Abstract
Introduction: The bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib demonstrates considerable activity in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). However, approximately 30% of patients do not respond to this treatment and the therapy invariably leads to drug resistance with a median response of 17.5 months. Infusion of autologous T cells transduced with chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) against the B-cell specific CD19 antigen (CART19) leads to dramatic clinical responses in the majority of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and the activity in B cell lymphoma is currently being evaluated in clinical trials. Bulky disease, as sometimes seen in MCL, may impair T cell infiltration. The features of ibrutinib that make it an interesting addition to CART19 include its efficacy in reducing tumor masses and its ability to mobilize neoplastic B cells into the peripheral blood, thereby potentially exposing them to the killing activity of CART19. Therefore, we sought to investigate the combination of the two novel targeted therapies, ibrutinib and CART19 in MCL.
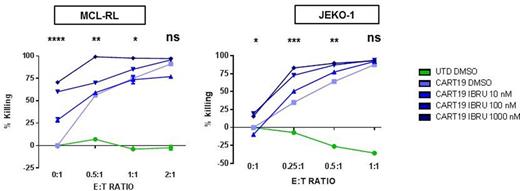
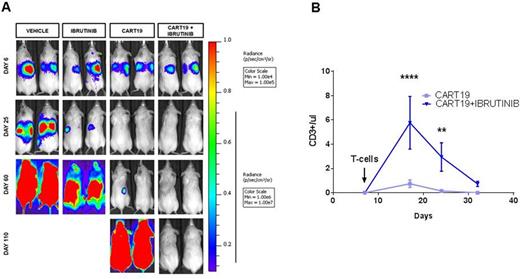
Results: In vitro studies with established MCL cell lines and with a novel cell line (MCL-RL) showed a range of responses to ibrutinib with an IC50 ranging from 10 nM to 10 µM; MCL-RL was the most sensitive cell line evaluated with an IC50 of 10nM, similar to primary MCL. Both ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant cell lines strongly activated CART19 in an antigen-specific manner as detected by CD107a degranulation, cytokine production and CFSE proliferation assays. Importantly, in vitro assays with MCL cell lines co-cultured with increasing doses of CART19 (E:T= 2:1, 1:1, 0.5:1, 0.25:1) combined with increasing concentrations of ibrutinib (0, 10, 100, 1000 nM) demonstrated strong additive tumor killing (Figure 1). Notably, supra-therapeutic doses of Ibrutinib (>/=1 uM) impaired cytokine production and T cell proliferation in vitro. In order to test this combination in vivo we established a novel MCL model, injecting i.v. luciferase-positive MCL-RL cells into NSG mice. This resulted in 100% MCL engraftment in liver and spleen, with eventual dissemination into lymph nodes and bone marrow. Treatment with three different doses of CART19 (0.5, 1 and 2 million cells/mouse) led to a dose dependent anti-tumor effect. A similar dose response to CART19 was also observed in the ibrutinib-resistant Jeko-1 cell line. We also treated MCL-RL xenografts with different doses (0, 25 and 125 mg/Kg/day) of ibrutinib, with a median overall survival respectively of 70, 81 and 100 days (p<0.001). Importantly, a direct in vivo comparison of the highest ibrutinib dose (125 mg/kg) and CART19 showed a significantly improved tumor control for mice treated with CART19. However, treatment with either CART19 or ibrutinib as single agents invariably led to late relapse. Therefore we sought to treat MCL-RL xenografts with the combination of CART19 and ibrutinib and compare it to the single agent activity. The combination resulted in significant improvement in tumor control compared to mice treated with the single agents with 80% of mice achieving long-term disease-free survival ( p=0.007 at day 110, representative mice shown in Figure 2A). Intriguingly, we found that mice treated with ibrutinib had higher numbers of circulating CART19 cells (Figure 2B).
Conclusions: Combining CART19 with ibrutinib represents a rational way to incorporate two of the most recent therapies in MCL. Our findings pave the way to a two-pronged therapeutic strategy in patients with MCL and other types of B-cell lymphoma.
Ruella:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Kenderian:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Maus:Novartis: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Milone:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Lacey:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Mato:Genentech: Consultancy; Pronai Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy. Schuster:Genentech: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Hoffman-LaRoche: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Nordic Nanovector: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Research Funding. Kalos:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. June:Novartis: Research Funding; University of Pennsylvania: Patents & Royalties: financial interests due to intellectual property and patents in the field of cell and gene therapy. Conflicts of interest are managed in accordance with University of Pennsylvania policy and oversight. Gill:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Wasik:Janseen and Novartis: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal