Introduction: The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib is the only FDA approved therapy for the treatment of symptomatic Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM), and has been associated with high response rates and durable progression-free survival (PFS). Factors associated with depth of response and PFS duration are not well established. We performed a retrospective study aimed at identifying predictive and prognostic factors in WM patients treated with ibrutinib.
Methods: We included consecutive patients with a diagnosis of WM treated with ibrutinib monotherapy evaluated at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute since January 2012 through March 2019. Patients with Bing-Neel syndrome (WM involving the central nervous system) were excluded. Baseline clinical and laboratory characteristics were gathered. MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations were assessed using polymerase chain reaction assays and Sanger sequencing. Responses at 6 months were assessed using criteria from IWWM3. PFS was defined as the time from ibrutinib initiation until last follow-up, death or progression. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were fitted for partial response (PR) and very good partial response (VGPR) at 6 months, and Cox proportional-hazard regression models were fitted for PFS.
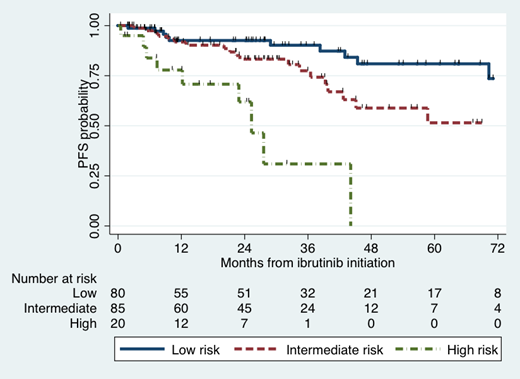
Results: A total of 252 patients were included in our analysis. Selected baseline characteristics include: age ≥65 years (60%), hemoglobin <11.5 g/dl (68%), platelet count <100 K/uL (12%), albumin <3.5 g/dl (39%), b2-microglobulin ≥3 mg/l (70%), serum IgM level ≥7,000 mg/dl (6%), bone marrow involvement ≥60% (54%), previously untreated for WM (33%), time to ibrutinib <3 years (46%). MYD88 L265P and CXCR4 mutations were detected in 98% and 38% of patients, respectively. At 6 months, 71% of patients obtained PR, and 17% VGPR. Multivariate logistic regression analyses showed higher odds of PR at 6 months for hemoglobin <11.5 g/dl (78% vs. 56%; OR 2.8, 95% CI 1.1-6.9; p=0.03) and serum albumin <3.5 g/dl (90% vs. 66%; OR 3.2, 95% CI 1.0-10; p=0.045), while CXCR4 mutations associated with lower odds (44% vs. 82%; OR 0.15, 95% CI 0.06-0.37; p<0.001). Multivariate logistic regression analyses showed higher odds of VGPR at 6 months for b2-microglobulin ≥3 mg/l (21% vs. 3%; OR 3.3, 95% CI 1.1-10; p=0.04) and lower odds for serum IgM level ≥4,000 mg/dl (9% vs. 23%; OR 0.3, 95% CI 0.1-0.8; p=0.02). The median follow-up was 30 months, and the median PFS has not yet been reached. The 5-year PFS rate was 60% (95% CI 48-69%). In the multivariate Cox regression analysis, worse outcomes were seen with CXCR4 mutations (5-year PFS: 45% vs. 71%; HR 2.8, 95% CI 1.4-5.8; p=0.004) and serum albumin <3.5 g/dl (5-year PFS: 36% vs. 68%; HR 2.7, 95% CI 1.3-5.5; p=0.007). A novel PFS risk score was designed using CXCR4 mutational status and serum albumin (Figure), which divided patients into 3 distinct groups: low risk (no risk factors: 43%; 5-year PFS 81%), intermediate risk (1 risk factor: 46%; 5-year PFS 51%) and high risk (2 risk factors: 11%; median PFS 25 months). The PFS difference between groups was statistically significant (p<0.001). The PFS risk score showed consistent results when evaluating previously treated and untreated patients, as well as patients on and off clinical trials.
Conclusion: Serum albumin and CXCR4 mutations emerge as important factors predictive of PR at 6 months and also prognostic of PFS in WM patients treated with ibrutinib. A novel PFS stratification tool that separates patients into 3 risk groups was established and would need further validation.
Castillo:Abbvie: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding. Hunter:Janssen: Consultancy. Treon:Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal