Abstract
Introduction
The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis was shown to be a major regulator for the interaction of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) with the niche and interruption of this pathway mobilizes HSCs from the bone marrow (BM).Therefore CXCR4 antagonists like AMD3100 (Plerixafor) are used in the clinic for the collection of HSCs from patients who fail to mobilize HSCs in response to G-CSF.In our previous studies, we could show that the serine/threonine kinase PIM1 is regulating the surface expression of the CXCR4 receptor on HSCs. In addition, PIM1-deficient HSCs fail to home to a wild type (WT) BM niche. Based on these results, we aimed to improve HSC mobilization by combining CXCR4 and PIM inhibition.
Methods
In order to study the mobilization efficiency in the murine model, mice were treated with AMD3100 alone or in combination with LGB321, a novel pan-PIM inhibitor. The mice were sacrificed at various timepoints and peripheral blood (PB) was isolated. The percentage of HSCs was then determined by flow cytometry. The mechanism of HSC mobilization was studied in isolated HSC and stroma populations by analyzing mRNA levels and surface expression of CXCR4, its ligand CXCL-12 and other factors, which are crucial for the interaction of HSCs and stromal cells.
Results
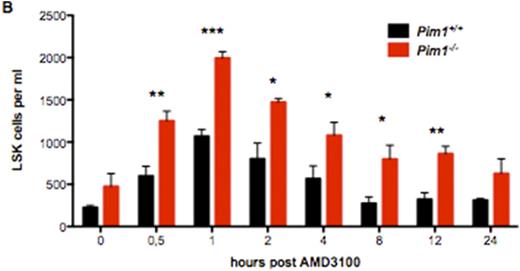
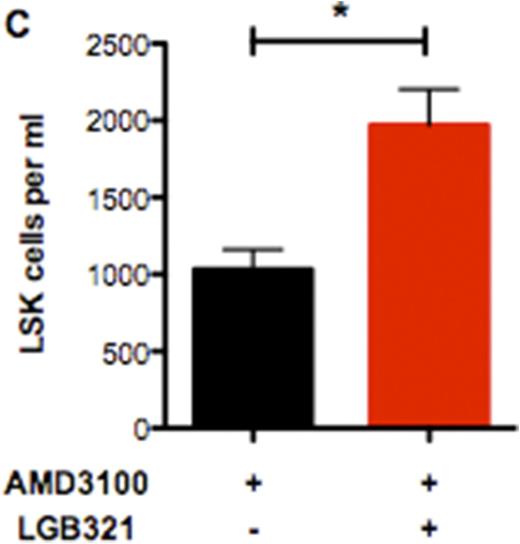
We found that CXCR4 inhibition using AMD3100 leads to a compensatory upregulation of CXCR4 surface expression on total BM cells as well as HSCs. This effect can be reverted by deficiency or inhibition of PIM1 (Figure 1A). As a consequence, HSC mobilization using AMD3100 is strongly enhanced and prolonged in Pim1-deficient mice compared to WT animals (Figure 1B). Likewise, treatment of WT animals with AMD3100 in combination with LGB321 leads to increased and prolonged HSC mobilization compared to animals treated only with AMD3100 (Figure 1C). Besides the downregulation of CXCR4 on HSCs, we found that the Cxcl-12 expression as well as CXCR4 surface expression in CXCL12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells is dramatically decreased in Pim1-deficient mice, which even further increases the mobilization capacity of Pim1-deficient mice.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate, that PIM1 inhibition counteracts the compensatory upregulation of the CXCR4 receptor on HSCs after Plerixafor treatment and decreases CXCL12 levels within the bone marrow niche. Therefore, targeting PIM kinases in combination with CXCR4 inhibition could improve the collection of stem cells in patients at risk for poor mobilization.
PIM1-deficiency or -inhibition enhances HSC mobilization in combination with AMD3100-treatment. (A) Statistical analysis of CXCR4 surface expression on Pim1-/- or WT LSK cells after AMD3100-treatment for 24h. PIM1-deficiency reverts the increased CXCR4 surface expression after AMD3100-treatment. (B) Time course of total LSK cells per ml PB of AMD3100-treated mice. Pim1-/- mice show significantly higher LSK counts. (C) Statistical analysis of total LSK cells per ml of LGB321+AMD3100 treated mice compared to AMD3100-only treated WT animals. PIM-inhibition significantly increases mobilization efficiency of AMD3100.
PIM1-deficiency or -inhibition enhances HSC mobilization in combination with AMD3100-treatment. (A) Statistical analysis of CXCR4 surface expression on Pim1-/- or WT LSK cells after AMD3100-treatment for 24h. PIM1-deficiency reverts the increased CXCR4 surface expression after AMD3100-treatment. (B) Time course of total LSK cells per ml PB of AMD3100-treated mice. Pim1-/- mice show significantly higher LSK counts. (C) Statistical analysis of total LSK cells per ml of LGB321+AMD3100 treated mice compared to AMD3100-only treated WT animals. PIM-inhibition significantly increases mobilization efficiency of AMD3100.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal