Background:
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal hematologic neoplasms stratified by risk by the international prognostic scoring system (IPSS) and IPSS-revised (IPSS-R) which measure risk by morphologic dysplasia, clinical cytopenias, blast count, and cytogenetic abnormalities. (PMID: 9058730, 22740453) The IPSS/IPSS-R do not consider clinical comorbid conditions, though MDS patients with higher burden of comorbid disease have higher rates of non-leukemic death, particularly those with cardiovascular and pulmonary disease. (19324411) Despite this, there has been limited investigation into how specific comorbid conditions may help define subgroups of patients with MDS.
Methods:
We identified 2676 cases of MDS as defined by ICD-9 code (238.72 - 238.75) in Vanderbilt's Synthetic Derivative (SD). The SD is a de-identified electronic health record (EHR) of over 2.2 million patients with a companion biorepository of DNA (BioVU) for a subset of these patients, including all of the patients with MDS. The 2676 cases were matched by age, gender, race, burden of comorbidities in EHR, and age at last appointment in EHR with 5287 controls. ICD-9 codes for other myeloid disease (e.g., myeloproliferative neoplasms, acute myeloid leukemia) or history of hematopoietic stem cell transplant were excluded among the controls.
Characterization of comorbidities, via phecode analysis, was conducted on all cases and controls. Phecodes are groups of related ICD-9 codes describing a clinical syndrome or medical problem, previously demonstrated to be useful in phenome-wide associated studies in EHRs. (28686612) A case was defined as having a phecode only if a representative ICD-9 code was present on two distinct days in the EHR. Next, a cluster analysis of the study population and their associated comorbidities, via a bipartite stochastic block model, was completed, and the study population was organized into hierarchical structure based upon the similarities in comorbidity patterns among patients.
Results:
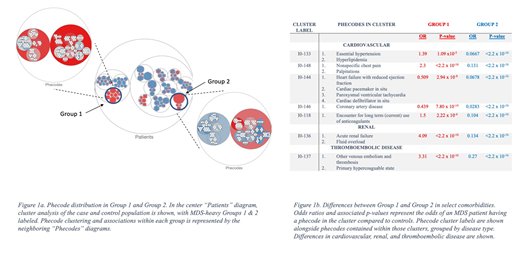
ICD-9 codes from the study population made up 181 phecodes, which were found in hierarchical cluster analysis to further cluster into 54 sub-groups and 16 larger groups. MDS patients clustered throughout all groups, the majority of which contained control patients; yet some MDS cases sub-clustered into groups that included a majority of MDS cases and these were further analyzed. Notably, two groups had equivalent size and MDS status were found to have significant differences in phecode profiles. Group 1 had 795 total patients with 783 MDS cases (98.5%) and Group 2 had 769 total patients with 684 MDS cases (88.9%), as per Fig 1a. There were no significant difference in sex between the two groups. Group 1 patients were significantly younger than Group 2 patients (58.3y vs 62.9y; p = 1.36 x 10-7), yet tended have increased risk of renal, cardiovascular and thromboembolic disease than Group 2, as per Fig 1b. Additionally, a higher proportion of Group 2 patients (695/769 or 90.4%) were alive at time of data extraction than Group 1 patients (451/795 or 56.7%) (OR 4.51, p = <2.2 x 10-16).
Conclusions:
By performing a phenome-wide analysis of patients with MDS in a large electronic health record (EHR), we reveal specific subgroups of MDS patients with distinct comorbidities and different survival, not affected by age or sex. This study demonstrates the ability to study comorbid conditions of MDS patients in an unbiased fashion, independent of disease specific risk factors that inform IPSS-R and which have historically been most important in stratifying risk in MDS. The role of comorbidity is instinctually clear to the adroit clinician, and this technique could provide distinct comorbid disease patterns which impute risk, or perhaps etiology in MDS.
Savona:TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Selvita: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Boehringer Ingelheim: Patents & Royalties; Celgene Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal