Key Points
Novel approach identifies pathogenicity of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 mutations and accurately distinguishes familial and acquired HLH.
Abstract
Familial forms of the severe immunoregulatory disease hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) arise from biallelic mutations in the PRF1, UNC13D, STXBP2, and STX11 genes. Early and accurate diagnosis of the disease is important to determine the most appropriate treatment option, including potentially curative stem cell transplantation. The diagnosis of familial HLH (FHL) is traditionally based on finding biallelic mutations in patients with HLH symptoms and reduced natural killer (NK)–cell cytotoxicity. However, patients often have a low NK-cell count or receive immunosuppressive therapies that may render the NK-cell cytotoxicity assay unreliable. Furthermore, to fully understand the nature of a disease it is critical to directly assess the effect of mutations on cellular function; this will help to avoid instances in which carriers of innocuous mutations may be recommended for invasive procedures including transplantation. To overcome this diagnostic problem, we have developed a rapid and robust method that takes advantage of the functional equivalence of the human and mouse orthologues of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 proteins. By knocking out endogenous mouse genes in CD8+ T cells and simultaneously replacing them with their mutated human orthologues, we can accurately assess the effect of mutations on cell function. The wide dynamic range of this novel system allowed us to understand the basis of, otherwise cryptic, cases of FHL or HLH and, in some instances, to demonstrate that previously reported mutations are unlikely to cause FHL. This novel approach provides valuable new information to enable more accurate diagnosis and treatment of patients with HLH or FHL who inherit mutations of undetermined pathogenicity.
Introduction
Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) is an inherited autosomal recessive form of a life-threatening hyperinflammatory condition, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), and makes up ∼25% of all HLH cases.1,2 FHL is a syndrome of severe immune homeostasis dysregulation. In some instances, it is thought to be caused by the inability of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and natural killer (NK) cells to clear virus infected cells, as infection with ubiquitous viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus is frequently associated with FHL; but in many instances the trigger remains unknown.
Since 1999, 4 genes have been linked to FHL: PRF1 encodes perforin (PRF1),3UNC13D encodes MUNC13-4,4STX11 encodes syntaxin-11,5 and STXBP2, encodes syntaxin-binding protein 2 (STXBP2 or MUNC18-2).6,7 Although perforin is an essential pore-forming effector protein stored in the secretory vesicles of CTL and NK cells, the other 3 proteins play a crucial role in the exocytosis of those vesicles. Ultimately, FHL is caused by failure of CTLs or NK cells to release functional perforin either because of mutations in perforin itself or in proteins that regulate its secretion into the immune synapse. In both cases, the outcome is the same ie, no perforin-mediated apoptosis of the target cells. The failure to initiate apoptosis results in uncontrolled activation and expansion of CD8+ T cells and macrophages. The over-activated and expanding macrophage population release increased amounts of inflammatory cytokines (eg, interleukin-6 [IL-6]) and phagocytose cells (including erythrocytes) in the bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes. The resulting immune dysregulation leads to a severe cytokine storm, with fever, pancytopenia, multiorgan failure, and central nervous system damage.8,9
FHL was traditionally seen as a condition affecting infants and young children, whereas acquired or secondary HLH could occur in people in all age groups. However, over the last 15 years this view has changed because it became apparent that many patients with FHL present much later in life, often with atypical or cryptic FHL,10,11 and might remain undiagnosed for years and/or be only treated symptomatically. Early diagnosis and curative therapy are crucial for preventing irreversible organ damage including central nervous system disease, one of the most serious and frequent sequelae of HLH, and ultimately, for the patient’s survival.12
Typically, the therapeutic approach to patients with secondary HLH is targeted at the underlying cause and symptoms, whereas FHL is diagnosed and treated according to the HLH-2004 protocol or with emerging nonchemotherapeutic therapies.10 Once patients with FHL have achieved control of their HLH symptoms and are in remission for 3 to 6 weeks, this is generally followed by hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) with curative intent. In some instances, HSCT is considered without a FHL diagnosis, particularly if there is severe refractory disease, or in which there is a suggestive mutation in a known disease-causing gene. However, HSCT has significant risks of mortality and morbidity, particularly for older patients. A recent prospective analysis of pediatric patients undergoing HLH-2004 and HSCT found a 5-year overall survival rate of 71% for children with proven FHL but significantly lower survival (52%) in children without genetically defined HLH who were older at presentation and had higher rates of HLH relapse.13 This highlights the importance of accurate genetic diagnosis in patients presenting with HLH, which may be secondary or be caused by other primary immunodeficiencies, for example X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), and may benefit from alternate conditioning regimens.14
In accordance with the HLH-2004 guidelines, abnormality in the laboratory-based NK-cell cytotoxicity assay is a criterion for FHL diagnosis, but a number of factors can lead to false-negative results, including: (i) a delay in testing NK-cell function beyond 36-hours of blood sampling, (ii) severe disease-associated pancytopenia and/or chemotherapy which often reduces NK cells to <1% of leukocytes in peripheral blood, making interpretation of NK-specific assays unreliable, and (iii) immunosuppressive therapy (eg, cyclosporine) which can significantly inhibit NK-cell cytotoxicity. In FHL, NK-cell cytotoxicity remains impaired during convalescence whereas it typically recovers in secondary HLH.15,16 However, not all patients achieve remission and thus retesting is often not feasible. FHL-associated genes are sequenced in the search for potential disease-causing mutations because this will influence the clinical decision to offer curative transplant. Although the pathogenicity of frame-shift and nonsense mutations is rarely, if ever, in doubt, the functional effect of missense mutations, which are found in >50% of patients with FHL17 is generally assessed using predictive structural algorithms, but not experimentally (PRF1 mutations are the only notable exception18). Currently available laboratory-based diagnostic tools either focus on assessing perforin or MUNC13-4 protein expression by flow cytometry,19-22 or studies that aim to estimate the likelihood of defective degranulation.23 Although both approaches provide clinicians with important information that facilitates diagnosis, to date no methodology has allowed for the analysis of the precise effect of missense mutations on protein function in all 4 FHL-associated genes, which leaves an important gap in our understanding of the disease. The ability to accurately predict the impact of an FHL mutation on protein function, ideally with a rapid turnaround time, would allow more definitive diagnosis of FHL and improve clinical care.
To address this need, we developed a novel experimental approach for testing the function of mutations in all 4 FHL-associated genes, which allowed us to resolve atypical cases of the disease. Our findings highlight the crucial importance of understanding the impact of a mutation on protein function, and of providing a straightforward experimental approach for distinguishing patients with FHL from those with HLH.
Methods
Human blood cells isolation
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated, cultured, and their function was assessed as previously described.24
CRISPR/Cas9 mediated gene knockout (KO)
Purified naïve murine CD8+ T cells were electroporated with Cas9 ribonucleoprotein to KO a gene of interest,25 then retrovirally transduced with recombinant PRF1, UNC13D, STXBP2, or STX11 complementary DNA cloned into MSCV-IRES-eGFP expression vector24 and activated either by SIINFEKL peptide (OT-I cells) or anti-CD3/CD28 presented by feeder BL/6 splenocytes. The transduced cells were sorted 72 hours later by flow cytometry based on the identical mean fluorescent intensity of green fluorescent protein reporter in all experimental groups. Levels of endogenous and recombinant proteins were assessed using western immunoblotting.24 Complementary DNA constructs and cloning strategy are described in the data supplement (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood website).
Functional assays
Ethics
This work was approved by the Peter MacCallum Animal Ethics (E655) and Human Ethics (0/14) committees. All participants gave written informed consent, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Detailed methodology is provided in the supplemental Information. The authors are willing to assist researchers and clinicians in setting up this experimental protocol.
Results
Case reports
Case #1 (P6)
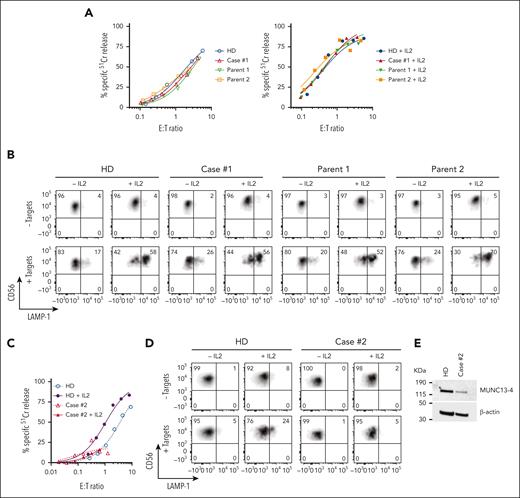
We previously reported a 3-month-old male patient, with reduced NK-cell function and biallelic missense mutations in UNC13D (c.1232 G>A [p.R411Q]; c.2588G>A [p.G863D]), who was diagnosed with FHL precipitated by cytomegaloviral and bocaviral infections.26 The patient underwent a matched sibling donor HSCT at the age of 4-months, conditioned with fludarabine, melphalan, and alemtuzumab, and has been in remission for 6 years. Initial high level of donor engraftment (90%) of the patient steadily reduced in the first month after transplant and had been stable between 7% to 9% for 5 years. Given his low donor chimerism we were concerned about a potential FHL relapse, however he remained well while having asymptomatic Epstein-Barr virus infection. Although 90% of the patient’s blood cells expressed the same disease-associated UNC13D mutations as before, the patient’s NK-cell cytotoxicity and degranulation capacity were indistinguishable from those of a healthy donor and from both parents (Figure 1A-B), suggesting that 1 or both of the UNC13D mutations may not be pathogenic.
Cytotoxic activity of NK cells from cases #1 and #2. (A) Case #1 (4 years after HSCT, showing 8% donor chimerism), his parents and unrelated healthy donor PBMCs were cultured overnight in the absence (left) or presence of 100 IU/ml of recombinant human (rh) IL-2 (right). The cytotoxic activity of NK cells was assessed against K562 target cells using 51Cr-release assay. Patients’ NK cells show similar activity to his parents and a healthy control despite the loss of donor chimerism. The assay was standardized with respect to the NK-cell percentage in PBMCs (CD3-/CD16+/CD56dim). (B) Case #1 NK cells show normal levels of degranulation as measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization in the presence of K562 target cells. (C) Case #2 PBMCs were incubated overnight in the absence or in the presence of 100 IU/mL of rh IL-2, and NK-cell cytotoxicity was assessed by 51Cr-release assay. The assay was standardized as in panel A. (D) Case #2 NK-cell degranulation was measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization using K562 as target cells. (E) Western immunoblotting, performed under reducing conditions, shows reduced MUNC13-4 expression in the isolated T cells from case #2, compared to a healthy donor control. PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Cytotoxic activity of NK cells from cases #1 and #2. (A) Case #1 (4 years after HSCT, showing 8% donor chimerism), his parents and unrelated healthy donor PBMCs were cultured overnight in the absence (left) or presence of 100 IU/ml of recombinant human (rh) IL-2 (right). The cytotoxic activity of NK cells was assessed against K562 target cells using 51Cr-release assay. Patients’ NK cells show similar activity to his parents and a healthy control despite the loss of donor chimerism. The assay was standardized with respect to the NK-cell percentage in PBMCs (CD3-/CD16+/CD56dim). (B) Case #1 NK cells show normal levels of degranulation as measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization in the presence of K562 target cells. (C) Case #2 PBMCs were incubated overnight in the absence or in the presence of 100 IU/mL of rh IL-2, and NK-cell cytotoxicity was assessed by 51Cr-release assay. The assay was standardized as in panel A. (D) Case #2 NK-cell degranulation was measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization using K562 as target cells. (E) Western immunoblotting, performed under reducing conditions, shows reduced MUNC13-4 expression in the isolated T cells from case #2, compared to a healthy donor control. PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Case #2 (P11)
A 44-year-old south Asian male of nonconsanguineous background with no significant history of medical conditions had recurrent hospital admissions since the age of 32 for episodes characterized by fevers, autoimmune molysis, and pancytopenia. It was subsequently identified during one of these episodes that there were associated features of hyperferritinemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hepatosplenomegaly, and significantly impaired NK-cell function consistent with HLH. Bone marrow biopsies were unremarkable for malignancy. His family history was notable for a sister who had died at the age of 20 years of an unknown febrile illness. During convalescence, NK-cell function remained grossly abnormal. Between the episodes, the patient was well. A gene panel study was performed that identified a novel homozygous missense mutation of uncertain significance in UNC13D (c.1135 G>A; p.Glu379Lys). Most recently, the patient has become significantly hypogammaglobulinemic owing to rituximab treatment (supplemental Information), requiring monthly immunoglobulin replacement (Figure 1C-E).
In both cases, the diagnosis of FHL was made on the perceived pathogenicity of biallelic UNC13D mutations and reduced NK-cell cytotoxicity inferred from assays carried out while the patient was unwell26 with active viral infection as well as had severe manifestations of HLH. However, the subsequent disease course highlighted a crucial unresolved clinical question: how can we efficiently resolve cryptic missense mutations to differentiate secondary HLH from FHL that requires HSCT?
Cytotoxic activity of mouse CTLs with deleted FHL genes is rescued by their human orthologues
To assess the effect of UNC13D missense mutations identified in cases #1 and #2, we knocked out UNC13D in primary human CD8+ T cells from healthy donors using CRISPR/Cas9 (supplemental Figure 2A), with an intention to subsequently express UNC13D mutants and assess their function. Surprisingly, despite a highly efficient gene KO, the cytotoxicity of the CD8+ T cells was only slightly reduced (supplemental Figure 2B). We then knocked out STX11 and STXBP2 genes, but this also had little effect on the activity of T cells. Unlike in the case of UNC13D deficiency, this observation was not entirely unexpected, because the activity of STX11 and STXBP2 deficient NK cells from patients with FHL is known to be IL-2 dependent. Even though T cells are rarely investigated in patients with FHL, it is conceivable that their cytotoxic activity may also recover in the presence of IL-2, which is required for T-cell growth and proliferation. It was only when all 3 genes were simultaneously disrupted that T-cell cytotoxicity was reduced by ∼80%, consistent with an additive effect of individual gene KO. Overall, as FHL gene KO failed to reduce human CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity, it became apparent that it was not possible to use these cells as a model for assessing the function of FHL-associated mutants. Given the high conservation of the amino acid sequences of mouse and human MUNC13-4 (88%), syntaxin-11 (85%), and STXBP2 (96%), we assessed whether the cytotoxicity of the gene-null mouse CD8+ T cells could be restored by expressing the respective human orthologue in these cells.
Three murine strains Prf1-/-, Unc13d (jinx), and Stx11−/− (but not Stxbp2−/− owing to embryonic lethality) have been established and validated as faithful models of FHL.27-30 It has been previously shown that the expression of human perforin in Prf1−/− and syntaxin-11 in Stx11−/− mouse T cells fully restored their ablated or severely reduced cytotoxicity.27,31 However, instead of using multiple gene KO mouse strains, we decided to KO endogenous genes of interest using CRISPR/Cas9 and re-express human wild-type (WT) or mutant orthologues in C57BL/6 mice that were transgenic for the T-cell receptor that recognizes ovalbumin peptide on H-2Kb, C57BL/6.OT-I (OT-I).
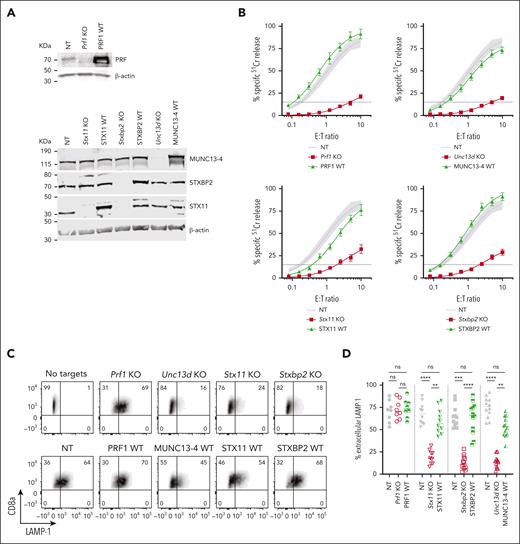
The CRISPR/Cas9 directed KO of mouse Prf1, Unc13d, Stx11, and Stxbp2 genes in CTLs showed a near complete loss of the endogenous proteins (Figure 2A), and profoundly reduced their cytotoxicity (Figure 2B, red curve): Prf1 KO, <2% activity; Unc13D KO, <4%; Stxbp2 KO, <7%, and Stx11 KO <20% activity compared to control (CTLs transfected with nontargeting [NT] guide RNA and transduced with an empty retroviral vector; NT). Although Stx11 KO cells had the highest residual activity, this was consistent with what is found in Stx11−/− mice27,29,32; unlike in human T or NK cells, IL-2 supplementation did not restore the function of Stx11 and Stxbp2 deficient mouse CTLs. To assess whether mouse CTLs were suitable for studying the function of FHL mutants, we retrovirally transduced the cells with the WT human orthologues of Prf1, Unc13d, Stx11, and Stxbp2 after knocking out the endogenous genes, and found that they restored CTL cytotoxicity to control levels (Figure 2B, green curve). To confirm that the restored cytotoxicity was because of the re-expressed human orthologue, we measured the cytotoxicity of WT-MUNC13-4, and 1 mutant each for STXBP2 and STX11, ranging from lower than endogenous mouse protein level to many fold overexpression; the different protein expression levels had no appreciable effect on CTL cytotoxicity (supplemental Figure 3A-F).
Knock-out (KO) of FHL-associated genes in mouse CTLs and complementation of their function with human WT orthologues. (A) Validation of single guide RNA for each FHL gene: western immunoblots, performed under reducing conditions, show the loss of endogenous mouse protein expression following CRISPR/Cas9 gene KO, and the expression of human WT orthologues in these cells. β-actin is shown as loading control. The residual protein levels compared to NT control were (mean ± SEM): Munc13-4 - 8.8±1.3% (n = 10); Stxbp2 – 9.7% ± 1.8% (n = 6); Stx11 – 8.1% ± 3.6% (n = 5). (B) Gene KO–dependent reduction in CTL cytotoxicity and its restoration by human WT orthologues, measured by 51Cr-release from antigenic SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells at indicated effector to target cell (E:T) ratios. Each value shown represents mean ± SEM of the following number of independent experiments: Prf1 KO and PRF1 WT, N = 10; Unc13d KO and UNC13D WT, N = 27; Stx11 KO and STX11 WT, N = 9; Stxbp2 KO and STXBP2 WT, N = 17. Shaded area represents the NT guide RNA (NT) control retrovirally transduced with empty MSCV GFP vector from N = 43 independent experiments (95% confidence interval is shaded gray), with the average value shown as a solid line. The levels of WT protein overexpression were (mean ± SEM): MUNC13-4 - 2.0 ± 1.0 (n = 6), STXBP2 – 3.3 ± 0.4 (n = 6), and STX11 – 4.2 ± 1.0 (n = 5). (C) Severely reduced degranulation in KO cells compared to NT control and restoration by human WT orthologues, using the same target cells as in panel B and measured as the externalization of LAMP-1/CD107a. (D) Summary of independent degranulation experiments: NT, Prf1 KO and PRF1 WT, N = 8; NT, Stx11 KO and STX11 WT, N = 10; NT, Unc13d KO and UNC13D WT, N = 12; NT, Stxbp2 KO and STXBP2 WT, N = 12. The results were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA; “ns” indicates no statistical difference, ∗∗ indicates P < .01, ∗∗∗ indicates P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗ indicates P < .0001. ANOVA, analysis of variance; GFP, green fluorescent protein; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Knock-out (KO) of FHL-associated genes in mouse CTLs and complementation of their function with human WT orthologues. (A) Validation of single guide RNA for each FHL gene: western immunoblots, performed under reducing conditions, show the loss of endogenous mouse protein expression following CRISPR/Cas9 gene KO, and the expression of human WT orthologues in these cells. β-actin is shown as loading control. The residual protein levels compared to NT control were (mean ± SEM): Munc13-4 - 8.8±1.3% (n = 10); Stxbp2 – 9.7% ± 1.8% (n = 6); Stx11 – 8.1% ± 3.6% (n = 5). (B) Gene KO–dependent reduction in CTL cytotoxicity and its restoration by human WT orthologues, measured by 51Cr-release from antigenic SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells at indicated effector to target cell (E:T) ratios. Each value shown represents mean ± SEM of the following number of independent experiments: Prf1 KO and PRF1 WT, N = 10; Unc13d KO and UNC13D WT, N = 27; Stx11 KO and STX11 WT, N = 9; Stxbp2 KO and STXBP2 WT, N = 17. Shaded area represents the NT guide RNA (NT) control retrovirally transduced with empty MSCV GFP vector from N = 43 independent experiments (95% confidence interval is shaded gray), with the average value shown as a solid line. The levels of WT protein overexpression were (mean ± SEM): MUNC13-4 - 2.0 ± 1.0 (n = 6), STXBP2 – 3.3 ± 0.4 (n = 6), and STX11 – 4.2 ± 1.0 (n = 5). (C) Severely reduced degranulation in KO cells compared to NT control and restoration by human WT orthologues, using the same target cells as in panel B and measured as the externalization of LAMP-1/CD107a. (D) Summary of independent degranulation experiments: NT, Prf1 KO and PRF1 WT, N = 8; NT, Stx11 KO and STX11 WT, N = 10; NT, Unc13d KO and UNC13D WT, N = 12; NT, Stxbp2 KO and STXBP2 WT, N = 12. The results were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA; “ns” indicates no statistical difference, ∗∗ indicates P < .01, ∗∗∗ indicates P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗ indicates P < .0001. ANOVA, analysis of variance; GFP, green fluorescent protein; SEM, standard error of the mean.
The results of degranulation assays, as measured by externalization of LAMP-1/CD107a, were consistent with the cytotoxicity assays. the loss of Unc13d, Stx11, and Stxbp2, which are directly involved in the exocytosis of the cytotoxic granules, led to a dramatic reduction in Lamp-1 externalization, but each respective human WT orthologue restored degranulation; as expected, the loss of Prf1 had no effect on CTL degranulation (Figure 2C-D). To further substantiate our observations, we explored the effect of the gene KO on the release of granzyme B (GzmB), which is copackaged in the cytotoxic secretory vesicles with perforin, using time-lapse total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Consistent with degranulation assays, the loss of Unc13d, Stx11, and Stxbp2 (but not Prf1) dramatically reduced GzmB release, but was restored with respective human WT orthologues (supplemental Figures 4 and 7).
As C57BL/6.OT-I mice are not routinely available in all laboratories, we determined whether similar assays can be carried out in WT (non T-cell receptor–transgenic) C57BL/6 mice using a redirected killing assay with Fcγ receptor–expressing P815 target cells, opsonized with anti-CD3 antibody.33 The gene KO and complementation assays mirrored the results observed with C57BL/6.OT-I mice, both for cytotoxicity and degranulation (supplemental Figure 5).
Distinguishing pathogenic from nonpathogenic mutations
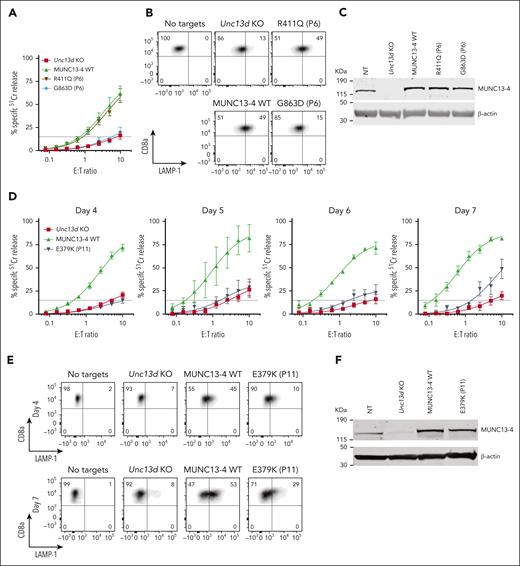
Having established an experimental system for assessing the function of FHL-associated genes, we investigated the molecular basis for the unusual immunopathologies exemplified in cases #1 and #2 by assessing their UNC13D mutations. For case #1, we found that the G863D-MUNC13-4 (c.2588G>A) mutation showed no detectable function in Unc13d KO cells on Day 4 (Figure 3A), but some activity was restored by Day 7 (supplemental Figure 8); it was therefore classified as pathogenic. In contrast, the R411Q-MUNC13-4 (c.1232G>A) mutation fully restored CTL function (Figure 3A). The degranulation assay produced consistent results, G863D-MUNC13-4 did not restore degranulation in Unc13d KO CTLs, whereas it was fully restored by R411Q-MUNC13-4 expression (Figure 3B). Interestingly, neither of the 2 mutations affected the stability of MUNC13-4 on western blot (Figure 3C), showing that normal protein expression levels are not an accurate predictor of function, as was previously demonstrated for some PRF1 mutations.34,35 Overall, our findings are able to explain normal NK-cell activity in case #1 (Figure 1) and long-term remission despite his loss of bone marrow chimerism. Concomitantly, we predict that case #1 has a low risk of relapse, and that his initial diagnosis of FHL can be revised to infection-associated secondary HLH.
Functional properties of MUNC13-4 mutants identified in case #1 (P6) and #2 (P11) and reconstituted in Unc13d KO mouse CTLs. (A) 51Cr-release assay using murine CTLs (as described in Figure 2) was conducted on day 4 of activation and shows ablated activity of G863D-MUNC13-4 and WT levels of cytotoxicity of R411Q-MUNC13-4 identified in case #1. Shown is mean ± SEM of N = 4 independent experiments. (B) Degranulation assay of case #1 MUNC13-4 mutations, as measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization. The degranulation levels mirror the cytotoxicity levels shown in panel A. SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 cells were used as targets. (C) Western immunoblot, performed under reducing conditions, showing endogenous mouse Munc13-4 protein expression, its level after CRISPR/Cas9 KO, and the overexpression of human WT-MUNC13-4 and R411Q-MUNC13-4, and G863D-MUNC13-4. β-actin is shown as loading control. (D) The effect of case #2 mutation E379K-MUNC13-4 on mouse Unc13d KO CTLs was assessed using 51Cr-release assay on days 4, 5, 6 and 7 of cell activation, using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells, at indicated E:T ratios. Each value shown represents mean ± SEM of N = 4 (for day 4), N = 2 (for day 5), N = 3 (for day 6) and N = 3 (for day 7) independent experiments. (E) Degranulation assay, as measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization of Unc13d deficient mouse CTLs transduced with E379K-MUNC13-4, using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells. (F) Western immunoblotting, performed on day 7 cells under reducing conditions, shows endogenous mouse Munc13-4 and the recombinant human WT-MUNC13-4 and E379K-MUNC13-4 protein expression; shown is 1 out of 5 independent experiments. E379K-MUNC13-4 expression level was 69% ± 11% compared to WT-MUNC13-4 (SEM of N = 5 independent experiments; P = .06, paired t test). β-actin is shown as loading control. SEM, standard error of the mean.
Functional properties of MUNC13-4 mutants identified in case #1 (P6) and #2 (P11) and reconstituted in Unc13d KO mouse CTLs. (A) 51Cr-release assay using murine CTLs (as described in Figure 2) was conducted on day 4 of activation and shows ablated activity of G863D-MUNC13-4 and WT levels of cytotoxicity of R411Q-MUNC13-4 identified in case #1. Shown is mean ± SEM of N = 4 independent experiments. (B) Degranulation assay of case #1 MUNC13-4 mutations, as measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization. The degranulation levels mirror the cytotoxicity levels shown in panel A. SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 cells were used as targets. (C) Western immunoblot, performed under reducing conditions, showing endogenous mouse Munc13-4 protein expression, its level after CRISPR/Cas9 KO, and the overexpression of human WT-MUNC13-4 and R411Q-MUNC13-4, and G863D-MUNC13-4. β-actin is shown as loading control. (D) The effect of case #2 mutation E379K-MUNC13-4 on mouse Unc13d KO CTLs was assessed using 51Cr-release assay on days 4, 5, 6 and 7 of cell activation, using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells, at indicated E:T ratios. Each value shown represents mean ± SEM of N = 4 (for day 4), N = 2 (for day 5), N = 3 (for day 6) and N = 3 (for day 7) independent experiments. (E) Degranulation assay, as measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization of Unc13d deficient mouse CTLs transduced with E379K-MUNC13-4, using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells. (F) Western immunoblotting, performed on day 7 cells under reducing conditions, shows endogenous mouse Munc13-4 and the recombinant human WT-MUNC13-4 and E379K-MUNC13-4 protein expression; shown is 1 out of 5 independent experiments. E379K-MUNC13-4 expression level was 69% ± 11% compared to WT-MUNC13-4 (SEM of N = 5 independent experiments; P = .06, paired t test). β-actin is shown as loading control. SEM, standard error of the mean.
The assessment of case #2 NK-cell function was constrained by the low NK-cell count in the peripheral blood (0.65% of total leukocytes), obfuscating NK-cell killing even at a high peripheral blood mononuclear cell:target ratio of 200:1 (Figure 1C-E). A low NK-cell count in the peripheral blood of patients with FHL or HLH is not uncommon, and this can impede a conclusive diagnosis. However, we found the expression of E379K-MUNC13-4 (c.1135G>A) in the patient’s CD8+ T cells to be reduced compared to control (Figure 1E), suggesting that this mutation destabilizes the protein. To explore why this patient had survived well into adulthood despite their apparently severely reduced NK or CTL function, we tested whether E379K-MUNC13-4 could complement the cytotoxicity of Unc13d KO CTLs but found that cytotoxicity was not restored (Figure 3D, day 4). This was a very surprising observation, because case #2 had late onset disease and, therefore, the mutation might have been expected to possess at least some activity. To explore this dilemma even further, we hypothesized that perhaps the mutated protein (which is constitutively expressed in patient cells) might, over time, provide some residual, but protective function. Given that in our recombinant system, we typically assess cytotoxicity on day 4 after transduction, we extended the culture period and assessed the function of E379K-MUNC13-4 on days 5, 6, and 7. In support of our hypothesis, this resulted in measurable but limited cytotoxicity at day 7 (Figure 3D, day 7), providing a possible explanation for the unusual clinical course of this patient. We also tested the activity of NT control cells on days 4, 5, 6, and 7 (supplemental Figure 6) and found that it did not change appreciably over this timeframe. Consistent with these results, the degranulation of E379K-MUNC13-4 expressing CTLs was severely reduced on day 4 compared to WT-MUNC13-4 expressing cells but increased ∼3-fold by day 7 (Figure 3E). Finally, the protein expression of E379K-MUNC13-4 was only slightly reduced (by 30%) compared to WT-MUNC13-4 (Figure 3F), suggesting that the mutant is unlikely to be structurally unstable. Consistent with the functional data, time-lapse total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy for mutants E379K- and G863D-MUNC13-4 shows significant reduction of GzmB release compared to WT-MUNC13-4, whereas mutant R411Q-MUNC13-4 shows a comparable level of release (supplemental Figure 7).
Prediction of the pathogenicity of FHL-associated mutations
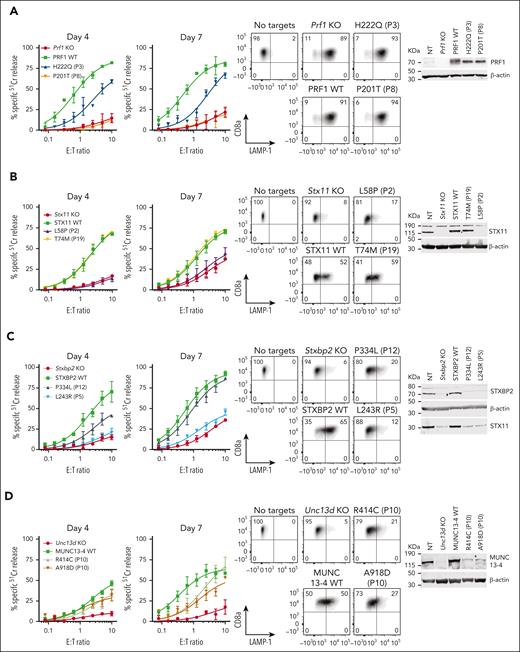
To test the predictive power of our novel experimental system, we assessed missense mutations identified previously in various categories of patients (Table 1): category I children presenting before the age of 5 years, whose biallelic mutations were expected to have no function, category II patients older than 5 years at their first presentation, in whom partial function was expected for at least 1 of the 2 mutant alleles, and category III carriers of 2 missense alleles, but in whom each mutation affects a different gene. Patients in category III were diagnosed with FHL despite 1 allele of each affected gene having an apparently normal sequence. We assumed that some mutations might bring about unexpected biochemical or cellular properties that take longer to be manifested (as we observed with E379K-MUNC13-4 above), and therefore tested the gene rescue phenotype of all the mutations on days 4 and 7 after the commencement of culture. Consistent with the stronger likelihood of category I patients inheriting complete loss-of-function (null) alleles, we discovered that none of the PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, or STXBP2 mutations we tested had any detectable activity (Figure 4; supplemental Figure 8), with P6 (case #1) being a notable exception (Figure 3) that ought to be reclassified as having secondary HLH.
Missense mutations associated with variable onset of FHL or found to be nonpathogenic
| Patient . | Age, y . | Gene . | Allele 1 . | Allele 2 . | Experimental outcome (% of WT activity) . | Allele Frequency (gnomAD36) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category I: mutations associated with an early (patients aged <5 years) onset of FHL | ||||||
| P137 | 0.167 | UNC13D | c.1208T>C p.L403P | c.1208T>C p.L403P | Null (supplemental Figure 8) | - |
| P238 | 0.167, 4, 5 | STX11 | c.173T>C p.L58P | c.173T>C p.L58P | Null (Figure 4B) | <0.1% |
| P339 | 0.167 | PRF1 | c.666C>A p.H222Q | c.666C>A p.H222Q | Null (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 9) | <0.1% |
| P440 | 0.583 | STXBP2 | c.1621G>A p.G541S | c.1621G>A p.G541S | Null (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% |
| P541 | 2 | STXBP2 | c.728T>G p.L243R | c.1247-1G>C p.V417LfsX126∗ | Null / Null (Figure 4C) | - / <0.1% |
| P6 (case #1)26 | 0.08 | UNC13D | c.1232G>A p.R411Q | c.2588G>A p.G863D | Normal / 22% (Figure 3A; supplemental Figure 8) | 0.8% / 0.37% East Asian |
| Category II: mutations associated with a late (patients aged >5 years) onset of FHL | ||||||
| P742 | 8 | PRF1 | c.577T>C p.F193L | c. 1229G>C p.R410P18 | 21% / TS18 (supplemental Figure 8) | - / <0.1% |
| P837 | 10 | PRF1 | c.601C>A p.P201T | c.853_855del p.K285del43 | 17% / Null (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 9) | - / <0.1% |
| P944 | 18 | PRF1 | c.1066C>T p.R356W | c.1349C>T p.T450M18 | 13%/TS18 (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% / <0.1% |
| P1015 | 9, 13 | UNC13D | c.1240C>T p.R414C | c.2753C>A p.A918D | 20%/17% (Figure 4D) | <0.1% / - |
| P11 (case #2) | 44 | UNC13D | c.1135G>A p.E379K | c.1135G>A p.E379K | 15% (Figure 3D) | - |
| P1245 | 45 | STXBP2 | c.1001C>T p.P334L | c.474_483del_insGA p.C158Wfs∗78∗ | 67%†/null (Figure 4C) | 0.1% / 0.1% Ashkenazi Jewish |
| P1346 | 14, 14, 15, 36, 42, 56 | STX11 | c.146G>A p.R49Q | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 6.5% East Asian, 1.7% African American |
| Category III: carriers of digenic mutations47 | ||||||
| P14 | 0.92 | PRF1 | c.992C>T p.S331L | - | 17% (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% |
| UNC13D | c.1232G>A p.R411Q | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.8% East Asian | ||
| P15 | 2.25 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.227C>T p.T76M | - | 22% (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.5% African American | ||
| P16 | 3 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.2243C>T p.A748V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% | ||
| P17 | 9, 13 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.2896C>T p.R966W | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.7% European | ||
| P18 | 28 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.182A>G p.Y61C | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | - | ||
| P19 | 0.167 | UNC13D | c.2030T>C p.I677T∗ | - | Not tested | - |
| STX11 | c.221C>T p.T74M | - | Normal (Figure 4B) | 0.7% South Asian | ||
| P20 | 5, 10 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| STXBP2 | c.1034C>T p.T345M | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 1.6% European | ||
| P21 | 21 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| STXBP2 | c.1586G>C p.R529P | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.24% European | ||
| P22 | 24 | PRF1 | c.50 delT p.L17Rfs∗29∗ | - | Null | 0.3% African American |
| STXBP2 | c.1459G>A p.V487M | - | Null (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.57% African American | ||
| Patient . | Age, y . | Gene . | Allele 1 . | Allele 2 . | Experimental outcome (% of WT activity) . | Allele Frequency (gnomAD36) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category I: mutations associated with an early (patients aged <5 years) onset of FHL | ||||||
| P137 | 0.167 | UNC13D | c.1208T>C p.L403P | c.1208T>C p.L403P | Null (supplemental Figure 8) | - |
| P238 | 0.167, 4, 5 | STX11 | c.173T>C p.L58P | c.173T>C p.L58P | Null (Figure 4B) | <0.1% |
| P339 | 0.167 | PRF1 | c.666C>A p.H222Q | c.666C>A p.H222Q | Null (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 9) | <0.1% |
| P440 | 0.583 | STXBP2 | c.1621G>A p.G541S | c.1621G>A p.G541S | Null (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% |
| P541 | 2 | STXBP2 | c.728T>G p.L243R | c.1247-1G>C p.V417LfsX126∗ | Null / Null (Figure 4C) | - / <0.1% |
| P6 (case #1)26 | 0.08 | UNC13D | c.1232G>A p.R411Q | c.2588G>A p.G863D | Normal / 22% (Figure 3A; supplemental Figure 8) | 0.8% / 0.37% East Asian |
| Category II: mutations associated with a late (patients aged >5 years) onset of FHL | ||||||
| P742 | 8 | PRF1 | c.577T>C p.F193L | c. 1229G>C p.R410P18 | 21% / TS18 (supplemental Figure 8) | - / <0.1% |
| P837 | 10 | PRF1 | c.601C>A p.P201T | c.853_855del p.K285del43 | 17% / Null (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 9) | - / <0.1% |
| P944 | 18 | PRF1 | c.1066C>T p.R356W | c.1349C>T p.T450M18 | 13%/TS18 (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% / <0.1% |
| P1015 | 9, 13 | UNC13D | c.1240C>T p.R414C | c.2753C>A p.A918D | 20%/17% (Figure 4D) | <0.1% / - |
| P11 (case #2) | 44 | UNC13D | c.1135G>A p.E379K | c.1135G>A p.E379K | 15% (Figure 3D) | - |
| P1245 | 45 | STXBP2 | c.1001C>T p.P334L | c.474_483del_insGA p.C158Wfs∗78∗ | 67%†/null (Figure 4C) | 0.1% / 0.1% Ashkenazi Jewish |
| P1346 | 14, 14, 15, 36, 42, 56 | STX11 | c.146G>A p.R49Q | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 6.5% East Asian, 1.7% African American |
| Category III: carriers of digenic mutations47 | ||||||
| P14 | 0.92 | PRF1 | c.992C>T p.S331L | - | 17% (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% |
| UNC13D | c.1232G>A p.R411Q | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.8% East Asian | ||
| P15 | 2.25 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.227C>T p.T76M | - | 22% (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.5% African American | ||
| P16 | 3 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.2243C>T p.A748V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | <0.1% | ||
| P17 | 9, 13 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.2896C>T p.R966W | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.7% European | ||
| P18 | 28 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| UNC13D | c.182A>G p.Y61C | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | - | ||
| P19 | 0.167 | UNC13D | c.2030T>C p.I677T∗ | - | Not tested | - |
| STX11 | c.221C>T p.T74M | - | Normal (Figure 4B) | 0.7% South Asian | ||
| P20 | 5, 10 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| STXBP2 | c.1034C>T p.T345M | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 1.6% European | ||
| P21 | 21 | PRF1 | c.272C>T p.A91V | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 10) | 4.3% European |
| STXBP2 | c.1586G>C p.R529P | - | Normal (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.24% European | ||
| P22 | 24 | PRF1 | c.50 delT p.L17Rfs∗29∗ | - | Null | 0.3% African American |
| STXBP2 | c.1459G>A p.V487M | - | Null (supplemental Figure 8) | 0.57% African American | ||
% of killing is based on day 7 data for all mutants.
Mutations in italic were previously tested by us using Prf1−/− CTLs18 or PRF1-KO human NK-cell line KHYG1.43
P10 represents 2 siblings with same compound heterozygote UNC13D mutations.15
TS, temperature sensitive. These 2 PRF1 mutants have been previously extensively tested in our laboratory and found to be misfolded and temperature sensitive.18
Mutations not tested in our system (most due to frameshift/deletion).
This mutant showed 30% cytotoxicity on day 4; despite a significant recovery of function, the degranulation remained severely reduced on day 7 (Figure 4C).
Effect of selected missense mutations in four FHL-associated genes expressed in mouse CTLs with endogenous orthologues knocked out. Cytotoxicity, degranulation, and protein expression data for PRF1: mutations from P3 and P8 from N = 2 independent experiments (see supplemental Figure 9 for additional data) (A), STX11: mutations from P2 and P19 from N = 2 independent experiments (B), STXBP2: mutations from P5 and P12 from N = 3 independent experiments (C), and UNC13D: compound heterozygous mutations from P10 from N = 3 independent experiments (D). 51Cr-release cytotoxicity assay was conducted on days 4 and 7 post activation using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells at indicated E:T ratios and represent mean ± SEM. Degranulation is measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization on effector cells on day 7 using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells. Western immunoblotting, performed on day 7 cells under reducing conditions, shows protein expression in KO, WT and mutant transduced cells. Equivalent cytotoxicity data for other mutations are shown in supplemental Figure 8. SEM, standard error of the mean.
Effect of selected missense mutations in four FHL-associated genes expressed in mouse CTLs with endogenous orthologues knocked out. Cytotoxicity, degranulation, and protein expression data for PRF1: mutations from P3 and P8 from N = 2 independent experiments (see supplemental Figure 9 for additional data) (A), STX11: mutations from P2 and P19 from N = 2 independent experiments (B), STXBP2: mutations from P5 and P12 from N = 3 independent experiments (C), and UNC13D: compound heterozygous mutations from P10 from N = 3 independent experiments (D). 51Cr-release cytotoxicity assay was conducted on days 4 and 7 post activation using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells at indicated E:T ratios and represent mean ± SEM. Degranulation is measured by LAMP-1/CD107a externalization on effector cells on day 7 using SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed EL4 target cells. Western immunoblotting, performed on day 7 cells under reducing conditions, shows protein expression in KO, WT and mutant transduced cells. Equivalent cytotoxicity data for other mutations are shown in supplemental Figure 8. SEM, standard error of the mean.
In contrast, category II patients, P7 to P12, were carriers of at least 1 mutation that produced measurable activity. This observation was consistent with our previous systematic analysis of many PRF1 mutants, in which we described a consistent association between the level of residual perforin activity and age of onset of FHL.18 One exception is the R49Q substitution in STX11, which was reported in several adult patients from China (P13).46 In them, we found that the mutant had WT-like function (supplemental Figure 8), which was consistent with 3 of the patients achieving full remission without HSCT. These findings and the high frequency of the R49Q-STX11 allele (>6%) in east Asian populations strongly suggest that the mutation is not disease-causing.
Finally, we explored category III patients in whom a diagnosis of FHL is made despite the 2 observed monoallelic mutations affecting different FHL-associated genes (digenic mutations).47 We found that in 8 out of 9 patients (P14-P21), at least one variant allele had WT activity, with P14 and P15 having reduced function in their one affected PRF1 or UNC13D allele. It is also worth noting that many of the patients reported with digenic mutations were carriers of the c.272C>T (A91V) polymorphism in PRF147; this is not entirely surprising, because A91V is extremely common among Caucasians (allele frequency 8%), and the probability of its coinheritance with another mutant allele is high. A recent epidemiological study of >13 000 participants recruited into an ASPREE study and who were older than 75 years revealed that both heterozygous and homozygous carriers of A91V had no increased risk of immune-mediated diseases or premature death.48 Indeed, even though A91V has been shown to be structurally unstable compared to WT-perforin, it nonetheless restored the function of Prf1 KO CTLs to normal levels (supplemental Figure 10). Out of 9 genotypes tested here, only 1 patient (P22) carried inactivating monoallelic null mutations in both PRF1 and STXBP2 and could potentially be predisposed to FHL. Otherwise, our functional analysis suggests that patients presenting with HLH symptoms, and who carry monoallelic mutations of 2 FHL-associated gene mutations should not be assumed to have FHL, and that their mutations need to be formally tested to designate their HLH as congenital or acquired.
Discussion
We developed and validated a novel, simple and readily applicable experimental platform for assessing the function of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 mutations in primary mouse CTLs (Figure 5). This novel approach helped us to retrospectively determine the molecular basis of atypical cases of suspected FHL, and in 1 case (case #1) to propose reclassifying the diagnosis as HLH because our experimental approach showed that one of the mutant alleles surprisingly generated a protein with WT activity. The unusual clinical presentation of case #2, coupled with their very low number of circulating NK cells made it impossible to distinguish HLH from FHL without functional assessment of the mutation that now firmly classifies the disease as FHL. We validated our system further by analyzing various mutations found in various categories of patients with FHL (Table 1), and our findings were consistent with the age of disease onset: complete loss of function in both alleles was found only in infants or very young children, whereas partial loss of function of ≥1 alleles was only identified in older children or adults. We also identified genotypes in which inherited mutations had no effect on protein function (P6, P13) and, importantly, demonstrated that the majority of cases of digenic mutations that were previously thought to be associated with FHL47 (category III) are unlikely to be responsible for disease. We found that only 2 out of 11 such missense mutations had no function, and out of the remaining 9 mutants, seven were functionally indistinguishable from the WT proteins. Cases such as P22, who coinherited monoallelic null mutations in both PRF1 and STXBP2, might still potentially develop FHL. However, this would be inconsistent with the fact that the killing capacity of CTL or NK cells in carriers of monoallelic mutations in FHL genes is generally indistinguishable from healthy donors. Speculatively, coinheritance of monoallelic null mutations in partner proteins, such as STX11 and STXBP2 or MUNC13-4 and RAB27A may have a more significant effect on cytotoxic lymphocyte function, but to the best of our knowledge no such cases have ever been reported. Overall, among fully-functional mutants identified in this study, only 2 were rare mutations (<0.1% allelic frequency); conversely, 2 mutants, T76M-MUNC13-4 (P15) and V487M-STXBP2 (P22), showed reduced activity but were relatively common (0.5% allelic frequency) among Africans or African Americans.
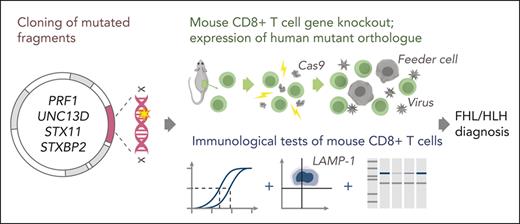
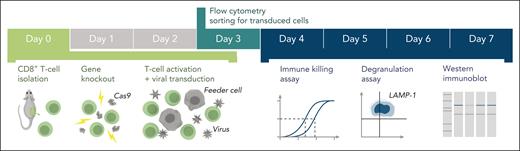
Schematic of the experimental workflow. Following identification of mutation(s) and before the experiment, cDNA fragments containing the mutation and the appropriate restriction enzyme cloning sites (supplemental Figure 1) are ordered from a commercial supplier and cloned into the WT cDNA in the MSCV-IRES-GFP backbone. Cloning, sequence verification, and plasmid amplification (maxi-prep) take 5 days. On day 0: naïve CD8+ T cells are isolated from a mouse spleen followed by nucleofection with Cas9 ribonucleoprotein to KO the desired genes. The KO cells are retrovirally transduced with recombinant human orthologues of the KO gene or empty MSCV-IRES-GFP vector as control and activated using BL/6 mouse T-cell depleted splenocyte “feeder cells,” simultaneously. On day 3 of cell expansion, the cells are sorted by flow cytometry with respect to their GFP reporter mean fluorescence intensity (identical for all samples on the day of sorting) to obtain pure populations expressing the desired protein. Experiments to test the function of the generated T cells can be conducted throughout days 4 to 7 and include 51Cr-release assays to test cytotoxicity, degranulation assays measuring LAMP-1/CD107a exposure to measure the exocytosis of cytotoxic granules, and western immunoblotting to determine the levels of protein expression. cDNA, complementary DNA; GFP, green fluorescent protein.
Schematic of the experimental workflow. Following identification of mutation(s) and before the experiment, cDNA fragments containing the mutation and the appropriate restriction enzyme cloning sites (supplemental Figure 1) are ordered from a commercial supplier and cloned into the WT cDNA in the MSCV-IRES-GFP backbone. Cloning, sequence verification, and plasmid amplification (maxi-prep) take 5 days. On day 0: naïve CD8+ T cells are isolated from a mouse spleen followed by nucleofection with Cas9 ribonucleoprotein to KO the desired genes. The KO cells are retrovirally transduced with recombinant human orthologues of the KO gene or empty MSCV-IRES-GFP vector as control and activated using BL/6 mouse T-cell depleted splenocyte “feeder cells,” simultaneously. On day 3 of cell expansion, the cells are sorted by flow cytometry with respect to their GFP reporter mean fluorescence intensity (identical for all samples on the day of sorting) to obtain pure populations expressing the desired protein. Experiments to test the function of the generated T cells can be conducted throughout days 4 to 7 and include 51Cr-release assays to test cytotoxicity, degranulation assays measuring LAMP-1/CD107a exposure to measure the exocytosis of cytotoxic granules, and western immunoblotting to determine the levels of protein expression. cDNA, complementary DNA; GFP, green fluorescent protein.
Our analysis also revealed a surprising lack of correlation between the level of protein expression and its function, because reduced expression has previously been suggested as one of the diagnostic criteria for FHL.20 For example, the UNC13D mutants G863D and E379K (Figure 3) both retained significant protein expression but had reduced function. Conversely, the P334L-STXBP2 mutant (Figure 4C) showed mildly reduced activity but a significantly reduced protein expression. These findings raise the important question of “how much” protein is required for retaining WT activity of effector lymphocytes. Interestingly, this mutant has been assessed in detail, and suggested that despite its instability it may still interact with STX11, which might explain the reason behind its partial activity and delayed onset of the disease.49 Within our new experimental workflow, we believe that although it is generally sufficient to test CTL function on day 4, additional testing on day 7 may provide a valuable additional information (as per case #2 here).
One possible limitation of this study is that it is restricted for technical reasons to assessing single mutants, whereas some patients inherit 2 (codominant) mutant alleles. Although monoallelic mutations may have a dominant-negative effect,50,51 or digenic null mutations may potentially have a synergistic effect on T or NK-cell function,52 there are few reported instances of this occurring clinically.47,50,51 We therefore believe a patient’s phenotype can in the great majority of cases be adequately explained by assessing the function of the mutant proteins tested individually, as demonstrated in this study.
A definitive diagnosis of FHL and the subsequent decision regarding HSCT should be made with a detailed and valid understanding of the impact of a given mutation on protein function, and, as a result, on immune homeostasis in the patient. Although the experimental frameworks for accurately linking genotype with phenotypes are reasonably well-developed for PRF1, this is currently not the case for the other FHL-related genes, leaving the clinical team with only limited information on how a given mutation may affect immune function. Based on the data presented here, we propose a simple and standard experimental system for testing FHL-associated mutations that would address many of the current gaps in understanding a mutation’s relevance to disease. This information would clearly enable the assignment of patients as having congenital or acquired HLH to be made with greater confidence. Given that several weeks typically pass in stabilizing a patient who presents acutely, locating a suitable donor and preparing the patient for HSCT transfer, our proposed workflow is easily achievable in a timeframe that can inform clinical decision-making. In addition to informing the management of current patients (often in an urgent setting) the technology may also be paramount for assessing the prognosis of asymptomatic siblings and to guide genetic counseling advice for prospective parents.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Centre for Advanced Histology and Microscopy, Core Flow Cytometry Facility, and Core Animal Facility (Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre).
This work was supported through a grant 2011020 from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (I.V.) and a fellowship from the Swiss National Science Foundation (A.W.H.).
Authorship
Contribution: T.N. and J.A.R.-S. designed and conducted experiments; A.K., H.H., D.H., C.W.T.C., K.F. and P.E.G. contributed to the clinical aspects of the study; A.W.H. contributed to data analysis; I.V. conceived the study; I.V. and J.A.T. cosupervized the study; and T.N., J.A.T. and I.V. cowrote the paper, with contributions from other authors.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Ilia Voskoboinik, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, 305 Grattan St, Melbourne, VIC 3000, Australia; e-mail: ilia.voskoboinik@petermac.org.
References
Author notes
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Ilia Voskoboinik (ilia.voskoboinik@petermac.org).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal