Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic cytokine produced by a variety of cell types, including bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Levels of IL-6 are increased in patients with CLL and correlated with adverse clinical features and short survival. In preliminary studies we observed that IL-6 induced resistance to the pan-histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors vorinostat (SAHA) and panobinostat (LBH589) in CLL cells. Activation of STAT3 induced by IL-6 in CLL cells was further enhanced by low concentration of SAHA and LBH589. We hypothesized that exposure of CLL cells to HDAC inhibitors would further expand the activation of STAT3 signaling by IL-6, and thus the ability of HDAC inhibitors to kill CLL cells may be blunted due to upregulation of STAT3 downstream antiapoptotic proteins. This study was designed to illuminate the role of the STAT3 pathway on the resistance to SAHA and LBH589 in CLL cells, and to evaluate the proapoptotic activity of the combination of SAHA and LBH589 with a STAT3-selective inhibitor, WP1066.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained from samples of 32 CLL patients. The characteristics of CLL patients were shown in Table 1. The PBMCs contained more than 90% of CD19+ B lymphocytes, which were detected by flow cytometry and were referred to as primary CLL cells. BMSCs were isolated from bone marrow mononuclear cells of healthy volunteers. Cytotoxicity of drugs was assessed by carrying out triplicate assays with the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), after a 48-hour incubation of primary CLL cells in the presence or absence of recombinant human IL-6, and half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were calculated. Effects of drugs on apoptosis of CLL cells, in the presence or absence of IL-6 or BMSCs, were evaluated by Annexin V/7AAD assay, morphological assessment of Giemsa-stained cytospin preparations and western blot analysis of the cleavage of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP). The levels of STAT3 phosphorylation (pSTAT3) and STAT3 downstream proteins were evaluated by western blotting.
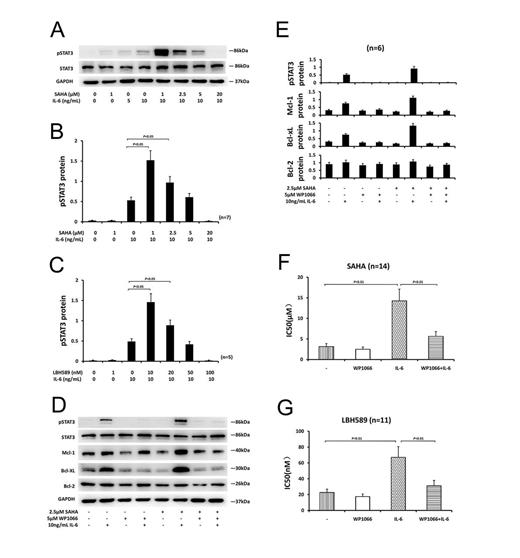
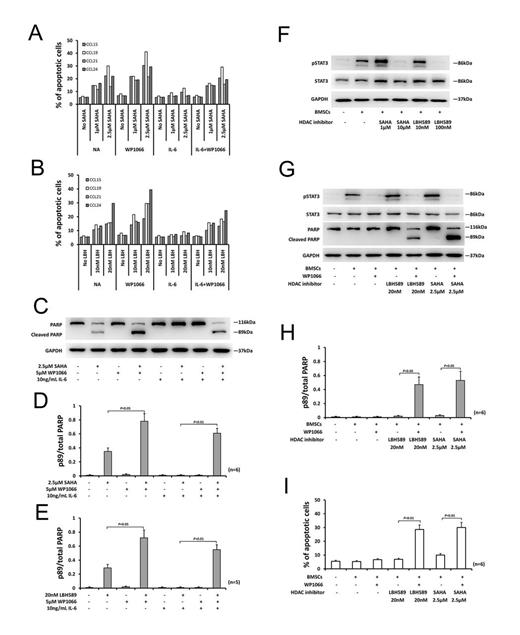
Results: IL-6-induced pSTAT3 was completely abolished by 4-hour incubation with 20µM of SAHA or 100nM of LBH589 before IL-6 was added. But when CLL cells were incubated with lower concentration of SAHA or LBH589 (e.g., SAHA, 1µM; LBH589 10nM), the level of pSTAT3 induced by IL-6 was further enhanced (Fig. 1A-C). Treatment of CLL cells with 10ng/mL IL-6 for 24 hours resulted in greater than 2-fold upregulation of the antiapoptotic proteins, Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL. The upregulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL induced by IL-6 was further enhanced in the presence of 1µM or 2.5µM of SAHA (Fig. 1D-E). IL-6 decreased the sensitivity of CLL cells to each of the HDAC inhibitors tested, as evidenced by an increase in the mean IC50 values. Co-incubation with 5µM of WP1066 blocked the protective action of IL-6 (Fig. 1F-G). Apoptosis induction by SAHA and LBH589 was reduced in the presence of IL-6 and this reduction could be inhibited by WP1066 (Fig. 2A-B). The antiapoptotic action of IL-6 and the ability of WP1066 to restrain cytoprotection by IL-6 were also confirmed by morphological assessment and PARP cleavage analysis (Fig. 2C-E). WP1066 decreased the pSTAT3 level and inhibited increases of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL proteins induced by IL-6 in the presence or absence of SAHA (Fig. 1D-E). Co-culture of CLL cells with BMSCs resulted in the activation of STAT3 in CLL cells and protected CLL cells from apoptosis induction by HDAC inhibitors, and this cytoprotection was reversed by WP1066 (Fig. 2F-I).
Conclusions: Our studies indicated that CLL cells were protected from HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis by IL-6 or co-culture with BMSCs. This protection may be mediated by activation of STAT3 signal pathway. Furthermore, WP1066 reversed the resistances of CLL cells to SAHA and LBH589 induced by IL-6 or co-culture with BMSCs. Our findings suggest that targeting the STAT3 pathway may be a novel way to improve the efficacy of HDAC inhibitor in CLL patients by overcoming antiapoptotic signaling of the microenvironment.
| Characteristic . | Case (n) . | Total (n) . |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32 | |
| ≥60 | 20 | |
| <60 | 12 | |
| Sex | 32 | |
| Male | 25 | |
| Female | 7 | |
| Rai stage | 32 | |
| 0 | 5 | |
| I | 9 | |
| II | 11 | |
| III | 4 | |
| IV | 3 | |
| IgVH mutational status | 25 | |
| Unmutated (≥98% homology) | 8 | |
| Mutated (<98% homology) | 17 | |
| ZAP70 | 22 | |
| ≥20% | 7 | |
| <20% | 15 | |
| CD38 | 24 | |
| ≥20% | 8 | |
| <20% | 16 | |
| FISHcytogenetics | 21 | |
| Normal karyotype | 10 | |
| 13q- | 7 | |
| 11q- | 2 | |
| 17p- | 1 | |
| Trisomy 12 | 2 |
| Characteristic . | Case (n) . | Total (n) . |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32 | |
| ≥60 | 20 | |
| <60 | 12 | |
| Sex | 32 | |
| Male | 25 | |
| Female | 7 | |
| Rai stage | 32 | |
| 0 | 5 | |
| I | 9 | |
| II | 11 | |
| III | 4 | |
| IV | 3 | |
| IgVH mutational status | 25 | |
| Unmutated (≥98% homology) | 8 | |
| Mutated (<98% homology) | 17 | |
| ZAP70 | 22 | |
| ≥20% | 7 | |
| <20% | 15 | |
| CD38 | 24 | |
| ≥20% | 8 | |
| <20% | 16 | |
| FISHcytogenetics | 21 | |
| Normal karyotype | 10 | |
| 13q- | 7 | |
| 11q- | 2 | |
| 17p- | 1 | |
| Trisomy 12 | 2 |
Lu:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Inc: LBH589 was kindly provided by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Inc. Other.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal