Introduction: Venetoclax (VEN), a selective BCL-2 inhibitor, has yielded exceptional response rates in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). VEN binds BCL-2 to directly inhibit sequestration of pro-apoptotic proteins such as the activator BIM. Free BIM can bind to BAX, enabling its oligomerization with BAK, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and subsequent apoptosis (PMID 24074954, 9687260, 19641500, 20164920). VEN has limited efficacy in relapsed-refractory AML as a single agent, but when used in combination with DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi; 5'azacitidine-AZA-or decitabine) or low-dose cytosine arabinoside (LDAC), 50-70% of untreated patients in recent clinical trials achieved complete remission (PMID 27520294, 30361262, 30892988). Despite this progress in AML therapy, the majority of AML patients treated with VEN ultimately relapse, and a large subset of patients never respond (PMID 30361262, 30892988). One postulated route of resistance to VEN is cellular upregulation of myeloid cell leukemia-1 protein (MCL-1), which, similarly to BCL-2, functions as an anti-apoptotic protein. VEN in combination with selective MCL-1 inhibitors has demonstrated added benefit over either agent alone in AML cells in vitro and in xenograft models but efficacy of this combination in the clinic has yet to be reported (PMID 30185627). Both MCL-1-dependent and MCL-1-independent mechanisms of VEN resistance are emerging (PMID 31048321, 30148320, 31262744) and new approaches aimed at addressing these are moving toward the clinic. Pevonedistat (PEV) was developed as a targeted inhibitor of NEDD-8 activating enzyme (NAE), which disrupts protein turnover mediated by Cullin-RING ligases (PMID 19360080) and has been shown to have activity in combination with AZA (PMID 29348128). PEV and AZA both upregulate NOXA, a BCL-2 family member that is known to suppress MCL-1 (PMID 26045051, Jin, Cojocari, Purkal et al.,unpublished data), so we postulated that PEV/AZA in combination synergizes with VEN in a triple combination with efficacy superior to VEN/AZA alone.
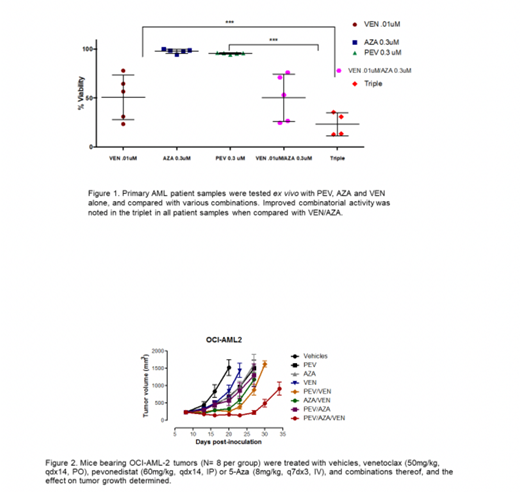
Methods/Results: AML cell lines were treated with PEV, AZA and VEN alone, and compared with various VEN/PEV/AZA combinations revealing improved combinatorial activity with the triplet in the majority of cell lines and associated NOXA induction. Similar results were seen in primary AML patient samples ex vivo (Figure 1). These combinations were compared in vivo in an OCI-AML2 cell line xenograft model, also illustrating significantly improved response with the PEV/AZA/VEN combination (Figure 2). CRISPR/Cas 9 deletion of PMAIP1 in AML cell lines demonstrated that NOXA deletion abrogates this synergy.
Discussion: Together, these results demonstrate that, in several pre-clinical models of AML, the PEV/AZA/VEN triple combination provides stronger anti-tumorigenic activity than either agent alone or the VEN/PEV and VEN/AZA combinations. Importantly, the three-drug combination may be effective in AML cells which do not respond to VEN/AZA alone. Further studies to delineate this mechanism of action, and a clinical trial (NCT03862157) testing the combination in newly diagnosed AML are underway.
Cojocari:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: DC, JP, ERB, JDL, and DCP are employees of AbbVie. JP, ERB, JDL & DCP are stockholders of AbbVie Inc. The design study conduct, and financial support for this research were provided by AbbVie. AbbVie Inc. participated in the interpretation of data, review. Purkal:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: DC, JP, ERB, JDL, and DCP are employees of AbbVie. JP, ERB, JDL & DCP are stockholders of AbbVie Inc. The design study conduct, and financial support for this research were provided by AbbVie. AbbVie Inc. participated in the interpretation of data, review. Leverson:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock or options. Boghaert:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: DC, JP, ERB, JDL, and DCP are employees of AbbVie. JP, ERB, JDL & DCP are stockholders of AbbVie Inc. The design study conduct, and financial support for this research were provided by AbbVie. AbbVie Inc. participated in the interpretation of data, review. Phillips:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: DC, JP, ERB, JDL, and DCP are employees of AbbVie. JP, ERB, JDL & DCP are stockholders of AbbVie Inc. The design study conduct, and financial support for this research were provided by AbbVie. AbbVie Inc. participated in the interpretation of data, review. Savona:AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Patents & Royalties; Celgene Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Selvita: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal