Introduction: Recent studies have shown that young to middle-aged adults who receive a pediatric-inspired chemotherapy regimen for treatment of Ph-neg ALL do not appear to require an alloHSCT if they achieve good response on MRD testing after induction and/or consolidation therapy. Patients (pts) who are not good MRD responders achieve better outcomes with alloHSCT than their counterparts who do not receive alloHSCT. However, it is not clear if this approach can specifically apply to adult ALL pts with HR features at baseline. The aim of the prospective ALL-HR-11 trial (NCT01540812) from the Spanish PETHEMA Group was to evaluate response of HR Ph-neg adult ALL patients to a different post-induction therapy (chemotherapy or alloHSCT) according to MRD levels (centrally assessed by 8-color flow cytometry [FCM]) at the end of induction (week 5) and consolidation therapy (week 17)..
Patients and methods: HR ALL included one or more of the following parameters at baseline: age 30-60y, WBC count >30x109/L for B-cell precursor ALL or >100x109/L for thymic T-ALL, pro-B, early or mature T-ALL, 11q23 or KMT2A rearrangements or complex karyotype. Induction therapy included vincristine, prednisone, daunorubicin and asparaginase (E coli native or PEG according to center availability) for 4 weeks (Induction-1). FLAG-Ida was administered as intensified induction (Induction-2) in pts not achieving CR or in those in CR with MRD≥0.1% at the end of induction. For pts in CR and MRD<0.1% early consolidation therapy included 3 cycles with rotating cytotoxic drugs with high-dose methotrexate, high-dose ARA-C and high-dose asparaginase (E coli native or PEG). These pts continued with delayed consolidation (identical to that of early consolidation) followed by maintenance therapy up to 2y in CR if MRD levels after consolidation were <0.01%; otherwise they were assigned to alloHSCT. Pts in CR after Induction-2 received one consolidation cycle and were assigned to alloHSCT. Main outcome measures were: complete response (CR), overall survival (OS) and cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR), assessed by competing risk analysis.
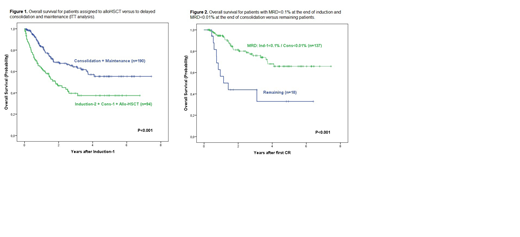
Results: On April 2019, 307 HR ALL pts were evaluable. Median (range) age was 40 (15-60) y, 192 were males, 211 precursor B-ALL and 96 T-ALL, with a median WBC count of 12.9 (0.2-564) x109/L. Results of Induction-1 (n=304, 3 on induction): therapy-related death: 12(4%), resistance: 39(13%), CR: 253(83%). MRD<0.1% at the end of induction was observed in 77% of CR patients. Induction-2 was administered to 88 patients (due to no CR: 37, or to CR and MRD≥0.1%: 51). Overall response rate: 277 (91%). The 5y CIR and OS probabilities for the whole series were of 44%±8% and 48%±7% (median follow-up: 2.06y [range: 0-7.55y]). By intention-to treat after Induction-1, 94 pts were assigned to alloHSCT and 190 to delayed consolidation and maintenance. The 5y CIR and OS probabilities were of 37%±13% and 38%±11%, respectively, for pts assigned to alloHSCT, and of 48%±10% and 55%±10%, respectively, for those assigned to chemotherapy (P<0.001 for OS [Figure 1], and P=0.243 for CIR). Patients with MRD<0.1% at the end of induction and MRD<0.01% at the end of consolidation (n=137) showed a 5y CIR and OS of 42%±11% and 66%±11%, respectively (P<0.001 for both, Figure 2). Patients with MRD levels <0.01% on day14 of induction-1, end-induction-1 and end-consolidation (n=17) showed 5y CIR and OS probabilities of 17%±19% and 90%±19%, respectively.
Conclusions: This trial, in which post-induction therapy was only based on MRD results assessed by FCM, suggests that avoiding alloHSCT does not hamper the outcome of HR Ph-neg adult ALL pts with adequate MRD response after induction and after consolidation. Better post-remission alternative therapies are specially needed for patients with poor MRD clearance.
Supported by grants PI14/01971 FIS, Instituto Carlos III, and SGR225 (GRE), Spain.
Montesinos:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Teva: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Esteve:Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal