Abstract
Introduction: Ibrutinib is a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has significant activity in treating lymphoma. While approved for patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL), its activity in other lymphomas and solid tumors is under investigation and its use is increasing dramatically. Overall it is well tolerated compared to chemotherapy, but bleeding has emerged as a common adverse event with rates as high as 50% and major bleeding around 3% (Jones, abstract #1990, 2014 ASH Annual Meeting). As the use of ibrutinib increases outside of a clinical trial setting, the rate of major bleeding is likely to rise.
Methods: To better understand the risk of bleeding in ibrutinib treated patients, we reviewed all patients at the University of Virginia and satellite clinics who were treated with ibrutinib between January 2012 and May 2016. Patients were required to be treated for at least 1 month with documented follow up for assessment of adverse events. Medical charts were reviewed for age, gender, ibrutinib indication and dose, length of treatment, concurrent medications, blood tests and bleeding events. All forms of anti-platelets and anticoagulants drugs, as well as medications interacting with cytochrome P450 3A4 (3A4), which metabolizes ibrutinib, were recorded. All bleeding events were recorded and graded according the Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events, v4.0. Major bleeding events were reviewed by all investigators.
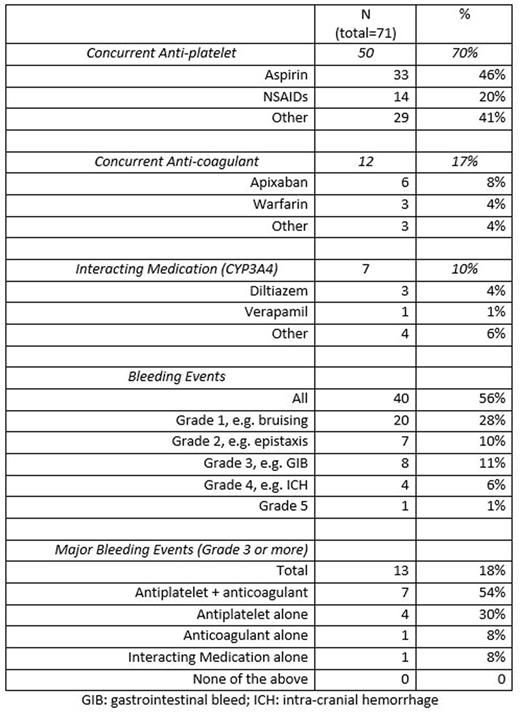
Results: Eighty-nine patients were identified. Eighteen patients were excluded for insufficient follow up leaving 71 patients for analysis. Median age was 73 years old (44-92) with 74% male. The most common indications for treatment were CLL (65%) and MCL (27%). Most patients were treated with either 420mg (64%) or 560mg (21%). Median length of time on ibrutinib was 412 days, most with ongoing use at time of data collection. Seventy percent of patients were also treated with an anti-platelet medication, mostly aspirin for CAD with several patients on multiple anti-platelet medications. Seventeen percent were treated with an anti-coagulant, mostly apixaban for atrial fibrillation. Thirteen percent of patients (9/71) were treated with combined anti-platelet and anti-coagulant medications. Ten percent of patients were treated with a medication that has a moderate or strong interaction with 3A4. Bleeding of any grade occurred in 56% of patients, mostly bruising and epistaxis. Major bleeding, defined as grade 3 or higher, occurred in 18% of patients. Three patients developed major bleeding after an invasive procedure without ibrutinib being held. One patient died as a result of peri-procedural bleeding. Of the 9 patients treated with combined anti-platelet and anti-coagulant therapy, 78% suffered a major bleeding event. Of the ten patients on ibrutinib alone, without concurrent use of an anti-platelet, anti-coagulant or 3A4 drug interaction, no major bleeding events occurred.
Conclusion: In this study examining real world use of ibrutinib, the rates of major bleeding are higher than previously reported. Most patients who suffered major bleeding were also treated with an anti-coagulant and/or anti-platelet medication. As the use of ibrutinib increases outside of clinical trials, a careful review of medications should be performed in addition to adherence to perioperative drug withholding guidelines. Patients requiring anti-coagulant and/or anti-platelet medications while on ibrutinib need careful consideration of the risks and benefits given the higher incidence of bleeding in this population.
Portell:AbbVie: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding. Williams:Janssen and Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; University of Virginia: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal