Background:Plant homeodomain finger 6 (PHF6) is a tumor suppressor gene involved in chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. It has been found to be frequently mutated in lymphoid leukemias, especially T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and mixed phenotypic acute leukemia, and mutated in approximately 3% of myeloid leukemias, but its role in myeloid neoplasms is less well-characterized. We consequently investigated the impact of PHF6 mutations in patients (pts) with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated all pts with MDS, CMML, or AML treated between 2017-2019. Patient characteristics and bone marrow data, including cytogenetic and next generation sequencing information, were assessed. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole bone marrow aspirate samples and subject to 81-gene target PCR-based sequencing using a next generation sequencing (NGS) platform. Response assessment was performed following 2006 International Working Group (IWG) criteria for pts with MDS or CMML and by 2003 IWG criteria for pts with AML. The Kaplan-Meier product limit method was used to estimate survival outcomes for each clinical/demographic factor. Univariate Cox proportional hazards regression was used to identify any association with each of the variables and survival outcomes.
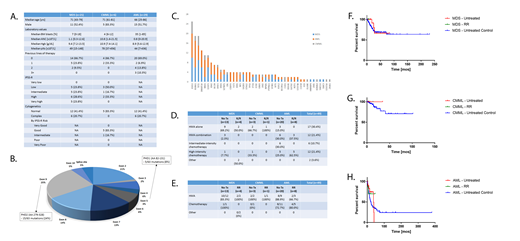
Results: A total of 56 pts with PHF6 mutations were identified: 21 with MDS, 6 with CMML, and 29 with AML (Figure A). Among these, 31 pts were male (55.4%). A total of 13 pts (61.9%) with MDS, 5 (83.3%) with CMML, and 12 (41.4%) with AML had normal karyotype, and only 6 pts (20.7%) had complex karyotype, all of which had AML. Forty-nine pts had 1 PHF6 mutation, and 7 pts had 2 PHF6 mutations. The median variant allelic frequency (VAF) was 10.20% for females and 30.98% for males, with 24 missense, 18 frameshift, 17 nonsense, and 3 splicing mutations identified. Five mutations (8%) occurred in PHD1 and 15 mutations (24%) in PHD2, the 2 zinc finger domains proposed in gene transcription regulation (Figure B). Sequential mutational data was available for 8 pts and revealed an overall increase in PHF6 VAF in 6 pts irrespective of response or therapy. The most commonly co-occurring mutations were those in ASXL1 in 25 pts, RUNX1 and TET2 in 19 pts each, and DNMT3A in 13 pts (Figure C).
Response was evaluable in 49 pts. Treatment consisted of hypomethylating agent (HMA) therapy alone in 17 pts (30.4%), HMAs in combination with other therapy in 12 pts (21.4%), intermediate-intensive chemotherapy in 6 pts (10.7%), and high-intensity chemotherapy in 12 pts (21.4%) (Figure D). Overall response rates (ORR) in evaluable pts were 83.3% in treatment-naïve MDS pts who received HMA-based therapy and 100% in those who received chemotherapy; 100% in relapsed/refractory (R/R) MDS pts who received HMA-based therapy; 100% in frontline HMA therapy for CMML pts and 0% in those who received frontline chemotherapy; 100% in R/R CMML pts who received HMA-based treatment; 88.9% in previously untreated AML pts who received HMA-based regimens and 72.7% in therapy-naïve AML pts who received chemotherapy-based regimens; and 66.7% in R/R AML pts who received HMAs and 80.0% in those who received chemotherapy (Figure E). With a median follow-up time of 15.2 months, median overall survival (OS) was not reached for both treatment-naïve and R/R MDS and CMML pts (Figures F and G), 37.0 months for previously untreated AML pts, and not reached for R/R AML pts (Figure H). When compared to newly-diagnosed MDS, CMML, and AML pts with wildtype PHF6 treated during this time period, there was a significant difference in median OS for MDS pts (p=0.001) but no significant differences in median OS for CMML or AML pts. For both treatment-naïve and R/R AML pts, there was no significant median OS difference between HMA-based therapy and chemotherapy-based treatments. Median transformation-free survival was not reached for MDS pts and 20.1 months for CMML pts.
Conclusions:PHF6 mutations are relatively uncommon in pts with MDS, CMML, or AML but appear to be associated with normal cytogenetics and mutations in ASXL1, RUNX1, TET2, and DNMT3A. In this small cohort of pts, a statistically significant difference in median OS for MDS pts was observed with no significant differences for CMML or AML pts.
Sasaki:Otsuka: Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy. Alvarado:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Abbott: Honoraria. Takahashi:Symbio Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Kadia:Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Bioline RX: Research Funding. Borthakur:AbbVie: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Xbiotech USA: Research Funding; BioTheryX: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Argenx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; FTC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cantargia AB: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Arvinas: Research Funding; Polaris: Research Funding; Strategia Therapeutics: Research Funding; Tetralogic Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Eisai: Research Funding; NKarta: Consultancy; BioLine Rx: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Oncoceutics, Inc.: Research Funding; Eli Lilly and Co.: Research Funding; PTC Therapeutics: Consultancy; BMS: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare AG: Research Funding; Oncoceutics: Research Funding. Jabbour:Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Adaptive: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cyclacel LTD: Research Funding. Kantarjian:Immunogen: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz Pharma: Research Funding; Astex: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Garcia-Manero:Amphivena: Consultancy, Research Funding; Helsinn: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astex: Consultancy, Research Funding; Onconova: Research Funding; H3 Biomedicine: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal