On page 587 of the January 22, 2015, issue, the figure contains an error. The figure shows 2 CD79a/b dimers associated with each B-cell receptor (BCR). It should have shown 1 CD79a/b dimer per BCR. The corrected figure is shown below. The error has been corrected in the online version, which now differs from the print version.
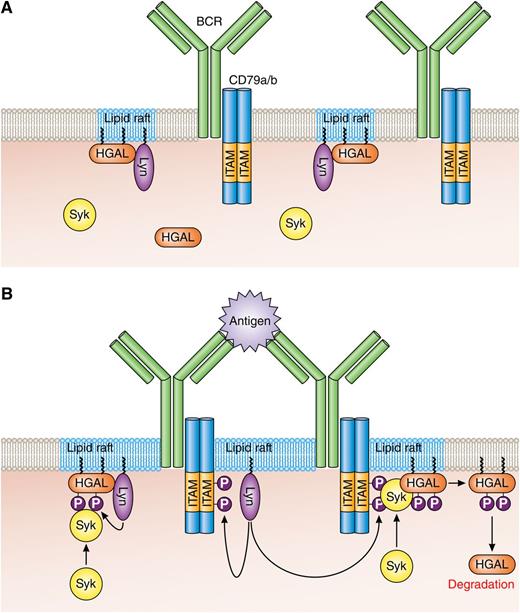
HGAL within lipid rafts enhances BCR signaling. (A) In resting B cells, HGAL is mainly located within lipid rafts together with Lyn. (B) In BCR-stimulated B cells, Lyn phosphorylates tyrosine residues within the ITAMs of CD79a/b, and this attracts and activates Syk. Coassociation of Syk with HGAL enhances Syk kinase activity and BCR signaling strength. Following BCR engagement, HGAL is shunted from lipid rafts to ultimately end up in the cell cytoplasm for destruction by the proteasome. Professional illustration by Patrick Lane, ScEYEnce Studios.
HGAL within lipid rafts enhances BCR signaling. (A) In resting B cells, HGAL is mainly located within lipid rafts together with Lyn. (B) In BCR-stimulated B cells, Lyn phosphorylates tyrosine residues within the ITAMs of CD79a/b, and this attracts and activates Syk. Coassociation of Syk with HGAL enhances Syk kinase activity and BCR signaling strength. Following BCR engagement, HGAL is shunted from lipid rafts to ultimately end up in the cell cytoplasm for destruction by the proteasome. Professional illustration by Patrick Lane, ScEYEnce Studios.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal