Abstract
Inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response via blockade of inositol-requiring enzyme-1α (IRE-1α) is currently a promising therapeutic strategy to treat B-cell leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. Because B cells play an important role in the development of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), we hypothesize that the ER stress response contributes to B-cell function and pathogenicity in cGVHD. Here, we report that the ER stress response mediated by IRE-1α and its target X-box binding protein-1 (XBP-1) plays a critical role in cGVHD pathophysiology and represents a potential therapeutic target to prevent cGVHD.
We tested the role of XBP-1 specifically in B cells by testing XBP-1 conditional knockout B cell grafts (XBP1fl/flCD19Cre+) in two mouse models of cGVHD. In the first model (B6 to BALB/c), recipients given XBP-1-deficient donor grafts showed significantly reduced cGVHD clinical scores, which were associated with reduced frequencies of donor-derived CD4 helper T cells within the lungs compared to the recipients of XBP-1fl/flCD19Cre- littermate donor grafts. XBP-1-deficient B cells produced significantly higher levels of IL-10 compared to WT control B cells after activation ex vivo. In the second model (B6 to B10.BR), the conversion of donor B cells to plasma cells (B220+CD38+CD138+) was reduced in both the spleens and lungs of recipients transplanted with XBP1fl/flCD19Cre+ grafts compared to those of the recipients given XBP1fl/flCD19Cre- grafts. Recipients given XBP1fl/flCD19Cre+ grafts also showed significantly higher total splenocytes and vastly increased splenic B-cell populations when compared with the recipients of XBP1fl/flCD19Cre- grafts.
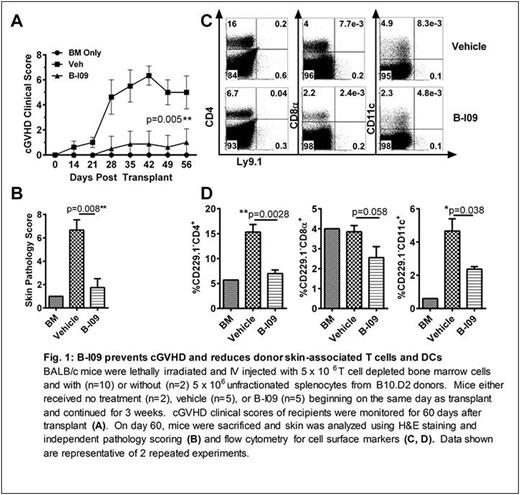
To expand on these findings, we tested if systemic XBP-1 blockade via a novel IRE-1α inhibitor, B-I09, would attenuate cGVHD. In a cutaneous model of cGVHD (B10.D2 to BALB/c), we found that prophylactic administration of B-I09 significantly reduced clinical features of cGVHD compared to vehicle controls (Fig. 1A). Validating these findings, hematoxylin and eosin stained skin sections of B-I09-treated mice had significantly lower pathology scores compared to vehicle controls (Fig. 1B). Isolated skin lymphocytes from recipients treated with B-I09 showed significant reductions in donor derived T cells and DCs compared to those treated with vehicle controls (Fig. 1C and D).
Taken together, our findings reveal a novel role of the IRE-1α/XBP-1 pathway of the ER stress response in cGVHD pathophysiology and provide a readily translatable strategy to prevent the development of cGVHD in the clinic.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal