Abstract
Small molecule Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitors are extensively studied in preclinical investigations and clinical trials in the treatment of hematological malignancies derived from B-cells. Ibrutinib, due to its safety and efficiency, has been recently approved for the treatment of patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) who received at least one prior therapy. Moreover, another Btk inhibitor AVL-292 is currently tested in clinical trials in patients with B Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas, CLL and Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia. Despite a huge therapeutic potential of Btk inhibitors we have recently demonstrated that both natural killer (NK) cells cytotoxicity and degranulation are significantly impaired upon ibrutinib treatment (Bojarczuk et al., Leukemia 2014). Since NK cells are effectors of innate immune system capable to kill tumor cells directly and in the mechanism of antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), which constitutes one of the major mechanism of monoclonal antibodies widely used in hematooncology, in our ongoing studies we are focused to determine in details the influence of various Btk inhibitors on NK cells cytotoxicity, degranulation, cytokine secretion and expression of activatory/inhibitory receptors.
All experiments were performed fully in vitro using human primary NK cells isolated from PBMC of healthy donors as well as NK92 and NK92.CD16 cell lines.
To determine cytolytic activity of NK cells CFSE/PI flow cytometry assay was used. Cytokine secretion and NK cells degranulation, evaluated as the expression of CD107a on the surface of NK cells, were determined with flow cytometry upon incubation with target cells for 4 h. Phenotype of NK cells pre-incubated with tested compounds was determined with flow cytometry using antibodies conjugated with fluorochromes.
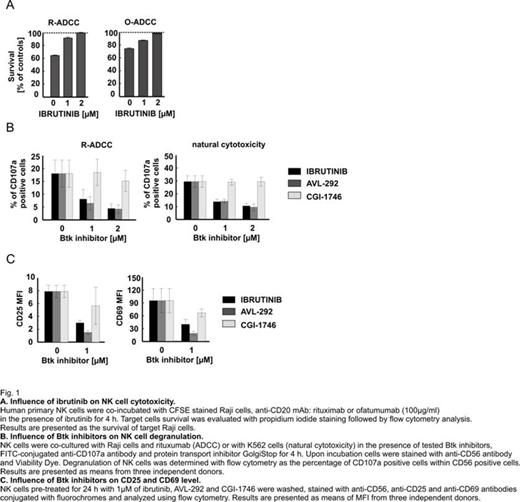
The initial results of our studies show that various Btk inhibitors differentially regulate NK cells antitumor activity. Ibrutinib and AVL-292 which covalently bind to cysteines at the position 481 significantly inhibit NK cells cytotoxicity. Interestingly, we have observed that pre-incubation of NK cells with ibrutinib as well as AVL-292 results in down-regulation of CD25 and CD69. This effect was not observed upon treatment of NK cells with CGI-1746, a reversible Btk inhibitor which blocks phosphorylation of BTK in Y551 and Y223. Expression of NK cells activatory receptors such as NKp30, NK44, NKp46, NKG2D, DNAM-1 and CD16 remained unchanged.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal