CD19 directed chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CART) therapy has shown remarkable activity in B cell lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukemia leading to the approval of two CART therapies. With the emergence of therapeutic anti-CD19 antibodies for the treatment of B cell malignancies, it remains to be elucidated whether such antibodies would interfere with the ability of CD19 targeting CARTs to exert their anti-tumor effect in a subsequent therapy. To address a part of this question, we investigated the potential for functional interference between the monoclonal anti-CD19 antibody tafasitamab (MOR208) and CD19 directed CART cells (CART19). CART19 cells were generated through lentiviral transduction of healthy donor T cells with a second generation CD19 CAR construct (FMC63-CD8h-CD8TM-41BBζ) which is similar to the construct used for the FDA-approved CART tisagenlecleucel. Tafasitamab, is an Fc-enhanced humanized monoclonal antibody which mediates antibody-dependent cellular toxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) and direct cytotoxicity. It is currently being studied in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in combination with the immunomodulatory agent lenalidomide (L-MIND) and the chemotherapeutic drug bendamustine (B-MIND).
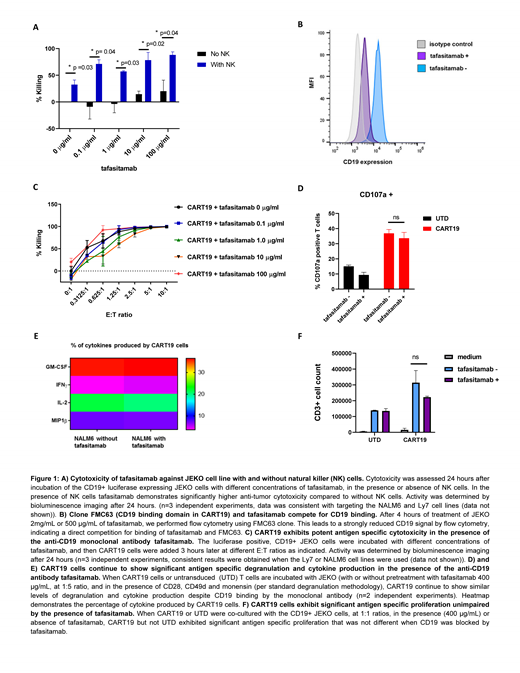
As a first step we confirmed the relevance of the tested CD19-positive target cell lines, JEKO (mantel cell lymphoma), Ly7 (DLBCL) and NALM-6 (ALL) based on functional activity of tafasitamab and CART19. In a 24 hours ADCC (tafasitamab titration plus natural killer (NK) cells; Figure 1A) and T cell cytotoxicity assays (CART19, E:T titrations; data not shown) distinct activity was observed for both therapies on all tested cell lines.
Secondly, we studied whether the observed CART19 activity may be influenced by tafasitamab in case of a direct CD19 binding competition between tafasitamab and the CAR. To test for such binding competition we incubated the CD19+ cell lines NALM6 or JEKO with up to 100 µg/ml tafasitamab, to saturate the receptors. Subsequent flow cytometry analysis using the FMC63 antibody (carrying the same CD19 binding domain as contained in CART19) failed to detect CD19 expression, indicating a direct binding competition between FMC63 and tafasitamab (Figure 1B). Next, to investigate the potential impact of such binding competition on CART19 cell effector functions, we co-cultured tafasitamab CD19+ JEKO cell line at increasing concentrations of up to 100µg/ml, and then added CART19 cells at different effector to target ratios to the cell culture. The presence of tafasitamab, binding to the CD19 antigen, did not affect important CART cell effector functions such as antigen specific killing (Figure 1C), degranulation (Figure 1D), cytokine production or proliferation of CART19 (Figure 1E).
In summary, our studies indicate that CART19 continue to exhibit potent antigen specific effector functions despite presence of tafasitamab and the related competition for CD19 binding. Besides the presented in vitro work the questions of therapeutic sequencing of tafasitamab and CART19 is being studied in xenograft models and will be presented at the meeting.
Sakemura:Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Cox:Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Schanzer:MorphoSys AG: Employment. Endell:MorphoSys AG: Employment, Patents & Royalties. Nowakowski:Selvita: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NanoString: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc.: Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Research Funding; Curis: Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kay:MorphoSys: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board; Infinity Pharmaceuticals: Other: DSMB; Celgene: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board; Agios: Other: DSMB. Kenderian:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Tolero: Research Funding; Humanigen: Other: Scientific advisory board , Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Lentigen: Research Funding; Morphosys: Research Funding; Kite/Gilead: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal