Background
Patients (Pts) with induction resistant Myeloma, either primary refractory or those relapsing early after completing induction, have dismal prognosis. To elucidate clinical and molecular pathways of refractoriness, we designed a clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a quadruple salvage regimen of Carfilzomib (CFZ)/ lenalidomide (LEN)/dexamethasone (DEX) / daratumumab (DARA) (KRD-D) in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) Pts with primary or secondary induction resistance (KYDAR trial) . Using a high resolution molecular tool of massively-parallel single-cell RNA-sequencing (MARS-seq) calibrated for this trial, we aimed to identify gene expression signatures associated with clinical response and resistance.
Methods
Population included forty NDMM Pts treated with a bortezomib-containing induction regimen, who either: i) Failed to achieve a minimal response after 2 cycles or a partial response after 4 cycles (Group A), ii) Had early relapse within 18 months from starting of therapy (group B) AND were not candidates (at screening) for autologous transplant. Following informed consent, all Pts were enrolled to receive KRD-D treatment in eighteen 28-day (d) cycles (Cy) or until disease progression/unacceptable toxicity. CFZ: 56 mg/m2 IV days 1,8,15 (Cy 1-9), d 1,15 (Cy 10-18). LEN: 25 mg (Frail: 15mg) d1-21; Dex 40mg (Frail: 20mg) weekly; DARA: IV 16mg/Kg weekly (Cy 1-2), q14d (Cy 3-6), q28d. After 18 cycles, Pts continued to receive DARA/Len. We applied longitudinally our calibrated protocol for scRNA-seq of MM PC (Ledergor et al 2018) to 31 KYDAR Pts at different time points, and compared them to NDMM and to healthy age and sex matched controls. Pts with partial response or better (IMWG criteria) after 3 cycles were defined as "responders".
Primary efficacy endpoints were safety and tolerability. Secondary endpoints included overall response rate (ORR); progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results
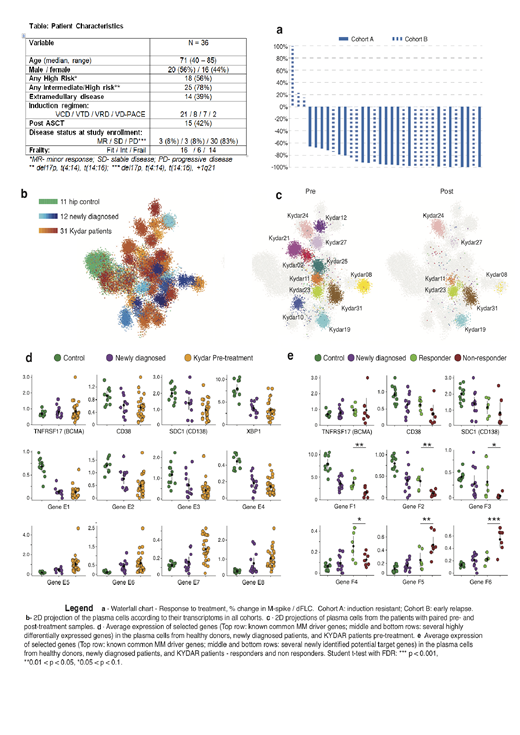
Forty Pts were enrolled across 13 medical centers in Israel. Data on 36 Pts with a cutoff date of June 2nd 2019 are presented and will be further updated at the meeting. Patients had highly aggressive MM characteristics (Table): 78% had intermediate/high risk FISH abnormalities, 39% had extramedullary disease, and 38% were frail. At a current median follow-up of 4 months (range 1-12m), 20 Pts are still under active therapy. Of the 16 Pts that discontinued therapy: 9 had progressed, 2 had an adverse event (AE), 1 died, and 3 discontinued due to other causes. All Pts had at least 1 AE, most were grade 1-2; There were 90 treatment emergent AE (TEAEs) and 18 regimen related grade 3-4 AEs. TEAEs occurring in ≥2 Pts included neutropenia (38%), thrombocytopenia (26%), infections (21%), anemia (18%), pneumonia (15%), diarrhea (9%) and rash (9%). Durable and deep responses were achieved (Fig. A). ORR was 91% (30/34): near CR-stringent CR 24% / very good partial response 47% / partial response 21% / stable disease 3% / progressive disease 6%. At median follow-up PFS is 85% and OS is 97%.
Applying MARS-seq, we profiled a total of 39,492 PC sampled from 11 control subjects, 12 newly diagnosed MM patients and 31 KYDAR Pts at different time points. We classified the different cell groups based on expression levels of the most variable genes and used the differentially expressed genes to annotate malignant PC types (Fig. C). We identified multiple genes and pathways that are differentially expressed between healthy controls, NDMM and induction-refractory KYDAR Pts (Fig D). Importantly comparing the responder and non-responder Pts, in the KYDAR trial we identify statistically significant genes for responding and non-responding group, including critical immune checkpoints and regulatory genes in the proteasome, and apoptotic pathways (Figure E).
Conclusions
KRD-D quadruple regimen was safe and well tolerated, and provided an effective salvage in a cohort of induction resistant MM Pts, with an ORR of 91%, with deep responses achieved in 71%, equivalent to 2nd line triplet regimens in non-selected MM. Single cell analysis showed a dramatic change in the PC transcriptome following therapy. Furthermore, differences in gene expression patterns between responders and non-responders unveil potentially druggable escape mechanisms used by the highly resistant tumors including immune checkpoints that may serve as perspective biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Cohen:Janssen Â: Consultancy; Amgen Â: Consultancy, Research Funding; Neopharm Â: Consultancy; Takeda Â: Consultancy; Madison Â: Consultancy; VBL Therapeutics Â: Employment. Ledergor:Immunai: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal