INTRODUCTION:
Primary plasma cell leukemia (pPCL) is the most aggressive form of multiple myeloma (MM). Recently, pPCL has been defined by as few as >5% circulating plasma cells (cPCs) detected morphologically on a peripheral blood smear. However, this technique may not be sufficiently sensitive and is dependent on inter-observer bias to properly identify and quantify cPCs. Multiparametric flow cytometry (MFC) provides a readily available and highly sensitive method to identify and quantify cPCs. However, an optimal quantitative cutoff for cPCs by MFC to define the presence of pPCL has not been established to date. Thus, this is the first study to date that determines an optimal cutoff of cPCs/ microliter that could identity patients with pPCL at diagnosis.
METHODS:
We retrospectively evaluated all newly diagnosed MM patients seen at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester from January 2007 to December 2017 who had their peripheral blood samples evaluated morphologically by peripheral blood smear and immunophenotypically by MFC prior to beginning therapy. Patients with a peripheral blood smear detecting >5% cPCs were classified as having pPCL. Six-color MFC was performed on peripheral blood mononuclear cells by isolated by Ficoll gradient, and stained with antibodies to CD45, CD19, CD38, CD138 and cytoplasmic Kappa and Lambda immunoglobulin light chains. The data was collected using Becton Dickinson FacsCanto II instruments collecting 150,000 events and analyzed using the BDFacs DIVA Software. The gating strategy employed first used the expression of CD38, CD138, and cytoplasmic immunoglobulin light chains to identify all plasma cells in the specimen. The cPCs were then discriminated from polyclonal/normal plasma cells based on differential CD19 and CD45 expression. The cPCs detected were reported as the number of clonal events/150,000 collected total events and converted to the absolute number of cPCs/microliter using their absolute lymphocyte count and monocyte count determined at the time of the blood draw for cPC MFC assessment. A receiver operator curve (ROC) was performed to determine the absolute cPCs/microliter by MFC that best identified those patients with >5% cPC on their peripheral blood smear. Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-Meier method and differences assessed using the log rank test.
RESULTS:
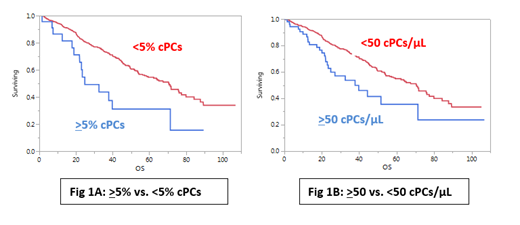
A total of 591 patients were included in this analysis of which 59% were male and the median age was 66 years (range: 27 - 95) with 22% being 75 years of age or older. From this cohort, 133 (24%) patients had high risk FISH cytogenetics, 172 (30%) were classified as ISS 3 at diagnosis, 83 (15%) had an elevated LDH level and 61 (17%) had a plasma cell labeling index (PCLI) of 2% or greater. There were 65 (11%) patients with any amount of cPCs detectable by peripheral blood smear of which only 22 (4% of the total population) met criteria for pPCL with >5% cPCs. With MFC, 403 (68%) patients had detectable cPCs. The median number of cPCs per microliter was 0.81 (0 - 10,455) with 273 (46%) having >1 cPC/microliter. A ROC analysis determined that the presence of >50 cPCs/microliter by MFC was the optimal cutoff to identify patients with >5% cPCs by blood smear with approximately a specificity of 94% and a sensitivity of 86%. The presence of >50 cPCs/microliter by MFC was associated with higher presence of high risk FISH cytogenetics, ISS 3 classification, elevated LDH and PCLI > 2%. The median time to next treatment (TTNT) for patients with and without >5% cPCs by peripheral blood smear was 18 months vs. 30 months (P < 0.001). The median TTNT for patients with and without >50 cPCs/microliter by MFC was 19 months vs. 30 months (P < 0.01). The median overall survival (OS) for patients with and without >5% cPCs by peripheral blood smear was 25 months vs. 71 months (P < 0.001; Fig 1A). The median OS for patients with and without >50 cPCs/microliter by MFC was 38 months vs. 71 months (P < 0.01; Fig 1B).
CONCLUSION:
This is the largest study that attempts to identify an optimal cutoff of cPCs/microliter by MFC for diagnosing pPCL patients. The presence of >50 cPCs/microliter is an optimal cutoff by MFC that best predicts for the presence of >5% cPCs by peripheral blood smear. However, there remains discordance in the OS outcomes between the two cutoffs by different methodologies for pPCL. This could signify the presence of biological processes associated with the presence of >5% cPCs when detected by peripheral blood smear that are not captured by MFC.
Dispenzieri:Pfizer: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Intellia: Consultancy; Akcea: Consultancy; Alnylam: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Dingli:Karyopharm: Research Funding; Rigel: Consultancy; Millenium: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; alexion: Consultancy. Lacy:Celgene: Research Funding. Kapoor:Amgen: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Glaxo Smith Kline: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cellectar: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria. Leung:Aduro: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Omeros: Research Funding; Prothena: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding. Russell:Imanis: Equity Ownership. Gertz:DAVA oncology: Speakers Bureau; Ionis/Akcea: Consultancy; Alnylam: Consultancy; Prothena Biosciences Inc: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Spectrum: Consultancy, Research Funding; Annexon: Consultancy; Appellis: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Medscape: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Physicians Education Resource: Consultancy; Abbvie: Other: personal fees for Data Safety Monitoring board; Research to Practice: Consultancy; Teva: Speakers Bureau; Johnson and Johnson: Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Proclara: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; i3Health: Other: Development of educational programs and materials; Springer Publishing: Patents & Royalties; Amyloidosis Foundation: Research Funding; International Waldenstrom Foundation: Research Funding. Kumar:Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal