Abstract
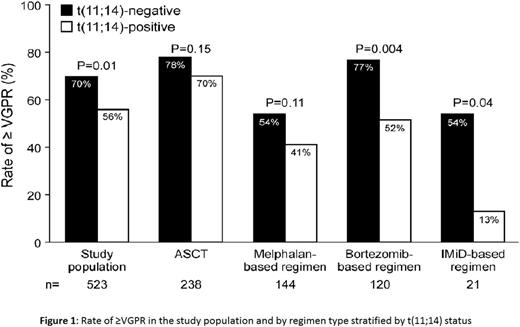
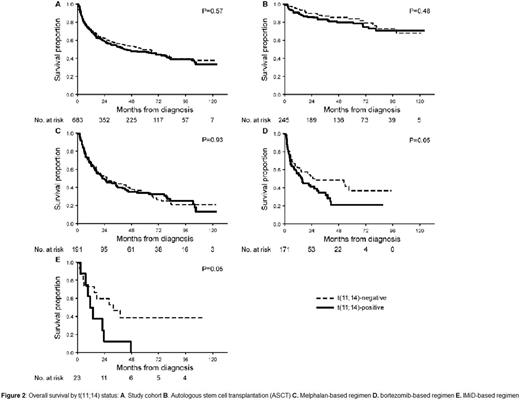
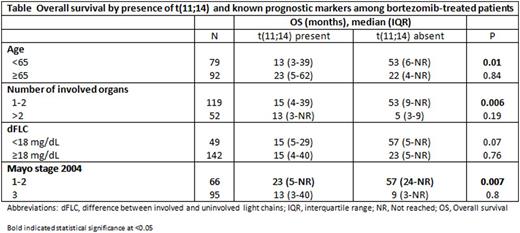
The impact of fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) on outcome in AL amyloidosis remains uncertain. We analyzed the response and overall survival (OS) of 692 AL amyloidosis patients with available FISH testing at diagnosis. First line treatment was categorized as autologous stem cell transplant or three non-transplant regimens (melphalan-based; bortezomib-based, and immunomodulatory drug (IMiD)-based). Forty-nine percent of patients had t(11;14), 37% del 13q/monosomy 13 and 19% had trisomy/tetrasomy. Analysis by abnormality type was restricted to t(11;14) and trisomy/tetrasomy sub-groups as chromosome 13 abnormalities were commonly associated with the other abnormalities. Patients with t(11;14) had lower rate of very good partial response or better (≥VGPR) compared to those lacking t(11;14) (56% vs 70%, P=0.001). By regimen stratification, this difference was maintained for bortezomib-based (52% vs 77%; P=0.004) and IMiD-based therapy (13% vs 54%; P=0.04) (Figure 1). Patients with trisomy/tetrasomy had no difference in the rate of ≥VGPR compared to those who did not (66% vs 63%, P=0.62), with no difference within regimen types. OS was similar between t(11;14)-positive and negative patients (median 43 vs 57 months; P=0.58). However, sub-analysis by regimen type showed a significantly inferior OS among t(11;14)-positive bortezomib-treated patients (median 15 vs 27 months; P=0.05) and t(11;14)-positive IMiD-treated patients (median 12 vs 32 months; P=0.05) (Figure 2). Among t(11;14)-positive bortezomib-treated patients, the OS difference was maintained among favorable-prognosis patients, but was absent for poor-prognosis sub-groups (Table). Trisomy/tetrasomy was associated with inferior OS (median 29 vs 69 months; P=0.001), a difference that was maintained for melphalan (median 15 vs 32 months; P=0.01) and borderline significance for bortezomib (median 14 vs 38 months; P=0.09). Multivariate analysis confirmed an independent effect on OS for trisomy/tetrasomy in the study cohort and for t(11;14) among bortezomib-treated patients. FISH analysis is essential in newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis, as it provides prognostic information among treatment groups and may influence the selection of induction treatment. Patients with t(11;14) should be considered for ASCT at diagnosis.
Dispenzieri:Celgene: Research Funding; Alnylam: Research Funding; pfizer: Research Funding; Prothena: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jannsen: Research Funding. Kumar:Glycomimetics: Consultancy; AbbVie: Research Funding; Array BioPharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kesios: Consultancy; Onyx: Consultancy, Research Funding; Noxxon Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; Skyline: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kapoor:Amgen: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal