Background: The current commonly used regimens in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) utilize steroids (dexamethasone or prednisone) in various combinations: bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (VRd), bortezomib, thalidomide and dexamethasone (VTd), daratumumab, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (DRd) and daratumumab, bortezomib, melphalan and prednisone (DVMP). However, steroid therapy may be associated with various adverse effects, including, but not limited to mood changes, insomnia, hypertension, hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, adrenal suppression, muscle weakness, and increased risk of opportunistic infections. A recent trial demonstrated improved tolerability of a regimen (Rd-R) involving an abbreviated course of dexamethasone, without compromising the efficacy in patients with intermediate-fit NDMM (Lorocca A., et al., ASH 2018). We designed a phase 2 clinical trial to examine the safety and efficacy of daratumumab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody in combination with an all-oral regimen of ixazomib, a proteasome inhibitor, lenalidomide, an immunomodulatory drug, and modified dose dexamethasone (IRd).
Patients and Methods: NDMM patients with measurable disease and adequate organ function were enrolled, irrespective of their transplant eligibility. The primary objective was to determine the rate of complete response (CR) to daratumumab-IRd. Treatment consisted of daratumumab, 16 mg/kg, weekly for two cycles, every other week during cycles 3-6 and then every 4 weeks, ixazomib, 4 mg days 1, 8, 15, lenalidomide, 25 mg days 1-21, and dexamethasone upto 40 mg intravenously weekly for no more than two cycles, followed by use only as a prophylactic premedication for daratumumab-associated infusion reactions. Myeloma risk stratification was assessed by cytoplasmic immunoglobulin fluorescence in-situ hybridization (cIg FISH) analysis.
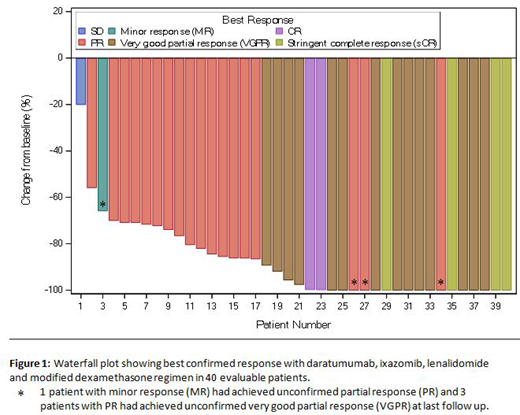
Results: Overall, 40 patients were accrued, with data available on all patients for analysis at the cutoff date of July 19, 2019. The median age at enrollment was 64.5 (33-81) years; 37.5% were female. Eight (20%) patients were high risk by FISH. The median number of cycles was 6 (2-11) and the median follow up was 6.1 (2-11.7) months. Among 40 patients who had received at least 2 cycles of therapy, responses were attained rapidly; at the end of cycle 2, 88% patients achieved at least a partial response and 33% at least a very good partial response (VGPR) that improved to 52% at the end of 4 cycles among 29 patients who had completed at least 4 cycles. The overall best confirmed response rate among all 40 patients (Figure 1) was 95%, including 10% stringent CR, 5% CR and 23% near CR (13% VGPR excluding nCR). Stem cell collection was completed in 17 patients so far, all of whom required filgrastim and plerixafor. The median CD34+ cell count was 7.7 (range 2.9-11.6) million/kg . All patients were alive and 39 (97.5%) patients were progression-free at last follow up. Four (10%) patients proceeded to autologous stem cell transplantation off study, per patient and/or investigator discretion (1 in CR, 2 in PR, 1 with progressive disease). Overall, 224 cycles have been administered across the study, with dose reduction/ hold required in a subset of patients; ixazomib (10%), lenalidomide (20%), daratumumab (0%) and dexamethasone (13%); the most frequent reasons for dose adjustment were skin rash and hematologic toxicities. A grade 3 or higher adverse event, at least possibly attributed to the study drugs, was observed in 40% of patients; hematologic in 30% (lymphopenia 25%, neutropenia 15%, thrombocytopenia 5% and anemia 2.5%) and non-hematologic in 18% of patients (hyperglycemia 8%, diarrhea 5%, infections 5%, ileus 2.5%, maculopapular rash 2.5%, and fatigue 2.5%). Updated results with additional 6 months of follow up and minimal residual disease assessment related data will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusion: Our early results suggest that the combination of daratumumab, ixazomib, lenalidomide and modified dose dexamethasone is well-tolerated, with excellent activity, and does not adversely impact stem-cell mobilization in patients with NDMM.
Kapoor:Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen: Research Funding; Glaxo Smith Kline: Research Funding; Cellectar: Consultancy. Gertz:Spectrum: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Prothena: Honoraria; Alnylam: Honoraria; Ionis: Honoraria. Dingli:alexion: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Millenium: Consultancy; Rigel: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Research Funding. Leung:Takeda: Research Funding; Prothena: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aduro: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Omeros: Research Funding. Dispenzieri:Pfizer: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Intellia: Consultancy; Akcea: Consultancy; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Alnylam: Research Funding. Lacy:Celgene: Research Funding. Kumar:Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Daratumumab in combination with Ixazomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone for the management of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal