Abstract
Introduction: Management of Ph+ ALL has changed since the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). We previously reported the preliminary findings of the GIMEMA LAL 1509 total therapy protocol, based on dasatinib plus steroids administration as induction therapy (Chiaretti et al, ASH 2014). The updated results on overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and the impact of a genetic-based prognostic stratification are hereby provided.
Methods: Steroids were administered from day -6 to day 31. Dasatinib (140 mg/day) was given between days 1 and 84. Patients reaching a complete molecular response (CMR, i.e. BCR/ABL1 to ABL1 ratio=0) at the end of induction (day 85) continued Dasatinib. Patients in complete hematologic remission (CHR), but not in CMR, underwent chemotherapy (clofarabine-cyclophosphamide) and/or an allogeneic transplant (HSCT), according to eligibility and donor availability. Dasatinib was administered until disease progression. Molecular testing was used to identify the presence of the BCR/ABL1 transcript on bone marrow samples, to define the fusion protein and to quantify BCR/ABL1 levels at baseline and follow-up (FU). Mutational screening was performed in relapsed cases, based on material availability. SNP array analysis was carried out using the Cytoscan HD arrays (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) to identify genomic aberrations.
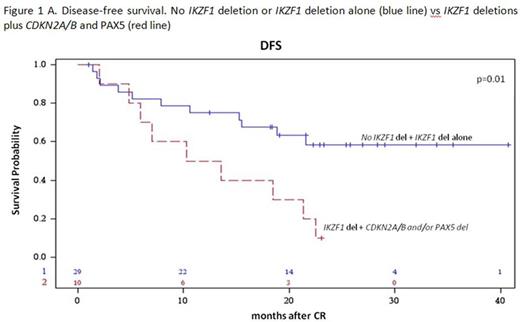
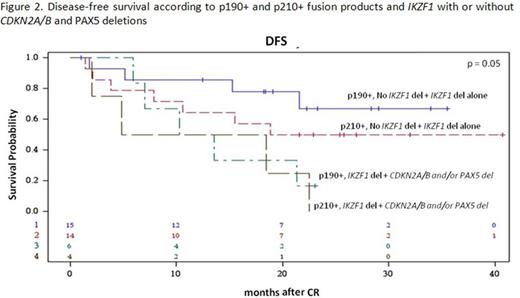
Results: 60/63 enrolled patients were eligible. Median age was 41.9 years (range 18.7-59.1), 34 were males and 26 females; median WBC count was 12.5 x 109/l (range 1.4-178.0); the p190 fusion product was detected in 33 patients, p210 in 18 and p190/p210 in 9. Median FU is 28.4 months (range 4.2-43.7). After the steroid pre-phase, 38 patients (63%) had a blast reduction ≥75%. At day 85, 58 patients were in CHR (97%), while 2, in CHR at day 57, lost it: both harbored the p210 fusion transcript. They both returned into CHR following chemotherapy. A sustained CMR was obtained in 11 patients (18.6%): 72% had a p190 fusion transcript. No deaths in induction occurred. Among the CMR patients, only 1 experienced a hematologic relapse, which carried a T315I mutation. Of the 46 non-CMR cases, 14 relapses occurred, 8 of which in p210+ patients. Overall, there have been 12 deaths in CHR. OS is 58.3% (95%CI: 44.4-76.3) at 36 months and DFS at 30 months is 48.9% (95%CI: 36.8.0-64.9). A better DFS was observed in patients who obtained a CMR compared to cases with minimal residual disease (MRD) at day 85 (75% vs 44%, p=0.06), and in p190+ vs p210+ patients (57.1% vs 39.6%, p=ns). Mutational screening, performed in 7/15 cases at hematologic relapse detected mutations in 5: 3 T315I and 2 V299L, of which 1 with a concomitant F317I and F317L. SNP array analysis, performed in 39 cases with available DNA, showed that the most frequent aberrations were deletions of IKZF1 (85%), PAX5 (38%), CDKN2A/B (33%), MLLT3 (33%), RB1 (28%) and JAK2 (28%). While IKZF1 deletions alone did not impact on CHR or CMRachievement and DFS, a significantly worse DFS (p=0.01) and increased cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR, p=0.024) were observed in cases harboring deletions of IKZF1 plus CDKN2A/B and PAX5 (DFS: 40% vs 65% at 18 months; CIR: 40% vs 14% at 18 months (Fig. 1A and B). The relevance of this finding was further refined by stratifying patients according to the fusion protein: the impact of IKZF1 plus CDKN2A/B and PAX5 deletions is prognostically relevant in p190+, but not in p210+ patients, possibly because of the worse outcome of the latter group (Fig. 2). Finally, this analysis identified a set of genes specifically deleted in CMR cases; investigations are ongoing on additional cases to validate their potential role in predicting response to TKI.
Conclusions: In this updated analysis of the GIMEMA 1509 trial, we confirm the effectiveness of a chemo-free induction in inducing CHR in almost all adult Ph+ ALL patients (97%) and CMR in a subgroup of cases (18.6%). OS and DFS at 36 months and 30 months, approaching 60% and 50%, are encouraging. More importantly, CMR achievement at day 85 is associated with extremely promising results, being 75% at 30 months, underlying that CMR should be regarded as a primary endpoint in Ph+ ALL. We confirm that p210+ patients may require an intensified approach, given the lower rate of CMR achievement and the higher relapse rate. Finally, we provide evidence that a broader genetic characterization at diagnosis allows a more refined prognostic stratification of Ph+ ALL patients.
Martinelli:Pfizer: Consultancy; Ariad: Consultancy; AMGEN: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; ROCHE: Consultancy; MSD: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Foà:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal