Abstract
Objective: All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)/arsenic trioxide (ATO) combination therapy for newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) has yielded high efficacy in clinical trials, but there are few studies focusing on the long-term follow-up of survival and complications.
Methods: In this study, we followed up 217 patients with newly diagnosed APL treated with ATRA/ATO combination therapy between 2001 and 2010. Health assessment for long-term complications and quality of life was performed for 112 of these patients, meanwhile the arsenic retention in their plasma, urine, hair and nails was detected by inductively coupled argon plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
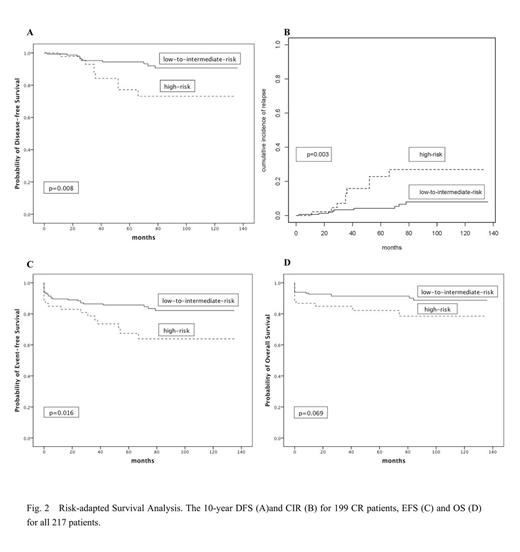
Results: A total of 199 patients (91.7%) achieved complete remission (CR). The estimated 10-year event-free survival (EFS), overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) were 78.0%, 86.3%, 87.0% and 12.0%, respectively. High white blood cell (WBC) count remained as the only unfavorable prognostic factor for remission duration and led to significant differences between low-to-intermediate and high-risk groups in EFS (82.1% vs. 63.9%, P=0.016), DFS (90.6% vs. 73.1%, P=0.008) and CIR (8.0% vs. 26.9%, P=0.003). For the 112 patients who received health assessment, there were no significant long-term complications associated with ATRA/ATO therapy, except for higher incidence of grade-1 liver dysfunction (15.2%) and hepatic steatosis (42.9%) compared to healthy controls (both P<0.001). The arsenic concentration in patients¡¯ plasma and urine excreted quickly to normal level right after the cessation of ATO, even lower than that of healthy controls (P<0.001 and P=0.009, respectively). However, in patients¡¯ hair and nails it slowly decreased to normal after 6 months off ATO, with no significant difference than the healthy controls. The results revealed no general retention of arsenic in patients during the long-term follow-up. And the quality of life was satisfactory in almost all patients.
Conclusion: This study with long-term follow-up clearly demonstrated that ATRA/ATO in newly diagnosed APL patients was associated with long-term survival, particularly for patients with low-to-intermediate risk diseases, as well as few complications, minimal arsenic retention and good quality of life.
Estimated 10-year Survival by Different Risk Stratification
| . | EFS . | OS . | DFS . | CIR . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 78.0% | 86.3% | 87.0% | 12.0% |
| Sanz¡¯s risk stratification | ||||
| Low-risk | 82.4% | 89.7% | 89.6% | 8.2% |
| Intermediate-risk | 81.8% | 88.2% | 91.0% | 8.0% |
| High-risk | 63.9% | 78.4% | 73.1% | 26.9% |
| P value | 0.048* | 0.165 | 0.029* | 0.009** |
| WBC-based stratification | ||||
| Low-to-intermediate-risk | 82.1% | 88.8% | 90.6% | 8.0% |
| High-risk | 63.9% | 78.4% | 73.1% | 26.9% |
| P value | 0.016* | 0.069 | 0.008** | 0.003** |
| . | EFS . | OS . | DFS . | CIR . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 78.0% | 86.3% | 87.0% | 12.0% |
| Sanz¡¯s risk stratification | ||||
| Low-risk | 82.4% | 89.7% | 89.6% | 8.2% |
| Intermediate-risk | 81.8% | 88.2% | 91.0% | 8.0% |
| High-risk | 63.9% | 78.4% | 73.1% | 26.9% |
| P value | 0.048* | 0.165 | 0.029* | 0.009** |
| WBC-based stratification | ||||
| Low-to-intermediate-risk | 82.1% | 88.8% | 90.6% | 8.0% |
| High-risk | 63.9% | 78.4% | 73.1% | 26.9% |
| P value | 0.016* | 0.069 | 0.008** | 0.003** |
*P<0.05, **P<0.01
Major Abnormalities in the Assessment of Long-term Complications (patients No.=112)
| Abnormal Findings . | Patients No. (%) . | Healthy Controls No. (%) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower WBC count | 1 (0.9)† | 0 | 1.000 |
| Cardiovascular events | |||
| Elevated myocardial enzymes | 5 (4.5)# | 1 (0.9) | 0.212 |
| Long Q-T interval | 0 | 0 | / |
| T wave change | 14 (12.5) | 15 (13.4) | 0.842 |
| Echocardiogram abnormality | 1 (0.9)ǂ | 0 | 1.000 |
| Liver, kidney and GI dysfunction | |||
| Liver dysfunction | 17 (15.2) | 2 (1.8) | <0.001 |
| Elevated creatinine | 0 | 0 | / |
| Albuminuria | 1 (0.9)ǂ | 0 | 1.000 |
| Fecal occult blood test | 0 | 0 | / |
| Hepatic steatosis | 48 (42.9) | 20 (17.9) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 6 (5.4) | 5 (4.5) | 0.757 |
| Neurological disorders | 1 (0.9)¡ì | 1 (0.9) D | 1.000 |
| Potential secondary tumor | |||
| Elevated serum tumor markers | 3†ø | / | / |
| Thoracic neoplasm on CXR | 0 | 0 | / |
| Abdominal neoplasm on BUS | 0 | 0 | / |
| Skin lesion | 8 (7.1) ŋ | 5 (4.5) ¦Ë | 0.391 |
| Breast cancer | 1 (0.9) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Abnormal Findings . | Patients No. (%) . | Healthy Controls No. (%) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower WBC count | 1 (0.9)† | 0 | 1.000 |
| Cardiovascular events | |||
| Elevated myocardial enzymes | 5 (4.5)# | 1 (0.9) | 0.212 |
| Long Q-T interval | 0 | 0 | / |
| T wave change | 14 (12.5) | 15 (13.4) | 0.842 |
| Echocardiogram abnormality | 1 (0.9)ǂ | 0 | 1.000 |
| Liver, kidney and GI dysfunction | |||
| Liver dysfunction | 17 (15.2) | 2 (1.8) | <0.001 |
| Elevated creatinine | 0 | 0 | / |
| Albuminuria | 1 (0.9)ǂ | 0 | 1.000 |
| Fecal occult blood test | 0 | 0 | / |
| Hepatic steatosis | 48 (42.9) | 20 (17.9) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 6 (5.4) | 5 (4.5) | 0.757 |
| Neurological disorders | 1 (0.9)¡ì | 1 (0.9) D | 1.000 |
| Potential secondary tumor | |||
| Elevated serum tumor markers | 3†ø | / | / |
| Thoracic neoplasm on CXR | 0 | 0 | / |
| Abdominal neoplasm on BUS | 0 | 0 | / |
| Skin lesion | 8 (7.1) ŋ | 5 (4.5) ¦Ë | 0.391 |
| Breast cancer | 1 (0.9) | 0 | 1.000 |
1 patient was later diagnosed as the 3rd relapse of APL.
££No acute myocardial infarction. 2 had histories of heart diseases before APL.
1 patient had rheumatic heart disease 1 week after initial therapy, who also had albuminuria probably due to diabetes.
1 patient had depression prior to APL and well controlled by Deanxit.
1 had essential tremor.
3 patients had a mild and transient elevation in NSE, CEA and CA125, respectively, and retests were normal.
2 patients had hyperpigmentation, 1 had hypopigmentation and 5 had hyperkeratosis/hyperplasia.
2 had hyperpigmentation and 3 had hyperkeratosis.
Zhao:National Natural Science Foundation of China (81300451): Research Funding. Chen:National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program) (2012AA02A505): Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal