Background and Significance
Although the prognosis of pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) has been significantly improved in recent years, adult patients continue to have dismal survival. This is partially due to the fact that adult patients tend to have more unfavorable cytogenetic characteristics such as MLL-AF4 fusion and BCR-ABL1 fusion. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent epigenetic modification on eukaryotic messenger RNA (mRNA), which plays important roles in many fundamental bioprocesses. The aberrant regulation of m6A modification is crucial for the initiation and progression of various cancers including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, the studies of m6A modification in B-ALL have been limited. Therefore, we began with the screening of essential m6A regulators in B-ALL with unfavorable cytogenetic characteristics.
Zinc Finger Protein 217 (ZNF217) is not only a Kruppel-like family of transcription factor but also a versatile m6A regulator. Although ZNF217 has been identified as a candidate oncogene and therapeutic target in many solid tumors, the potential function of ZNF217 in leukemia, especially in B-ALL, remains unknown.
Experimental Approach and Results
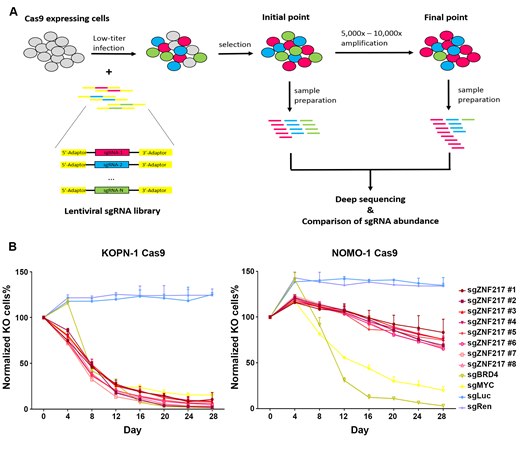
To determine which m6A machinery associated genes play essential roles in the survival/viability of B-ALL cells, we performed CRISPR/Cas9-based library screening using single-cloned B-ALL cells expressing Cas9. The sgRNA library contained sgRNAs targeting all the reported m6A machinery associated genes (including METTL3, METTL14, FTO; 25 sgRNAs per gene), 11 common essential genes, and scramble controls. The screening results suggested a set of m6A machinery associated genes, especially ZNF217, might be essential for the survival of B-ALL cells. To further rank these genes by their essentiality in B-ALL, we performed Model-based Analysis of Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout (MAGeCK). In our MAGeCK negative-selection ranking, ZNF217 was ranked as the top 1 candidate, indicating ZNF217 might be the most essential m6A regulator in B-ALL.
In agreement with these results, ZNF217 is also highly expressed in B-ALL. We analyzed the published gene expression datasets and found ZNF217 is highly expressed in B-ALL patients with different cytogenetic changes, including MLL-AF4 fusion and BCR-ABL1 fusion, compared to normal CD19+CD10+ B-cell progenitors.
To further validate the function of ZNF217, we perform growth competition experiments using B-ALL cells with either MLL-AF4 fusion or BCR-ABL1 fusion. We found that knockout of ZNF217 significantly decreased the competitive fitness of both B-ALL subtypes. In addition, we also found that knockout of ZNF217 in AML cells did not show significant effect on cell survival, suggesting the function of ZNF217 may be specific in B-lineage.
Conclusions
In summary, by use of CRISPR-Cas9 screening, we identified ZNF217 as an essential gene in B-ALL cells. We found ZNF217 is highly expressed in various subtypes of B-ALL patients, and our data suggest that ZNF217 is required for the survival of B-ALL cells, but not that of AML cells. Overall, our data indicate that ZNF217 plays an essential oncogenic role in B-ALL.
Figure Legend
A. Experimental scheme of CRISPR/Cas9-based library screening
B. Growth competition assays using B-ALL cells (left) and AML cells (right)
Chen:Genovel Biotech Corp: Other: scientific founder and Chairman.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal