Background: The treatment paradigm of adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is primarily derived from successful pediatric chemotherapy regimens. Pegasparagase (PEG) is a key component of pediatric therapy and is the backbone of cytotoxic ALL regimens. However, among the adult population the use of PEG has been limited by the difficulty in tolerating prolonged asparagine depletion. Hepatotoxicity is among the most common adverse events reported with the use of PEG, with grade 3/4 hepatotoxicity seen in 20% of young adults compared to 40-60% of older adults. Incorporating PEG into the treatment of ALL patients under 40 remains an accepted practice despite some studies that report up to 75% of patients have grade 3/4 adverse events as a result of asparagine depletion. In a study of 85 patients with ALL, 3-year overall survival (OS) was significantly different between patients older and younger than 35 (52% vs 83% p = 0.003). Whether this difference is due to PEG toxicity or to other factors remains to be determined. At NYU hospitals, PEG-containing protocols are frequently deployed to treat adult ALL. In our study, we sought to look at the difference in PEG toxicity and response rate (RR) in patients older and younger than 35 and whether these toxicities contributed to a delay in subsequent treatments and to a worse outcome.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients older than 18 diagnosed with ALL or lymphoblastic lymphoma, who received at least 1 dose of PEG at our institution between 2014 and 2018. All patients received PEG as part of their first line treatment protocol. Our main objective was to compare the tolerability and toxicity profile of intravenous PEG in patients ≥35 years old versus <35. Our secondary objective was to investigate its effects on chemotherapy delay, RR, and relapse rate.
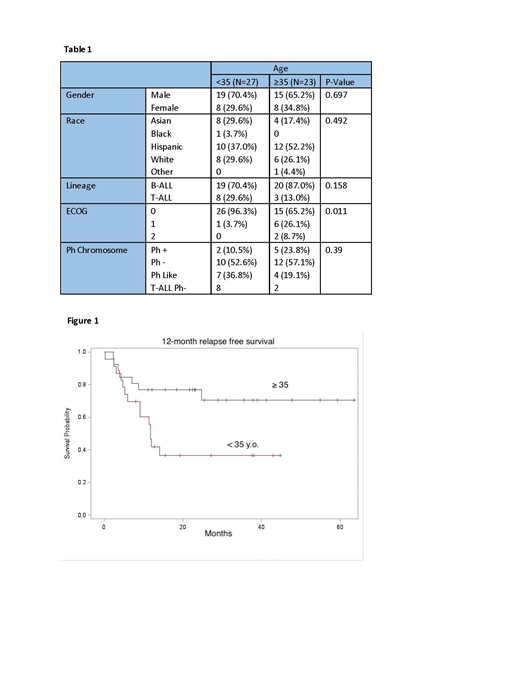
Results: Out of a total of 50 patients, 23 were age ≥ 35 (46%). Mean age was 34.4 (Range: 18.9-63.1). The 2 groups shared similar distributions in gender, race, and Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) subtypes (Table 1). The older group received significantly less PEG, 5114.8 vs. 25353.7 units (p=0.0007) and 1.65 vs. 3.59 doses (p<0.0001) compared to the younger group. Grade 1-4 toxicity profiles were similar as both groups had high hepatotoxicity rates: transaminitis 100% vs. 89% (p=0.079) and hyperbilirubinemia 78% vs. 78% (p=0.104) in the older vs younger group, respectively. Grade 3-4 hepatotoxicity was significantly more pronounced in patients ≥35 years old (transaminitis 65% vs. 33% [p=0.0245], hyperbilirubinemia 48 vs. 15% [p=0.0111]). Coagulopathy rates evaluated with hypofibrinogenemia and thrombosis were similar between the older and the younger groups at 52% vs. 44% [p=0.104] and 17% vs. 7%, [p=0.855], respectively, and the frequency of pancreatitis and anaphylaxis were 4% vs. 18.5% (p=0.422) and 0% vs. 14.8% (p=0.115), respectively. In the older group, only 13% completed the planned PEG dosages compared to 59% in the younger group (p=0.0008), and delay in other chemotherapy by more than 30 days due to PEG hepatotoxicity occurred in 55% of older patients compared to 22% of younger patients (p=0.02). MRD negativity rate after induction was similar in the older and younger group (50% vs. 60% [p=0.491], respectively), but the 12-month relapse free survival was significantly lower in the older group (41%, [95% CI: 55.7%-89%] vs. 77%, [95% CI: 21%-61%], p=0.022) (Figure 1).
Conclusions: Patients aged ≥ 35 received significantly less PEG during their treatments but were more likely to develop severe grade 3-4 hepatotoxicity compared to their younger counterparts. The response rates were similar with comparable MRD negativity rates after induction regardless of total amount of PEG administered. However, relapse occurred more frequently in the older group, possibly resulting from more frequent delays in administering other chemotherapy agents due to PEG toxicity. Incorporation of PEG is important in the treatment of ALL but should be used with caution in patients ≥35 years old, and will likely require dose and schedule modifications. A larger prospective trial investigating adequate dosing and scheduling of PEG in this age group is warranted, specifically comparing delays in chemotherapy, relapse, and survival rates in regimens with and without PEG.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal