Background and significance:MLL-gene rearrangements occur in ~10% of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and 70% of infant B-ALL and define a group of patients with dismal outcomes. MLL belongs to the family of histone methyltransferases and plays a critical role in maintaining hematopoietic stem cells (Jude et al. 2007). Analyzing gene expression data from 207 children with high-risk ALL, we found that BCL6 is a predictor of poor clinical outcome in B-ALL, particularly in cases with MLL rearrangements. Thus, while the mechanisms of drug-resistance in MLL-rearranged B-ALL are largely unknown, we studied here a potential role of BCL6 in promoting the aggressive and refractory phenotype in this subtype of B-ALL.
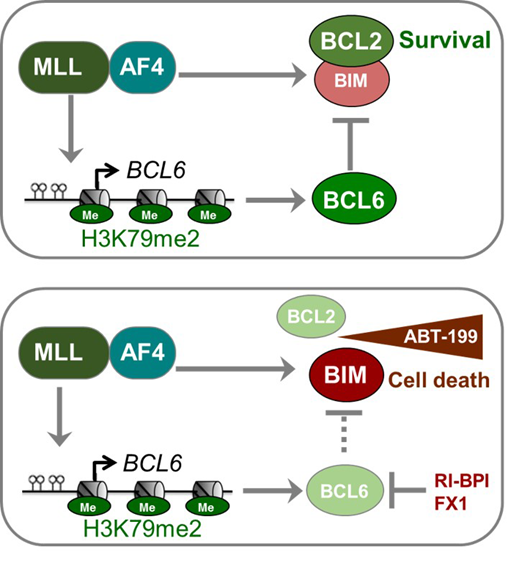
Results: Immunohistochemical staining of bone marrow biopsies from 10 of 11 MLL-rearranged B-ALL samples studied revealed aberrant expression of BCL6, a transcription factor that promotes oncogenic B-cell transformation and drug-resistance in B-ALL (Duy et al. Nature 2011). Our genetic and ChIP-seq analyses showed that MLL-AF4 and MLL-ENL fusions directly bound to the BCL6 promoter and upregulated BCL6 expression. While oncogenic MLL-fusions strongly induced aberrant BCL6 expression in B-ALL cells, germline MLL was required to upregulate Bcl6 in response to physiological stimuli during normal B-cell development. Inducible expression of Bcl6 increased MLL mRNA levels, which was reversed by genetic deletion and pharmacological inhibition of Bcl6, suggesting a positive feedback loop between MLL and BCL6. Highlighting the central role of BCL6 in MLL-rearranged B-ALL, conditional deletion and pharmacological inhibition of BCL6 compromised leukemogenesis in transplant recipient mice and restored sensitivity to vincristine chemotherapy in MLL-rearranged B-ALL patient samples. Oncogenic MLL-fusions strongly induced transcriptional activation of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only molecule BIM, while BCL6 was required to curb MLL-induced expression of BIM. Notably, peptide (RI-BPI) and small-molecule (FX1) BCL6-inhibitors derepressed BIM and synergized with the BH3-mimetic ABT-199 in eradicating MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells. These findings uncover MLL-dependent transcriptional activation of BCL6 as a previously unrecognized requirement of malignant transformation by oncogenic MLL-fusions and identified BCL6 as a novel target for the treatment of MLL-rearranged B-ALL.
Discussion: Pharmacological inhibition of BCL6 using a retro-inverso peptide inhibitor (RI-BPI) compromised MLL-rearranged B-ALL leukemia-initiation and subverted vincristine-resistance. A central mechanistic aspect of BCL6-function in MLL-rearranged B-ALL involves transcriptional repression of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only molecule Bim (BCL2L11). Profiling for BH3-only proteins in various B-ALL subtypes revealed that MLL-rearranged B-ALL is associated with increased expression of the pro-apoptotic protein BIM (Benito et al. 2015). ABT-199 (venetoclax) is a BH3-mimetic that disrupts the interaction between BCL2 and BIM, leading to BIM release and induction of apoptosis. Previous studies have found that MLL-rearranged leukemia cells are sensitive to the BCL2 inhibitor ABT-199. Besides BCL2, we here identified BCL6 as a central antagonist of pro-apoptotic BIM function in MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells. In genetic experiments, we showed that oncogenic MLL-fusions strongly activated BCL2L11 transcription reinforcing the notion that constitutively high Bim expression levels represents an important and selective vulnerability in MLL-rearranged B-ALL. Both BCL2 and BCL6 represent crucial antagonists of BIM in MLL-rearranged B-ALL, BCL2 mediating BIM-sequestration and BCL6 being required for transcriptional repression of BIM. In support of this scenario, peptide (RI-BPI) and small molecule (FX1) inhibitors of BCL6 strongly synergized with blockade of BCL2-mediated BIM sequestration (ABT-199) in killing MLL-rearranged B-ALL cells.
Armstrong:AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Epizyme, Inc.: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Imago Biosciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Cyteir Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Janssen: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Accent Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Mana Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; C4 Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Syros Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; OxStem Oncology: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Melnick:Janssen: Research Funding; Constellation: Consultancy; Epizyme: Consultancy. Milne:OxStem Ltd.: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal