Abstract
Introduction
Many investigators rely on mouse models to study immune responses against factor IX protein (FIX) products. While it is recognized that there are distinct differences in immune responses towards FIX in different mouse strains, there is an absence of studies conducted on mice with a F9 gene deletion. Our laboratory has developed protocols to prevent or reverse ongoing anti-hFIX IgG inhibitors in hemophilia B mice with a F9 gene deletion (F9-/Y) on both a BALB/c and C3H/HeJ background. Interestingly C3H/HeJ F9-/Y mice develop high titer anti-FIX IgG1 inhibitors and anaphylaxis, while BALB/c F9-/Y mice have mild anti-hFIX IgG1 inhibitors without anaphylaxis. The C3H/HeJ mouse strain is deficient for the innate immune sensor toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) while a congenic C3H/OuJ strain has functional TLR4. Several recent studies have indicated an important link between coagulation and innate immunity and TLR4 has been linked to sensitivity in food allergy models. Together these studies suggest that TLR4 may have a role in modulating FIX immunity. Here we report results from a study exploring B and T cell responses against FIX protein therapy on two different mouse strains BALB/c and C3H/HeJ with the same F9 gene deletion and the role of TLR4 in modulating FIX immunity.
Methods
BALB/c and C3H/HeJ F9-/Y mice were challenged weekly with recombinant FIX protein. Humoral immune responses were determined by IgG1 and IgG2a anti-hFIX ELISA, Bethesda assay for inhibitors and B cell ELISpot on bone marrow and spleen cells to measure FIX specific antibody secreting B cells. T cell studies measured the TH1 (IFN-γ) and TH2 (IL-4) cytokine responses in splenocytes at the mRNA and protein level in response to FIX protein. Antibody responses were also measured in C3H/HeJ/OuJ F9-/Y mice with restored TLR4 function following FIX challenge.
Results
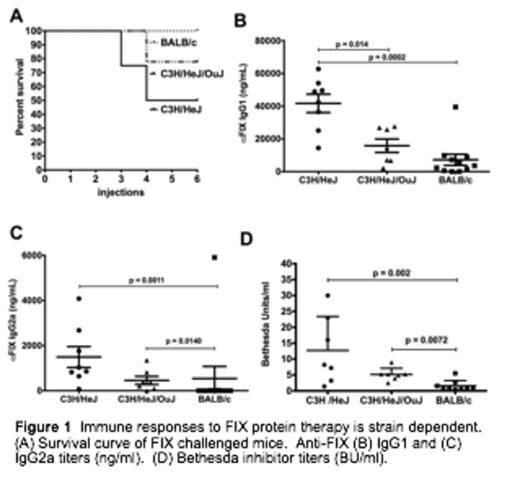
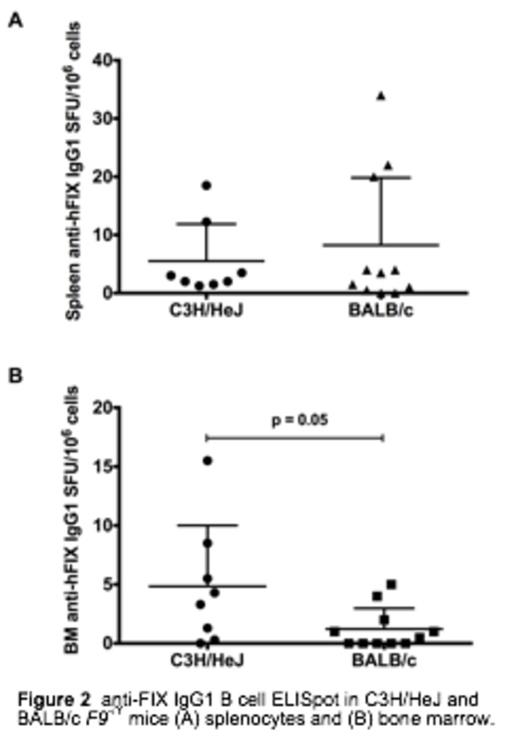
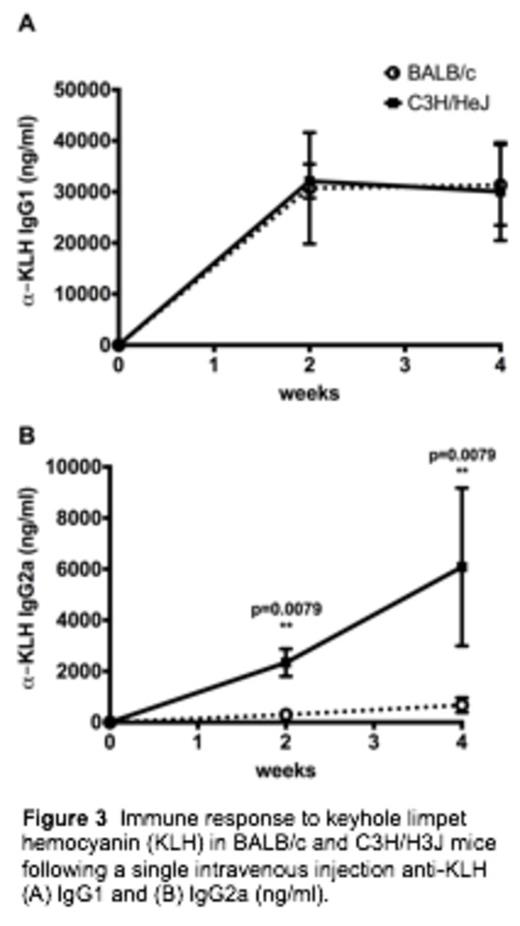
BALB/c F9-/Y mice have a TH2 skewed response and a reduction in anti-hFIX secreting plasma cells in the bone marrow. Independent antigen challenge revealed both strains generated equivalent IgG1 antibody titers to an intravenously delivered antigen suggesting the reduced anti-FIX response in BALB/c mice is antigen specific. C3H/HeJ F9-/Y mice have a mixed TH1 and TH2 response (mainly TH2). Importantly TLR4 signaling has an important modulatory role in the C3H background on the levels of anti-hFIX IgG1 and incidence of anaphylaxis.
Conclusions
The background strain has an important impact on FIX immune responses, which in permissive strains can be modulated by mutations in innate immune sensors.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal