)];[(Arg1266Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP36∗ | EF30 | MDS | 22 | c.[814G>A];[814G>A] | p.[(Asp272Asn)];[(Asp272Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP37∗ | EF23 | MDS | 22 | c.[1606-141_1752-2788del];[1606-141_1752-2788del] | p.[(?)];[(?)] | Variant unknown (20%) | N/A |
| EP38∗ | EF31 | MDS-F | 25 | c.[4421_4422del];[1424del] | p.[(Arg1474ThrfsTer10)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.742C>T, p.(Arg248Trp) (9%); c.818G>T, p.(Arg273Leu) (13%) | No |
| EP39 | EF32 | MDS | 29 | c.[1424del];[1847+1G>A] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(?)] | c.524G>A, p.Arg175His (27%); c.818G>A, p.(Arg273His) (5%) | No |
| EP40∗ | EF33 | MDS | 36 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.517G>A, p.(Val173Met)(72%) | No |
| EP41 | EF34 | MDS | 36 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.524G>A, p.(Arg175His) (6%) | NRAS c.38G>A p. (Gly13Asp) (2%); CBL c.1273_1281del p.(Gly425_Glu427del) (0.5%) |
| EP42∗,† | EF17 | MDS | 38 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP43∗ | EF33 | MDS/AML | 38 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.532C>G, p.(His178Asp) (35%) | No |
| EP44 | EF35 | MDS/AML | 40 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.817C>T, p.(Arg273Cys) (38%) | No |
| EP45 | EF32 | AML | 20 | c.[1424del];[1847+1G>A] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(?)] | IHC TP53+++ | NA |
| EP46∗ | EF17 | AML | 59 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.818G>T, p.(Arg273Leu) (VAF N/A) | N/A |
| EP47∗ | EF26 | AML | 65 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.577C>T, p.(His193Tyr); c.818G>A, p.(Arg273His) (VAF N/A) | N/A |
| EP48∗ | EF28 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 3 | c.[2919_2923del];[2919_2923del] | p.[(Lys974HisfsTer3)];[(Lys974HisfsTer3)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP49∗ | EF2 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 4 | c.[1973G>A];[1973G>A] | p.[(Ser658Asn)];[(Ser658Asn)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP50∗ | EF1 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 11 | c.[3409_3410del];[3763C>T] | p.[(Met1137GlufsTer7)];[(Arg1255Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP51∗ | EF1 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 18 | c.[3409_3410del];[3763C>T] | p.[(Met1137GlufsTer7)];[(Arg1255Ter)] | N/A | N/A |
| EP52 | EF35 | Sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants | 41 | c.[1424del];[1424del] | p.[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)];[(Ile475ThrfsTer36)] | c.490A>G, p.(Lys164Glu) (9%) | No |
Note the updated transcript (NM_0202027.7). Most previous studies reported variants in a previous transcript version; hence, the discrepancy in some cases.
MDS-F, MDS with fibrosis; N/A, not applicable; PB, peripheral blood.
Previously reported.
Not tested.
Clinical features in ERCC6L2 subjects with and without HM
| Variable . | ERCC6L2 subjects without malignancy, n = 33 . | ERCC6L2 subjects with malignancy, n = 15 . | P . | Data available, n . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | ||||
| Median, y (range) | 12 (2-57) | 29 (12-65) | .0007 | 33; 15 |
| CBC | ||||
| Median leukocytes, 1 × 10⁹/L (range) | 3.25 (1.3-7.7) | 2.85 (1.2-5.8) | .2891 | 28; 12 |
| Median ANC, 1×10⁹/L (range) | 1.16 (0.25-3.9) | 0.65 (0.1-4.7) | .6350 | 26; 12 |
| Median hemoglobin, g/dL (range) | 10.80 (3.4-15) | 10.10 (5.9-14) | .1918 | 29; 13 |
| Median MCV, fL (range) | 101.5 (90-114) | 98.0 (87-105) | .3720 | 8; 5 |
| Median platelets, 1 × 10⁹/L (range) | 63.50 (4-195) | 80.0 (10-175) | .9623 | 30; 13 |
| Median reticulocytes, 1 × 10⁹/L (range) | 58.0 (33.0-104.1) | 29.1 (11.9-98.0) | .0530 | 15; 6 |
| TP53 status | ||||
| N of patients with TP53 clone (%) | 15∗ (84.2) | 11 (100) | .1845 | 19; 11 |
| N of mutations, range | 0–4 | 1–2 | 18; 11 | |
| Median VAF % (range) | 12.0 (1.3-36.0) | 38.0 (6.0-94.0) | .0020 | 16; 9 |
| BM | ||||
| Hypocellular, n (%) | 25 (96) | 4 (36) | <.0001 | 26; 11 |
| Normal, n (%) | 1 (4) | 2 (18) | ||
| Hypercellular, n (%) | N/A | 5 (45) |
| Variable . | ERCC6L2 subjects without malignancy, n = 33 . | ERCC6L2 subjects with malignancy, n = 15 . | P . | Data available, n . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | ||||
| Median, y (range) | 12 (2-57) | 29 (12-65) | .0007 | 33; 15 |
| CBC | ||||
| Median leukocytes, 1 × 10⁹/L (range) | 3.25 (1.3-7.7) | 2.85 (1.2-5.8) | .2891 | 28; 12 |
| Median ANC, 1×10⁹/L (range) | 1.16 (0.25-3.9) | 0.65 (0.1-4.7) | .6350 | 26; 12 |
| Median hemoglobin, g/dL (range) | 10.80 (3.4-15) | 10.10 (5.9-14) | .1918 | 29; 13 |
| Median MCV, fL (range) | 101.5 (90-114) | 98.0 (87-105) | .3720 | 8; 5 |
| Median platelets, 1 × 10⁹/L (range) | 63.50 (4-195) | 80.0 (10-175) | .9623 | 30; 13 |
| Median reticulocytes, 1 × 10⁹/L (range) | 58.0 (33.0-104.1) | 29.1 (11.9-98.0) | .0530 | 15; 6 |
| TP53 status | ||||
| N of patients with TP53 clone (%) | 15∗ (84.2) | 11 (100) | .1845 | 19; 11 |
| N of mutations, range | 0–4 | 1–2 | 18; 11 | |
| Median VAF % (range) | 12.0 (1.3-36.0) | 38.0 (6.0-94.0) | .0020 | 16; 9 |
| BM | ||||
| Hypocellular, n (%) | 25 (96) | 4 (36) | <.0001 | 26; 11 |
| Normal, n (%) | 1 (4) | 2 (18) | ||
| Hypercellular, n (%) | N/A | 5 (45) |
ANC, absolute neutrophile count; MCV, mean corpuscular volume.
A clone was identified in 1 additional patient during follow-up.
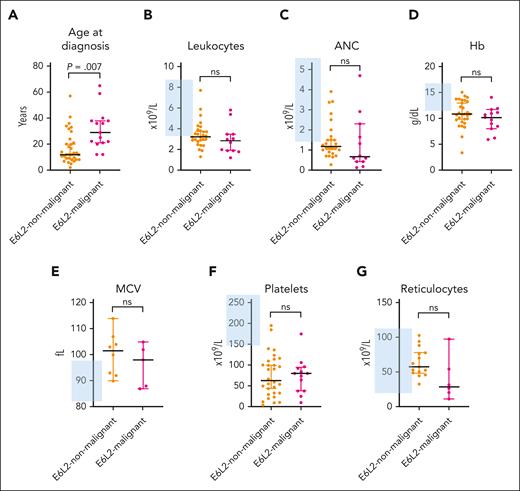
The major complete blood count (CBC) values at baseline investigation are shown in Table 3 and Figure 2. Almost all study subjects initially presented with various degrees of thrombocytopenia (93%). In addition, we observed anemia, macrocytosis, leukopenia, and neutropenia in 64%, 53%, 72%, and 68% of the subjects, respectively. Reticulocyte levels were within the normal range in 83% of subjects. Patients in the malignant and nonmalignant stages of ERCC6L2 disease had similar CBC values upon referral to a hematologist (Table 3; Figure 2).
Comparison of subjects with ERCC6L2 disease with and without an HM. (A) Median age at diagnosis with 95% CI, using Mann-Whitney U test; P = .0007. (B-G) CBC parameter median values of subjects with available CBC data with 95% CI, using unpaired t test. The blue-shaded area denotes the Finnish reference values for the CBC parameters. E6L2, ERCC6L2; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; Hb, hemoglobin; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; ns, nonsignificant.
Comparison of subjects with ERCC6L2 disease with and without an HM. (A) Median age at diagnosis with 95% CI, using Mann-Whitney U test; P = .0007. (B-G) CBC parameter median values of subjects with available CBC data with 95% CI, using unpaired t test. The blue-shaded area denotes the Finnish reference values for the CBC parameters. E6L2, ERCC6L2; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; Hb, hemoglobin; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; ns, nonsignificant.
We studied the original hematopathological reports of 19 Finnish patients from the first BM sample (trephine biopsy, n = 18 and aspirate, n = 19; supplemental Table 2). Six of 13 patients with BMF (46%) and 4 of 6 patients with HM (67%) had erythroid predominance in their BMs. Dysplastic features were present in at least 1 cell lineage in 9 patients with BMF (69%) and all patients with HM. Dysplasia was restricted to erythropoiesis and megakaryocytes. Two patients initially experienced increased reticulin fibrosis, and 1 patient developed severe fibrosis (grade 3/3) during follow-up.
We detected a complex karyotype, defined as at least 3 independent chromosomal abnormalities, in 56% of the patients with HM (n = 9/16, including 14 initial diagnoses and 2 whose disease progressed during follow-up). TP53 mutation analysis was performed using the BM/blood of 29 patients, 90% of whom had at least 1 mutated clone (n = 26/29, excluding copy number analyses in most of the patients). The number of observed mutations varied from 0 to 4, with a median of 1. The median TP53 variant allele frequency (VAF) was 19.0% (range, 1.3%-94.0%). Patients without HM had significantly smaller TP53 clones than those with malignant conditions; the median VAFs of TP53 clones were 12.0% and 38.0%, respectively (P = .002). Definite information on whether the TP53 mutations were mono- or biallelic was unavailable. Two patients had a TP53 mutation VAF ≥50%, and 1 patient had a chromosome 17 deletion, presumptive for biallelic TP53 alteration.23 Data on the few somatic mutations other than TP53 were available for 22 of 52 patients (Table 2; supplemental Table 1).
Genealogical study
Figure 1 illustrates the ERCC6L2 variants present in the study subjects. The various types of mutations are dispersed across the gene. We identified a founder mutation (NM_020207.7) c.1424delT (p.Ile475ThrfsTer36) in the Finnish patients (homozygotes, n = 22 and compound heterozygotes, n = 1). To further investigate this phenomenon, we performed a genealogical study of Finnish families. We traced ancestors from the Finnish Population Registries and microfilm copies accessible through the National Archives of Finland. The majority of the grandparents originated from an isolated region in Northeastern Finland (Figure 3A). Four of the 9 most geographically clustered families showed a distant interfamilial relationship in a small rural village, confirming the founder effect of the c.1424delT variant of ERCC6L2 in the Finnish population (Figure 3B).
Genealogical study of the Finnish families. (A) AF distribution of the ERCC6L2 1424delT variant in Finland and the birthplaces of the grandparents of 9 Finnish families. The blue dots represent the birthplaces of the grandparents. AFs according to the gnomAD and FinnGen databases.16,24 (B) A pedigree of the 4 Finnish families with ERCC6L2 indices shows that the parents share a common ancestor in the seventeenth century. The diamond symbol indicates the index patient.
Genealogical study of the Finnish families. (A) AF distribution of the ERCC6L2 1424delT variant in Finland and the birthplaces of the grandparents of 9 Finnish families. The blue dots represent the birthplaces of the grandparents. AFs according to the gnomAD and FinnGen databases.16,24 (B) A pedigree of the 4 Finnish families with ERCC6L2 indices shows that the parents share a common ancestor in the seventeenth century. The diamond symbol indicates the index patient.
Extrahematological features
Extrahematological features were described for some patients with ERCC6L2-related disease: 4 had neurologic or neuropsychiatric conditions; 2 of the 4 were from consanguineous families; 3 had microcephaly; 1 had recurrent bacterial and/or viral infections; and 2 patients had been diagnosed with autoimmune diseases. Two adult patients had a history of solid tumor malignancy (melanoma and breast cancer at the age of 21 and 35 years, respectively). The patient with breast cancer suffered from severe radiation injury after a 50 Gy postoperative radiation (supplemental Table 1).
Treatments and survival
Treatment data were available for 41 subjects. Thirteen individuals underwent surveillance, with or without occasional transfusions as the only treatment strategy. Two patients with BMF had androgen (oxymetholone and danazol) as the initial treatment. Treatment outcomes were not reported, but 1 of them subsequently underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). In addition, 1 patient with BMF received immunosuppressive treatment with antithymocyte globulin, steroids, and cyclosporine for 8 days before the diagnosis of ERCC6L2 disease and then underwent HSCT. A patient with MDS with fibrosis, initially treated with decitabine, had stable disease as treatment response before undergoing HSCT. One patient with MDS/AML with mutated TP53 received investigational therapy in a clinical trial (anti-TIM3 antibody combined with a hypomethylating agent), reaching a complete morphological remission with incomplete hematological recovery before undergoing HSCT. All the patients with AML M6 (n = 6) underwent induction chemotherapy (supplemental Table 1). Three of the patients with AML M6 reached remission but relapsed after receiving an HSCT (at 4, 7, and 13 months, respectively), and 3 were resistant to chemotherapy and did not undergo transplantation (supplemental Table 1). One patient was initially diagnosed with T-ALL and achieved remission after induction chemotherapy. Although continuing T-ALL therapy, the patient developed MDS/AML with a mutated TP53 and underwent HSCT. As an initial treatment, 15 patients underwent HSCT (BMF, n = 9 and MDS, n = 6).
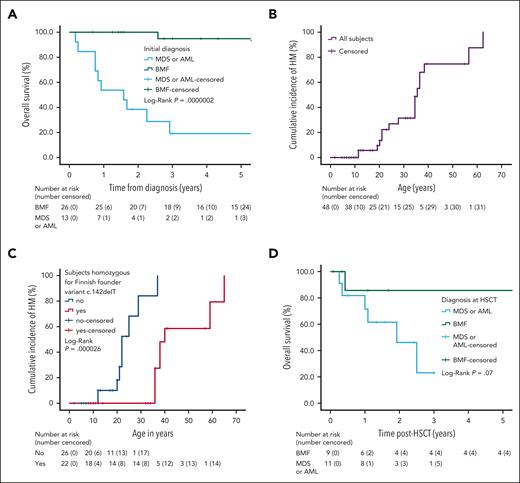
Follow-up data were available for 40 individuals (77%) whose initial conditions were BMF, n = 26; MDS or AML, n = 12; and T-ALL, n = 1; as well as having 1 sibling with biallelic ERCC6L2 mutation but without a diagnosis of BMF or HM. The median follow-up time was 3.0 years (range, 0.2-28 years). During the follow-up time, 3 patients with BMF developed an HM: 1 at 4 months and 1 at 25 years after diagnosis. In 1 case, the progression time was not reported. In addition, 3 patients with an initial diagnosis of MDS progressed to AML at 2, 6, and 8 months. Patients with an initial diagnosis of BMF had a mean survival of 26.7 years (95% CI, 23.3-30.1; median not definable as only 2 patients succumbed during the follow-up) and 3- and 5-year OS of 95% (95% CI, 85%-100%). For patients with MDS and AML and 1 with an initial diagnosis of T-ALL who progressed to MDS/AML with mutated TP53, the 3-year OS was 19% (95% CI, 0-39), and the median survival was 1.6 years (95% CI, 0.6-2.6; Figure 4A). The initial diagnosis of HM (all with TP53 status tested had mutated TP53) was associated with a remarkable increase in the risk of mortality compared with the initial diagnosis of BMF (HR 34.5; 95% CI, 4.3-273.8; P < .001).
OS and cumulative incidence of HM among subjects with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants. (A) Kaplan-Meier curves displaying the OS of patients with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants and initial diagnosis of BMF, MDS, or AML, including 1 patient with T-ALL progressing to MDS/AML in this patient group. (B) Onset of HM based on age (n = 48). (C) Onset of HM, based on age, in subjects with and without the homozygous mutation of ERCC6L2 1424delT (Finnish founder mutation). (D) OS of patients with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants and allogeneic HSCT per the diagnosis while receiving a transplant.
OS and cumulative incidence of HM among subjects with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants. (A) Kaplan-Meier curves displaying the OS of patients with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants and initial diagnosis of BMF, MDS, or AML, including 1 patient with T-ALL progressing to MDS/AML in this patient group. (B) Onset of HM based on age (n = 48). (C) Onset of HM, based on age, in subjects with and without the homozygous mutation of ERCC6L2 1424delT (Finnish founder mutation). (D) OS of patients with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants and allogeneic HSCT per the diagnosis while receiving a transplant.
The median age at the onset of HM in all patients was 37.0 years (95% CI, 31.5-42.5; range, 12-65 years; Figure 4B). Interestingly, patients with a homozygous ERCC6L2 c.1424delT, Finnish founder mutation, were significantly older than other patients with respect to the median age at the onset of HM: 40.0 years (95% CI, 36.1-43.9) and 22.0 years (95% CI, 18.8-25.2), respectively (P = .000026; Figure 4C). However, the OS was similar in both groups (P = .267; supplemental Figure 1).
Twenty-three subjects (44%) underwent HSCT (follow-up data available for 20/23). Two pediatric patients with BMF did not have TP53 clones (aged 11 and 10 years at the time of testing), but all the others tested had TP53 mutations. The median follow-up time after HSCT was 1.5 years (range, 0.1-12.5 years). Figure 4D shows the post-HSCT survival data: the mean survival time of patients with BMF was 10.8 years (95% CI 7.6-13.9; n = 9, with 1 death during the monitoring), and the median survival time was 1.9 years for those with HM at HSCT (95% CI, 0.6-3.2; n = 11, with 6 deaths during the follow-up). Patients with BMF had a 1 or 3 years of OS of 88% (95% CI, 64-100) compared with patients with HM at HSCT with 1 year OS of 46% (95% CI, 13-79) and 2 or –3 years of OS of 28% (95% CI, 0-61; P = .07). We observed 7 deaths after HSCT: 4 due to disease relapse (3 AML and 1 MDS with fibrosis at the time of HCST) and 3 due to transplant-related mortality (2 MDS and 1 BMF).
Discussion
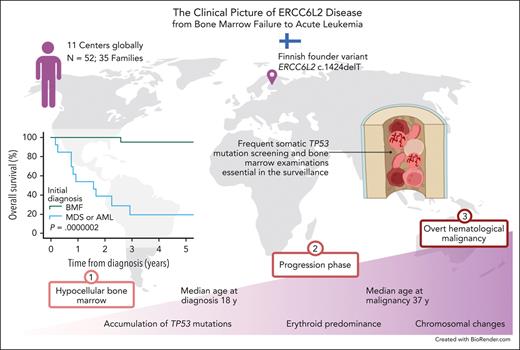
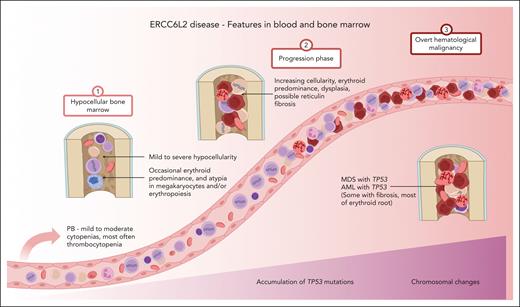
Recessively inherited ERCC6L2 disease is a novel discovery among life-threatening inherited BMFs. Since the first 2 patients were described in 2014,1 a substantial amount of information has accumulated, enabling us to draw a clinical picture of the ERCC6L2 disease (Figure 5). In addition to the analysis of clinical data and foundational characteristics, we present follow-up data of 1165 person-years.
ERCC6L2 disease. Characteristic features of ERCC6L2 disease are illustrated on a 3-phase continuum. In phase 1, individuals present with hypocellular BM with or without small TP53 mutated clonal hematopoiesis. Phase 2 depicts disease acceleration, including BMF, with increasing (possible biallelic) TP53 mutations progressing toward myeloid malignancy. Phase 3 represents overt HM with complex karyotype. PB, peripheral blood; M6, French-American-British subtype of acute erythroid leukemia. Figure created with BioRender.com.
ERCC6L2 disease. Characteristic features of ERCC6L2 disease are illustrated on a 3-phase continuum. In phase 1, individuals present with hypocellular BM with or without small TP53 mutated clonal hematopoiesis. Phase 2 depicts disease acceleration, including BMF, with increasing (possible biallelic) TP53 mutations progressing toward myeloid malignancy. Phase 3 represents overt HM with complex karyotype. PB, peripheral blood; M6, French-American-British subtype of acute erythroid leukemia. Figure created with BioRender.com.
Classically inherited BMFs, such as Fanconi anemia and Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS), are usually recognized in childhood. They characteristically present with extrahematopoietic features, including visible skeletal abnormalities, suggestive of a congenital syndrome.25 In comparison, our data propose that ERCC6L2 disease manifestations are more disguised, leading to the identification of the underlying hematological condition later in life, usually in adolescence.
Suspicion of an underlying blood disease usually rises based on changes in the patient’s CBC. The vast majority (90%) of ERCC6L2 subjects presented with thrombocytopenia independent of the initial diagnosis. Notably, in ERCC6L2 disease, we detected, on average, only modest alterations in CBC, which might have been easily overlooked in most subjects. Furthermore, we did not observe reticulocytopenia in patients with BMF. Despite the ambiguity of the CBC, our data showed that BM examination most often uncovered an underlying BM pathology in patients with biallelic ERCC6L2 variants, especially evident in trephine biopsy. The inconclusiveness of the CBC, in regard to the state of the BM, is a phenomenon also described in SDS.26
A limitation of this study was the lack of a central pathology review. Based on the subanalysis of hematopathological reports of 19 Finnish patients at initial investigations, we observed erythroid predominance in a considerable number of patients. This effect was more prominent among patients with HM. It is tempting to propose that the erythroid proliferation is a pathognomonic feature of ERCC6L2 disease, indicating a susceptibility for HM of the erythroid root (Figure 5).8 Furthermore, we noted a shift from hypocellular BM toward hypercellularity in patients with or progressing to an HM. Another potential ERCC6L2-specific feature was the tendency to develop secondary reticulin fibrosis in the BM, which was detected in 6 cases (supplemental Table 1). The importance of the BM niche was advocated in a recent study using both patient samples and ERCC6L2-silenced cells, which suggested that biallelic ERCC6L2 mutations also affect the mesenchymal stromal cells, which are paramount for fibrogenesis.14
A prototype for somatic rescue was described in SAMD9/9L-mutated MDS with a nonrandom loss of chromosome 7, which was identified in 61% of the patients in a recent study.27 Our data demonstrate that identifying somatically TP53-mutated clones at the initial presentation is essential. The mutagenesis occurred in patients with ERCC6L2 already at the stage of BMF. Similar to SDS, we hypothesize that TP53 mutations in ERCC6L2 disease act in somatic restoration,28 a phenomenon in which acquired somatic genetic alterations can improve failing hematopoietic cell fitness.29 We observed no other recurrent somatic mutations, but further genetic studies are needed to validate our observations. Supporting the hypothesis of somatic genetic compensation, at least 3 patients experienced severe pancytopenia in their childhood/teens, but later regained a normal CBC (supplemental Table 1).In contrast, TP53 mutagenesis most likely contributes to the strikingly younger median age of onset of HM at 37 years in patients with ERCC6L2 in comparison with the median age of onset from 60 to 70 years in patients with MDS or AML with mutated TP53 but without inherited predisposition.9
We found no specific genotype-phenotype association in the ERCC6L2 disease. Notably, subjects with the homozygous c.1424delT mutation, the Finnish founder mutation, were significantly older at the onset of HM than those with other biallelic ERCC6L2 variants. Although the age of onset of HM is different, the disease courses, including TP53 mutations and aggressive HM with complex karyotypes, were similar across ERCC6L2 genotypes. However, selection bias may skew the results because ERCC6L2 disease is a novel entity among inherited BMF syndromes, and individuals with modest disease patterns are yet to be discovered. With the increasing recognition of ERCC6L2 disease, we aspire to clarify the genotype-phenotype correlation in more detail and at all disease stages.
From our data, we were unable to conclude the syndromic features of ERCC6L2 disease. The initial reports described neurological involvement in subjects with biallelic ERCC6L2 mutations in consanguineous families.1,2 Thereafter, our studies among Finnish patients did not detect neurological symptoms.8,10 Similarly, majority of the subjects in this study (92%) presented with no neurologic or neuropsychiatric symptoms. We suspect that neurological defects may be a result of reduced heterozygosity in consanguineous families, and we recommend awareness of these features. Regarding further extrahematopoietic involvement, we identified only two ERCC6L2 patients with solid malignancies. Therefore, it is likely that cancer predisposition to ERCC6L2 disease is limited to having HMs. However, considering the relatively young median age at disease onset and limited follow-up time, further surveillance and revisiting of the solid tumor predisposition are warranted.
We also want to highlight the young female patient with breast cancer who suffered from extreme radiation toxicities. ERCC6L2 involvement in DNA repair is well-established in the literature,1-7 and radiosensitivity in the loss of ERCC6L2 has also been reported in the human haploid cell line HAP1.6 In addition, Zhang et al2 observed that fibroblasts from a patient with a biallelic ERCC6L2 germ line variant showed increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Although there was 1 case in our series, the defective ERCC6L2 may translate to a condition that leads to excessive chemotherapy- or radiation-related toxicities, so further monitoring of adverse events is needed. Susceptibility to infections or autoimmune conditions was not overrepresented in our study and was noted in only 3 subjects. Nonetheless, Liu et al5 showed that ERCC6L2 is required for immunoglobulin class switching in murine B-cell lines, suggesting that immunological impacts should be further investigated in ERCC6L2 disease.
The median OS from birth was 49.6 years (95% CI, 36.7-62.5; supplemental Figure 2) for all ERCC6L2 subjects, placing ERCC6L2 disease in the middle among other inherited BMFs. The reported median OS times from birth are 67 years in Diamond-Blackfan anemia, 51 in dyskeratosis congenita, 41 in SDS, and 39 in Fanconi anemia.30 The OS of ERCC6L2 individuals was significantly dependent on the disease stage at referral. The poor survival rate of patients with TP53-mutated myeloid malignancy is known, and it is also reflected in our data. A similar OS has been reported among patients with SDS and MDS or AML.31 Contributing to the same notion regarding disease rigor, most of the observed deaths were due to HM.
Myeloid malignancies with TP53 mutations remain almost incurable.9 Similarly to SDS,32 this poses a major challenge in ERCC6L2 disease, and performing allogeneic HSCT before HM ameliorates the prognosis. The survival data for patients who underwent HSCT are limited and need to mature because the surveillance time period is still relatively short (median, 1.5 years), and the number of study subjects who underwent transplants is small thus far. The timing of HSCT is essential and should be weighed together with excessive susceptibility to toxicities associated with DNA repair defects in general and transplant-related complexities as well as with individual psychosocial circumstances. Furthermore, clinically asymptomatic siblings considered as potential stem cell donors should be thoroughly examined.
While walking a tightrope with the timing of HSCT, patients with ERCC6L2 disease require surveillance with repetitive blood and BM analyses, including screening for TP53 mutations. Uniformly with SDS, CBC abnormalities may be minor, or even absent, despite disease progression.31 Thus, regular BM examination is needed to gauge the potential progression of the disease by detecting prominent changes in the cellularity, increases in erythroid predominance or dysplasia, and somatic mutations in TP53. Reticulin content is only shown via a trephine biopsy, which is also more accurate in the assessment of BM cellularity. Despite the potential discomfort to patients, we suggest annual BM analysis (preferably with trephine biopsy), at least for those with TP53 mutation(s). Regular BM monitoring was supported by Myers et al31 who showed better OS for patients with SDS with BM surveillance before the development of malignancy compared with that for those without.
In this study, ERCC6L2 disease was markedly overrepresented among individuals of Finnish ethnicity (44%), which is consistent with the definition of FDH disease. The AF of c.1424delT in the Finnish population was 0.6%. In comparison, the European non-Finnish AF was 0.0029%, indicating an allele enrichment in Finland (gnomAD version 3.1.2).16 Typical for FDH diseases, the AF is still higher in the northeastern part of Finland, reaching up to 1.36% (FinnGen DF5).24 In addition, we identified 15 distinct Finnish core families in our study, fulfilling the criteria for FDH diseases. Here, we conclude that ERCC6L2 c.1424delT is a Finnish founder variant and that ERCC6L2 disease is the first cancer syndrome, to our knowledge, that can be added to FDH.
In summary, our study draws a continuum of ERCC6L2 disease from inconspicuous BMF to dire HM (Figure 5). These findings indicate the importance of early recognition and active surveillance in patients with biallelic germ line ERCC6L2 variants. Until the development of novel versatile therapies, HSCT is the only potentially curative treatment for ERCC6L2 disease; however, this requires a timely approach.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lotta Katainen and Minna Eriksson for the skillful technical help, and Olavi Koivisto for valuable consulting in biostatistics. The authors thank Kimmo Porkka and Esa Pitkänen for supporting our research. The authors acknowledge the participants and investigators of the FinnGen study.
This study was supported by grants from the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation; Cancer Foundation Finland; Finnish Special Governmental Subsidy for Health Sciences, Research, and Training; Helsinki University Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Research Funding; Blood Disease Research Foundation; Finnish Medical Foundation; and the Finnish Association of Hematology.
Authorship
Contribution: M.H. collected and analyzed the clinical data, drafted the manuscript, and performed the statistical analyses; I.K. created the figures, performed the statistical analyses, and contributed to the final content of the manuscript; S.P.M.D. shared the collected data of Finnish patients and revised the manuscript; O.K. and U.W.-K. designed the study, coordinated data collection from multinational collaborators, and finalized the manuscript; T. Vulliamy, I.D., J.S., L.L., R.P.d.L., T.L., F.S.d.F., T.S., O.L., E.H.-L., G.B., B.T., A.S., F.B., S.J., A.A.K., T.F.Z., H.T., C.M., I.C., K.J., U.S., and R.N. contributed to the recruitment of patients in the study and to their management; T. Varilo performed genealogical studies; and all authors revised and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: T.S. has provided consulting for Celgene, AbbVie, Janssen-Cilag, and Bristol Myers Squibb and has had a congress fee provided by Novartis, Takeda, not related to this study. U.W.-K. has received honoraria from Sanofi, Novartis, and Pfizer and has provided consulting for Gilead, Pfizer, and Jazz, not related to this study. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Ulla Wartiovaara-Kautto, Department of Hematology, Comprehensive Cancer Center, Helsinki University Hospital, PO Box 372, 00029 HUS, Helsinki, Finland; e-mail: ulla.wartiovaara-kautto@hus.fi; and Outi Kilpivaara, Applied Tumor Genomics Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Biomedicum Helsinki 1, Room C501B2, PO Box 63, 00014 University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland; e-mail: outi.kilpivaara@helsinki.fi.
References
Author notes
∗O.K. and U.W.-K. contributed equally to this study.
The data supporting the findings of this study is available upon request from the corresponding authors, Outi Kilpivaara (outi.kilpivaara@helsinki.fi) and Ulla Wartiovaara-Kautto (ulla.wartiovaara-kautto@hus.fi).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal