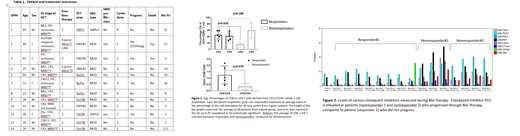
Background: Patients with high-risk or multiply relapsed B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have a very high rate of relapse, even after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). In an effort to reduce the risk for relapse, we investigated the role of blinatumomab (Blin), a bi-specific T cell immunotherapy targeting CD19, as maintenance therapy following allogeneic HCT for adult patients with advanced B ALL. We rationalized that this is an ideal agent with little cytotoxicity, and the potential to provide immune protection against disease relapse during the first year post HCT when graft versus leukemia (GVL) is still maturing. Methods: Adult patients with B-ALL deemed high risk for relapse defined as disease stage beyond CR1, any active disease including MRD, or presence of high risk molecular mutations or karyotype at time of HCT, or patients with evidence of MRD immediately following HCT, were eligible for study enrollment; prior Blin treatment was allowed. Patients with active disease defined as >5% malignant blasts or active GVHD requiring steroid therapy post HCT were excluded. Patients were scheduled to receive 4 cycles of Blin as a continuous intravenous infusion at the dose of 28 microgram/24 hours over 4 weeks, with the first cycle to be administered within the first 3 months post HCT after count recovery; the subsequent cycles were administered at 6, 9, and 12 months following HCT (day of hematopoietic progenitor cell infusion). Dose escalation for cycle 1 and hospitalization for observation during cycles 1 and 2 followed standard FDA issued guidelines. Results: 14 patients enrolled to date with 12 patients treated with median age 30 years (range, 21-65 years); two patients did not proceed with treatment due to graft versus host disease (GVHD). Patient characteristics and outcomes are listed in Table 1. The median days to start of therapy post HCT was 84 (range, 38-105 days). The treatment was well tolerated with no reported cytokine release syndrome, GVHD, graft failure, or grade 5 adverse events (AE). A cumulative 26 cycles of Blin were administered with 7 Blin-related grade 3 or 4 AEs reported (leukopenia n=4, transaminitis n=2, rash n=1). Grade 2 neurotoxicity manifesting as confusion and dysphagia requiring temporary suspension of therapy and short course steroids noted in 1 patient. Median follow up was 8.5 months post HCT (range 2-35 months). All 4 patients who were MRD positive prior to start of Blin have progressed and 2 have died. None of the 8 patients who were MRD negative post transplant has relapsed. We performed multiparametric flow cytometry studies on serial peripheral blood patient samples collected prospectively at multiple time points to measure T cell subsets, T-cell function and cell surface expression of various checkpoint inhibitors including PD1, TIGIT, Tim3, 2B4 and CD160. Samples were studied on an X-20 Fortessa, and the data analyzed using Kaluza software. Interestingly, the 4 patients who progressed on Blin maintenance had lower CD8 to CD4 ratio compared to non-progressors (17:60 vs. 46:42) (Figure 1). Furthermore, compared to healthy controls, we observed higher levels of checkpoint molecules as multiple checkpoints per cell. PD1 and TIGIT upregulation and co-expression were more common in progressing patients compared to non-progressors (Figure 2). Conclusion: We observed that Blin maintenance following allogeneic HCT for B ALL is well tolerated. More patients need to be treated to confirm the efficacy of this approach. This approach is encouraging for high risk ALL patients who are MRD negative post transplant. Strategies to increase CD8 levels and blockade against checkpoint inhibitors may overcome resistance to therapy.
Kebriaei:Amgen: Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Pfizer: Honoraria; Kite: Honoraria. Ravandi:Xencor: Consultancy, Research Funding; Selvita: Research Funding; Macrogenix: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Menarini Ricerche: Research Funding; Cyclacel LTD: Research Funding. Jabbour:Adaptive: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cyclacel LTD: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kantarjian:AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Jazz Pharma: Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Research Funding; Ariad: Research Funding. Champlin:Sanofi-Genzyme: Research Funding; Johnson and Johnson: Consultancy; Actinium: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal