Background:
The treatment paradigm of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has changed significantly in the last decade with approval of multiple new targeted agents. Small molecule drugs such as ibrutinib, venetoclax, idelalisib and other targeted agents have improved the outcomes of patients with CLL treated in clinical trials. However, it is unclear if the population level outcomes of CLL have improved since the first approval of bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor Ibrutinib in February,2014.
Methods: Using SEER database, we identified patients aged ≥ 20 years with pathologically confirmed CLL (ICD-0-3 code 9823/3) diagnosed between 2011-2016 and actively followed. Patients were divided into two groups by the period of diagnosis - 2011-2013, 2014-2016, reflecting the period pre-and post-ibrutinib approval. Overall survival (OS) was compared between the two groups using Kaplan-Meier method and log rank test. Cox proportional hazard regression method was used to determine the influence of period and demographic factors on OS. Statistical analysis was performed with significant two-sided p< 0.05.
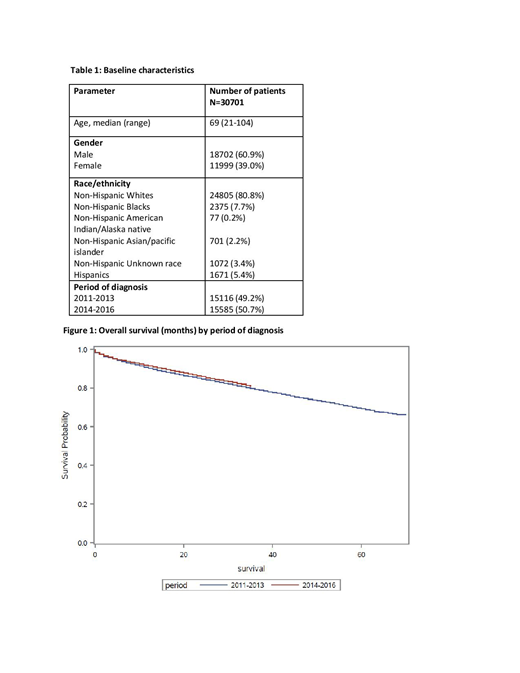
Results: A total of 30701 patients with a median age of 69 years (range 21-104) were included. Males (60.9%) and White race (80.8%) contributed to the majority as summarized in table 1. Median OS was not reached. OS at 30 months was significantly higher for patients diagnosed from 2014-2016 (83.3%) compared to those diagnosed from 2011-2013 (81.7%) (p=0.004) (figure 1). On multivariate analysis, diagnosis from 2014-2016 (HR 0.90, 95% CI 0.85-0.96, p: 0.002) and females (HR 0.74, 95% CI 0.70-0.78, p< 0.001) had lower mortality risk, whereas, increasing age (HR 1.07, 95% CI 1.07-1.08, p< 0.001), Hispanics (HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.05-1.32, p< 0.004), Non-Hispanic blacks (HR 1.41, 95% CI 1.28-1.54, p< 0.001) had higher risk of mortality.
Conclusions: Survival of patients with CLL at the population level is improving since approval of Ibrutinib. Non-biological factors such as age, gender and race/ethnicity continue to influence the survival even in the era of novel agents, highlighting the need for continued research to address these discrepancies.
Atallah:Jazz: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Helsinn: Consultancy; Helsinn: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding. Hamadani:Janssen: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Sanofi Genzyme: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Medimmune: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka: Research Funding. Guru Murthy:Cardinal Health Inc.: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal