Introduction: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) developing secondary after other hematologic diseases, or therapy related after cytotoxic treatment for solid tumors or rheumatologic diseases (s/tAML) is clinically, genetically & prognostically distinct from de novo diseases. Data indicate that s/tAML patients (pts) have inferior outcome compared to de novo cases after chemotherapy & therefore often require consolidation therapy using allogeneic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Leukemic stem cells (LSC) initiate & maintain AML. They are also believed to exist within the CD34+/CD38- &/or high GPR56 expressing bone marrow (BM) population, which have been shown to impact adversely on outcome. The prognostic impact of LSC markers in de novovs s/tAML after HSCT with non-myeloablative conditioning intensity - where the therapeutic approach also relies on immunological graft-versus-leukemia effects - is unknown.
Methods: We analyzed 379 AML pts who received an allogeneic peripheral blood HSCT in complete remission (CR, 82%) or CR with incomplete peripheral recovery (CRi, 18%) between 1999 & 2018 after non-myeloablative (3x30 mg/m2 Fludarabine & 2 Gy total body irradiation) conditioning. At diagnosis, cytogenetic & flow cytometric analyses were performed centrally. For pts with pre-treatment BM available the mutation status of CEBPA, NPM1 & presence of FLT3-ITD by fragment analyses as well as expression levels of GPR56 by qPCR were assessed. Using a next-generation targeted amplicon sequencing approach we analyzed a panel comprising 54 recurrently mutated (mut) genes in myeloid malignancies on the MiSeq platform (Illumina). Median follow up after HSCT was 3.7 years.
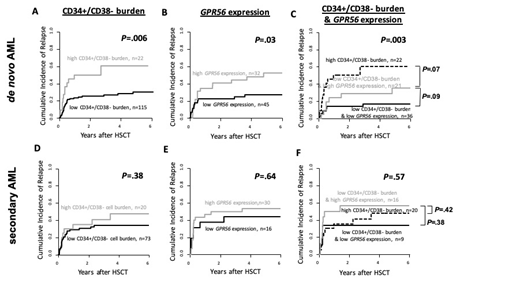
Results: 229 pts (60%) had de novo & 150 pts (40%) had AML secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS, n=82), myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN, n=22) or MDS/MPN (n=10), or therapy related after Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (n=9), solid tumors (n=25) or rheumatologic diseases (n=2). At diagnosis, s/tAML pts had lower white blood counts (P=.03), lower blasts in BM (P<.001) or blood (P=.007) & a higher BM CD34+/CD38- cell burden (P=.01) & GPR56 expression (P=.04). They also had worse European LeukemiaNet risk (P=.007), were less likely to have a normal karyotype by trend (P=.06), to have a core binding factor AML (P=.02), to be NPM1mut (P=.003), DNMT3Amut (P=.03) & to harbor a FLT3-ITD (P=.002) but more likely to be JAK2mut (P<.001). Comparing pts with s/tAML vsde novo AML, there was no significant different cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR, P=.85) or overall survival (OS, P=.29). Next, we evaluated the prognostic impact of the LSC-associated populations in pts with de novo or s/tAML separately. In pts with de novo AML, we observed a significantly higher CIR & shorter OS for pts harboring a high CD34+/CD38- cell burden (high vs low, 6% cut, P=.006 [Fig. 1A] & P=.003) & a higher CIR but not significantly different OS for pts with a low GPR56 expression (high vs low, median cut, P=.03 [Fig. 1B] & P=.95). Combining both parameters, we observed a stepwise higher CIR & shorter OS for pts with low expression of both variables vs pts with a low CD34+/CD38- cell burden but high GPR56 expression vs pts with a high CD34+/CD38-cell burden (P=.003 [Fig. 1C] & P=.05). In contrast, in pts with s/tAML, there was no prognostic significance of the CD34+/CD38- cell burden (CIR P=.38 [Fig. 1D] & OS P=.95), the GPR56 expression (CIR P=.64 [Fig. 1E] & OS P=.82) & both markers combined (CIR P=.57 [Fig. 1F] & OS P=.98). Also in multivariate analyses, the combination of both markers significantly impacted CIR (Hazard ratio 2.49, P<.001 after adjustment for donor type) & was the only significant factor for OS (Odds Ratio 0.68, P=.04) in de novo AML but not in s/tAML.
Conclusion: While there was no significantly different CIR or OS in s/tAML compared to de novo AML pts undergoing non-myeloablative HSCT we observed a significant impact on outcome for the known LSC-associated prognosticators CD34+/CD38- cell burden & GPR56 expression levels at diagnosis only in de novo AML pts. Different underlying disease biology & possibly different LSC-associated populations may be relevant for disease reoccurrence in s/tAML.
Jentzsch:Novartis: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Niederwieser:Daichii: Speakers Bureau; Cellectis: Consultancy. Platzbecker:Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Schwind:Daiichi Sankyo: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal