Abstract
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) with activity in lymphoid malignancies occurring primarily through immune modulation (eg, T-cell immune synapse enhancement and NK-cell/T-cell effector augmentation) and antiproliferative effects. Food and Drug Administration–approved for bortezomib-resistant, relapsed/refractory mantle-cell lymphoma, lenalidomide has demonstrated efficacy in several additional lymphoma subtypes. There are many ongoing clinical trials examining the use of lenalidomide alone or in combinatorial therapy. It will be important in these studies to delineate reliable, predictive biomarkers to optimally integrate lenalidomide into lymphoma treatment paradigms.
Introduction
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) that has been studied extensively in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). There have been a multitude of preclinical and clinical studies that have helped define the role of lenalidomide in NHL.
Mechanisms of action
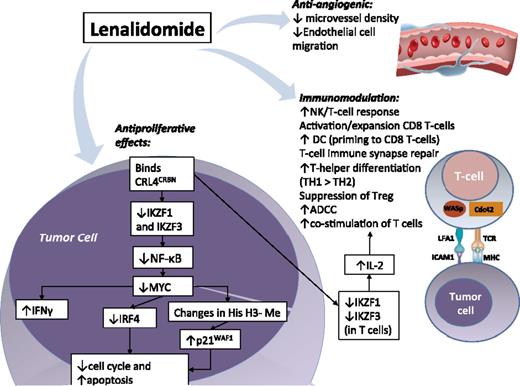
The most prominent mechanisms of action of lenalidomide in lymphoid malignancies appear to be immunomodulatory, antiproliferative, and antiangiogenic (Figure 1).
Mechanisms of action of lenalidomide in lymphoid malignancies. Direct antitumor effects primarily mediated by lenalidomide binding CRL4CRBN, altering affinity for E3-ubiquitin ligase substrates. Lymphoid transcription factors IKZF1 (Ikaros) and IKZF3 (Aiolos) are preferentially ubiquitinated and degraded rapidly with lenalidomide, causing decreased NF-κB, decreased MYC and IRF4, increased p21WAF1, and suppression of cell cycle via degradation of cyclin-dependent kinases. There is also increased interferon production via decreased IRF4 (suppresses IFN response), which promotes cellular death. Other CRL4CRBN substrates may be affected, but are less defined. Immunomodulatory properties: Improvement in T-cell and NK-cell antitumor activity is seen with lenalidomide, including IL-2–driven costimulation of T cells (via increased degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in T cells). Regulatory T cells are suppressed and there is a skewing toward Th1 population with lenalidomide. The NK- and T-cell effects of lenalidomide in lymphoma are synergistically enhanced with rituximab in preclinical studies. Anti-angiogenic properties: lenalidomide decreases angiogenesis in part via decreased microvessel density and it inhibits tumor growth and dissemination of disease through depletion of monocytes and macrophages associated with lymphangiogenesis. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-directed cytotoxicity; Cdc42, cell division control protein 42; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CRL4CRBN, Cullen 4 ring-E3 ubiquitin ligase–cereblon complex; FL, follicular lymphoma; His H3-Me, histone H3 methylation; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IFN, interferon; IKZF1, Ikaros; IKZF3, Aiolos; IRF4, interferon regulatory factor 4; LFA-1, lymphocyte function–associated antigen 1; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor; WASp, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein.
Mechanisms of action of lenalidomide in lymphoid malignancies. Direct antitumor effects primarily mediated by lenalidomide binding CRL4CRBN, altering affinity for E3-ubiquitin ligase substrates. Lymphoid transcription factors IKZF1 (Ikaros) and IKZF3 (Aiolos) are preferentially ubiquitinated and degraded rapidly with lenalidomide, causing decreased NF-κB, decreased MYC and IRF4, increased p21WAF1, and suppression of cell cycle via degradation of cyclin-dependent kinases. There is also increased interferon production via decreased IRF4 (suppresses IFN response), which promotes cellular death. Other CRL4CRBN substrates may be affected, but are less defined. Immunomodulatory properties: Improvement in T-cell and NK-cell antitumor activity is seen with lenalidomide, including IL-2–driven costimulation of T cells (via increased degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in T cells). Regulatory T cells are suppressed and there is a skewing toward Th1 population with lenalidomide. The NK- and T-cell effects of lenalidomide in lymphoma are synergistically enhanced with rituximab in preclinical studies. Anti-angiogenic properties: lenalidomide decreases angiogenesis in part via decreased microvessel density and it inhibits tumor growth and dissemination of disease through depletion of monocytes and macrophages associated with lymphangiogenesis. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-directed cytotoxicity; Cdc42, cell division control protein 42; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CRL4CRBN, Cullen 4 ring-E3 ubiquitin ligase–cereblon complex; FL, follicular lymphoma; His H3-Me, histone H3 methylation; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IFN, interferon; IKZF1, Ikaros; IKZF3, Aiolos; IRF4, interferon regulatory factor 4; LFA-1, lymphocyte function–associated antigen 1; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor; WASp, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein.
Immunomodulatory
Elegant preclinical studies showed that T-cell immune synapse dysfunction in follicular lymphoma (FL) can be “repaired” with lenalidomide.1 Tumor-infiltrating T cells from FL patients had significant reduction in formation of the F-actin immune synapse vs healthy donor cells. Lenalidomide reversed these abnormalities by enhancing the immune synapse, an important finding also demonstrated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).2 In addition, lenalidomide has been shown to reduce T regulatory cells, activate CD8 T cells, and skew T-helper (TH) subsets with TH1 > TH2 response.3
In other NHL experiments, lenalidomide combined with rituximab resulted in antitumor effects via increased NK cell function, enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, improved NK cell–mediated synapse formation, and CD20 capping.4-7 Zhu et al also reported that induction of apoptosis in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) and CLL cells occurred primarily through NK cell activation.8
Antiproliferative effects
A significant discovery in the mechanism of lenalidomide was identification of the importance of cereblon (encoded by the CRBN gene). Ito et al first showed that CRBN was required for the teratogenic effects of thalidomide leading to downregulation of fibroblast growth factor.9 Subsequent research has shown that silencing of CRBN diminishes the effect of lenalidomide and results in resistant cancer cells.10 Gene expression studies with CRBN knockdown showed that many of the affected genes were targets of critical transcription factors (eg, MYC, SP1, and TP53). It has also been shown that myeloma cells are addicted to an interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4)-controlled network with MYC as a direct downstream target and an autoregulatory circuit involving MYC and IRF4.11
Lenalidomide directly binds CRBN, reduces IRF4 and MYC expression, increases P21WAF-1 expression, and changes the immunomodulatory activity of T cells in myeloma models.12 Subsequent investigations with lenalidomide in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells identified a direct tumoricidal effect with downregulation of IRF4 and SPIB transcription factors requiring CRBN expression.13,14 Moreover, this effect has been preferentially noted in nongerminal center (non-GC) DLBCLs, which are more dependent on IRF4 and NF-κB than GC-DLBCL because of oncogenic mutations in CARD11 and MYD88.13,15
Cereblon has also been shown to be vital in lenalidomide-induced T-cell stimulation.16 Kronke et al showed that lenalidomide enhanced CRL4CRBN binding to Ikaros (IKZF1) and Aiolos (IKZF3) in myeloma and T-cell lines causing their ubiquitination and degradation (Figure 1).17 Ikaros and Aiolos are highly involved in the biology of T- and B-cells. Gandhi et al demonstrated in NHL cells that lenalidomide induced CRL4 interaction with and downregulated Ikaros and Aiolos, both transcriptional repressors of IL-2; the resultant IL-2 expression induced T-cell costimulation/activation. Lenalidomide also exerts direct antiproliferative activity in mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL)18 and CLL cells, the latter occurring in a cereblon- and p21-dependent, but p53-independent manner.19
Antiangiogenic
Reddy et al showed that lenalidomide diminishes angiogenesis (decreased microvessel density) in NHL xenograft models.5 Related data in MCL mouse models revealed that lenalidomide inhibited tumor growth and dissemination by depleting monocytes and macrophages associated with lymphangiogenesis.20 Lenalidomide has also been shown to upregulate the tumor-suppressor gene SPARC, which has antiproliferative, antiadhesive, and antiangiogenic properties in 5q– syndrome21 ; similar preliminary findings were noted in NHL,22 which remains to be validated.
Clinical data
Phases 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials have defined the safety and efficacy of lenalidomide in multiple NHL subtypes including MCL, FL, DLBCL, and T-cell lymphoma (Table 1).23-46
Lenalidomide clinical study results in lymphoma
| Series/Author . | Year . | No. patients . | Arms . | Conclusions† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mantle cell: untreated | ||||
| Phase 1/2 | ||||
| Jerkeman et al23 * | 2011 | 12 | BR + lenalidomide (dose escalated) induction; len maint 10-15 mg, d 1-21 × 5 mo | Lenalidomide MTD 10 mg d 1-14; (cycle 1 tox: allergic/cutaneous), ORR 100%, CR 90% |
| 2-y PFS 74%, 2-y OS 87% | ||||
| Ruan et al24 * | 2013 | 38 | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab; len maint 10 mg, d 1-21 until PD | ORR 84%, 53% CR |
| DOR: NR; 2-y PFS 84% | ||||
| Mantle cell: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase 1/2 | ||||
| Wang et al25 | 2012 | 52 | Lenalidomide (dose escalated) + rituximab | Lenalidomide MTD 20 mg, ORR 57%, CR 36%, |
| DOR 19 mo, PFS 11mo, OS 24 mo | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Habermann et al26 | 2009 | 15 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 53%, CR 20% |
| DOR 13.7 mo, PFS 5.6 mo | ||||
| Witzig et al27 (NHL-003) | 2011 | 57 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 42%, CR 21% |
| DOR: NR, PFS 5.7 mo | ||||
| Zaja et al28 | 2012 | 33 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + dexamethasone | ORR 52%, CR 24% |
| DOR 18 mo, PFS 12 mo, OS 20 mo | ||||
| Eve et al29 | 2012 | 26 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) × 6 cycle; then len maint | ORR 31%, CR 8% |
| DOR 22 mo, PFS 3.9 mo; maint len PFS 14.6 mo | ||||
| Goy et al30 (MCL-001) | 2013 | 134 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) (all pts pretreated with bortezomib) | ORR 28%, CR 8%, |
| DOR 17 mo, PFS 4 mo, OS 19 mo | ||||
| Indolent NHL: untreated | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Fowler et al31 | 2014 | 50 FL, 30 MZL, 30 SLL | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR 98%, PFS 89% |
| Indolent NHL: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Witzig et al (NHL-001)32 | 2009 | 22 | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 27% |
| DOR: NR (>17 mo), PFS 4.4 mo | ||||
| Tuscano et al33 | 2014 | 22 FL | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR 77% |
| PFS (all) 12.4 mo | ||||
| Chong et al34 | 2015 | 30 FL, 14 MCL, | Lenalidomide 10 mg daily (× five 28-d cycles) and 4 wk rituximab (cycle 3) | ORR with len: 30%; after len + ritux: 63% |
| 4 SLL, 2 MZL (all rituximab-refractory) | DOR len + ritux: 25 mo, PFS 22 mo | |||
| Aggressive B-cell NHL: untreated | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Reddy et al35 * | 2013 | 43 DLBCL | Maint lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21) vs lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21) + rituximab | len vs len + ritux: |
| 2-y PFS: 90% vs 86% | ||||
| 2-y OS: 95% vs 81% | ||||
| Vitolo et al36 (REAL-07) | 2014 | 45 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (15 mg d 1-14) + R-CHOP | CR 86%, PR 6% |
| 2-y PFS 80% | ||||
| 2-y OS 92% | ||||
| Nowakowski et al37 | 2014 | 60 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-10) + R-CHOP | ORR 98%, CR 80%, |
| EFS 59% OS 78% | ||||
| Aggressive B-cell NHL: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase1/2 | ||||
| Feldman et al38 | 2014 | 16 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (dose escalation) + RICE; then maint len 25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d × 12 mo | MTD: 25mg d1-4 q 14 d |
| ORR 73%, CR 60% | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Wiernick et al39 (NHL-002) | 2008 | 5 FLG3, 26 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR: FL 60%, DLBCL, 19% TL 33% |
| DLBCL, 3 TL | PFS (all) 4 mo | |||
| Hernandez et al40 | 2011 | DLBCL 23 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR: Non-GCB: 53%, GCB 9% |
| GCB, 17 | PFS 6.2 mo vs 1.7 mo OS 14 mo vs 13.5 mo | |||
| non-GCB | ||||
| Witzig et al27 (NHL-003) | 2011 | 19 FLG3, | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR: FL 42%, DLBCL 28%, TL 45% |
| 108 DLBCL, | PFS: FL 8.9 mo, DLBCL 2.7 mo, TL 5.4 mo | |||
| 33 TL | ||||
| Zinzani et al41 | 2013 | 23 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR 35% |
| DOR 32 mo | ||||
| Wang et al42 | 2013 | 4 FLG3, 32 | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR: FL 25%, DLBCL 28%, TL 56% DLBCL: PFS 2.8 mo, OS 10.2 mo, TL: PFS 4.3 mo, OS 11.5 mo |
| DLBCL, 9 TL | ||||
| Aggressive T-cell NHL: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Zinzani et al43 | 2011 | 10 PTCL NOS | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 30% |
| Morschhauser et al44 (EXPECT) | 2013 | 54 PTCL | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 22%, |
| DOR 3.6 mo, PFS 2.5 mo (4.6 mo in AITL) | ||||
| Querfeld et al45 | 2013 | 32 MF/Sézary | Initially lenalidomide 25 mg d 1-21; amended to 10 mg with incremental (5 mg) dose escalation | ORR 28%, |
| DOR 10 mo, PFS 8 mo, OS 43 mo | ||||
| Toumishey et al46 | 2014 | 40 TCL | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | Rel/ref PTCL: ORR 24%, |
| DOR 5 mo, PFS 4 mo, OS 12 mo | ||||
| Untreated PTCL: ORR 50%, | ||||
| DOR 21 mo, PFS 4 mo, OS 12 mo | ||||
| Series/Author . | Year . | No. patients . | Arms . | Conclusions† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mantle cell: untreated | ||||
| Phase 1/2 | ||||
| Jerkeman et al23 * | 2011 | 12 | BR + lenalidomide (dose escalated) induction; len maint 10-15 mg, d 1-21 × 5 mo | Lenalidomide MTD 10 mg d 1-14; (cycle 1 tox: allergic/cutaneous), ORR 100%, CR 90% |
| 2-y PFS 74%, 2-y OS 87% | ||||
| Ruan et al24 * | 2013 | 38 | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab; len maint 10 mg, d 1-21 until PD | ORR 84%, 53% CR |
| DOR: NR; 2-y PFS 84% | ||||
| Mantle cell: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase 1/2 | ||||
| Wang et al25 | 2012 | 52 | Lenalidomide (dose escalated) + rituximab | Lenalidomide MTD 20 mg, ORR 57%, CR 36%, |
| DOR 19 mo, PFS 11mo, OS 24 mo | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Habermann et al26 | 2009 | 15 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 53%, CR 20% |
| DOR 13.7 mo, PFS 5.6 mo | ||||
| Witzig et al27 (NHL-003) | 2011 | 57 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 42%, CR 21% |
| DOR: NR, PFS 5.7 mo | ||||
| Zaja et al28 | 2012 | 33 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + dexamethasone | ORR 52%, CR 24% |
| DOR 18 mo, PFS 12 mo, OS 20 mo | ||||
| Eve et al29 | 2012 | 26 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) × 6 cycle; then len maint | ORR 31%, CR 8% |
| DOR 22 mo, PFS 3.9 mo; maint len PFS 14.6 mo | ||||
| Goy et al30 (MCL-001) | 2013 | 134 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) (all pts pretreated with bortezomib) | ORR 28%, CR 8%, |
| DOR 17 mo, PFS 4 mo, OS 19 mo | ||||
| Indolent NHL: untreated | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Fowler et al31 | 2014 | 50 FL, 30 MZL, 30 SLL | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR 98%, PFS 89% |
| Indolent NHL: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Witzig et al (NHL-001)32 | 2009 | 22 | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 27% |
| DOR: NR (>17 mo), PFS 4.4 mo | ||||
| Tuscano et al33 | 2014 | 22 FL | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR 77% |
| PFS (all) 12.4 mo | ||||
| Chong et al34 | 2015 | 30 FL, 14 MCL, | Lenalidomide 10 mg daily (× five 28-d cycles) and 4 wk rituximab (cycle 3) | ORR with len: 30%; after len + ritux: 63% |
| 4 SLL, 2 MZL (all rituximab-refractory) | DOR len + ritux: 25 mo, PFS 22 mo | |||
| Aggressive B-cell NHL: untreated | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Reddy et al35 * | 2013 | 43 DLBCL | Maint lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21) vs lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21) + rituximab | len vs len + ritux: |
| 2-y PFS: 90% vs 86% | ||||
| 2-y OS: 95% vs 81% | ||||
| Vitolo et al36 (REAL-07) | 2014 | 45 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (15 mg d 1-14) + R-CHOP | CR 86%, PR 6% |
| 2-y PFS 80% | ||||
| 2-y OS 92% | ||||
| Nowakowski et al37 | 2014 | 60 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-10) + R-CHOP | ORR 98%, CR 80%, |
| EFS 59% OS 78% | ||||
| Aggressive B-cell NHL: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase1/2 | ||||
| Feldman et al38 | 2014 | 16 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (dose escalation) + RICE; then maint len 25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d × 12 mo | MTD: 25mg d1-4 q 14 d |
| ORR 73%, CR 60% | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Wiernick et al39 (NHL-002) | 2008 | 5 FLG3, 26 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR: FL 60%, DLBCL, 19% TL 33% |
| DLBCL, 3 TL | PFS (all) 4 mo | |||
| Hernandez et al40 | 2011 | DLBCL 23 | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR: Non-GCB: 53%, GCB 9% |
| GCB, 17 | PFS 6.2 mo vs 1.7 mo OS 14 mo vs 13.5 mo | |||
| non-GCB | ||||
| Witzig et al27 (NHL-003) | 2011 | 19 FLG3, | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR: FL 42%, DLBCL 28%, TL 45% |
| 108 DLBCL, | PFS: FL 8.9 mo, DLBCL 2.7 mo, TL 5.4 mo | |||
| 33 TL | ||||
| Zinzani et al41 | 2013 | 23 DLBCL | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR 35% |
| DOR 32 mo | ||||
| Wang et al42 | 2013 | 4 FLG3, 32 | Lenalidomide (20 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) + rituximab | ORR: FL 25%, DLBCL 28%, TL 56% DLBCL: PFS 2.8 mo, OS 10.2 mo, TL: PFS 4.3 mo, OS 11.5 mo |
| DLBCL, 9 TL | ||||
| Aggressive T-cell NHL: relapsed/refractory | ||||
| Phase 2 | ||||
| Zinzani et al43 | 2011 | 10 PTCL NOS | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 30% |
| Morschhauser et al44 (EXPECT) | 2013 | 54 PTCL | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | ORR 22%, |
| DOR 3.6 mo, PFS 2.5 mo (4.6 mo in AITL) | ||||
| Querfeld et al45 | 2013 | 32 MF/Sézary | Initially lenalidomide 25 mg d 1-21; amended to 10 mg with incremental (5 mg) dose escalation | ORR 28%, |
| DOR 10 mo, PFS 8 mo, OS 43 mo | ||||
| Toumishey et al46 | 2014 | 40 TCL | Lenalidomide (25 mg d 1-21 q 28 d) | Rel/ref PTCL: ORR 24%, |
| DOR 5 mo, PFS 4 mo, OS 12 mo | ||||
| Untreated PTCL: ORR 50%, | ||||
| DOR 21 mo, PFS 4 mo, OS 12 mo | ||||
AITL, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma; autoSCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; CHOP, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, oncovin, and prednisone; CR, complete remission; d, days; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; FLG3, follicular lymphoma grade 3; GCB, germinal center B-cell; ICE, ifosfamide carboplatin, etoposide; Len, lenalidomide; maint, maintenance; MF, mycoses fungoides; mo, months; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; NR, not reached; ORR, overall response rate; OS, overall survival; PD, progressive disease; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial remission; PTCL NOS, peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified; pts, patients; R, rituximab; rel/ref: relapsd/refractory; SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma; TCL, T-cell lymphoma; TL, transformed lymphoma; yr, year.
Indicates abstract data.
All survival times are medians, unless otherwise specified.
Mantle-cell lymphoma
Relapsed/refractory.
In a single-agent study (NHL-002)39 of relapsed/refractory aggressive NHL histologies, the overall response rate (ORR) of lenalidomide in MCL was 53%, with 14% complete remission (CR) (Table 1). Mature follow-up of NHL-002 showed a median duration of response (DOR) of 13.7 months.26 Eve et al treated 26 relapsed/refractory MCL cases with maintenance lenalidomide in responding patients to lenalidomide induction (Table 1).29 In NHL-003, 57 relapsed/refractory MCL patients had an ORR of 42%.47 Collectively, adverse effects (AEs) were primarily hematologic, with 5% of patients having thromboembolic events. Notably, the risk of thromboembolism in NHL does not differ from the risk in multiple myeloma. Longer-term follow-up of NHL-003 (median 20 months) showed a DOR of 16.3 months and progression-free survival (PFS) of 8.8 months in this heavily pretreated group of patients.47 Second malignancies were noted in 4 of 57 patients (2 shortly after starting lenalidomide). Continued follow-up of this and other lenalidomide studies are needed to examine the risk of second cancers and other late effects.
A prospective, single-arm, phase 2 International clinical trial (EMERGE, MCL-001) of 134 bortezomib-resistant, relapsed/refractory MCL patients showed meaningful clinical benefit across multiple prognostic groups to single-agent lenalidomide.30 Grade 3-4 AEs were similar to prior trials (43% neutropenia, 28% thrombocytopenia, 11% anemia). Grade 3 nonhematologic AEs included 7% fatigue, 6% diarrhea, and 5% dyspnea. These data led to Food and Drug Administration approval of lenalidomide in June 2013 for MCL patients whose disease relapsed or progressed after 2 prior therapies, one of which included bortezomib.
In an update to MCL-001, median time to CR was 4.1 months and median overall survival (OS) was 20.9 months.48 Dose reductions or interruptions as a result of AEs occurred in 40% and 58% of patients, respectively, and the average lenalidomide dose intensity was 20 mg per day. In addition, lower Ki67 levels (<30%) appeared to correlate with improved CR, DOR, and OS.
Untreated.
There are ongoing clinical trials incorporating lenalidomide into treatment paradigms for untreated MCL (supplemental Tables 1 and 2, available on the Blood Web site). Jerkeman et al evaluated lenalidomide combined concurrently with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) in newly-diagnosed older MCL patients.23 The phase 1 study identified an unexpected high rate of grade 3-4 allergic reactions and cutaneous toxicity, and there were 3 treatment-related deaths (Table 1). The study was amended to omit lenalidomide from cycle 1 (ie, starting cycle 2). Ruan et al presented data using lenalidomide combined with rituximab for first-line treatment of MCL.24 Treatment was well tolerated with grade 3-4 toxicities of 39% neutropenia, 13% thrombocytopenia, 7% anemia, 23% rash, and 7% tumor flare. Preliminary efficacy data were promising (Table 1).
Follicular lymphoma
Relapsed/refractory disease.
NHL-001 documented the single-agent efficacy of lenalidomide for relapsed/refractory indolent NHL (Table 1)32 ; ORR was modest, but responding patients had durable remissions. Tuscano et al reported results with lenalidomide and rituximab in relapsed/refractory indolent NHL half of whom were rituximab-refractory (Table 1).33 In addition, UPenn published results of a carefully planned and well-done phase 2 study in rituximab-refractory FL and MCL showing that lenalidomide had activity as a single-agent and that lenalidomide/rituximab combination therapy may overcome rituximab resistance.34 There is an ongoing phase 3 trial (the “AUGMENT” study) evaluating lenalidomide combined with rituximab vs single-agent lenalidomide in relapsed/refractory indolent NHL (supplemental Table 2).
Untreated patients.
Fowler et al evaluated lenalidomide and rituximab in 110 untreated FL patients.31 Responses were high, and at completion of therapy, most patients demonstrated molecular response. There are several ongoing randomized studies examining lenalidomide as part of frontline therapy for FL patients. This includes a randomized phase 2 study examining lenalidomide therapy after immunochemotherapy induction (the “BIONIC” trial) and a phase 3 study comparing the efficacy of rituximab plus lenalidomide vs rituximab plus chemotherapy in untreated FL (the “RELEVANCE” trial) (supplemental Figure 1).
DLBCL
Relapsed/refractory.
Lenalidomide has activity in relapsed/refractory DLBCL (Table 1). In NHL-002 and NHL-003, the ORRs in DLBCL were 19% and 28%, respectively.27,39 The differential efficacy of lenalidomide in DLBCL based on cell of origin was evaluated by Hernandez et al40 ; lenalidomide appeared to be more effective in non-GC DLBCL with an ORR of 53% vs 9% for the GC subtype.
Zinzani et al reported data on 23 elderly DLBCL patients treated with rituximab and lenalidomide (with lenalidomide maintenance),41 and Wang et al confirmed the clinical activity of lenalidomide/rituximab in relapsed/refractory de novo and transformed DLBCL (Table 1).42 Feldman et al studied the addition of lenalidomide to standard salvage chemotherapy for relapsed/refractory DLBCL before autologous stem cell transplantation followed by lenalidomide maintenance.38 Ongoing studies are assessing lenalidomide combined with other chemotherapy backbones (supplemental Table 2).
Untreated.
The addition of lenalidomide to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, oncovin, and prednisone (R2-CHOP) was evaluated in older, untreated DLBCL patients (Table 1).36 Efficacy appeared to be high, although ∼70% of patients had grade 3-4 hematologic AEs. Nowakowski et al added modified lenalidomide to R-CHOP, which was well tolerated and it appeared to overcome the negative prognostic impact of the non-GC phenotype in DLCBL.37 A large, randomized phase 2 trial randomizing untreated DLBCL patients to R2-CHOP vs R-CHOP (supplemental Figure 1) and a similarly designed industry-led study (only ABC-type DLBCL; the ROBUST study) are underway.
T-cell lymphoma
Relapsed/refractory.
The EXPECT phase 2 trial studied patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) treated with single-agent lenalidomide (Table 1).44 The majority of patients (85%) had angioimmunoblastic (AITL) and PTCL–not otherwise specified histologies. Efficacy was documented, although serious AEs were seen in 54% of patients, with 6 deaths unrelated to progression. In additional single-agent studies, Tournishey et al reported results in untreated and relapsed/refractory PTCL,46 whereas Querfeld et al showed clinical activity in relapsed/refractory mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome (Table 1).45 In the latter study, tumor flare was seen in many patients, which prompted an amendment for lower initial lenalidomide dosing.
Untreated.
There are limited data examining lenalidomide in the front-line setting for PTCL. A trial investigating the efficacy of lenalidomide combined with CHOP in AITL is ongoing, and another study is evaluating romidepsin and lenalidomide in untreated PTCL (supplemental Table 2).
Future directions
Biomarkers
Clinical studies have examined potential biomarkers of lenalidomide efficacy,28,29,34 and pivotal studies are ongoing in distinct NHL subsets (eg, non-GC DLBCL). In relapsed/refractory MCL, Zaja et al showed that microvessel density, macrophage, and NK cell counts were altered with lenalidomide,28 and Ki67 is being studied as a biomarker.48 Despite breakthrough studies that identified CRBN as a critical lenalidomide target,9-12,49 there are challenges in its use as a biomarker (eg, messenger RNA/protein correlation). The CRBN-associated transcription factors, Ikaros/Aiolos, may serve as more functional biomarkers16 as well as downstream substrates (eg, IRF4 and MYC). Other potential lenalidomide-related biomarkers include components of PI3K signaling (eg, GSK3β)50 and the T-cell immune synapse with granzyme B expression.51,52
Novel combinations
In DLBCL cells, azacytidine and lenalidomide increased CRBN expression and enhanced cytotoxicity,53 whereas ibrutinib and lenalidomide synergistically suppressed IRF4.13 In vitro FL and MCL studies confirmed synergistic activity with bortezomib and lenalidomide.54 In T-cell lymphoma models, romidepsin combined with lenalidomide resulted in increased oxidative stress and alteration of PI3K and MAP kinase/ERK-signaling pathways.55 Conversely, preclinical studies in CLL suggest that the PI3Kδ inhibitor, idelalisib, antagonizes the immune-modulating properties of lenalidomide.
It will be important to translate these findings in clinical studies to confirm efficacy as well as safety. The latter was highlighted in two phase 1 studies combining lenalidomide with the PI3Kδ inhibitor, idelalisbub (and rituximab), where prohibitive toxicities suggestive of severe cytokine-release syndrome (eg, rash, fevers, hypotension) were seen.56 Other clinical studies combining lenalidomide with novel/targeted agents have shown good tolerability and encouraging efficacy,57 whereas additional novel combinatorial trials are underway (eg, obinutuzumab, romidepsin, everolimus, ibruitinib) (supplemental Table 2).
In addition, translational studies of new cereblon-binding agents (eg, CC-122) are eagerly anticipated.58 CC-122 is a first-in-class, pleiotropic pathway modifier that binds cereblon and induces Aiolos and Ikaros degradation in DLBCL and T cells.59 In DLBCL, it results in depression of interferon-stimulated genes/proteins, ultimately resulting in apoptosis.60 Furthermore, CC-122 appears to have distinct activity from lenalidomide in part as it is active in both GC and non-GC DLBCL.58,60
Conclusions
Owing to its unique immunomodulatory and antiproliferative activity, as well as its relative ease of use, lenalidomide has garnered clinical consideration in multiple NHL subtypes. Durable responses with manageable side effects have moved lenalidomide into the front-line setting of randomized clinical trials for various NHL subtypes. In addition, combinatorial therapy with novel/targeted therapeutic agents is of particular interest. Finally, continued understanding of the biological mechanisms and the associated validation of predictive biomarkers will be critical in optimally integrating lenalidomide into NHL treatment paradigms.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
Authorship
Contribution: A.K. and A.M.E. designed research, performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; M.C. designed research, performed research, and wrote the paper; and J.S. performed research and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.M.E. is on the advisory board and speakers bureau (with honorarium) for Celgene. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Andrew M. Evens, Tufts Medical Center, Division of Hematology/Oncology, 800 Washington St, Boston, MA 02111; e-mail: aevens@tuftsmedicalcenter.org.
References
Author notes
A.K. and M.C. contributed equally to this paper.