Abstract
Inhibitors of B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling have proven effective in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). An important downstream mediator of BCR signaling is phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3Kd), which through activation of AKT, controls cell survival, growth and proliferation. Since it is expressed predominantly in cells of hematopoietic origin, PI3Kd is a promising target in CLL, and the novel PI3Kd inhibitor idelalisib is effective in treating relapsed/refractory CLL. However, a subset of patients relapse under therapy, and the mechanisms leading to resistance are not understood.
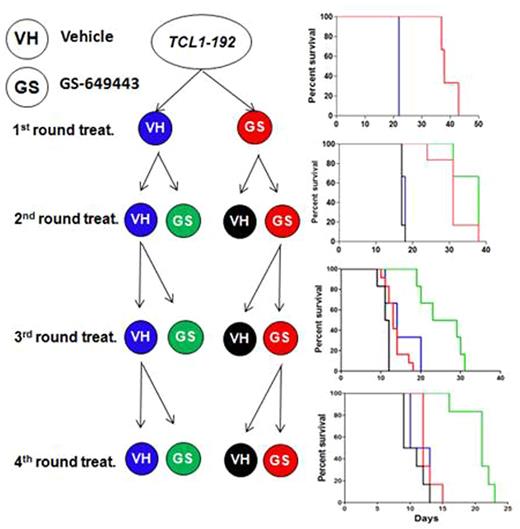
To generate and study resistance mechanisms in vivo, a tool compound GS-649443 with favorable murine pharmacokinetic properties in vivo as compared to Idelalisib was used. GS-649443 is a highly specific and potent small molecule inhibitor of the PI3K isoform d, with an IC50 of 0.3nM and 86/420/4120 fold selectivity over PI3K isoforms g/b/a respectively. We performed an in vivo serial transfer and treatment scheme to generate specific resistance against GS-649443 using the transferable murine CLL clone TCL1-192(Chen SS et al., 2013). 5 million TCL1-192 cells were transferred by intravenous injection into the tail vein of CB17.SCID mice, followed by treatment with vehicle (N=12) or 5mg/kg GS-649443 (N=12) twice daily by oral gavage, starting from day 10. Analysis of the animals (N=6 vs. 6) at the death of the vehicle treated mice (11 days) showed a drastic reduction in spleen weight (median 0.650g vs. 0.345g, P=0.005), liver weight (median2.025g vs. 1.145g, P=0.0022) and WBC count (median220.4 cells/nl vs. 1.7 cells/nl, P=0.0078) as compared to vehicle treated mice. Also, GS-649443 treatment almost doubled the survival of the mice in comparison to vehicle treatment (Fig. 1, P=0.0011). To generate resistance against GS-649443 in vivo, TCL1-192 cells were kept under selection pressure using serial transfers and subsequent treatment. After three rounds of transfer and treatment, the mice treated with GS-649443 failed to respond and showed a survival identical to vehicle controls (Fig.1).
Mutations acquired over time during the serial transfers in TCL1-192 cells from resistant mice were identified using whole exome sequencing. 64 treatment specific mutations were identified with a tumor variant allele frequency of ≥10%. Intriguingly, no single recurrent mutation that would likely contribute to drug resistance was identified. This is similar to the observation in patients refractory to idelalisib (abstract Ghia et al., submitted to ASH 2016). However, a subset of the genes such as Grb2, Mylk, Srfbp1, Ptk2, Cd44 and Prkd1 harboring mutations could be functionally grouped into integrin and extracellular matrix signaling. Consistent with this, all the resistant tumors showed a significant upregulation of genes involved in the integrin receptor complex such as talin 1 (P=0.004), talin 2 (P=0.004) and vinculin (P=0.009).
RNAseq analysis for detecting changes in gene expression identified an upregulation of Igf1r expression in the resistant samples compared to vehicle treated samples (P<0.0001), which could be confirmed at the protein level using western blotting. The upregulation of Igf1r may be attributed to downregulation of WT1 in all the resistant samples (P=0.0061). WT1 is a transcriptional repressor of Igf1r, whose expression is mediated by PI3K/AKT. Treatment with GS-649443 in general led to an increase in Igf1r levels in all tumor samples compared to vehicle treatment but the increase was much more robust in the resistant TCL1-192 samples. Targeting Igf1r using linsitinib as a single agent failed to show a response (P=0.6538) since Igf1r was found to revert to normal levels in the absence of GS-649443. In contrast,the combination treatment with linsitinib and GS-649443 significantly improved survival of mice with resistant TCL1-192 as well as mice with sensitive TCL1-192 (P=0.0074 vs. P=0.0023).
The synergy between the receptor tyrosine kinases such as IGF1R and integrin mediated signaling is established in different cancers and a similar mechanism may play a role in compensating for the inhibition of BCR mediated PI3K/AKT signaling. In conclusion, resistance to a tool PI3Kd inhibitor is not mediated by unique recurrent mutations but by alterations in survival signaling with mutations playing a probable cooperative role.
Treatment scheme for generation of resistance in vivo.
Tausch:Celgene: Other: Travel support; Amgen: Other: Travel support; Gilead: Other: Travel support, Speakers Bureau. Yahiaoui:Gilead Sciences: Employment. Munugalavadla:Gilead Sciences: Employment, Equity Ownership. Tannheimer:Gilead Sciences: Employment. Stilgenbauer:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Hoffmann-La Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal